Thorn with stroke
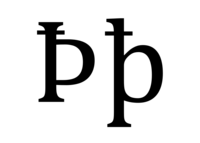
Ꝥ (minuscule: ꝥ), or Þ (thorn) with stroke was a scribal abbreviation common in the Middle Ages. It was used for Old English: þæt (Modern English "that"), as well as Old Norse: þor-, the -þan/-ðan in síðan,[1] þat, þæt, and þess. In Old English texts, the stroke tended to be more slanted, while in Old Norse texts it was straight. In Middle English times, the ascender of the þ was reduced (making it similar to the Old English letter Wynn, ƿ), which caused the thorn with stroke abbreviation ( ![]() ) to be replaced with a thorn with a small t above the letter (
) to be replaced with a thorn with a small t above the letter ( ![]() ).
).
Unicode encodes Ꝥ as U+A764 Ꝥ LATIN CAPITAL LETTER THORN WITH STROKE (HTML Ꝥ), and ꝥ at U+A765 ꝥ LATIN SMALL LETTER THORN WITH STROKE (HTML ꝥ).
A thorn with a stroke on the descender also exists, used historically as an abbreviation for the word "through".[2] The codepoints are U+A766 Ꝧ LATIN CAPITAL LETTER THORN WITH STROKE THROUGH DESCENDER (HTML Ꝧ), and U+A767 ꝧ LATIN SMALL LETTER THORN WITH STROKE THROUGH DESCENDER (HTML ꝧ).
References[]
- ^ AM 655, p1 recto, lines 4, 14, & 17 [1]
- ^ http://www.lel.ed.ac.uk/ihd/laeme2/tagged_data/cotowlbt.html.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
- Michael Everson (editor), Peter Baker; et al. (30 January 2006). "Proposal to add medievalist characters to the UCS" (PDF). Retrieved 25 November 2017.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - "Proposal to add LATIN LETTER THORN WITH DIAGONAL STROKE to the UCS" (PDF). 17 October 2017. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Andrew West, What's that?, an article about the proposal to add medievalist characters to the UCS
- Unicode Character 'Latin capital letter thorn with stroke' (U+A764)
- Unicode Character 'Latin small letter thorn with stroke' (U+A765)
- Letters with stroke
- Latin-script letters
- Typography stubs