Steering
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|

Steering is a system of components, linkages, etc. that allows a vehicle to follow a desired course. An exception is the case of rail transport, by which rail tracks combined with railroad switches (also known as 'points' in British English) provide the steering function. The primary purpose of the steering system is to allow the driver to guide the vehicle.
Introduction[]
The most conventional steering arrangement is to turn the front wheels using a hand–operated steering wheel which is positioned in front of the driver, via the steering column, which may contain universal joints (which may also be part of the collapsible steering column design), to allow it to deviate somewhat from a straight line. Other arrangements are sometimes found on different types of vehicles; for example, a tiller or rear–wheel steering. Tracked vehicles such as bulldozers and tanks usually employ differential steering—that is, the tracks are made to move at different speeds or even in opposite directions, using clutches and brakes, to achieve a change of direction.
Land vehicle steering[]
Basic geometry[]

Ackermann steering

Bell-crank steering
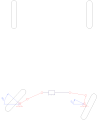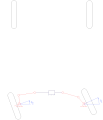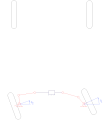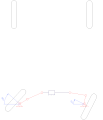
Rack-and-pinion steering
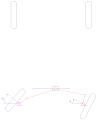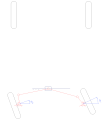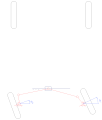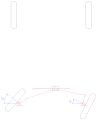
Short rack-and-pinion steering

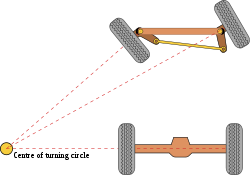
The basic aim of steering is to ensure that the wheels are pointing in the desired directions. This is typically achieved by a series of linkages, rods, pivots and gears. One of the fundamental concepts is that of caster angle—each wheel is steered with a pivot point ahead of the wheel; this makes the steering tend to be self-centering towards the direction of travel.
The steering linkages connecting the steering box and the wheels usually conform to a variation of Ackermann steering geometry, to account for the fact that in a turn, the inner wheel travels a path of smaller radius than the outer wheel, so that the degree of toe suitable for driving in a straight path is not suitable for turns. The angle the wheels make with the vertical plane, known as camber angle, also influences steering dynamics as do the tires.
Rack and pinion, recirculating ball, worm and sector[]
This section may be confusing or unclear to readers. (July 2021) |



Many modern cars use rack and pinion steering mechanisms, where the steering wheel turns the pinion gear; the pinion moves the rack, which is a linear gear that meshes with the pinion, converting circular motion into linear motion along the transverse axis of the car (side to side motion). This motion applies steering torque to the swivel pin ball joints that replaced previously used kingpins of the stub axle of the steered wheels via tie rods and a short lever arm called the steering arm.
The rack and pinion design has the advantages of a large degree of feedback and direct steering "feel". A disadvantage is that it is not adjustable, so that when it does wear and develop lash, the only resolution is replacement.
BMW began to use rack and pinion steering systems in the 1930s, and many other European manufacturers adopted the technology. American automakers adopted rack and pinion steering beginning with the 1974 Ford Pinto.[1]
Older designs use two main principles: the worm and sector design and the screw and nut. Both types were enhanced by reducing the friction; for screw and nut it is the recirculating ball mechanism, which is still found on trucks and utility vehicles. The steering column turns a large screw which meshes with the nut by recirculating balls. The nut moves a sector of a gear, causing it to rotate about its axis as the screw is turned; an arm attached to the axis of the sector moves the Pitman arm, which is connected to the steering linkage and thus steers the wheels. The recirculating ball version of this apparatus reduces the considerable friction by placing large ball bearings between the screw and the nut; at either end of the apparatus the balls exit from between the two pieces into a channel internal to the box which connects them with the other end of the apparatus; thus, they are "recirculated".
The recirculating ball mechanism has the advantage of a much greater mechanical advantage, so that it was found on larger, heavier vehicles while the rack and pinion was originally limited to smaller and lighter ones; due to the almost universal adoption of power steering, however, this is no longer an important advantage, leading to the increasing use of rack and pinion on newer cars. The recirculating ball design also has a perceptible lash, or "dead spot" on center, where a minute turn of the steering wheel in either direction does not move the steering apparatus; this is easily adjustable via a screw on the end of the steering box to account for wear, but it cannot be eliminated because it will produce excessive internal forces at other positions and the mechanism will wear very rapidly. This design is still in use in trucks and other large vehicles, where rapidity of steering and direct feel are less important than robustness, maintainability, and mechanical advantage.
The worm and sector was an older design, used for example in Willys and Chrysler vehicles, and the Ford Falcon (1960s). To reduce friction the sector is replaced by a roller or rotating pins on the rocker shaft arm.
Generally, older vehicles use the recirculating ball mechanism, and only newer vehicles use rack-and-pinion steering. This division is not very strict, however, and rack-and-pinion steering systems can be found on British sports cars of the mid-1950s, and some German carmakers did not give up recirculating ball technology until the early 1990s.
Other systems for steering exist, but are uncommon on road vehicles. Children's toys and go-karts often use a very direct linkage in the form of a bellcrank (also commonly known as a Pitman arm) attached directly between the steering column and the steering arms, and the use of cable-operated steering linkages (e.g. the capstan and bowstring mechanism) is also found on some home-built vehicles such as soapbox cars and recumbent tricycles.
Power steering[]
Power steering helps the driver of a vehicle to steer by directing some of its power to assist in swiveling the steered road wheels about their steering axes. As vehicles have become heavier and switched to front-wheel drive, particularly using negative offset geometry, along with increases in tire width and diameter, the effort needed to turn the wheels about their steering axis has increased, often to the point where major physical exertion would be needed were it not for power assistance. To alleviate this, auto makers have developed power steering systems, or more correctly power-assisted steering, since on road-going vehicles there has to be a mechanical linkage as a fail-safe. There are two types of power steering systems: hydraulic and electric/electronic. A hydraulic-electric hybrid system is also possible.
A hydraulic power steering (HPS) uses hydraulic pressure supplied by an engine-driven pump to assist the motion of turning the steering wheel. Electric power steering (EPS) is more efficient than hydraulic power-steering, since the electric power-steering motor only needs to provide assistance when the steering wheel is turned, whereas the hydraulic pump must run constantly. In EPS, the amount of assistance is easily tunable to the vehicle type, road speed, and driver preference. An added benefit is the elimination of the environmental hazard posed by leakage and disposal of hydraulic power-steering fluid. In addition, electrical assistance is not lost when the engine fails or stalls, whereas hydraulic assistance stops working if the engine stops, making the steering doubly heavy as the driver must now turn not only the very heavy steering—without any help—but also the power-assistance system itself.
Speed-sensitive steering[]
A development of power steering is speed-sensitive steering, where the steering is heavily assisted at low speed and lightly assisted at high speed. Auto makers perceive that motorists might need to make large steering inputs while manoeuvering for parking, but not while traveling at high speed. The first vehicle with this feature was the Citroën SM with its Diravi layout,[2] although rather than altering the amount of assistance as in modern power steering systems, it altered the pressure on a centering cam which made the steering wheel try to "spring" back to the straight-ahead position. Modern speed-sensitive power steering systems reduce the mechanical or electrical assistance as the vehicle speed increases, giving a more direct feel. This feature is gradually becoming more common.[timeframe?]
Four-wheel steering[]










Four-wheel steering is a system employed by some vehicles to improve steering response, increase vehicle stability while maneuvering at high speed, or to decrease turning radius at low speed.
Active four-wheel steering[]
In an active four-wheel steering system, all four wheels turn at the same time when the driver steers. In most active four-wheel steering systems, the rear wheels are steered by a computer and actuators.[3] The rear wheels generally cannot turn as far as the front wheels. There can be controls to switch off the rear steering and options to steer only the rear wheels independently of the front wheels. At low speed (e.g. parking) the rear wheels turn opposite to the front wheels, reducing the turning radius, sometimes critical for large trucks, tractors, vehicles with trailers and passenger cars with a large wheelbase, while at higher speeds both front and rear wheels turn alike (electronically controlled), so that the vehicle may change position with less yaw and improved build-up of the lateral acceleration, enhancing straight-line stability.[3][4] The "snaking effect" experienced during motorway drives while towing a travel trailer is thus largely nullified.[dubious ]
Four-wheel steering found its most widespread use in monster trucks, where maneuverability in small arenas is critical, and it is also popular in large farm vehicles and trucks. Some of the modern European Intercity buses also utilize four-wheel steering to assist maneuverability in bus terminals, and also to improve road stability. Mazda were pioneers in applying four-wheel steering to automobiles, showing it on their 1984 Mazda MX-02 concept car, where the rear wheels counter-steered at low speeds.[5] Mazda proceeded to offer a version of this electronic four-wheel steering system on the Mazda 626 and MX6 in 1988. The first rally vehicle to use the technology was the Peugeot 405 Turbo 16, which debuted at the 1988 Pikes Peak International Hill Climb.[6]
Previously, Honda had four-wheel steering as an option in their 1987–2001 Prelude and Honda Ascot Innova models (1992–1996). General Motors offered Delphi's Quadrasteer in their Silverado/Sierra and Suburban/Yukon. Due to low demand, GM discontinued the technology at the end of the 2005 model year.[7] Nissan/Infiniti offer several versions of their HICAS system as standard or as an option in much of their line-up.
In the early 2000s, a new generation of four-wheel steering systems was introduced into the market. In 2001 BMW equipped the E65 7 series with an all-wheel steering system (optional, called 'Integral Active Steering'), which is available on the current 5, 6, and 7 series,[8][9][4] as an option. Renault introduced an optional all-wheel steering called '4control'[10][11][12] in 2009, at first on the Laguna GT, which is currently available on the Talisman,[11] Mégane[10] and Espace[12] vehicle lines. In 2013, Porsche introduced a system on the 911 Turbo as standard equipment.[13] Since 2016, the Panamera has been offered with optional all-wheel steering.[14] The 2014 Audi Q7 was launched with an optional system.[15] Also the Japanese OEMs offer luxury segment vehicles equipped with all-wheel steering, such as Infiniti on its QX70 model ('Rear Active Steering')[16] and Lexus on the GS.[17] Italian manufacturers have launched the technology in the model years 2016–17 with the Ferrari F12tdf,[18] the Ferrari GTC4Lusso[19] as well as the Lamborghini Aventador S Coupé.[20]
Crab steering[]
Crab steering is a special type of active four-wheel steering. It operates by steering all wheels in the same direction and at the same angle. Crab steering is used when the vehicle needs to proceed in a straight line but at an angle: when changing lanes on a highway at speed, when moving loads with a reach truck, or during filming with a camera dolly.
Rear wheel steering can also be used when the rear wheels may not follow the path taken by the front wheel tracks (e.g. to reduce soil compaction when using rolling farm equipment).
Passive rear-wheel steering[]
Many modern[timeframe?] vehicles have passive rear-wheel steering. On many vehicles, when cornering, the rear wheels tend to steer slightly to the outside of a turn, which can reduce stability. The passive steering system uses the lateral forces generated in a turn (through suspension geometry) and the bushings to correct this tendency and steer the wheels slightly to the inside of the corner. This improves the stability of the car through the turn. This effect is called compliance understeer; it, or its opposite, is present on all suspensions. Typical methods of achieving compliance understeer are to use a Watt's link on a live rear axle, or the use of toe control bushings on a twist beam suspension. On an independent rear suspension it is normally achieved by changing the rates of the rubber bushings in the suspension. Some suspensions typically have compliance oversteer due to geometry, such as Hotchkiss live axles, semi-trailing arm IRS, and rear twist beams, but may be mitigated by revisions to the pivot points of the leaf spring or trailing arm, or additional suspension links, or complex internal geometry of the bushings.
Passive rear-wheel steering is not a new concept, as it has been in use for many years,[timeframe?] although not always recognised as such.
Articulated steering[]

Articulated steering is a system by which a vehicle is split into front and rear halves which are connected by a vertical hinge. The front and rear halves are connected with one or more hydraulic cylinders that change the angle between the halves, including the front and rear axles and wheels, thus steering the vehicle. This system does not use steering arms, king pins, tie rods, etc. as does four-wheel steering. If the vertical hinge is placed equidistant between the two axles, it also eliminates the need for a central differential in four-wheel drive vehicles, as both front and rear axles will follow the same path, and thus rotate at the same speed. Articulated haulers have very good off-road performance.
Vehicle-trailer-combinations such as semi-trailers, road trains, articulated buses, and internal transport trolley trains can be regarded as passively-articulated vehicles.
Rear-wheel steering[]
A few types of vehicle use only rear-wheel steering, notably fork lift trucks, camera dollies, early pay loaders, Buckminster Fuller's Dymaxion car, and the ThrustSSC.[21]
In cars, rear-wheel steering tends to be unstable because, in turns, the steering geometry changes, hence decreasing the turn radius (oversteer), rather than increasing it (understeer). Rear-wheel steering is meant for slower vehicles that need high-maneuverability in tight spaces, e.g. fork lifts.
For heavy haulage or for increased manoeuvrability, some semi-trailers are fitted with rear-wheel steering, controlled electro-hydraulically. The wheels on all or some of the rear axles may be turned through different angles to enable tighter cornering, or through the same angle (crab steering) to move the rear of the trailer laterally.
On August 10 2021, the Genesis G80 Sports, applied with a rear-wheel steering system for the first time, was unveiled.[22] The RWS actively controls the rear-wheel steering angle.[23]
Reducing the rotation radius when driving at low speeds below 60 km/h improves convenience and agility when driving in U-turns, narrow alleys, and parking. Furthermore, applying the rear-wheel steering system reduces the minimum turning radius down to the Hyundai Motors Sonata level. In high-speed driving, the vehicle inhibits lateral slippage and improves turn stability and lane following fast lane changes, high-speed turns, and emergency avoidance situations.[24]
Steer-by-wire[]


The aim of steer-by-wire technology is to completely remove as many mechanical components (steering shaft, column, gear reduction mechanism, etc.) as possible. Completely replacing conventional steering system with steer-by-wire has several advantages, such as:
- The absence of steering column simplifies the car interior design.
- The absence of steering shaft, column and gear reduction mechanism allows much better space utilization in the engine compartment.
- The steering mechanism can be designed and installed as a modular unit.
- Without mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the road wheel, it is less likely that the impact of a frontal crash will cause the steering wheel to impact the driver.
- Steering system characteristics can easily be adjusted to change the steering response and feel.
As of 2020 there are no production cars available that rely solely on steer-by-wire technology due to safety, reliability and economic concerns, but this technology has been demonstrated in numerous concept cars and the similar fly-by-wire technology is in use in both military and civilian aviation applications.
Safety[]
For safety reasons all modern cars feature a collapsible steering column (energy absorbing steering column) which will collapse in the event of a heavy frontal impact to avoid excessive injuries to the driver. Airbags are also generally fitted as standard. Non-collapsible steering columns fitted to older vehicles very often impaled drivers in frontal crashes, particularly when the steering box or rack was mounted in front of the front axle line, at the front of the crumple zone. This was particularly a problem on vehicles that had a rigid separate chassis frame with no crumple zone. Many modern vehicle steering boxes or racks are mounted behind the front axle on the front bulkhead, at the rear of the front crumple zone.
Collapsible steering columns were invented by Béla Barényi and were introduced in the 1959 Mercedes-Benz W111 Fintail, along with crumple zones. This safety feature first appeared[when?] on cars built by General Motors after an extensive and very public lobbying campaign enacted by Ralph Nader. Ford started to install collapsible steering columns in 1968.[25]
Audi used a retractable steering wheel and seat belt tensioning system called procon-ten, but it has since been discontinued in favor of airbags and pyrotechnic seat belt pre-tensioners.
Cycles[]
This section is empty. You can help by . (August 2021) |
Differential steering[]
Differential steering is the primary means of steering tracked vehicles, such as tanks and bulldozers; it is also used in certain wheeled vehicles commonly known as skid-steers, and implemented in some automobiles, where it is called torque vectoring, to augment steering by changing wheel direction relative to the vehicle.
Regulations[]
In the European Union, Russia and Japan, UNECE regulation 79 is related to steering.
In the United States, Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards 203 and 204 are related to impact protection for the driver from the steering control system and steering control rearward displacement while 49 Code of Federal Regulations § 393.209 is related to steering wheel systems.
Watercraft steering[]
Ships and boats are usually steered with a rudder. Depending on the size of the vessel, rudders can be manually actuated, or operated using a servomechanism, or a trim tab or servo tab system. Boats using outboard motors steer by rotating the entire drive unit. Boats with inboard motors sometimes steer by rotating the propeller pod only (i.e. Volvo Penta IPS drive). Modern ships with diesel-electric drive use azimuth thrusters. Boats power by oars or paddles are steered by generating a higher propulsion force on the side of the boat opposite of the direction of turn. Jet skis are steered by weight-shift induced roll and water jet thrust vectoring.
The rudder of a vessel can steer the ship only when water is passing over it. Hence, when a ship is not moving relative to the water it is in or cannot move its rudder, it does not respond to the helm and is said to have "lost steerage". The motion of a ship through the water is known as "making way". When a vessel is moving fast enough through the water that it turns in response to the helm, it is said to have "steerage way".[26] That is why boats on rivers must always be under propulsion, even when traveling downstream.
Aircraft and hovercraft steering[]
Airplanes are normally steered when airborne by the use of ailerons, spoilerons, or both to bank the aircraft into a turn; although the rudder can also be used to turn the aircraft, it is usually used to minimise adverse yaw, rather than as a means to directly cause the turn. On the ground, aircraft are generally steered by turning the nosewheel or tailwheel (using a tiller or the rudder pedals) or differential braking at low speeds, and using the rudder at high speeds. Missiles, airships and large hovercraft are usually steered by a rudder, thrust vectoring, or both. Small sport hovercraft have similar rudders, but steer mostly by the pilot shifting their weight from side to side and unbalancing the more powerful lift forces beneath the skirt. Jet packs and flying platforms are steered by thrust vectoring only. Helicopters are steered by cyclic control, changing the thrust vector of the main rotor(s), and by anti-torque control, usually provided by a tail rotor (see helicopter flight controls).
See also[]
- Active Yaw Control (AYC)
- Bump Steer
- Camber angle
- Camber thrust
- Caster angle
- Countersteering
- DIRAVI
- Dry steering
- HICAS
- Kingpin
- Opposite lock
- Power steering
- Skid steer
- Steer-by-wire
- Steering damper
- Steering kickback
- Steering ratio
- Steering wheel
- Steering wheel (ship)
- Tiller
- Torque steering
- Turning radius
- Vehicle dynamics
References[]
- Encyclopedia of German Tanks of World War Two by Peter Chamberlain and Hilary Doyle, 1978, 1999
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-07-10. Retrieved 2015-07-24.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-05-11. Retrieved 2015-05-28.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cars | AKC® - Active Kinematics Control - ZF Friedrichshafen AG". www.zf.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ Jump up to: a b AG, BMW. "BMW 5 Series Sedan: Driving dynamics & Efficiency". www.bmw.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ Lindell, Hannu (1985-03-19). "Nelosten vuosi" [Year of the Four]. Tekniikan Maailma (in Finnish). Vol. 41 no. 5/85. Helsinki: TM-Julkaisu. p. Automaailma 3. ISSN 0355-4287.
- ^ "1988 Peugeot 405 T16 GR Pikes Peak". Retrieved 2015-03-16.
- ^ Murphy, Tom; Corbett, Brian (2005-03-01). "Quadrasteer Off Course". Wards Auto World. Archived from the original on 2011-03-23. Retrieved 2010-06-11.
- ^ AG, BMW. "BMW 7 Series Sedan : M Performance". www.bmw.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ AG, BMW. "BMW 6 Series Coupé : Driving dynamics". www.bmw.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Feature | All-New MEGANE Sport Tourer | Cars | Renault UK". Renault. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Equipements | Talisman | Véhicules Particuliers | Véhicules | Renault FR". Renault (in French). Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Equipements | Espace | Véhicules Particuliers | Véhicules | Renault FR". Renault (in French). Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Porsche 911 Turbo - Rear-axle steering - Porsche Great Britain". Porsche Great Britain - Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG. Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Porsche The new Panamera - Rear-axle steering - Porsche Great Britain". Porsche Great Britain - Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Audi Q7 > Audi configurator UK". www.uk.audi.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "INFINITI QX70 Specs - Performance Features & Engine Options". Infiniti. Archived from the original on 2017-04-06. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "News&Events, Neuigkeiten". www.lexus.de (in German). Archived from the original on 2017-02-22. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Ferrari F12tdf: Track-Level Performance on the Road - Ferrari.com". Ferrari GT - en-EN. Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "GTC4LUSSO T: maximum control for a unique driving experience". GTC4Lusso T. Archived from the original on 2017-04-07. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Lamborghini Aventador S Coupé". www.lamborghini.com. Archived from the original on 2017-04-25. Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- ^ "Thrust SSC - Engineering". Archived from the original on 2010-11-12. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
- ^ "2022 Genesis G80 Sport Unveiled With Rear-Wheel Steering". 《Motor1》. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ^ "Genesis G80 Luxury Sedan Will Spawn a Sport Variant with Rear-Wheel Steering". 《Car and Driver》. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ "Genesis G80 Sport Sedan Adds Rear-Wheel Steering". 《Caars Direct》. Retrieved July 6, 2021.
- ^ Smart, Jim. "Collapsible Steering Column Installation". Archived from the original on 2006-12-28.
- ^ Smyth, William Henry; Belcher, Edward (1867). The sailor's word-book: An alphabetical digest of nautical terms, including some more especially military and scientific ... as well as archaisms of early voyagers, etc. London: Blackie and Son. p. 654.
External links[]
| Look up steering in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Automotive steering technologies
- Vehicle dynamics




