Treason laws in the United States
In the United States, there are both federal and state laws prohibiting treason.[1] Treason is defined on the federal level in Article III, Section 3 of the United States Constitution as: "levying War against [the United States], or in adhering to their Enemies, giving them Aid and Comfort." Most state constitutions include similar definitions of treason, specifically limited to levying war against the state, "adhering to the enemies" of the state, or aiding the enemies of the state, and requiring two witnesses or a confession in open court.[2] Fewer than thirty people have ever been charged with treason under these laws.[3]
Constitutionally, citizens of the United States owe allegiance to at least two sovereigns. One is the United States, and the other is their state. They can therefore potentially commit treason against either, or against both.[4] At least fourteen people have been charged with treason against various states; at least six were convicted, five of whom were executed.[citation needed] Only one person has ever been executed for treason against the federal government: William Bruce Mumford, who was convicted of treason and hanged in 1862 for tearing down a United States flag during the American Civil War. However, this was under martial law, not Article Three of the United States Constitution.[5]
While treason is a criminal matter under federal and state laws, it may be considered a civil matter under tribal law.[6] The Indian Civil Rights Act limits sentences for crimes by tribal courts to no more than one year in jail and a $5,000 fine.[7]
Federal[]
Definition: In Article III, Section 3 of the United States Constitution, treason is specifically limited to levying war against the US, or adhering to their enemies, giving them aid and comfort.[2]
Penalty: U.S. Code Title 18: Death,[8] or not less than 5 years' imprisonment (minimum fine of $10,000, if not sentenced to death). Any person convicted of treason against the United States will lose the right to hold public office in the United States.[9]
The terms used in the definition derive from English legal tradition, specifically the Treason Act 1351. Levying war means the assembly of armed people to overthrow of the government or to resist its laws. Enemies are subjects of a foreign government that is in open hostility with the United States.[10] Those who assemble to levy war, as well as those who conspire with them, can be prosecuted.[11] The American definition is narrower than that of English law, which spanned other classes of treason such as counterfeiting and bringing indignity upon the king.[12]
State[]
Alabama[]
Definition: The constitution of Alabama defines treason in similar terms to the United States Constitution.[13]
Penalty: Not less than 10 years and not more than 99 years' imprisonment (eligible for parole after lesser of one-half of sentence or 15 years) or life imprisonment (eligible for parole after 10 years).
A treason conviction also results in loss of voting rights for life without the possibility of voting restoration.[14]
Arkansas[]
Definition: Arkansas legislation defines treason similarly to the United States Constitution, limiting it to "levying war against the state" or giving "aid and comfort" to the enemies of the state. Also similarly, conviction requires the testimony of two witnesses to the same overt act, or confession in open court.[15]
Penalty: Death,[16] or life imprisonment without the possibility of parole.[15]
California[]
Definition: Treason against the state of California is defined similarly to the United States Constitution. The California Constitution states that "treason against the State consists only in levying war against it, adhering to its enemies, or giving them aid and comfort. A person may not be convicted of treason except on the evidence of two witnesses to the same overt act or by confession in open court."[17] This is reiterated in Section 37 of the California Penal Code.[18]
Penalty: Death,[19] or life imprisonment without the possibility of parole.[20]
Colorado[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment without the possibility of parole.[21]
Delaware[]
Definition: The constitution of Delaware defines treason in similar terms to the United States Constitution.[22]
Florida[]
Penalty: Not less than 5.5 years and not more than 30 years' imprisonment (minimum sentencing guidelines).
Georgia[]
Penalty: Death, or by imprisonment for life or for not less than 15 years.[23][24]
Idaho[]
The state constitution of Idaho specifically disallows gubernatorial respite or reprieve for a conviction for treason.[25]
Illinois[]
Penalty: Not less than 6 years and not more than 30 years' imprisonment.
Joseph Smith and Hyrum Smith[]
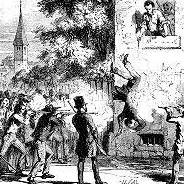
After escaping custody on charges of treason against Missouri and fleeing to Illinois, Joseph Smith and Hyrum Smith were charged with treason in Illinois, which at that time was a capital offense. Augustine Spencer swore out a warrant alleging that the Smith brothers had committed treason by "calling out the Legion to resist the force under the command of the Governor." On June 24, 1844, a warrant was issued charging that "Joseph Smith, late of the county aforesaid, did, on or about the nineteenth day of June. A. D. 1844, at the county and state aforesaid, commit the crime of treason against the government and people of the State of Illinois." (Ludlow, pp. 1346–1348)[26]
Bail could not be granted for a charge of treason, so Smith was placed in jail where he was accompanied by his brother, Hyrum Smith, and other associates. On June 27, Smith and Hyrum were killed by a mob in jail while they were awaiting trial. (Ludlow, p. 860)[26]
Louisiana[]
Penalty: Death,[27] or life imprisonment. In Louisiana, all life imprisonment sentences exclude the possibility of parole.[28]
Maine[]
Definition: The state constitution of Maine defines treason in similar terms to the United States Constitution.[29]
Massachusetts[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving not less than 15 years and not more than 25 years.
Minnesota[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 17 years.
Mississippi[]
Penalty: Death or life imprisonment.[30]
Missouri[]
Definition: Treason is defined in the constitution of the State of Missouri.[31]
Penalty: Not less than 10 years and not more than 30 years' imprisonment (eligible for parole after serving one-half of sentence) or life imprisonment (eligible for parole after serving 30 years).
Joseph Smith and others[]
Joseph Smith and five others were charged with treason under Missouri law in 1838, spending over five months in prison, but escaped while awaiting trial.[32] Joseph Smith and Hyrum Smith were later charged with treason against Illinois (above)[33]
Nevada[]
Penalty: Not less than 2 years and not more than 10 years' imprisonment (if imprisonment is imposed).
New York[]
Penalty: 15-40 years in prison or Life imprisonment and a $100,000 fine. Though treason doesn't have a New York Penal Law Statute, it is punished as a class A-1 felony.[34]
North Carolina[]
Article I, Section 29, of the State Constitution is similar to Article III, Section 3 of the United States Constitution, limiting the legal definition of "treason" to levying war against the State or giving "aid and comfort" to the enemies of the State. Conviction requires two witnesses to the act itself, or a confession in open court.[4]
John Sevier[]
John Sevier, then governor of the State of Franklin and later the first governor of the State of Tennessee, was charged with treason against the State of North Carolina in October, 1788. After being transported to North Carolina, he was freed. The charge was never brought to trial.[35]
North Dakota[]
Penalty: Not more than 20 years' imprisonment.
Oregon[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 25 years.
Rhode Island[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 20 years.
Thomas Dorr[]
Thomas Wilson Dorr was convicted of treason against Rhode Island in 1844 for leading a rebellion against the state government, and sentenced to life imprisonment.[36] Dorr served twelve months of his sentence. He was released in 1845 after the Rhode Island state legislature passed an Act of General Amnesty. In January 1854 the legislature passed an act annulling the verdict of the Rhode Island Supreme Court.[37]
South Carolina[]
Penalty: Death or not more than 30 years' imprisonment (if committed during time of war) or not more than 20 years' imprisonment (if not committed during time of war).[38]
South Dakota[]
Definition: The state constitution of South Dakota defines treason in similar terms to the United States Constitution.[39]
Tennessee[]
Tennessee has repealed its treason law.[40] However, a person convicted of treason can never be eligible to vote in Tennessee.[41][42]
Texas[]
Penalty: Not less than 1 year and not more than 20 years' imprisonment.
Vermont[]
Definition: levying war or conspiring to levy war against the state, or adhering to the enemy. This definition, in Title 13, Chapter 75, § 3401 of Vermont Statutes, echoes the definition found in the United States Constitution.
Penalty: Death by electrocution. Vermont criminal law maintains the death penalty specifically for treason. No other crime is punishable by the sentence of death. The method of execution is specified as electrocution.[43] Vermont's electric chair, last used in 1954, is stored in the Vermont History Center in Barre, Vermont.[44]
Virginia[]
Penalty: Not less than 20 years' imprisonment or life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 15 years (if imprisonment is imposed).
Raid on Harper's Ferry[]
John Brown was charged with treason against the Commonwealth of Virginia, along with conspiracy and first-degree murders after he led his raid on Harper's Ferry in 1859. In Virginia v. John Brown, he was found guilty on all three charges. He was consequently hanged.[45] Edwin Coppie (also known as Edwin Coppock) and Aaron Dwight Stevens were also charged, convicted, and hanged for treason against the Commonwealth of Virginia and other crimes. The charges of treason against John Anthony Copeland Jr. and Shields Green were dropped, since their lawyer argued successfully that since they were not citizens of the United States, according to the Dred Scott decision, they could not commit treason; they were convicted and hung for other crimes.[46][47][48][49] Albert Hazlett and John E. Cooke were charged with treason against the Commonwealth of Virginia and found not guilty of treason, but were convicted of other crimes.[50]
Washington[]
Definition: The state constitution and statutory law of Washington define treason in similar terms to the United States Constitution, except that adhering to enemies and giving them aid are distinct forms of treason, not elements of a single form.[51][52]
Penalty: Death,[53] life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 20 years, or any term of years. Treason is a "Class A" felony under sentencing guidelines, and current guidelines provide for a maximum sentence of life in prison and/or a $50,000 fine.[54]
West Virginia[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with the possibility of parole after serving 10 years or not less than 3 years and not more than 10 years' imprisonment (latter sentence able to be imposed at discretion of jury or court if defendant pleads guilty).
Wisconsin[]
Penalty: Life imprisonment with or without the possibility of parole (eligible in 20 years, if sentenced to life with parole).
Tribal law[]
The U.S. federal government recognizes tribal nations as "domestic dependent nations". Tribal sovereignty is a form of parallel sovereignty within the U.S. constitutional framework, constrained by but not subordinate to other sovereign entities.[55]
There is at least one case of punishment for treason under tribal law. In 1992, the Tonawanda Band of Seneca convicted several members of treason, stripped their tribal membership, and sentenced them to permanent banishment from the Tonawanda Reservation for attempting to overthrow the traditional government.[56][57]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ *18 U.S.C. § 2381
*"State Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 23 May 2017. - ^ Jump up to: a b Stimson, Frederic Jesup (1908). The Law of the Federal and State Constitutions of the United States: With an Historical Study of Their Principles, a Chronological Table of English Social Legislation, and a Comparative Digest of the Constitutions of the Forty-six States. Boston Book Company. p. 183. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ Podger, Pamela J. (9 December 2001). "Few ever charged or convicted of treason in U.S. history / Many Americans fought for other religious, political, cultural beliefs". San Francisco Chronicle. Hearst Communications. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Orth, John V.; Newby, Paul M. (2013). The North Carolina State Constitution (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 86. ISBN 9780199300655. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ^ Larson, Carlton F. W. (17 February 2017). "Five myths about treason". The Washington Post. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ Wilkins, David E.; Wilkins, Shelly Hulse (2017). Dismembered: Native Disenrollment and the Battle for Human Rights. University of Washington Press. p. 84. ISBN 9780295741598.
- ^ Deer, Sarah; Garrow, Carrie E. (2004). Tribal Criminal Law and Procedure. Rowman Altamira. p. 357. ISBN 9780759115200. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Capital Punishment at the Federal Level - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "18 U.S. Code § 2381 - Treason". LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 2020-06-11.
- ^ US v. Greathouse et al., Abb. U. S., 364 (N. D. Cal. 1863).
- ^ [4 Cranch R. 473-4; Const. art. 3, s. 3. Vide Treason; Fries' Trial; Pamphl
- ^ Blackstone, William (1770) Commentaries on the Laws of England vol. 4
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 3. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ "Felon Voting Quiz - Felon Voting - ProCon.org". felonvoting.procon.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Arkansas - Capital Murder with 10 Aggravating Circumstances, and Treason - Death Penalty - ProCon.org". deathpenalty.procon.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Arkansas Capital Punishment Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "ARTICLE 1 :: DECLARATION OF RIGHTS (Section 18)". Justia Law. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ "California Code, Penal Code - PEN § 37". Findlaw. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ "California Capital Punishment Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "The History of Capital Punishment in California". www.cdcr.ca.gov. State of California. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ "Governor signs bill abolishing Colorado's death penalty, commutes sentences of state's 3 death row inmates". The Colorado Sun. March 23, 2020.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 69. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ "Georgia Capital Punishment Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Georgia - Treason - Death Penalty - ProCon.org". deathpenalty.procon.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 103. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ludlow, Daniel (1992). Encyclopedia of Mormonism. New York: Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-02-879602-4. OCLC 24502140.
- ^ "Louisiana Capital Punishment Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Nellis, Ashley (22 September 2010). "Throwing Away the Key: The Expansion of Life Without Parole Sentences in the United States" (PDF). Federal Sentencing Reporter. 23 (1): 28. doi:10.1525/fsr.2010.23.1.27. ISSN 1053-9867. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 161. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ "Mississippi - Capital Homicide with 8 Aggravating Circumstances, Treason, and Aircraft Piracy - Death Penalty - ProCon.org". deathpenalty.procon.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 214. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ Bushman, Richard Lyman (2007). Joseph Smith: Rough Stone Rolling (Reprint ed.). Vintage. pp. 349–549. ISBN 9781400077533.
- ^ Bentley, Joseph I. (1992), "Smith, Joseph: Legal Trials of Joseph Smith", in Ludlow, Daniel H (ed.), Encyclopedia of Mormonism, New York: Macmillan Publishing, pp. 1346–1348, ISBN 978-0-02-879602-4, OCLC 24502140;Oaks & Hill (1975, p. 18).
- ^ . August 12, 2021 https://www.theblanchlawfirm.com/practice-areas/major-felonies/class-a-felony/. Retrieved August 12, 2021. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ^ Jones Jr, James B. (2015). Hidden History of Tennessee Politics. Arcadia Publishing. p. 19. ISBN 9781625853745. Retrieved 16 June 2017.
- ^ "Past Americans Charged With Treason". Fox News. Associated Press. 17 December 2001. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ "Rhode Island Governors". Retrieved 24 August 2013.
- ^ "Code of Laws - Title 25 - Chapter 7 - Treason; Sabotage". www.scstatehouse.gov. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 366. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ "Tenn. Code Ann. § 39-5-801". LexisNexis. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ "Tenn. Code Ann. § 40-29-204". LexisNexis. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Tenn. Code Ann. § 40-29-105". LexisNexis. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Vermont - Abolishment of the death penalty except for treason - Death Penalty - ProCon.org". deathpenalty.procon.org. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Picard, Ken (22 June 2005). "Killing Time". Seven Days. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "The raid on Harpers Ferry". www.pbs.org. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ "John A. Copeland Jr. - Ohio History Central". www.ohiohistorycentral.org. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ "Avalon Project - Life, Trial and Execution of Captain John Brown; 1859". avalon.law.yale.edu. Lillian Goldman Law Library. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ "Muddy Boots". muddyboots76.blogspot.com. 15 December 2009. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ Mackey, Thomas C. (2014). A Documentary History of the American Civil War Era: Volume 3, Judicial Decisions, 1857-1866. Univ. of Tennessee Press. pp. 220–221. ISBN 9781621900238. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ "John Brown Papers held by Jefferson County Circuit Clerk's Office". www.wvculture.org. West Virginia Division of Culture and History. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- ^ Maddex, Robert (2005). State Constitutions of the United States. CQ Press. p. 415. ISBN 9781452267371.
- ^ "RCW 9.82.010. Defined—Penalty". app.leg.wa.gov. Washington State Legislature. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "Washington Capital Punishment Laws - FindLaw". Findlaw. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ "2016 Washington State Adult Sentencing Guidelines Manual" (PDF). Washington State Caseload Forecast Council. 12 December 2016. pp. 15, 133. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ^ Lenzerini, Federico (2006). "Sovereignty Revisited: International Law and Parallel Sovereignty of Indigenous Peoples" (PDF). Texas International Law Journal. 42 (1): 155–189. Retrieved 17 June 2017.
- ^ "Poodry v. Tonawanda Band of Seneca Indians, 85 F. 3d 874 - Court of Appeals, 2nd Circuit 1996". Google Scholar. 1996. Retrieved 17 June 2017.
- ^ Wilkins, David E.; Wilkins, Shelly Hulse (2017). Dismembered: Native Disenrollment and the Battle for Human Rights. University of Washington Press. pp. 81–84. ISBN 9780295741598.
- State law in the United States
- United States criminal law
- State constitutions of the United States
- Treason in the United States
- United States criminal constitutional law