Tyranny of the majority
| Part of the Politics series |
| Democracy |
|---|
|
|
The tyranny of the majority (or tyranny of the masses) is an inherent weakness to majority rule in which the majority of an electorate pursues exclusively its own objectives at the expense of those of the minority factions. This results in oppression of minority groups comparable to that of a tyrant or despot, argued John Stuart Mill in his 1859 book On Liberty.[1]
The scenarios in which tyranny perception occurs are very specific, involving a sort of distortion of democracy preconditions:
- Centralization excess: when the centralized power of a federation make a decision that should be local, breaking with the commitment to the subsidiarity principle.[2] Typical solutions, in this condition, are concurrent majority and supermajority rules.
- Abandonment of rationality: when, as Tocqueville remembered, a decision "which bases its claim to rule upon numbers, not upon rightness or excellence".[3] The use of public consultation, technical consulting bodies, and other similar mechanisms help to improve rationality of decisions before voting on them. Judicial review (e.g. declaration of nullity of the decision) is the typical way after the vote.
In both cases, in a context of a nation, constitutional limits on the powers of a legislative body, and the introduction of a Bill of Rights have been used to counter the problem.[4] A separation of powers (for example a legislative and executive majority actions subject to review by the judiciary) may also be implemented to prevent the problem from happening internally in a government.[4]
Term[]
A term used in Classical and Hellenistic Greece for oppressive popular rule was ochlocracy ("mob rule"); tyranny meant rule by one man—whether undesirable or not.
While the specific phrase "tyranny of the majority" is frequently attributed to various Founding Fathers, only John Adams is known to have used it, arguing against government by a single unicameral elected body. Writing in defense of the Constitution in March 1788,[5] Adams referred to "a single sovereign assembly, each member…only accountable to his constituents; and the majority of members who have been of one party" as a "tyranny of the majority", attempting to highlight the need instead for "a mixed government, consisting of three branches". Constitutional author James Madison presented a similar idea in Federalist 10, citing the destabilizing effect of "the superior force of an interested and overbearing majority" on a government, though the essay as a whole focuses on the Constitution's efforts to mitigate factionalism generally.
Later users include Edmund Burke, who wrote in a 1790 letter that "The tyranny of a multitude is a multiplied tyranny."[6] It was further popularised by John Stuart Mill, influenced by Tocqueville, in On Liberty (1859). Friedrich Nietzsche used the phrase in the first sequel to Human, All Too Human (1879).[7] Ayn Rand wrote that individual rights are not subject to a public vote, and that the political function of rights is precisely to protect minorities from oppression by majorities and "the smallest minority on earth is the individual".[8] In Herbert Marcuse's 1965 essay "Repressive Tolerance", he said "tolerance is extended to policies, conditions, and modes of behavior which should not be tolerated because they are impeding, if not destroying, the chances of creating an existence without fear and misery" and that "this sort of tolerance strengthens the tyranny of the majority against which authentic liberals protested".[9] In 1994, legal scholar Lani Guinier used the phrase as the title for a collection of law review articles.[10]
Examples[]
The "no tyranny" and "tyranny" situations can be characterized in any simple democratic decision-making context, as a deliberative assembly.
Abandonment of rationality[]
Herbert Spencer, in "The Right to Ignore the State" (1851), pointed the problem with the following example:[11]
Suppose, for the sake of argument, that, struck by some Malthusian panic, a legislature duly representing public opinion were to enact that all children born during the next ten years should be drowned. Does anyone think such an enactment would be warrantable? If not, there is evidently a limit to the power of a majority.
Usual no-tyranny scenario[]
This section possibly contains original research. (June 2016) |
This section does not cite any sources. (September 2019) |
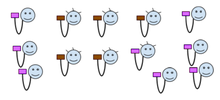
Suppose a deliberative assembly of a building condominium with 13 voters, deciding, with majority rule, about "X or Y",
Suppose that the final result is "8 votes for X and 5 votes for Y", so 8, as a majority, purple wins. As collectively (13 voters) the decision is legitimate.
It is a centralized decision about all common use rooms, "one color for all rooms", and it is also legitimate. Voters have some arguments against "each room with its color", rationalizing the centralization: some say that common rooms need uniform decisions; some prefer the homogeneous color style, and all other voters have no style preference; an economic analysis demonstrates (and all agree) that a wholesale purchase of one color paint for all rooms is better.
Federated centralization excess[]
Centralization excess is the most usual case. Suppose that each floor has some kind of local governance, so in some aspects the condominium is a "federation of floors". Suppose that only on the third floor the majority of residents manifested some preference to "each floor with different color" style, and all of the third floor residents likes the red color. The cost difference, to purchase another color for one floor, is not significant when compared with the condominium contributions.
In these conditions some perception of tyranny arrives, and the subsidiarity principle can be used to contest the central decision.
Tyranny emerging[]
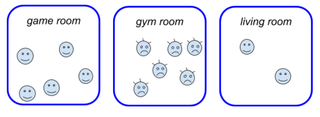
In the above no-tyranny scenario, suppose no floor federation, but (only) a room with some local governance. Suppose that the gym room is not used by all, but there is a "community" of regulars, there is a grouping of voters by its activity as speed-cyclists (illustrated as spiked hair), that have the gym room key for some activities on Sundays. They are acting collectively to preserve the gym room for a local cyclists group.
In this situation the following facts hold:
- There is a subset of voters and some collective action, uniting them, making them a cohesive group.
- There is some centralization (a general assembly) and some central decision (over local decision): there is no choice of "each room decision" or "each regulars' community decision". So it is a central decision.
- The subsidiarity principle can be applied: there is an "embryonic local governance" connecting the cyclists, and the other people (voters) of the condominium recognise the group, transferring some (little) responsibility to them (the keys of the gym room and right to advocate their cycling activities to other residents).
There is no "enforced minoritarianism"; it seems a legitimate characterization of a relevant (and not dominant) minority. This is a tyranny of the majority situation because:
- there is a little "global gain" in a global decision (where X wins), and a good "local gain" in local decision (local Y preference);
- there is relevant voting for a local decision: 6 voters (46%) are gym room regulars, 5 that voted Y. The majority of them (83%) voted Y.
In this situation, even with no formal federation structure, the minority and a potential local governance emerged: the tyranny perception arrives with it.
Concurrent majority[]
Secession of the Confederate States of America from the United States was anchored by a version of subsidiarity, found within the doctrines of John C. Calhoun. Antebellum South Carolina utilized Calhoun's doctrines in the Old South as public policy, adopted from his theory of concurrent majority. This "localism" strategy was presented as a mechanism to circumvent Calhoun's perceived tyranny of the majority in the United States. Each state presumptively held the Sovereign power to block federal laws that infringed upon states' rights, autonomously. Calhoun's policies directly influenced Southern public policy regarding slavery, and undermined the Supremacy Clause power granted to the federal government. The subsequent creation of the Confederate States of America catalyzed the American Civil War.
19th century concurrent majority theories held logical counterbalances to standard tyranny of the majority harms originating from Antiquity and onward. Essentially, illegitimate or temporary coalitions that held majority volume could disproportionately outweigh and hurt any significant minority, by nature and sheer volume. Calhoun's contemporary doctrine was presented as one of limitation within American democracy to prevent traditional tyranny, whether actual or imagined.[2]
Viewpoints[]
Critique by Robert A. Dahl[]
Robert A. Dahl argues that the tyranny of the majority is a spurious dilemma (p. 171):[12]
Critic: Are you trying to say that majority tyranny is simply an illusion? If so, that is going to be small comfort to a minority whose fundamental rights are trampled on by an abusive majority. I think you need to consider seriously two possibilities; first, that a majority will infringe on the rights of a minority, and second, that a majority may oppose democracy itself.
Advocate: Let's take up the first. The issue is sometimes presented as a paradox. If a majority is not entitled to do so, then it is thereby deprived of its rights; but if a majority is entitled to do so, then it can deprive the minority of its rights. The paradox is supposed to show that no solution can be both democratic and just. But the dilemma seems to be spurious.
Of course a majority might have the power or strength to deprive a minority of its political rights. [...] The question is whether a majority may rightly use its primary political rights to deprive a minority of its primary political rights.
The answer is clearly no. To put it another way, logically it can't be true that the members of an association ought to govern themselves by the democratic process, and at the same time a majority of the association may properly strip a minority of its primary political rights. For, by doing so the majority would deny the minority the rights necessary to the democratic process. In effect therefore the majority would affirm that the association ought not to govern itself by the democratic process. They can't have it both ways.
Critic: Your argument may be perfectly logical. But majorities aren't always perfectly logical. They may believe in democracy to some extent and yet violate its principles. Even worse, they may not believe in democracy and yet they may cynically use the democratic process to destroy democracy. [...] Without some limits, both moral and constitutional, the democratic process becomes self-contradictory, doesn't it?
Advocate: That's exactly what I've been trying to show. Of course democracy has limits. But my point is that these are built into the very nature of the process itself. If you exceed those limits, then you necessarily violate the democratic process.
Trampling the rights of minorities[]
Regarding recent American politics (specifically initiatives), Donovan et al. argue that:
One of the original concerns about direct democracy is the potential it has to allow a majority of voters to trample the rights of minorities. Many still worry that the process can be used to harm gays and lesbians as well as ethnic, linguistic, and religious minorities. ... Recent scholarly research shows that the initiative process is sometimes prone to produce laws that disadvantage relatively powerless minorities ... State and local ballot initiatives have been used to undo policies – such as school desegregation, protections against job and housing discrimination, and affirmative action – that minorities have secured from legislatures.[13]
Public choice theory[]
The notion that, in a democracy, the greatest concern is that the majority will tyrannise and exploit diverse smaller interests, has been criticised by Mancur Olson in The Logic of Collective Action, who argues instead that narrow and well organised minorities are more likely to assert their interests over those of the majority. Olson argues that when the benefits of political action (e.g., lobbying) are spread over fewer agents, there is a stronger individual incentive to contribute to that political activity. Narrow groups, especially those who can reward active participation to their group goals, might therefore be able to dominate or distort political process, a process studied in public choice theory.
Class studies
Tyranny of the majority has also been prevalent in some class studies. Rahim Baizidi uses the concept of "democratic suppression" to analyze the tyranny of the majority in economic classes. According to this, the majority of the upper and middle classes, together with a small portion of the lower class, form the majority coalition of conservative forces in the society.[14]
Vote trading[]
Anti-federalists of public choice theory point out that vote trading can protect minority interests from majorities in representative democratic bodies such as legislatures.[citation needed] They continue that direct democracy, such as statewide propositions on ballots, does not offer such protections.[weasel words]

See also[]
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Tyranny of the majority |
- Administrative law – Branch of law governing administrative agencies
- An Enemy of the People – 1882 play by Henrik Ibsen
- Argumentum ad populum – Fallacy of claiming the majority is always correct
- Authoritarian personality – Psychological trait/personality type
- Cancel culture – Modern form of ostracism
- Consensus decision-making – Making decisions based on a group's approval
- Conformity – The act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms
- Consociationalism – Form of democracy in which power is shared among the various groups within the society
- Criticism of democracy – Issues and problems associated with democratic political systems
- Dictatorship of the proletariat – Marxist political concept
- Democracy
- Dominant minority
- Elective dictatorship
- Enabling Act of 1933 – Transfer of the Reichstag's power to the government under Hitler
- General will – Term in political philosophy
- Individualist anarchism – Branch of anarchism that emphasize the individual and their will
- Majoritarianism – Political philosophy
- Minoritarianism
- Minority rights
- Ochlocracy
- Populism – Political philosophy that supports needs and desires of "the people" over those of "the elite"
- Social anarchism – Branch of anarchism emphasizing communal individuality and mutual aid
- Spiral of silence
- Totalitarianism – Concept for a political system in which the leader or state holds total authority over their citizenry
- Tragedy of the commons – Self-interests causing depletion of a shared resource
- Utilitarianism – Philosophical and ethical principle
References[]
- ^ John Stuart Mill. [1]
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lacy K. Ford Jr., "Inventing the Concurrent Majority: Madison, Calhoun, and the Problem of Majoritarianism in American Political Thought", The Journal of Southern History, Vol. 60, No. 1 (Feb., 1994), pp. 19–58 in JSTOR
- ^ P. J. Deneen (2015) "Equality, Tyranny, and Despotism in Democracy: Remembering Alexis de Tocqueville", 2015s theimaginativeconservative.org article.
- ^ Jump up to: a b A Przeworski, JM Maravall, I NetLibrary Democracy and the Rule of Law (2003) p. 223
- ^ John Adams, A Defence of the Constitutions of Government of the United States of America, Vol. 3 (London: 1788), p. 290-291, 310.
- ^ Burke, Edmund (1844). Correspondence of Edmund Burke between the year 1774 - 1797. Rivington.
- ^ See for example maxim 89 of Friedrich Nietzsche, Human, All Too Human: First Sequel: Mixed Opinions and Maxims, 1879
- ^ Ayn Rand (1961), "Collectivized 'Rights,'" The Virtue of Selfishness.
- ^ The Repressive Tolerance by Herbert Marcuse
- ^ Lani Guinier, The Tyranny of the Majority (Free Press: 1994)
- ^ "Herbert Spencer, The Right to Ignore the State (1851)". www.panarchy.org. Retrieved 2019-11-18.
- ^ Dahl, Robert (1989). Democracy and Its Critics.
- ^ Todd Donovan; et al. (2014). State and Local Politics. Cengage Learning. p. 131. ISBN 9781285441405.
- ^ Baizidi, Rahim (2019-09-02). "Paradoxical class: paradox of interest and political conservatism in middle class". Asian Journal of Political Science. 27 (3): 272–285. doi:10.1080/02185377.2019.1642772. ISSN 0218-5377. S2CID 199308683.
Further reading[]
- Beahm, Donald L. (2002). Conceptions of and Corrections to Majoritarian Tyranny. Lanham: Lexington Books.
- Nyirkos, Tamas (2018). The Tyranny of the Majority: History, Concepts, and Challenges. New York: Routledge.
- Volk, Kyle G. (2014). Moral Minorities and the Making of American Democracy. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Alexis de Tocqueville on Tyranny of the Majority from EDSITEment from the National Endowment for the Humanities
- Authoritarianism
- Democracy
- Libertarian terms
- Political terminology
- Political theories
- Abuse
- Majority
- Majority–minority relations
