Solar purpura
| Solar purpura | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Senile purpura | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
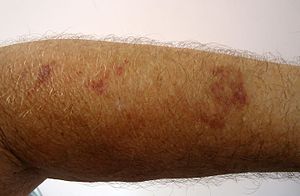
Solar purpura (also known as "Actinic purpura," and "Senile purpura") is a skin condition characterized by large, sharply outlined, 1- to 5-cm, dark purplish-red ecchymoses appearing on the dorsa of the forearms and less often the hands.[1]: 825
The condition is most common in elderly people of European descent. It is caused by sun-induced damage to the connective tissue of the skin.[2]
No treatment is necessary. The lesions typically fade over a period of up to 3 weeks.[3]
See also[]
- List of cutaneous conditions
References[]
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Scheinfeld NS (2009). "Skin Disorders in Older Adults: Vascular, Lymphatic, and Purpuric Dermatides, Part 1". Consultant 49 (6)
- ^ Actinic Purpura at eMedicine
External links[]
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Categories:
- Vascular-related cutaneous conditions
- Cutaneous condition stubs