Washington and Old Dominion Railroad
 The former W&OD 57, a General Electric 70-ton diesel–electric switcher locomotive built in 1956, at the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's Riverside Yard in Baltimore in January 1969.[1] | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Washington, D.C., Arlington, Virginia |
| Reporting mark | WOD |
| Locale | Virginia |
| Dates of operation | 1912–1968 |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Length | 72 miles (116 kilometres) |
The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad (colloquially referred to as the W&OD) was an intrastate short-line railroad located in Northern Virginia. The railroad was a successor to the bankrupt Washington and Old Dominion Railway and to several earlier railroads, the first of which began operating in 1859. The railroad closed in 1968.
The Railroad's oldest line extended from Alexandria on the Potomac River northwest to Bluemont at the base of the Blue Ridge Mountains near Snickers Gap, not far from the boundary line between Virginia and West Virginia. The railroad's route largely paralleled the routes of the Potomac River and the present Virginia State Route 7 (VA Route 7).
The single-tracked line followed the winding course of Four Mile Run upstream from Alexandria through Arlington to Falls Church. At that point, the railroad was above the Fall Line and was able to follow a more direct northwesterly course in Virginia through Dunn Loring, Vienna, Sunset Hills (now in Reston), Herndon, Sterling, Ashburn and Leesburg.
The line turned sharply to the west after passing through Clarke's Gap in Catoctin Mountain west of Leesburg. Its tracks then continued westward through Paeonian Springs, Hamilton, Purcellville and Round Hill to reach its terminus at Bluemont.
A branch connected the line to Rosslyn. The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Trail (W&OD Trail), the Bluemont Junction Trail, the Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway Trail, several other trails, Interstate 66 (I-66), and Old Dominion Drive (VA Route 309) have replaced much of the railroad's route.
History[]
Predecessors of the W&OD (1855–1911)[]

Lewis McKenzie, between 1860 and 1875

Originally incorporated as the Alexandria and Harper's Ferry Railroad, construction on the line began in 1855 by the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire (AL&H) Railroad under the presidency of Lewis McKenzie.[2] Initially intended to cross the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Shenandoah River to reach the coal fields in the western part of Hampshire County, Virginia, that are now within Mineral County, West Virginia, the AL&H began operating to Vienna in 1859 from a terminal near Princess and Fairfax Streets in Alexandria's present Old Town neighborhod.[3]
In 1860, the AL&H reached Leesburg in Loudoun County, with plans to extend the line westward through Hillsborough, Vestal's Gap, Berryville, Winchester and Romney. The line would terminate in Paddy Town (now Keyser, West Virginia), where it would make connections with the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.[3][4][5][6] Construction may have proceeded pursuant to those plans, as an 1864 Confederate army map shows that the railroad's tracks had passed Leesburg, crossed Catoctin Mountain at Clarke's Gap and passed Hillsborough.[7]
Because of its proximity to Washington, D.C., the line saw much use and disruption during the Civil War.[8] After the war, the name of the line was changed in 1870 to the Washington and Ohio Railroad.[9] After changing its planned route to enable it to cross the Blue Ridge through Snickers Gap rather than the more northerly Vestal's Gap, the railroad extended its line from Leesburg to Hamilton in 1870 and to Round Hill in 1874.[10]
Upon acquisition by new owners in the 1880s, the line's name was changed twice: first to the Washington and Western Railroad in 1882 and in the next year to the Washington, Ohio and Western (WO&W) Railroad.[11] However, the line did not serve Washington, Ohio, or the West.
In 1886, the Richmond and Danville Railroad, whose trunk line travelled between Washington, D.C., and Atlanta with connections to New York City, New Orleans, Mississippi and Florida, leased the WO&W.[12][13] The Richmond and Danville also acquired a branch that paralleled the WO&W while traveling between Manassas and Strasburg, Virginia, where it connected to railroads in the Shenandoah Valley west of the Blue Ridge that the WO&W did not reach (see: Manassas Gap Railroad).[12][13] In 1888, the Richmond and Danville began to operate the WO&W's trains between Washington, D.C., and Round Hill.[12][13]
In 1894, the newly formed Southern Railway absorbed the Richmond and Danville Railroad and acquired the WO&W.[14][15][16] In 1900, the Southern Railway extended the line westward for four miles from Round Hill to Bluemont (formerly Snickersville).[17] The Southern Railway designated the line as its Bluemont Branch.[14][15]


By 1908, steam locomotives were hauling Southern Railway passenger trains from the new Union Station in Washington, D.C., to Alexandria Junction (north of old town Alexandria), where they switched to travel westward on the Bluemont Branch.[14][18] Connecting trains shuttled passengers between Alexandria Junction and the former AL&H terminal in old town Alexandria.[14] On weekends, express trains carried vacationers from Washington to Bluemont and other towns in western Loudoun County in which resorts had developed.[14][15][19]
Meanwhile, in 1906, electric trolleys began to run on the Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad (GF&OD) northwest to Great Falls from Georgetown in Washington, D.C.[20][21] The line, which John Roll McLean and Stephen Benton Elkins owned at the time, crossed the Potomac River on the old Aqueduct Bridge and passed through Rosslyn. The trolleys then traveled northwest on a double-tracked line through Arlington and Fairfax County to reach an amusement park (trolley park) that the railroad company constructed and operated near the falls.[20]
Maps[]
 Confederate States Army map of Maryland and northern Virginia showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad, 1864
Confederate States Army map of Maryland and northern Virginia showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad, 1864 United States military map of Washington, D.C. and northeastern Virginia, showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad, 1865
United States military map of Washington, D.C. and northeastern Virginia, showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad, 1865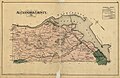 G.M. Hopkins map of Alexandria County, Virginia, showing the route of the Washington and Ohio Railroad, 1878
G.M. Hopkins map of Alexandria County, Virginia, showing the route of the Washington and Ohio Railroad, 1878 Richmond & Danville Railroad system map showing branch to Round Hill,1891
Richmond & Danville Railroad system map showing branch to Round Hill,1891 Richmond & Danville Railroad system map showing branch to Round Hill, 1893
Richmond & Danville Railroad system map showing branch to Round Hill, 1893 Southern Railway system map showing branch to Round Hill, 1895
Southern Railway system map showing branch to Round Hill, 1895
Washington and Old Dominion Railway (1911–1936)[]

In 1911, McLean and Elkins formed a new corporation, the Washington and Old Dominion Railway.[22] In that year, they concluded negotiations with the Southern Railway to lease the Southern's Bluemont Branch and to take over all service on the branch on July 1, 1912.[23] The lease excluded the portion of the Southern's route that connected Potomac Yard with the former AL&H terminal in old town Alexandria.[23]
In 1912, the GF&OD became the "Great Falls Division" of the W&OD Railway, while the Southern's Bluemont Branch became a part of the W&OD Railway's "Bluemont Division".[24] The W&OD electrified all of its operations over the next four years, becoming an interurban electric trolley system that carried passengers, mail, milk and freight.[25]
From that time onward, W&OD trains crossed over Potomac Yard on a long trestle constructed earlier for the Southern Railway.[26] In contrast to the Southern Railway's earlier Bluemont Branch service, the W&OD Railway's Bluemont Division did not serve Washington's Union Station.[27]
To join its two lines, the W&OD Railway constructed in 1912 a double-tracked Bluemont Division connecting line that traveled between two new junctions in Arlington: Bluemont Junction on the Alexandria-Bluemont line and Thrifton Junction on the Georgetown-Great Falls line.[23][28] The connecting line passed through Lacey (near the west end of Ballston), crossing on a through girder bridge over a competing interurban electric trolley line, the Fairfax line of the Washington-Virginia Railway (see Northern Virginia trolleys).[29][30] The rival line carried passengers between Rosslyn, Clarendon, Ballston, Falls Church, Vienna and Fairfax City.[31]
The railway's electrification system distributed 650 volts direct current (DC) to its Bluemont Division cars and trains through overhead catenary lines.[32] Single overhead lines carried the Great Falls Division's electricity over its tracks.[33] Stationary and movable electrical substations containing Westinghouse alternating current (AC) to DC converters were located at various points along the railway's routes.[32][34]
The W&OD's main passenger line ran from Georgetown and Rosslyn through Thrifton Junction, Bluemont Junction and westward to Bluemont.[35] However, after crossing the Potomac River from Georgetown, many W&OD passengers transferred in Rosslyn to the trolleys of the competing Washington-Virginia Railway.[36] Most of the W&OD's freight trains ran between Potomac Yard, Bluemont Junction and either Rosslyn or various locations along the Bluemont Division.[35]
In 1923, the W&OD Railway ceased operating from Georgetown when the federal government replaced the aging Aqueduct Bridge with the new Francis Scott Key Bridge.[37] At the same time, the railroad constructed a new passenger station in Rosslyn which became its "Washington" terminal.[37]
The W&OD Railway fell upon hard times in the 1930s during the Great Depression.[38] In 1932, the railway went into bankruptcy and was placed in receivership.[39] The railway also discontinued passenger service between Bluemont Junction and Alexandria during 1932.[40]
In 1934, the railway abandoned operations on the Great Falls Division between Thrifton Junction and Great Falls. The abandoned railway route then became Old Dominion Drive (Virginia State Route 309).[37][41][42] In 1979, the old rail trestle of the Great Falls Division over Difficult Run was demolished after years of carrying automobile traffic on Old Dominion Drive.[43]
Washington and Old Dominion Railroad (1936–1965)[]

Davis Elkins
In 1936, the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad, a new corporation that Davis Elkins (the son of Stephen Benton Elkins) had created, assumed operation of the remnants of the W&OD Railway, which consisted only of the Railway's Bluemont Division and the portion of the former Great Falls Division that had remained between Rosslyn and Thrifton (which was no longer a junction).[44][45] Shortly thereafter, in 1939, the railroad abandoned the western end of its line, which had connected the towns of Purcellville and Bluemont.[44]
In 1945, the W&OD Railroad acquired ownership of the section of line between Potomac Yard and Purcellville that the W&OD Railway had earlier leased from the Southern Railway.[46] The Southern Railway retained ownership of the easternmost section of the railroad's route, which still connected Potomac Yard to the Southern's freight and passenger stations in old town Alexandria.
During the 1940s, the W&OD Railroad converted all of its lines' operations from electric to diesel or gasoline power.[45][47] The railroad discontinued its electrified passenger service in 1941, but temporarily resumed passenger service during World War II using gas–electric motor cars and cars pulled by diesel–electric locomotives.[48] Passenger and mail service finally ended in 1951; thereafter, the railroad carried only freight.[49] The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) purchased the W&OD Railroad in 1956, but did not change the railroad's name.[50]
The 1960s were a decade of decline and closure for the W&OD. The Virginia highway department began negotiations to purchase the Rosslyn spur in 1960 and was trying to buy the mainline as early as 1962 for the construction of a road that was to become Interstate 66 (I-66).[51] In July 1962, the highway department bought the Rosslyn spur for $900,000. In September 1963, the railroad stopped operating to Rosslyn. The railroad removed its tracks between Lacey (south of Washington Boulevard) and Rosslyn by November 1964.[52][53]
Abandonment (1965—1968)[]
In February 1965, the Commonwealth of Virginia contracted to buy 30.5 miles (49.1 km) of the mainline from Herndon to Alexandria for $3.5 million. The C&O Railway then petitioned the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) for permission to abandon the railroad's remnant. The purchase would eliminate the need to build a grade separation where the railroad crossed the Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway (now part of Interstate 395 (I-395)) at grade and at another grade separation for I-66. The purchase would also provide 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of right-of-way for I-66, saving the state $5 million.[54]
Business interests in Loudoun County, the Arlington County Chamber of Commerce, various state, county and local officials, railway labor organizations and 21 of the 133 shippers who still used the railroad's freight service opposed the purchase. The Northern Virginia Transportation Commission (NVCC), which was interested in converting the line to a commuter rail service, also opposed the purchase.[54] The Washington Metropolitan Area Transit Authority (WMATA), which at the time was planning to construct a rapid transit system for the Washington area, tried to postpone the abandonment in the hopes of using part of the right-of-way for transit.[55]
The highway department simultaneously made plans to secretly sell all but 4 miles (6.4 km) of the route to the Virginia Electric and Power Company (VEPCO) (now Dominion Virginia Power), whose transmission lines were running along the railroad's right-of-way.[56] As a result, the highway department would sell to VEPCO the remaining 17.5 miles (28.2 km) of right-of-way, including the 12 miles (19.3 km) north of Herndon. The sale would thus prevent the NVCC from buying the land for mass transit.[57]
In August 1967, transit advocates led by Del. Clive L. DuVal II (Fairfax-Falls Church) and WMATA secured a 60-day postponement of the abandonment while they put together a plan to use the right-of-way for transit.[58] However, according to WMATA general manager Jackson Graham, the estimated cost of using the full right-of-way for commuter rail was $70 million. Because WMATA did not expect the proposed transit line to be able to generate enough ridership to be cost-effective, WMATA rejected that option.[59]

On November 10, 1967, WMATA announced that it had come to an agreement with the highway department that would give WMATA a two–year option to buy a 5 miles (8.0 km) stretch of the right of way from Glebe Road (Virginia Route 120) to the Capital Beltway (now Interstate 495 (I-495)), where I-66 was to be built. WMATA would operate mass transit in the highway's median strip. WMATA would have a 2-year option to buy the 10 miles (16.1 km) of right-of-way from the Beltway to Herndon for the use of commuter trains, an option that WMATA did not exercise.[60] A last minute offer to buy the railroad at its salvage cost and keep it running that the railroad's customers made was rejected in 1967.[61]
In 1968, the ICC decided to permit the C&O to abandon and sell its line. After initially planning to run their last train on January 30, 1968, a temporary restraining order kept the line open until August 27, 1968.[62] On the last day, B&O switcher 9155 pulled two empty lumber cars to Potomac Yard from the Murphy and Ames Lumber Company siding in Falls Church.[63] On August 30, the railroad shipped its three diesel locomotives to the B&O's Baltimore engine terminal, from which a salvage dealer purchased them.[63] By 1969, the C&O had removed all of its tracks and ties, except for some tracks that were crossing paved roads. In 1974, the railroad's bridge over the Capital Beltway was demolished to enable the highway to be widened.[64]
Legacy[]
The Virginia highway department retained the section of the railroad's route that crossed the Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway along the Arlington-Alexandria boundary and the portion of the route in Arlington immediately east of Falls Church, on which it built I–66.[65] WMATA then constructed a part of Washington Metro's Orange Line within the median strip of I-66 on that portion of the railroad's former route.[66]
In 1977, VEPCO agreed to sell to the Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority (NVRPA) (now NOVA Parks) for $3.6 million the portion of its right-of-way that lay west of the Alexandria/Arlington boundary.[65] The NVRPA then incorporated that portion of the right-of-way into its Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park, within which it constructed the W&OD Trail.[67] NVRPA completed the trail to Purcellville in 1988.[68]
In 1999, Virginia Department of Historic Resources staff determined that the "Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Historic District" was eligible for listing on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).[69] A 2000 NRHP registration form states that the Historic District is eligible for the listing because the District "is associated with events that have made a significant contribution to the broad patterns of our history". The form contains an in-depth description of the District's historical resources and of the railroad's history, as well as maps that show the locations of the Districts's major historical features.[70]


On June 18, 1979, the Heritage Conservation and Recreation Service of the United States Department of the Interior added the Herndon depot to the NRHP.[71] On May 28, 2010, the National Park Service added the Purcellville train station to the NRHP.[72] The Virginia Department of Historic Resources has added both stations to the Virginia Landmarks Register.[73]
Bluemont Division, Alexandria-Bluemont line[]

Most of the Bluemont Division's passenger cars or trains ran on the W&OD Railway's Great Falls Division's line from Georgetown over the Aqueduct Bridge through Rosslyn to Thrifton Junction. From Thrifton Junction, the trains ran on the Bluemont Division's connecting line to Bluemont Junction, where they met other Bluemont Division passenger cars or trains that ran from Alexandria, following Four Mile Run in Arlington. Some of the Bluemont Division cars or trains then continued their trips through Falls Church, Vienna, Herndon, Sterling, Ashburn, Leesburg, Clarke's Gap and Purcellville to terminate in Bluemont, Virginia, at the base of the Blue Ridge Mountains, following a route that was similar to that of Virginia State Route 7.[74]
After the W&OD Railroad closed, the Southern Railway and its successor, the Norfolk Southern Railway, operated a spur between the Alexandria waterfront and a north-south route that traveled through Potomac Yard before the Yard closed in 1989.[75] The spur formerly served trains traveling from the eastern end of the Bluemont Division to the Southern Railway's freight and passenger stations in old town Alexandria.[75] As the Southern Railway owned and operated the spur and the stations, this section of track remained in operation after the W&OD closed.[75] Railroad operations ended on the spur in 2012–2013 when GenOn Energy's Potomac River Generating Station and the Robinson Terminal's Oronoco Street warehouse closed.[76]
A paved trail in Alexandria's linear Mt. Jefferson Park has replaced part of the Bluemont Division's course through that city.[77] NOVA Parks' 44.6 miles (71.8 km)-long W&OD Trail travels in the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park within the Bluemont Division's former right-of-way from the Alexandria/Arlington boundary through Bluemont Junction to Purcellville.[78] The section of the Bluemont Division between Purcellville and Bluemont has not become a part of any trail, as the W&OD Railroad abandoned this section in 1938, thirty years before the remainder of its line closed.
Stations[]
The stations on the Alexandria-Bluemont line of the W&OD's Bluemont Division (with locations of sites in 2008) were:
| Station[79] | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | W&OD Trail Mile[80] | Side of Tracks[81] | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandria Passenger Terminal[82][83] | Northeast corner of Princess Street and N. Fairfax Street | 38°48′29″N 77°02′30″W / 38.808041°N 77.041572°W | City of Alexandria | --------- | West | circa 1863 | Operated by Southern Railway |
| Alexandria Freight House[83][84] | Northwest corner of Princess Street and N. Lee Street | 38°48′29″N 77°02′27″W / 38.808024°N 77.040972°W | City of Alexandria | --------- | East | Operated by Southern Railway | |
| W&OD locomotive maintenance shed | Northwest of intersection of Massey Lane and Hunting Creek Drive | 38°49′21″N 77°02′46″W / 38.8224781°N 77.0460114°W | City of Alexandria | --------- | Northeast | Undated | East end of W&OD Railroad; Northeast of Southern Railway junction on east side of Potomac Yard |
| Alexandria Junction[77][85] | Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway,[86] between Calvert Avenue and Stewart Avenue, west of Richmond Highway (U.S. Route 1) | 38°49′46″N 77°03′16″W / 38.8294239°N 77.0544899°W | City of Alexandria | --------- | Southwest | circa 1918 Undated Undated |
Site of track connecting to Washington & Ohio Junction on Washington and Alexandria Railway (Southern Railway main line).[87] Connecting track removed in 1912.[88] Historical markers near site:[89][90][91] 1) The Bluemont Line 2) St. Asaph Racetrack 3) Crossroads of Transportation |
| St. Elmo[77][92] | Commonwealth Avenue (northwest side) at intersection with Ashby Street near northwest end of Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway[86] | 38°50′00″N 77°03′32″W / 38.833237°N 77.058899°W | City of Alexandria | --------- | Southwest | 1932 1932 |
Crossing of Washington-Mt. Vernon line of Washington-Virginia Railway[77] Historical marker near site: The Electric Railway[89][90][93] |
| Cowdon[92] | Opposite side (east side) of S. Shirlington Road from Mile Zero of W&OD Trail (0.1 mile west of Henry G. Shirley Memorial Highway (I-395)) | 38°50′39″N 77°05′08″W / 38.8441553°N 77.0854908°W | Arlington County[94] | 0[95] | South | Also named Nauck Station.[96] Historical markers near site:[97] (1) Washington and Old Dominion Trail (2) Tracks Into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad (3) Nauck: A Neighborhood History | |
| Barcroft[98] | Columbia Pike (VA Route 244) (south side) & W&OD Trail | 38°51′23″N 77°06′34″W / 38.8563063°N 77.109569°W | Arlington County | 1.6[99] | Southwest | circa 1910 | Formerly Arlington Mill station |
| Barcroft Freight House | Columbia Pike (VA Route 244) (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°51′24″N 77°06′36″W / 38.856686°N 77.109947°W | Arlington County | 1.6[99] | Northeast | circa 1967 | |
| Glencarlyn[100] | W&OD Trail in Glencarlyn Park (near north side of Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) overpass) | 38°52′01″N 77°07′29″W / 38.866845°N 77.124667°W | Arlington County | 2.7[99] | Southwest | 1896–1912 1918 |
Agency station. Formerly Carlin Springs station. Historical marker at site.[101] |
| Bluemont Junction[100][102][103] | W&OD Trail between Wilson Boulevard and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′22″N 77°07′57″W / 38.872834°N 77.1325073°W | Arlington County | 3.4[104] | Northeast | Electrical substation (1913) 1934 (aerial) 1950s 1960s 1960s 1966 1968 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 circa 1968 |
Junction with Thrifton-Bluemont Junction connecting line Wye on east side of tracks.[102] Station and electrical substation within wye[102] Station near south side of electrical substation in 1916.[102] Station adjacent to south side of electrical substation after 1918 Historical markers at site:[97] 1) Bluemont Junction 2) The Great Falls Line 3) Rosslyn Station 4) Bluemont Junction, c. 1934 Historical marker near site:[97] Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
| Torrison[100] | Wilson Boulevard (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°52′30″N 77°08′02″W / 38.875115°N 77.133958°W | Arlington County | 3.6[104] | Northeast | ||
| Fostoria[105] | North Ohio Street (west side) & W&OD Trail | 38°52′55″N 77°08′46″W / 38.8820761°N 77.1462268°W | Arlington County | 4.4[104] | Southwest | Historical marker near site:[106] Brandymore Castle | |
| Falls Church (East Falls Church)[105] | Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29) (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°53′14���N 77°09′45″W / 38.887358°N 77.162583°W | Arlington County | 5.6[104] | Southwest | Westward view of Southern Railway and Washington, Arlington and Falls Church Railroad stations, circa 1910 Before 1940 1951 Undated 1960s circa 1966 1968 1970 1970s Undated distant view of East Falls Church station from west |
Agency station Historical marker at site:[97][107] East Falls Church Station Historical marker near site:[108] East Falls Church Three stations near site[109] |
| Rothsay[105] | W&OD Trail southeast of Oak Street | 38°53′26″N 77°10′36″W / 38.890611°N 77.176551°W | City of Falls Church | 6.5[110] | Northeast | Historical marker near site:[97] Train Wrecks | |
| West Falls Church (West End)[111] | W. Broad Street (VA Route 7) (east side) & W&OD Trail | 38°53′30″N 77°11′07″W / 38.891653°N 77.185282°W | City of Falls Church | 7.0[110] | South | 1890s Undated |
Historical marker at site:[97] West Falls Church Station Historical marker near site:[97] Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
| Evans | W&OD Trail near Fowler Street | 38°53′30″N 77°11′35″W / 38.8915798°N 77.1931091°W | Fairfax County | 7.4[110] | |||
| Green | Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority right-of-way near Interstate 66 and Avon Lane; 0.4 miles south of W&OD Trail | 38°53′21″N 77°12′47″W / 38.8892103°N 77.2130942°W | Fairfax County | --------- | |||
| Dunn Loring[112] | Sandburg Street (west side) & W&OD Trail | 38°53′30″N 77°13′21″W / 38.891734°N 77.222471°W | Fairfax County | 9.1[113] | North | 1950s 1963 Undated Undated |
Agency station. Historical markers at site:[97] 1) Dunn Loring Station 2) Camp Alger 3) Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
| Wedderburn[112] | W&OD Trail, 0.2 miles west of Cedar Lane | 38°53′46″N 77°14′23″W / 38.8962268°N 77.239755°W | Fairfax County | 10.1[113] | South | Undated | |
| Franklin | W&OD Trail, between Owaissa Road SE and Adahi Road SE (0.1 mile southeast of bridge abutment of Fairfax line of Washington-Virginia Railway on north side of W&OD Trail) |
38°53′56″N 77°14′40″W / 38.8988987°N 77.2443151°W | Town of Vienna | 10.3[113] | |||
| Park Street | Park St. SE & W&OD Trail | 38°54′04″N 77°15′34″W / 38.901013°N 77.259515°W | Town of Vienna | 11.3[113] | West of site of Civil War Battle of Vienna, Virginia Historical markers near site:[97] 1) "Civil War Action at Vienna". 2) Electric Trains on the W&OD 3) The Great Falls Line | ||
| Church Street | Church Street NE & W&OD Trail | 38°54′12″N 77°15′56″W / 38.903232°N 77.265419°W | Town of Vienna | 11.7[113] | Adjacent to Vienna Station of Washington-Virginia Railway | ||
| Vienna[114] | 231 Dominion Road NE at Ayr Hill Avenue NE (southeast side) & W&OD Trail | 38°54′15″N 77°16′01″W / 38.904142°N 77.266974°W | Town of Vienna | 11.8[115] | Southwest | 1894–1912 circa 1913 1950 1960 circa 1960 1966-1967 Undated |
Agency station. National Register of Historic Places nomination form for station prepared in 2002[116] Historical marker at site:[97] Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Historical markers near site:[97] 1) Vienna Station 2) Vienna Centennial Park |
| Clarks Crossing[117] | Clarks Crossing Road (southwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°55′16″N 77°17′09″W / 38.921097°N 77.285804°W | Fairfax County | 13.3[115] | Northeast | ||
| Piney | Piney Branch & W&OD Trail (northwest of Peppermill Place) | 38°55′32″N 77°17′18″W / 38.925563°N 77.288336°W | Fairfax County | 13.7[115] | Historical marker near site:[97] Terror by the Tracks | ||
| Lowland | Lowland Station Road & W&OD Trail | 38°55′42″N 77°17′34″W / 38.928382°N 77.292686°W | Fairfax County | 14.0[115] | |||
| Hunters[118] | Hunter Mill Road (VA Route 674) (east side) & W&OD Trail | 38°55′57″N 77°18′18″W / 38.9325737°N 77.3049277°W | Fairfax County | 14.7[119] | Southwest | Before 1912 circa 1950 Undated |
Historical markers near site:[97] 1) Hunter Station circa 1900 2) Hunter Station 3) Strategic Junction: Hunter Mill Road and the AL&H Railroad 4) Crossroads to War |
| Pinecrest | W&OD Trail near Michael Faraday Court | 38°56′58″N 77°19′57″W / 38.949535°N 77.33245°W | Fairfax County | 16.7[119] | |||
| Soapstone Siding | W&OD Trail | Fairfax County | |||||
| Sunset Hills[120] | Old Reston Avenue (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°57′21″N 77°21′06″W / 38.955869°N 77.351789°W | Fairfax County | 17.7[121] | Northeast | 1966 1968 1968 |
Agency station. Formerly Wiehle station. Historical markers near site:[97] 1) Sunset Hills Station 2) Sunset Hills Station 3) Train Wrecks 4) Wiehle's Town Hall |
| Thornton | W&OD Trail east of Town Center Parkway, Reston | 38°57′23″N 77°21′41″W / 38.956330°N 77.361367°W | Fairfax County | 18.4[121] | |||
| Jackson | Sugarland Run & W&OD Trail, between Fairfax County Parkway and Herndon Parkway E | 38°57′34″N 77°22′16″W / 38.959511°N 77.371025°W | Fairfax County | 18.8[121] | |||
| Coral[122] | Coral Road (northeast side) & W&OD Trail | 38°57′57″N 77°22′47″W / 38.9657322°N 77.3796594°W | Town of Herndon | 19.6[121] | Southwest | ||
| Herndon[122][123] | 717 Lynn Street at Station Street (south side) & W&OD Trail | 38°58′13″N 77°23′09″W / 38.970170°N 77.385700°W | Town of Herndon | 19.9[121] | Southwest | 1890 1905 Before 1912 1951 1968 |
Agency station. Wye northwest of station (northeast side of tracks).[122] Electrical substation attached to southeast side of station.[122] Station listed on National Register of Historic Places in 1979.[71] Historical markers near site:[97] 1) Herndon Station 2) Mosby's Herndon Station Raid 3) Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad 4) The Rail Strike of 1916 |
| Herndon Heights[124] | Crestview Drive (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 38°58′48″N 77°23′56″W / 38.9800163°N 77.3988855°W | Town of Herndon | 20.9[125] | Northeast | ||
| Oak Grove | Locust Lane & W&OD Trail (near Dominion Lane) | 38°59′02″N 77°24′14″W / 38.983871°N 77.403995°W | Loudoun County | 21.3[125] | |||
| Lynn | W&OD Trail | 38°59′17″N 77°24′29″W / 38.988077°N 77.408059°W | Loudoun County | 21.6[125] | |||
| Buchanan | Warwick Court & W&OD Trail | 38°59′46″N 77°25′17″W / 38.996040°N 77.421470°W | Loudoun County | 22.6[125] | |||
| Sterling[126] | W&OD Trail, north of Ruritan Circle (Old Church Road) (VA Route 859) | 39°00′25″N 77°25′44″W / 39.006996°N 77.4289852°W | Loudoun County | 23.4[127] | West | Before 1912 1927 |
Agency station. Formerly Guilford station. Historical marker at site:[97] Sterling Station |
| Smiths[128] | W&OD Trail; 0.4 miles southeast of crossing of Smith's Switch Road and W&OD Trail | 39°01′25″N 77°27′13″W / 39.0236389°N 77.453565°W | Loudoun County | 25.1[127] | Historical marker near site:[97] Rails to Dulles Airport | ||
| Normans (Smith's)[129] | 0.1 mile northwest of crossing of Smith's Switch Road and W&OD Trail; 0.03 miles northwest of W&OD Trail rest stop. | 39°01′41″N 77°27′39″W / 39.0279918°N 77.4607506°W | Loudoun County | 25.7[130] | Northeast | 1920s | Historical markers near site: 1) Norman's Station[97] 2) Tracks into History: The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad[131] |
| Ashburn[132] | Ashburn Road (VA Route 641) (east side) & W&OD Trail | 39°02′38″N 77°29′14″W / 39.043974°N 77.487305°W | Loudoun County | 27.5[130] | Northeast | circa 1911 Undated 1967 1967 |
Agency station. Formerly Farmwell station.[133] Historical marker at site:[97] Ashburn Station |
| Graves | W&OD Trail (west of west end of Graves Lane) | 39°03′00″N 77°29′52″W / 39.050115°N 77.497644°W | Loudoun County | 28.1[130] | |||
| Belmont Park[123] | Belmont Ridge Road (VA Route 659) & W&OD Trail | 39°03′49″N 77°30′40″W / 39.063594°N 77.511082°W | Loudoun County | 29.4[134] | Historical marker near site: Belmont[135] | ||
| Trap Rock | Luck Stone Quarry & W&OD Trail (0.5 miles west of Belmont Ridge Road (VA Route 659)) |
39°03′49″N 77°30′40″W / 39.063594°N 77.511082°W | Loudoun County | 29.9[134] | North | Served Trap Rock Quarry (now Leesburg plant of Luck Stone Corp.). Historical marker near site:[97] Diesel Trains on the W&OD | |
| Compher | Cochrane Mill Road & W&OD Trail | 39°04′26″N 77°31′42″W / 39.073773°N 77.528232°W | Loudoun County | 30.6[134] | |||
| Pleasant View | W&OD Trail (west of intersection of Trailview Boulevard and Breakstone Drive) | 39°04′52″N 77°31′57″W / 39.081007°N 77.532438°W | Loudoun County | 31.2[136] | |||
| Lawson[137] | Lawson Road SE (southeast side) & W&OD Trail | 39°05′59″N 77°32′47″W / 39.0997139°N 77.5464445°W | Town of Leesburg | 32.7[136] | Northeast | ||
| Leesburg Freight House[137] | Harrison Street SE (west side) & W&OD Trail | 39°06′40″N 77°33′50″W / 39.1111031°N 77.5640023°W | Town of Leesburg | 34.2[138] | Northeast | 1966 1967 |
Wye on northeast side of tracks Freight House inside of wye Historical marker at site:[97] Leesburg Freight Station Historical markers near site:[97] 1) The Leesburg Lime Company 2) Stationmaster's House 3) The Depot 4) Norman-Harding Barn (The "Wharf") 5) McKimmey's Mill |
| Leesburg Passenger Station[137] | S. King Street (U.S. Route 15) (west side) & W&OD Trail | 39°06′44″N 77°33′58″W / 39.112156°N 77.566164°W | Town of Leesburg | 34.4[138] | Northeast | 1906 circa 1908 colorized postcard 1909 colorized postcard Before 1912 Before 1912 1951 1960s |
Agency station. Historical marker at site:[97] Leesburg Passenger Station Historical markers near site:[97] 1) Electric Trains on the W&OD 2) The Great Falls Line |
| Dry Mill | W&OD Trail, north of intersection of Dry Mill Road and Woodburn Road | 39°06′42″N 77°35′34″W / 39.111715°N 77.592852°W | Loudoun County | 35.8[138] | |||
| Clarkes Gap[139] | Dry Mill Road (northwest side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′16″N 77°36′35″W / 39.1378331°N 77.6096374°W | Loudoun County | 38.0[140] | Northeast | Before 1912 1930 |
Agency station. Historical marker at site:[97] Clarkes Gap |
| Paeonian Springs[139] | Simpson Circle (west side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′52″N 77°37′10″W / 39.147768°N 77.619438°W | Loudoun County | 39.2[140] | South | Before 1912 1920s |
Agency station. Historical marker at site:[97] Paeonian Springs Station |
| Hamilton[141] | Hamilton Station Road (east side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′39″N 77°39′05″W / 39.144091°N 77.651303°W | Loudoun County | 40.9[142] | South | Before 1912 Before 1912 Undated Undated |
Agency station. Historical markers at site:[97] 1) Hamilton Station 2) Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
| Ivandale[143] | Ivandale Road (east side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′47″N 77°40′12″W / 39.1463955°N 77.6699495°W | Loudoun County | 42.0[142] | North | ||
| Florance | N. Maple Avenue (VA Route 722) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′28″N 77°42′12″W / 39.141012°N 77.703284°W | Town of Purcellville | 43.8[144] | Historical marker near site:[97] Electric Trains on the W&OD | ||
| Purcellville[145] | N. 21st Street (northeast side) and W&OD Trail | 39°08′19″N 77°42′58″W / 39.1384821°N 77.7161211°W | Town of Purcellville | 44.8[144] (End) |
South | 1923–1951 Undated 1940 Undated 1951 1970s 1988 |
Agency station. Listed on National Register of Historic Places in 2010.[72] Historical markers at site:[97] 1) Purcellville Station 2) Beyond Purcellville Historical marker near site:[97] Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
| Simmons | --------- | ||||||
| Round Hill Passenger Station[146] | 35 Main Street (southeast side of Main street) | 39°08′10″N 77°46′08″W / 39.1360397°N 77.7688479°W | Town of Round Hill | --------- | South | Before 1912 looking northeast Before 1912 looking northeast circa 1912 looking south circa 1912 looking west |
Agency station. Electrical substation adjacent to south side of station. |
| Round Hill Freight House[146] | 34 Main Street (northwest side of Main Street) | 39°08′10″N 77°46′09″W / 39.1360668°N 77.7692932°W | Town of Round Hill | --------- | North | circa 1912 looking west 1970 |
|
| Scotland Heights[147] | Scotland Heights Road (northeast side) | Loudoun County | --------- | Southwest | |||
| Homestead | --------- | ||||||
| Bluemont Terminal[148] | Railroad Street (VA Route 753), north of Snickersville Turnpike (VA Route 734) | 39°06′40″N 77°49′56″W / 39.111066°N 77.832169°W | Town of Bluemont | --------- | Northwest | circa 1905 circa 1905 circa 1912 1939 |
Agency station. Wye on southeast side of tracks, opposite station. Original station constructed circa 1900; later burned. Replaced by smaller station. |
Existing remnants of the Bluemont Division, Alexandria-Bluemont line[]
The following remnants of the Alexandria-Bluemont Line existed in 2000 and later.[149] Some were photographed in 1997 or in subsequent years:
Existing stations[]
| Station | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | Operator | Use | Photo | Notes | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vienna | 231 Dominion Road NE at Ayr Hill Avenue NE (southeast side) & W&OD Trail | 38°54′15″N 77°16′01″W / 38.904142°N 77.266974°W | Town of Vienna | Northern Virginia Model Railroaders, Inc.[150] | Museum and model railroad layout | 2007[151] undated[152] |
Nomination form for National Register of Historic Places prepared in 2002.[116] |  Vienna Depot, July 2018 |
| Sunset Hills | Old Reston Avenue (west side) & W&OD Trail | 38°57′21″N 77°21′06″W / 38.955869°N 77.351789°W | Fairfax County | NOVA Parks | Vacant | 2009[153] | Former headquarters office of Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park. | |
| Herndon | 717 Lynn Street at Station Street (south side) & W&OD Trail | 38°58′13″N 77°23′09″W / 38.970170°N 77.385700°W | Town of Herndon | Herndon Historical Society[156] | Herndon Depot Museum and visitor center | 2006[157] | Listed on National Register of Historic Places in 1979.[71] |  Herndon Depot, August 2012 |
| Leesburg Freight House | Market Station[159] at Harrison Street SE (west side) and Royal Street SE (201 Harrison Street SE) | 39°06′46″N 77°33′46″W / 39.112851°N 77.562854°W | Town of Leesburg | Metro Management Services[160] | Pizza restaurant[161] | 2008[162] | Moved two blocks north of original location in 1984.[163] Historical marker on building: The Depot |
|
| Clarkes Gap Passenger Shelter | Simpson Circle (west side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′52″N 77°37′10″W / 39.147768°N 77.619438°W | Loudoun County | NOVA Parks | Trailside shelter | 2007[164] 2017[165] |
Replaced burned Clarkes Gap station. Preserved by former W&OD Railroad employee. Relocated to former site of Paeonian Springs station by NOVA Parks.[166] | |
| Hamilton | Hamilton Station Road (east side) & W&OD Trail | 39°08′36″N 77°39′02″W / 39.143375°N 77.650509°W | Loudoun County | Loudoun County Milling Company | Mill equipment storage | undated[167] 2010[168] 2020[169] |
||
| Purcellville | 21st Street N (east side) and W&OD Trail | 39°08′19″N 77°42′58″W / 39.1384821°N 77.7161211°W | Town of Purcellville | Town of Purcellville[170] | Loudoun Visitors Center.[171] Public meeting space |
2009[172] 2009[173] Interior, undated[174] |
Preserved and restored by Purcellville Preservation Association.[175] Listed on National Register of Historic Places in 2010.[72] |
 Purcellville Station, August 2008 |
| Round Hill Passenger Station | 35 Main Street (south side of Main Street) | 39°08′10″N 77°46′08″W / 39.1360397°N 77.7688479°W | Town of Round Hill | Private property owner | Residence | 1997[176] 2014[177] |
||
| Round Hill Freight House | 34 Main Street (northwest side of Main Street) | 39°08′10″N 77°46′09″W / 39.1360668°N 77.7692932°W | Town of Round Hill | Private property owner | 2019[179] |
Bridges[]
| Crossing | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | W&OD Trail Mile | Remnant | Photo | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Russell Road | Russell Road (west side) between W. Glebe Road and Kentucky Avenue | 38°50′17″N 77°03′53″W / 38.838109°N 77.064588°W | City of Alexandria | ------------ | Abutment of former railroad bridge | undated[180] undated[77] |
|
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Columbia Pike and Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) | 38°51′51″N 77°07′07″W / 38.864051°N 77.118632°W | Arlington County | 2.3[99] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutments under trail bridge, July 2020 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Columbia Pike and Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) | 38°51′55″N 77°07′14″W / 38.865205°N 77.120540°W | Arlington County | 2.4[99] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutments under trail bridge, July 2020 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Columbia Pike and Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) | 38°51′57″N 77°07′22″W / 38.865765°N 77.122731°W | Arlington County | 2.5[99] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutments under trail bridge, July 2020 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) and N. Carlin Springs Road | 38°52′03″N 77°07′34″W / 38.86762°N 77.125987°W | Arlington County | 2.8[99] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutments under trail bridge, July 2020 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between N. Carlin Springs Road and Wilson Boulevard | 38°52′25″N 77°07′59″W / 38.873653°N 77.133143°W | Arlington County | 3.4[104] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutment under trail bridge, July 2020 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Wilson Boulevard and N. Patrick Henry Drive | 38°52′42″N 77°08′16″W / 38.878464°N 77.137713°W | Arlington County | 3.9[104] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutment under trail bridge, September 2017 | |
| Four Mile Run | W&OD Trail between Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29) and Little Falls Street | 38°53′17″N 77°09′55″W / 38.888191°N 77.165407°W | Arlington County | 5.9[110] | Abutments under trail bridge |  Abutment under trail bridge, June 2020 | |
| Piney Branch | W&OD Trail between Ayr Hill Avenue NE and Hunter Mill Road | 38°55′32″N 77°17′18″W / 38.925642°N 77.288381°W | Fairfax County | 13.6[115] | Abutments under trail bridge | 2010[181] | |
| Difficult Run | W&OD Trail between Ayr Hill Avenue NE and Hunter Mill Road | 38°55′51″N 77°17′54″W / 38.930942°N 77.29834°W | Fairfax County | 14.3[115] | Abutments and pier under trail bridge | 2009[182] |  Pier and abutment under trail bridge, October 2020 |
| Broad Run | W&OD Trail between Sully Road and Panorama Parkway | 39°01′06″N 77°26′42″W / 39.01845°N 77.444923°W | Loudoun County | 24.6[127] | Abutments and pier under trail bridge | undated[183] | |
| Beaverdam Run | W&OD Trail between Smiths Switch Road and Ashburn Village Boulevard | 39°01′55″N 77°28′02″W / 39.031905°N 77.467293°W | Loudoun County | 26.2[130] | Abutments under trail bridge | ||
| Goose Creek | W&OD Trail between Belmont Ridge Road and Cochrane Mill Road | 39°04′10″N 77°31′10″W / 39.0694962°N 77.5195634°W | Loudoun County | 30.1[134] | Abutments and pier supporting trail bridge | 2007[184] undated[185] |
|
| Sycolin Creek | W&OD Trail between Belmont Ridge Road and Cochrane Mill Road | 39°04′20″N 77°31′29″W / 39.0723241°N 77.5247133°W | Loudoun County | 30.4[134] | Span, abutments and pier of railroad bridge (now trail bridge). | undated[186] | |
| Tuscarora Creek | W&OD Trail between Cochran Mill Road and Lawson Road SE | 39°05′44″N 77°32′32″W / 39.0955841°N 77.5422603°W | Town of Leesburg | 32.3[136] | Abutments and piers of railroad bridge south of W&OD Trail | ||
| Clarke's Gap | W&OD Trail and Dry Mill Road | 39°08′22″N 77°36′39″W / 39.1395702°N 77.6109248°W | Loudoun County | 38.2[140] | Stone arch above former W&OD line. | 2007[187] |  Stone arch at Clarke's Gap, August 2008 |
| Unnamed stream | W&OD Trail west of Simpson Circle in Paeonian Springs | 39°08′53″N 77°37′19″W / 39.148105°N 77.622067°W | Loudoun County | 39.4[140] | Stone arch culvert under former W&OD line (now under W&OD Trail) | undated[188] | |
| ----- | Simmons Road (VA Route 716) east of Round Hill | Loudoun County | Remnant of W&OD viaduct on Simmons Road | April 7, 2020 |
Other remnants[]
| Remnant | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | W&OD Trail Mile | Side of W&OD Trail | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former Norfolk Southern Railway spur | Tracks between Pendleton Street (east of intersection with N. Fairfax St.) and CSX main line near Slaters Lane | 38°49′01″N 77°02′22″W / 38.81694°N 77.039523°W | City of Alexandria | ------------ | ------------ | ------------ | No longer in operation; formerly owned by Southern Railway |
| Floor of electrical substation at Bluemont Junction | Between soccer field and 1971 Southern Railway caboose east of W&OD Trail in Bluemont Junction Park (between Bluemont Junction Trail and Wilson Boulevard) | 38°52′23″N 77°07′57″W / 38.872955°N 77.132521°W | Arlington County | 3.4[104] | East | 2009[189] | In Bluemont Junction Historical Railroad Display[190] in Bluemont Junction Park[191] |
| Coal trestle with rails and ties[192] | 0.05 mile west of Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29); south of W&OD Trail | 38°53′15″N 77°09′48″W / 38.8875844°N 77.1634462°W | Arlington County | 5.6[104] | South | 2007[193] | Formerly used to unload coal from hopper cars and fuel oil from tank cars. Partially demolished in June 2014. Designated as local historic district in September 2014.[194] |
| Leesburg Stationmaster's House | Market Station[160] at Harrison Street SE (west side) and South Street SE (205 Harrison Street SE) | 39°06′44″N 77°33′47″W / 39.1123206°N 77.563042°W | Town of Leesburg | ------------ | ------------ | 2008[195] Undated[196] |
Moved to Market Station[160] (south of relocated freight station). Used as cigar and pipe store.[196] Historical marker on building: Stationmaster's House |
| Round Hill Electrical Substation | Adjacent to south side of former passenger station at 35 Main Street (southeast side of Main Street) | 39°08′09″N 77°46′08″W / 39.1359357°N 77.7688774°W | Town of Round Hill | ------------ | ------------ | 1997[197] | Private residence Enclosed by house |
Existing trails and parks along railroad route[]
Rail trails[]
- Trail in Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway between Richmond Highway (U.S. Route 1) and Commonwealth Avenue, Alexandria[86]
- Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Trail (W&OD Trail)
Other trails[]
- Unpaved trail connecting Russell Road and Landover Street, Alexandria.[198]
- Section of Mount Vernon Trail adjacent to Norfolk Southern Railway spur between Pendleton Street and E. Abingdon Drive, Alexandria[199]
Linear parks[]
- Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway, Alexandria[77][86]
- Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park
Great Falls Division[]
Great Falls Division stations[]
The stations on the Great Falls Division of the W&OD (with locations of sites in 2008) were:
| Station[200] | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | Side of Tracks[201] | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Georgetown[202] | M Street, N.W., between 35th and 37th Streets, N.W. | 38°54′19″N 77°04′13″W / 38.90519°N 77.070293°W | District of Columbia | West | Terminal station of GF&OD and W&OD until 1923. Adjacent to Georgetown Car Barn, which served Washington's electric street cars. | |
| Rosslyn[202] | Passenger Terminal (1923 to 1938): Fort Myer Drive (west side) between George Washington Memorial Parkway and Lee Highway |
38°53′58″N 77°04′18″W / 38.89957°N 77.071785°W | Arlington County | West | Undated photo of front of station Undated colorized postcard & 1923 interior photo of passenger terminal |
The GF&OD and W&OD stopped at a passenger shelter from 1904 to 1923. The W&OD terminated behind a passenger station on Fort Myer Drive from 1923 to 1938. The railroad terminated near a maintenance shop in the present route of I-66 a short distance west of Fort Myer Drive from 1938 to 1964. All of the Rosslyn stations and termini were near the present site of the Key Bridge Marriott Hotel. Historical Marker: Rosslyn Station[203] |
| Colonial[202] | I-66 at N. Nash Street | 38°53′55″N 77°04′25″W / 38.89866°N 77.07374°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Rosslyn Freight House[202] | I-66 near N. Oak Street | 38°53′55″N 77°04′32″W / 38.898682°N 77.075433°W | Arlington County | North | ||
| Mackeys[202] | I-66 at N. Quinn Street | 38°53′52″N 77°04′44″W / 38.8978717°N 77.078914°W | Arlington County | Northwest | ||
| Park Lane[202] | I-66 east of N. Uhle Street; north of Lee Highway | 38°53′50″N 77°05′04″W / 38.89709°N 77.084509°W | Arlington County | Southwest | ||
| Pearce[202] | I-66 near N. Adams Street | 38°53′54″N 77°05′22″W / 38.89823°N 77.089466°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Clark[202] | I-66 near N. Calvert Street | 38°53′52″N 77°05′35″W / 38.89782°N 77.092985°W | Arlington County | South | Near east side of Spout Run. | |
| Thrifton[202] | I-66 between Lee Highway and Spout Run Parkway | 38°53′48″N 77°05′53″W / 38.896626°N 77.098048°W | Arlington County | South | North of Lyon Village shopping center near southeast end of Maywood Historic District.[204] Named for Hugh A. Thrift.[205] East of junction with Thrifton – Bluemont Junction connecting line. | |
| Dominion Heights[206] | Lee Highway (between traffic lanes) at N. Monroe Street (east side)[207] | 38°53′46″N 77°06′15″W / 38.8960055°N 77.1040356°W | Arlington County | South | Adjacent to Maywood Historic District[207] | |
| Cherrydale[206] | Intersection of Lee Highway and Old Dominion Drive at Military Road (east side) | 38°53′49″N 77°06′30″W / 38.8969741°N 77.1083701°W | Arlington County | Southwest | circa 1908 | |
| Harrison[206] | Old Dominion Drive at N. Thomas Street | 38°53′58″N 77°06′51″W / 38.89947°N 77.114174°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Greenwood[206] (Lee Heights)[208] |
Old Dominion Drive at Lorcom Lane (northwest side); east of N. Upton Street | 38°53′57″N 77°07′01″W / 38.8991534°N 77.1170604°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Maplewood[206] | Old Dominion Drive between traffic lanes north of Lee Highway; west of N. Abingdon Street | 38°53′55″N 77°07′17″W / 38.89867°N 77.12139°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Livingston[206] (Livingstone Heights)[209] |
Old Dominion Drive at 24th Street N. (north side) | 38°54′03″N 77°07′28″W / 38.90073°N 77.124431°W | Arlington County | Southwest | 24th Street N. was Livingstone Street prior to 1935 (named for Colin H. Livingstone)[210] | |
| Lyonhurst[206] | Old Dominion Drive at 25th Street N. | 38°54′07″N 77°07′33″W / 38.90189°N 77.125799°W | Arlington County | Southwest | Named for the nearby estate of Frank Lyon (now Missionhurst) | |
| Summit[206] | Old Dominion Drive at 26th Street N. (southeast side) | 38°54′10″N 77°07′38″W / 38.902907°N 77.127108°W | Arlington County | Southwest | ||
| Rixey[206] | Old Dominion Drive at N. Glebe Road (east side) | 38°54′15″N 77°07′43″W / 38.9042925°N 77.1286476°W | Arlington County | Northeast | undated | Named for the nearby estate of Dr. Presley Marion Rixey. Marymount University now occupies the Rixey estate. Later station on southwest side of tracks.[211] |
| Jewell[212] | Old Dominion Drive at Rock Spring Road (north side) | 38°54′28″N 77°07′58″W / 38.90781°N 77.132692°W | Arlington County | Southwest | undated | Named for Charles Jewell |
| Vanderwerken[212] | Old Dominion Drive at Little Falls Road (northwest side) | 38°54′35″N 77°08′13″W / 38.90980°N 77.136987°W | Arlington County | North | Named for Gilbert Vanderwerken | |
| Franklyn Park (Franklin Park)[212] | Old Dominion Drive at Franklin Park Road | 38°54′55″N 77°08′54″W / 38.91540°N 77.148453°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | 1910 |
|
| Rockwell[212] | Old Dominion Drive near Dominion Crest Lane | 38°55′06″N 77°09′00″W / 38.9183177°N 77.1500731°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | ||
| Chesterbrook[212] | Old Dominion Drive at Kirby Road (northwest side) | 38°55′18″N 77°09′13″W / 38.9215898°N 77.1535599°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | ||
| El Nido[213] | Old Dominion Drive at Birch Road | 38°55′26″N 77°09′42″W / 38.92394°N 77.161762°W | Fairfax County | North | ||
| Selva[213] | Old Dominion Drive at 6th Place | 38°55′35″N 77°09′57″W / 38.92639°N 77.165893°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | ||
| Viresco[213] | Old Dominion Drive between Pimmit Run and Linway Terrace | 38°55′44″N 77°10′04″W / 38.928889°N 77.1678776°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | Southeast side of B&O Railroad right-of-way[105][214] | |
| Lawnvale[213] | Old Dominion Drive near Holmes Place | 38°55′51″N 77°10′22″W / 38.9309379°N 77.1728396°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | ||
| McLean[213] | Old Dominion Drive at Chain Bridge Road (northwest side) | 38°56′03″N 77°10′40″W / 38.93404°N 77.177692°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | Named for John Roll McLean | |
| Ingleside[213] | Old Dominion Drive at Ingleside Avenue | 38°56′09″N 77°10′59″W / 38.93582°N 77.182946°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | ||
| Balls Hill[215] | Old Dominion Drive at Balls Hill Road (east side) | 38°56′30″N 77°11′39″W / 38.94159°N 77.19419°W | Fairfax County | West | ||
| Hitaffer[215] | Old Dominion Drive at Swinks Mill Road (south side) | 38°56′48″N 77°12′41″W / 38.9466559°N 77.2114956°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | ||
| Jackson[215] | Old Dominion Drive northwest of Swinks Mill Road | 38°56′51″N 77°12′50″W / 38.9474402°N 77.2139579°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | undated | |
| Spring Hill[216] | Old Dominion Drive at Spring Hill Road (east side) | 38°57′10″N 77°13′35″W / 38.95275°N 77.226382°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | ||
| Prospect Hill[216] | Old Dominion Drive at Bellview Place | 38°57′30″N 77°14′11″W / 38.95836°N 77.236467°W | Fairfax County | Northeast | undated | |
| Belleview[216] | Old Dominion Drive at Bellview Road | 38°57′40″N 77°14′25″W / 38.96098°N 77.240308°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | undated | |
| Glendale[217] | Old Dominion Drive at Towlston Road | 38°58′12″N 77°14′58″W / 38.96998°N 77.249559°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | ||
| Peacock[217] | Old Dominion Drive at Peacock Station Road (east side) | 38°58′25″N 77°15′12″W / 38.97348°N 77.253223°W | Fairfax County | Southwest | undated | |
| Fairview[217] | Old Dominion Drive at Falls Run Road | 38°58′40″N 77°15′26″W / 38.97777°N 77.257141°W | Fairfax County | West | ||
| Elkins[217] | Old Dominion Drive at Georgetown Pike (north side) | 38°58′54″N 77°15′25″W / 38.98177°N 77.25686°W | Fairfax County | West | undated undated |
Named for Stephen Benton Elkins. |
| Dickeys Road | Old Dominion Drive in Great Falls Park | 38°59′36″N 77°15′20″W / 38.99338°N 77.255688°W | Fairfax County (National Park Service) | Named for Dickey's Inn. Near former site of Matildaville. | ||
| Great Falls[217] | Old Dominion Drive in Great Falls Park | 38°59′48″N 77°15′19″W / 38.99663°N 77.255355°W | Fairfax County (National Park Service) | Inside turnaround | undated postcard |
Terminal station of GF&OD and Great Falls Division of W&OD. |
Thrifton-Bluemont Junction connecting line[]
The Thrifton-Bluemont Junction connecting line, a component of the W&OD's Bluemont Division, opened in 1912. The line connected the W&OD's Great Falls Division (formerly the Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad) with the Bluemont Division's Alexandria-Bluemont line.
The line closed in sections in 1963 and 1968.[218] I–66 and the adjacent Custis Trail replaced the line between Thrifton and Washington Boulevard in Ballston. Arlington County's Bluemont Junction Trail replaced the line between Washington Boulevard and Bluemont Junction.
Bluemont Junction, where the Bluemont Junction Trail now meets the W&OD Trail, presently contains an Arlington County railroad display that features a Southern Railway bay window caboose.[219] The caboose was built in 1971, three years after the W&OD Railroad closed.[220]
The stations on the Thrifton-Bluemont Junction connecting line (with locations of sites in 2008) were:
| Station[221] | Location | Coordinates | Jurisdiction | Side of Tracks | Photo | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrifton[202] | I-66 between Lee Highway and Spout Run Parkway | 38°53′48″N 77°05′53″W / 38.896626°N 77.098048°W | Arlington County | South | North of Lyon Village shopping center near southeast end of Maywood Historic District.[204] Named for Hugh A. Thrift.[205] East of junction with Great Falls Division. | |
| Hayes[222] | N. Lincoln Street (east side) and I-66 | 38°53′26″N 77°06′13″W / 38.890676°N 77.103577°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Douglas[222] | N. Quincy Street (east side) and I-66 | 38°53′23″N 77°06′29″W / 38.889619°N 77.108164°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Waverley Hills | N. Stafford Street and I-66 | 38°53′20″N 77°06′41″W / 38.888851°N 77.11128°W | Arlington County | Formerly Clements Avenue Station[222] | ||
| Clarenford[222] | N. Utah Street (east side) and I-66 | 38°53′17″N 77°06′51″W / 38.888162°N 77.114207°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Lacey[222] | N. Glebe Road (east side) and I-66 | 38°53′12″N 77°07′03″W / 38.886592°N 77.11757°W | Arlington County | Southeast | ||
| Washington Boulevard[223] | Washington Boulevard and I-66 | 38°53′07″N 77°07′08″W / 38.8853499°N 77.1187931°W | Arlington County | |||
| Waycroft | N. Buchanan Street and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′50″N 77°07′09″W / 38.8806°N 77.119198°W | Arlington County | 0.2 mile south of crossing of Fairfax line of Washington-Virginia Railway Historical marker near site: Lacey Car Barn.[30][224] | ||
| Garrison[222] | N. George Mason Drive at Wilson Boulevard (north side) and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′42″N 77°07′15″W / 38.87842°N 77.120832°W | Arlington County | Southeast | Undated | |
| Arlington Avenue[223] | N. Jefferson Street and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′19″N 77°07′35″W / 38.872016°N 77.126295°W | Arlington County | |||
| Bon Air[222] | N. Kensington Street (northeast side) and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′15″N 77°07′41″W / 38.870886°N 77.128151°W | Arlington County | South | ||
| Bluemont Junction[100][102][103] | W&OD Trail between Wilson Boulevard and Bluemont Junction Trail | 38°52′22″N 77°07′57″W / 38.872834°N 77.1325073°W | Arlington County | Northeast | 1934 (aerial) 1950s 1960s 1968 1968 |
Junction with Bluemont Division, Alexandria-Bluemont Line Wye on east side of tracks.[102] Station and electrical substation within wye[102] Station near south side of electrical substation in 1916.[102] Station adjacent to south side of electrical substation after 1918 Historical markers at site:[97] 1) Bluemont Junction 2) The Great Falls Line 3) Rosslyn Station 4) Bluemont Junction, c. 1934 Historical marker near site:[97] Tracks into History: The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad |
Existing roads, trails and parks along railroad route[]
Road[]
I-66 between Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29) and Washington Boulevard.[225]
Rail Trail[]
Bluemont Junction Trail between Washington Boulevard and Mile 3.3 of Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Trail.[226]
Other Trail[]
Custis Trail between Lee Highway (U.S. Route 29) and Washington Boulevard.[227]
Linear park[]
Bluemont Junction Park between Fairfax Drive and W&OD Trail.[191][228]
Surviving Locomotives[]
At least four locomotives that the W&OD had owned or leased still survived in 2017.
- B&O 8413, a General Motors' (GM) Electro-Motive Corporation (later part of GM's Electro-Motive Division (EMD)) SW1 diesel–electric switcher locomotive assembled in 1940 with construction number 1111, was one of the first SW1s that Electro-Motive built.[229] After acquisition, the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) initially numbered the locomotive as 213, but subsequently changed the number to 8413.[229] Leased by the W&OD in 1968, B&O #8413 was one of the last locomotives to operate on the W&OD before the railroad closed during the same year.[230] After four transfers of ownership, Cargill purchased the locomotive, which became Cargill #6751.[229][231][232] Cargill moved the locomotive to Ogden, Utah, in 1993 for use in the company's Globe Mill.[229][232] Following Cargill's donation of the locomotive in 2010, the Utah Central Railway and the Union Pacific Railroad delivered it to the Utah State Railroad Museum at Ogden's Union Station on May 21, 2011, where it was photographed in 2020.[229][232][233]
- C&O 5015 is an American Locomotive Company (ALCO) S-2 diesel–electric switcher locomotive that the W&OD leased from the C&O.[230] Built in 1946 with a 1000-horsepower engine, the locomotive was used during the W&OD's final decade of operations.[230] After serving five more railroads, the locomotive became Columbia & Reading Railway #2-26 in 2009. It was operating in Columbia, Pennsylvania, on that line as CORY 2-26 in 2020.[234]
- W&OD 47, a General Electric (GE) 44-ton centercab switcher, built and delivered to the W&OD in December 1941 with construction number 15041 and a 380-horsepower engine, was the railroad's first diesel–electric locomotive.[235] It was joined by the similar #48 and #49, both built in August 1942.[230] Sold to the Fonda, Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad in 1950 and renumbered to 30, the former W&OD 47 went to Cargill in Houston, Texas in 1967.[230][236] Cargill subsequently reassigned it to Denver, Colorado.[237] After serving on the Great Western Railway of Colorado as #44, the locomotive retained its number when it became the Burlington Junction Railway's (BJRY's) first when the BJRY opened in 1985.[236][238] BJRY44 subsequently operated in Mount Pleasant, West Burlington and Burlington, Iowa. The locomotive was photographed in Burlington during 2018.[236][238][239]

- W&OD 50 is a 50-ton steeplecab Baldwin-Westinghouse electric locomotive built in October 1920 with four Westinghouse type 562-D-5 100 horsepower motors as Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) serial number 53784 and brought to the W&OD Railway during the same year.[240] After retiring the locomotive in 1945, the W&OD Railroad sold it in 1947 to the Cedar Rapids & Iowa City Railway, which renumbered it to 58.[241][242] In 1955 it was sold to the Kansas City, Kaw Valley & Western Railway as #507.[243] It was sold in 1962 to the Iowa Terminal Railroad and renumbered to 50, becoming #50 of the Iowa Traction Railroad in 1987.[241][244][245] Upon purchase in October 2012, the line was renamed to the Iowa Traction Railway.[246] The Iowa Traction Railway was operating the locomotive in Mason City, Iowa, in 2020, the locomotive's 100th year.[247]
Maps[]
W&OD Railway and Railroad system maps[]
- "Washington and Old Dominion Railway system map". c. 1920. Archived from the original on January 7, 2011. Retrieved May 26, 2019 – via r2parts.net.
- "Washington and Old Dominion Railroad system map". December 17, 1951. Retrieved May 26, 2019 – via WorthPoint. Archived May 26, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
Pre-Civil War maps[]
- 1859 map showing the planned route of the Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad between the Washington, D.C. area, Leesburg, Winchester, Romney, and Paddy Town: Mitchell, S. Augustus (1859). "Railroad map of the eastern, western and northern states, and Canada, showing conspicuously the lines of communication between the ports of the Atlantic and the great west and north west". Philadelphia: Mitchell's Map Publication Office. LCCN 98688326. OCLC 42763387. Retrieved July 23, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- c. 1860 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad (A.L.&.H. R.R.) between the city of Alexandria and Leesburg, with mileages of stations from Alexandria: Blythe, Washington (c. 1860). "Map of Alexandria, Fairfax, Prince William, Stafford, and Portions of the Adjacent County's". LCCN 80693560. OCLC 6533537. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1861 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad (unlabeled) between Alexandria County and Leesburg, with mileages between stations: Lloyd, James T. (1861). "Lloyd's official map of the state of Virginia from actual surveys by order of the Executive 1828 & 1859: Corrected and revised by J.T. Lloyd to 1861". New York: J.T. Lloyd. LCCN 98688567. OCLC 42954161 – via Library of Congress.
Civil War maps[]
- July 1861 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between Alexandria County and Leesburg and the railroad's planned route through Clarks Gap, Hillsborough, Vestal's Gap, Berryville, Winchester and Lockhardt's Gap: Bureau of Topographical Engineers, War Department, Washington, D.C. (July 1861). "Part of map of portions of the milit'y dep'ts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia". LCCN 2002627436. OCLC 50713008. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Library of Congress catalog note: "Probable Confederate copy of Bureau of Topographical Engineers original."
- 1862 topgraphical map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad in the city of Alexandria and Alexandria County (now Arlington County): Arnold, E.G., C.E. (1862). "Topographical Map of the Original District of Columbia and Environs: Showing the Fortifications around the City of Washington". New York: G. Woolworth Colton. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via etsy.com. Archived July 24, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
- January 1, 1862, map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad in Alexandria County, Falls Church, Fairfax County and Loudoun County, Virginia: Topographical Engineers Office at the Headquarters of General Irvin McDowell, Arlington (January 1, 1862). "Map of N. Eastern Virginia and Vicinity of Washington". New York: J. Schedler. LCCN 91685686. OCLC 24735754. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress. Library of Congress catalog note: "Accompanied by sheet: Presented to Brig. Genl. S. Williams, A.A. Genl. Hd. Qrs. Army, by order of Maj. Genl. McClellan, Comd. in Chf. U.S.A. [signed] A.W. Whipple, Maj. T.E."
- September 17, 1862, map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between Alexandria County and Leesburg and the railroad's planned route through Clark's Gap, Hillsborough, Vestal's Gap, Berryville, Winchester and Lockhardt's Gap: Bureau of Topographical Engineers, War Department, Washington, D.C. (September 17, 1862). "Part of map of portions of the milit'y dep'ts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia". LCCN 99447370. OCLC 45489352. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
For Head Quarters, Maj. Genl. McClellan
CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - October 6, 1862, map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between Falls Church and Leesburg and the railroad's planned route through Clark's Gap, Vestal's Gap, Berryville, Winchester and Lockhardt's Gap: Bureau of Topographical Engineers, War Department, Washington, D.C. (October 6, 1862). "Part of map of portions of the milit'y dept's of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia". LCCN 2002627442. OCLC 52747761. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Copied by William L. Sheppard, Draftsman, Engineer Bureau, C.S.A., September 6, 1864; forwarded to Lieut. Gen'l J. A. Early, September 6, 1864)
CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - c. 1862 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between the city of Alexandria and Arlington Mills: Sneden, Robert Knox (c. 1862). "Map of Alexandria, Virginia". Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- October 30, 1862, map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between Falls Church and Pimmit Run: Sneden, Robert Knox (October 30, 1862). "Map of Falls Church and vicinity of Lewinsville, Virginia: shewing [sic] Union picket lines October 30th 1862". OCLC 8085380439. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1864 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between the city of Alexandria and Farmwell (later Ashburn) station: Michler, Nathaniel (1864). "Map of Fairfax and Alexandria counties, Virginia, and parts of adjoining counties". LCCN 2006627694. OCLC 70282039. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Recd. Engineer Bureau, April 25th 1864. with letter April 23d '64, fm. Capt. Michler, [signed] J.C. Woodruff, Maj. of Engineers
- 1864 Confederate Army of Northern Virginia map showing tracks of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad (unlabeled) passing Leesburg, crossing Catoctin Mountain at Clarke's Gap and passing Hillsborough: "Northern Virginia with adjacent parts of Maryland and West Virginia". 1864. LCCN 2006627692. OCLC 70282038. Retrieved July 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Copied by J. Paul Hoffman, Topl. Office A.N. Va.; Approved, S. Howell Brown, 1st Lt. Engs: Troops, In Chg: Topl. Dept., A.N. Va., March 23rd 1864.
- 1865 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad between the city of Alexandria and Falls Church: United States War Department, Engineer Bureau (1865). "Extract of military map of N.E. Virginia showing forts and roads". Washington, D.C.: Engineer Bureau, United States War Department. LCCN 88690679. OCLC 17480595. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Post-Civil War maps[]
- Circa 1878 map showing the route of the Washington and Ohio Railroad in the city of Alexandria and Alexandria County, Virginia: Hopkins, Griffith Morgan, Jr. (c. 1878). "Map of Alexandria County, Virginia". Atlas of fifteen miles around Washington, including the counties of Fairfax and Alexandria, Virginia. Philadelphia: G.M. Hopkins. pp. 66–67. LCCN map53000779. OCLC 16951180. Retrieved February 12, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1883 map showing the entire route of the Washington, Ohio and Western Railroad (Alex. Loudoun & Hampshire R.R.) except in the city of Alexandria: "Map showing the route of the Washington and Atlantic Railroad and its connections". New York: G.W. & C.B. Colton & Co. 1883. Retrieved February 12, 2020.
- 1900 map showing the route of the Southern (Washington & Ohio) Railway in the City of Alexandria and Alexandria County, Virginia: Howell and Taylor (1900). "Map of Alexandria County, Virginia for the Virginia Title Co". Washington, D.C.: Alexander B. Graham, Photo-Litho. LCCN 89692758. OCLC 156983473. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1900 map of Alexandria County (now Arlington County) and the City of Alexandria, showing the route of the Southern Railway: Graham, Andrew B., photo-lithographer (1900). "Alexandria City showing connections to Washington". Alexandria, Virginia: M.B. Harlow. LCCN 89692658. OCLC 20094588. Retrieved July 22, 2021 – via Library of Congress.
- 1907 map showing the route of the Southern Railway (Bluemont Branch) and the Great Falls and Old Dominion Railway (G. F. & O. D. RY.): Noetzel, Gregor (1907). "Map of Alexandria County, Virginia: formerly part of the District of Columbia". Washington, D.C.: G.G. Boteler. LCCN 89692766. OCLC 20854717. Retrieved October 8, 2019 – via Library of Congress website.
Topographic maps[]
- 1884 topographic map of the city of Alexandria and Alexandria County, showing the route of the Washington, Ohio and Western Railroad (Washington and Ohio R.R.): Greene, F.V., Captain, Corps of Engineers (1884). "Topographical map of the District of Columbia and a portion of Virginia Compiled Under the Direction of Major G. Lydecker, Corps of Engineers: Engineer Commissioner D.C." LCCN 88693423. OCLC 18163568. Retrieved February 11, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1893 topographic map of northwestern Loudoun County, showing the route of the Washington, Ohio and Western Railroad between Round Hill and Goose Creek: Gannett, Henry; Thompson, Gilbert (November 1893). "Reconnaissance Map: Virginia - West Virginia - Maryland: Harpers Ferry Sheet". United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. Retrieved January 20, 2020 – via Virginia Historical Topographic Maps, Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection, Perry–Castañeda Library, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas.
- 1894 topographic map of the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the route of the Richmond and Danville Railroad (Washington, Ohio & Western Branch) between the railroad's Alexandria terminal and Hunters Road station: "The Vicinity of Washington, D.C.: Entered according to Act of Congress, in the year 1894". Philadelphia: Griffith M. Hopkins, C.E. LCCN 88693364. OCLC 18019645. Retrieved January 20, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1894 topographic map showing the entire route of the Washington, Ohio and Western Railroad except in the city of Alexandria: Goode, Richard U. (1894). "Map of northern Virginia". United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. Retrieved May 26, 2019 – via Library of Congress.
- 1894 topographic map of the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the route of the Virginia Midland Division (later, the Bluemont Branch) of the Southern Railway between Herndon and the city of Alexandria: Gannett, Henry; Thompson, Gilbert (November 1894). "Reconnaissance Map: Virginia - Maryland: Mt. Vernon Sheet". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved January 20, 2020 – via Virginia Historical Topographic Maps, Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection, Perry–Castañeda Library, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas.
- 1898 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the route of the Washington & Round Hill Branch (later, the Bluemont Branch) of the Southern Railway between Alexandria and Wedderburn: "Washington and Vicinity". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1898. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via University of Alabama Map Library.
- 1908 topographic map of northwestern Loudoun County, showing the route of the Bluemont Branch of the Southern Railway between Sterling and Ashburn: Sutton, Frank (1908). "Topography: Maryland - Virginia: Seneca Quadrangle". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. Retrieved January 20, 2020 – via Virginia Historical Topographic Maps, Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection, Perry–Castañeda Library, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas.

- 1915 topographic map of northwestern Fairfax County, showing the route of the W&OD Railway's Bluemont Division between Vienna and Herndon and the Great Falls Division (Electric RR) between Difficult Run and Great Falls: Marshall, R. B.; Sutton, Frank (October 1915). "Topography: Virginia: Fairfax Quadrangle". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. Retrieved July 25, 2020 – via Historic Prince William. Archived July 25, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
- 1915 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the routes of the W&OD Railway's Bluemont Division between Alexandria and Wedderburn and between Thrifton and Bluemont Junction, and the Great Falls Division between Georgetown and Great Falls: Marshall, R. B.; Sutton, Frank (1915). "Topography: Maryland — District of Columbia — Virginia, Washington and vicinity". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. LCCN 87691472. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1917 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the routes of the W&OD Railway's Bluemont Division between Alexandria and Wedderburn and between Thrifton and Bluemont Junction, and the Great Falls Division between Georgetown and Great Falls: Marshall, R. B.; Sutton, Frank (1917). "Washington and Vicinity: Maryland: District of Columbia: Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. LCCN 87691475. OCLC 15519039. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1929 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the routes of the W&OD Railway's Bluemont Division between Alexandria and Wedderburn and between Thrifton and Bluemont Junction, and the Great Falls Division between Rosslyn and Great Falls:"Washington and Vicinity: Maryland: District of Columbia: Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1929. LCCN 87693006. OCLC 15653164. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1943 topographic map of northeastern Loudoun County, showing the route of the W&OD Railroad between Goose Creek and Leesburg: "Leesburg". Washington, D.C.: United States Army Corps of Engineers: Army Map Service. Retrieved January 22, 2020 – via Quadrangles of Virginia - Army Map Service: University of Alabama.
Copied in 1946 from Virginia, 1:31,680, USGS, Leesburg, 1943
- 1944 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Arlington County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the routes of the W&OD Railroad between Rosslyn and Bluemont Junction, between Alexandria and Bluemont Junction, and between Bluemont Junction and Wedderburn: "Washington and vicinity, District of Columbia-Maryland-Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1944. LCCN 87693081. OCLC 15653577. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1951 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Arlington County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the routes of the W&OD Railroad between Rosslyn and Bluemont Junction, between Alexandria and Bluemont Junction, and between Bluemont Junction and Wedderburn: "Washington and vicinity, District of Columbia-Maryland-Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1951. LCCN 87693097. OCLC 15653616. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1956 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Arlington County and Falls Church, showing the routes of the W&OD Railroad between Rosslyn and Bluemont Junction, between Alexandria and Bluemont Junction, and between Bluemont Junction and West Falls Church: "Washington and vicinity, District of Columbia-Maryland-Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1956. LCCN 87693124. OCLC 15653798. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- 1965 topographic map of Washington, D.C, the city of Alexandria, Arlington County and Falls Church, showing the route of the W&OD Railroad between Alexandria and Vienna: "Washington and vicinity, District of Columbia-Maryland-Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1965. LCCN 87693153. OCLC 15653990. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Timetables[]
Passenger service[]
- Time Table—No. 1, Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad Company, To Take Effect on and after Monday, January 16, 1860. In Harwood, p. 13.
- "Southern Railway: Between Washington, Alexandria and Bluemont: Schedule effective July 1, 1900". Archived from the original on November 16, 2002. Retrieved November 11, 2012 – via Town of Round Hill, Virginia, government website. (First timetable for Bluemont passenger service.)
- Southern Railway Company: Circular No. 9816: Effective Sunday, May 28, 1911: Complete Schedule Between Washington and Bluemont. In Harwood, p. 29.
- Schedule of Trains: Effective June 11, 1916: Washington and Old Dominion Railway: Great Falls Division. In Harwood, p. 56.
- Washington and Old Dominion Railway: Bluemont Division: Washington—Bluemont Junction—Bluemont (March 1926). In Harwood, p. 72.
- "Schedule No. 3-A: Washington and Old Dominion Railroad: Effective January 31, 1944: Rosslyn - Bluemont Junction - Purcellville". Retrieved January 21, 2020 – via McCray, Paul. "Washington & Old Dominion Railroad, 1847 to 1968: A Photographic History".
- "Timetable: Rosslyn–Bluemont Junction-Purcellville". Washington and Old Dominion Railroad. February 1946. Retrieved April 30, 2021 – via Facebook.
Mail service[]
- Fisher, A.A. (May 20, 1924). "Alexandria & Bluemont Junction C.P. (Washington & Old Dominion Ry.) (Electric)." (PDF). Schedule of Mail Trains, No. 445: Third Division, Railway Mail Service. United States Government Printing Office. p. 10. Retrieved January 21, 2020 – via wx4.org: The Dome O' Foam.
- Fisher, A.A. (May 20, 1924). "Washington & Bluemont R.P.O. (Washington & Old Dominion Ry.) (Electric)." (PDF). Schedule of Mail Trains, No. 445: Third Division, Railway Mail Service. United States Government Printing Office. p. 91. Retrieved January 21, 2020 – via wx4.org: The Dome O' Foam.
- Fisher, A.A. (May 20, 1924). "Washington & McLean C.P. (Wash. & Old Dominion Ry.) (Electric)." (PDF). Schedule of Mail Trains, No. 445: Third Division, Railway Mail Service. United States Government Printing Office. p. 120. Retrieved January 21, 2020 – via wx4.org: The Dome O' Foam.
- Johnson, J.W. (August 15, 1939). "Washington & Bluemont R.P.O. (Washington & Old Dominion R.R.) (Electric)." (PDF). Schedule of Mail Trains, No. 528: Third Division, Railway Mail Service. United States Government Printing Office. p. 93. Retrieved January 21, 2020 – via wx4.org: The Dome O' Foam.
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b (1) Locomotive described in Harwood, p. 137.
(2) Coordinates of Riverside Yard in Baltimore: 39°16′05″N 76°36′22″W / 39.268118°N 76.606029°W - ^ Williams, p. 3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, pp. 12—15.
- ^ Williams, p. 4.
- ^ (1) 1859 map showing the planned route of the Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad between the Washington, D.C. area, Leesburg, Winchester, Romney and Paddy Town: Mitchell, S. Augustus (1859). "Railroad map of the eastern, western and northern states, and Canada, showing conspicuously the lines of communication between the ports of the Atlantic and the great west and north west". Philadelphia: Mitchell's Map Publication Office. LCCN 98688326. OCLC 42763387. Retrieved July 23, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
(2) c. 1860 map showing the route of the Alexandria, Loudoun, and Hampshire Railroad (A.L.&.H. R.R.) between the town of Alexandria and Leesburg, with mileages of stations from Alexandria: Blythe, Washington (c. 1860). "Map of Alexandria, Fairfax, Prince William, Stafford, and Portions of the Adjacent County's". LCCN 80693560. OCLC 6533537. Retrieved January 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress. - ^ Union and Confederate Army maps showing planned route of Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad through Vestal's Gap and Winchester:
(1) "Part of Map of portions of the military depts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia. Compiled in the Bureau of Topographical Engr. War Department &c, July 1861". LCCN 2002627436. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved May 27, 2019 – via Library of Congress. Library of Congress note: "Probable Confederate copy of Bureau of Topographical Engineers original."
(2) Clark, John S. (September 15, 1862). "Part of Map of portions of the military depts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia. Compiled in the Bureau of Topographical Engr. War Department &c, July 1861. Washington, D.C., 1862". LCCN 99448520. OCLC 45872041. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved May 27, 2019 – via Library of Congress.
(3) Bureau of Topographical Engineers (September 17, 1862). "Part of Map of portions of the military depts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia. Compiled in the Bureau of Topographical Engineers, War Department &c, July 1861". Washington, D.C. LCCN 99447370. OCLC 45489352. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved May 27, 2019 – via Library of Congress.
(4) Sheppard, William L., Engineer Bureau, Confederate States of America (copier) (September 6, 1864). "Part of Map of portions of the military depts of Washington, Pennsylvania, Annapolis, and North Eastern Virginia". Compiled in the Bureau of Topographical Engineers, War Department, Washington, D.C., October 6, 1863". LCCN 2002627442. OCLC 52747761. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved May 27, 2019 – via Library of Congress. - ^ 1864 Army of Northern Virginia map showing tracks of the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad (unlabeled) passing Leesburg, crossing Catoctin Mountain at Clarke's Gap and passing Hillsborough: "Northern Virginia with adjacent parts of Maryland and West Virginia". 1864. LCCN 2006627692. OCLC 70282038. Retrieved July 25, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
Copied by J. Paul Hoffman, Topl. Office A.N. Va.; Approved, S. Howell Brown, 1st Lt. Engs: Troops, In Chg: Topl. Dept., A.N. Va., March 23rd 1864.
- ^ (1) Williams, pp. 8–10.
(2) "Photograph of United States Military Railroad locomotive (Clarke) (formerly of the Alexandria, Loudoun & Hampshire Railroad) at roundhouse in Alexandria during the Civil War". Archived from the original on November 7, 2005. - ^ (1) Harwood, p. 21.
(2) The Washington and Ohio Rail Road Company (1873). "The Washington and Ohio Railroad. A Glance at the country through which it passes, between Washington D.C., and the Ohio River, a distance of 325 miles". Philadelphia: Collins, Printer. Retrieved July 24, 2019 – via Internet Archive. - ^ (1) Williams, p. 27.
(2) Harwood, p. 20—22. - ^ Williams, pp. 27–28.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c (1) 1882 system map of Richmond and Danville Railroad Archived May 31, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
(2) 1893 system map of Richmond and Danville Railroad - ^ Jump up to: a b c (1) Harwood, p. 24.
(2) Williams, p. 28. - ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Williams, pp. 42–43.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Harwood, p. 26.
- ^ "1895 system map of Southern Railway". Archived from the original on November 11, 2009.
- ^ Falknor, Susan Freis (March 11, 2008). "History of Bluemont - Railroad days". Welcome to Bluemont: Articles. Bluemont, Virginia: Bluemont Citizens Association. Archived from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ "Undated photograph of Southern Railway passenger train at Vienna station". Archived from the original on November 7, 2018. Retrieved November 7, 2018 – via Google Plus.
- ^ "Complete Schedule Between Washington and Bluemont". Southern Railway Company. May 28, 1911. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) at Harwood, p. 29. - ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, pp. 33–41.
- ^ Williams, pp. 44, 71.
- ^ Harwood, p. 45.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Harwood, p. 46.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 46, 49.
- ^ Williams, pp. 45, 72.
- ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 32, 46–47.
(2) "W&OD bridge over Potomac Yard north of the Yard's St. Asaph station" (photograph). Archived from the original on October 22, 2018. Retrieved October 22, 2018 – via Pinterest. - ^ Williams, pp. 43–44.
- ^ Williams, p. 72.
- ^ Williams, pp. 107, 144, 156.
- ^ Jump up to: a b ""Lacey Car Barn" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 14, 2017. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
In 1896, the Washington, Arlington & Falls Church Railway began running electric trolleys from Rosslyn to Falls Church on the present routes of Fairfax Drive and I-66. By 1907, the line linked downtown Washington to Ballston, Vienna, and the Town of Fairfax. In 1910, the railway built at this location a car barn, rail yard, workshop, electrical substation, and general office. In 1912, the rival Washington & Old Dominion Railway began crossing the tracks on a bridge 200 yards west of here, traveling the present route of I-66 from Rosslyn. The line to Fairfax closed in 1939, but Metrorail's Orange Line follows its route through Arlington.
- ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 31, 33.
Washington—Virginia Railway system map (c. 1915). Washington—Virginia Railway Company (publisher). In "Figure 18: A map of the electric train line" (PDF). South Railroad Street Park Master Plan: General Management Plan and Conceptual Development Plan. Fairfax County Park Authority. September 27, 2006. p. 19. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 7, 2019. Retrieved January 20, 2020. - ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, pp. 48–49.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 39, 48–49.
- ^ Williams, pp. 70–71.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, p. 47.
- ^ Harwood, p. 38.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c (1) Williams, p. 74.
(2) Harwood, pp. 68–69. - ^ (1) Williams, pp. 74, 93.
(2) Harwood, pp. 73–79. - ^ (1) Williams, p. 93.
(2) Harwood, p.73. - ^ Harwood, p. 76.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 77–78.
- ^ King, 1934 (map)
- ^ Hanson, Christoper (April 9, 1979). "A Rusted Old Trestle Falls, A Relic of the Car Era". The Evening Star.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, pp. 79–80.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Williams, p. 91.
- ^ (1) Harwood, p. 90.
(2) Williams, p. 94. - ^ Harwood, pp. 83–84.
- ^ (1) Harwood pp. 81, 83–88, 137–138.
(2) Williams, pp. 93–94. - ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 90–91
(2) Williams, p. 95. - ^ (1) Harwood, p. 97.
(2) Williams, p. 96. - ^ (1) "Senate Enacts W.& O.D. Bill". The Washington Post. March 9, 1960.
(2) Dewar, Helen (January 21, 1962). "Virginia Drops Plan To Buy W&OD Line". The Washington Post. - ^ "Rail Spur Quiet for While: But the Old W&OD Route Soon Will Hum With Autos". The Washington Post. November 16, 1964.
- ^ "W&OD Rail Spur Bought by State". The Washington Post. July 10, 1962.
- ^ Jump up to: a b (1) "ICC Examiner Favors Death of W&OD Line". The Washington Post. March 8, 1966.
(2) "Want W&OD to Stay". The Washington Post. March 17, 1965.
(3) Douglas, Walter B (February 9, 1965). "Railroad Agrees to Sell Right of Way to Virginia". The Washington Post. - ^ Flor, Lee (August 30, 1967). "Delay of Transit Talk May Bear on W&OD".
- ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 106–107.
(2) Williams, p. 109. - ^ "Secret Deal Disclosed on W&OD Line". The Washington Post. March 10, 1966.
- ^ (1) "DuVal Asks Salvaging Of W&OD". The Washington Post. June 21, 1967.
(2) Jay, Peter A. (August 2, 1967). "Transit Unit Wins Delay In Rail Case". The Washington Post. - ^ (1) "Law to Save W&OD Rails To Be Sought". The Washington Post. September 13, 1967.
(2) "Two Steps Advance Accord on Transit". The Washington Post. September 9, 1967. - ^ (1) Corrigen, Richard (November 2, 1967). "WMATA Agrees On Rail Bed Route". The Washington Post.
(2) "Ailing Va. Railroad Allowed to Quit in '68". The Washington Post. January 25, 1968. - ^ "Plant Owners Along W&OD Again Try to Keep Line Going". The Washington Post. November 20, 1967.
- ^ (1) McLaughlin, Maureen (January 30, 1968). "Judge's Order Delays Closing of W&OD". The Washington Post.
(2) "W&OD Limping to Extinction". The Washington Post. August 3, 1968. - ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, p. 106.
- ^ (1) Yarbrough, Charles (November 4, 1969). "Dulles Seen as Our Savior". The Washington Evening Star.
(2) Braaten, David (April 7, 1974). "Bridge Taking a Hike". The Washington Evening Star.
(3) Beckham, Nancy (June 12, 1970). "Old Station at End of Line". Washington Evening Star. - ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, pp. 106–107.
- ^ Harwood, p. 112.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 108–109.
- ^ Harwood, p. 109.
- ^ (1) Ezell, Raymond (Virginia Department of Transportation Fredericksburg District) (February 29, 2012). "Archaeological Survey: Proposed Sycolin Road Overpass of Route 7/15 Bypass Leesburg, Loudoun County, Virginia: Management Summary" (PDF). Virginia Department of Transportation. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 27, 2012. Retrieved January 26, 2020.
(2) Dutton + Associates, LLC., Midlothian, Virginia (October 2016). "VDHR #053-0276: Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Historic District (Eligible)" (PDF). Pre-Application Analysis for Cultural Resources of the Idylwood Substation at Shreve Road Project. Virginia State Corporation Commission. p. 5-1. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved January 26, 2020.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
(3) Schlupp, Catherine; Staton, Heather Dollins (Dovetail Cultural Resource Group, Fredericksburg, Virginia) (October 2016). "Phase IB Architectural Survey of the Proposed Soapstone Connector, Fairfax County Virginia" (PDF). Fairfax County, Virginia government. p. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 26, 2018.
(4) "Transform I-66 Inside the Beltway: Eastbound Widening Environmental Assessment: Architectural Phase I Survey Report" (PDF). United States Department of Transportation: Federal Highway Administration and Virginia Department of Transportation. November 2016. p. 7. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved January 26, 2020. - ^ Neville, Ashley M. (Gray & Pape, Inc., Richmond, Virginia) (July 25, 2000). "United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service: National Register of Historic Places Registration Form: Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Historic District (Virginia Department of Historic Resources (DHR) No. 053-0276)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on January 26, 2020. Retrieved January 26, 2020. In Appendix J of Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority - Pre-filed Direct Testimony of Mr. Hafner, Mr. Mcray and Mr. Simmons, November 30, 2005 (Part 4), Case No. PUE-2005-00018, Virginia State Corporation Commission. Obtained in "Case Docket Search". Virginia State Corporation Commission. Retrieved September 28, 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c (1) David, Elizabeth S., Historic Preservation Planner, Fairfax County Office of Comprehensive Planning (April 1979). "Herndon Depot" (PDF). United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service: National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form. Richmond, Virginia: Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 28, 2021. Retrieved July 23, 2010.
(2) "Herndon Depot: National Register Information System ID: 79003039". NPGallery Digital Asset Management System. United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
(3) Greenberg, Ronald M. (Acting Chief, National Register of Historic Places). "Virginia: Herndon. Herndon Depot, Elden St." (PDF). Federal Register: March 18, 1980: Part II: Department of the Interior: Heritage Conservation and Recreation Service: National Register of Historic Places; Annual Listing of Historic Properties. 45 (54): 17484. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
(4) "Herndon Depot". National Register of Historic Places: Virginia – Fairfax County. National Register of Historic Places.com. Archived from the original on September 6, 2015. Retrieved January 28, 2020. - ^ Jump up to: a b c (1) Kalbian, Maral S; Peters, Margaret T. (November 20, 2009). "National Register of Historic Places Registration Form (United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service): Purcellville Train Station" (PDF). Richmond, Virginia: Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 27, 2018. Retrieved October 27, 2018. and accompanying five photos
(2) Director, National Park Service (June 4, 2010). "Weekly list of actions taken on properties for the National Register of Historic Places: 5/24/10 through 5/28/10" (PDF). National Register of Historic Places 2010 Weekly Lists. United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 28, 2019. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
(3) "Purcellville Train Station: National Register Information System ID: 10000307". NPGallery Digital Asset Management System. United States Department of the Interior: National Park Service. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
(4) "Purcellville Train Station". National Register of Historic Places: Virginia – Loudoun County. National Register of Historic Places.com. Archived from the original on February 18, 2017. Retrieved January 28, 2020. - ^ (1) "235-0001 Herndon Depot". Richmond, Virginia: Virginia Department of Historic Resources. August 29, 2018. Archived from the original on January 16, 2021. Retrieved January 28, 2020.
(2) "286-5001-0233 Purcellville Train Station". Richmond, Virginia: Virginia Department of Historic Resources. January 22, 2020. Archived from the original on September 27, 2020. Retrieved January 28, 2020. - ^ (1) Williams, p. 43.
(2) Washington and Old Dominion Railway timetables:
Bluemont Division: Williams, pp. 40, 68.
Great Falls Division: Williams, p. 67. - ^ Jump up to: a b c Harwood p. 112.
- ^ (1) Sullivan, Patricia (September 29, 2012). "GenOn power plant in Alexandria is set to close". Local. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on June 15, 2018. Retrieved June 15, 2018.
(2) Sullivan, Patricia (September 25, 2013). "Sale of Robinson Terminal warehouses to bring development to Alexandria waterfront". Local. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on June 15, 2018. Retrieved June 15, 2018. - ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Stone, Jim. "The Washington & Old Dominion Railroad in Del Ray". Alexandria, VA: Del Ray Citizens Association. Archived from the original on March 29, 2008. Retrieved January 17, 2010.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 108–109, 112.
- ^ Locations of stations existing in 1916 according to distances in Harwood, pp. 139–141 and Interstate Commerce Commission. "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- ^ W&OD Trail mileages from detailed maps of portions of trail accessed from "Map of the W&OD". The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Side of tracks from Interstate Commerce Commission. "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- ^ Harwood, p. 9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "1949 Aerial photograph and 1951 map (T1951) of Alexandria, Virginia". HistoricAerials.com. 2011. Archived from the original on August 1, 2013. Retrieved July 25, 2013.
- ^ Harwood p. 10.
- ^ "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 1" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d (1) "Mount Jefferson Park & Greenway" (PDF). 2015 Neighborhood Parks Improvement Plan. City of Alexandria government. November 19, 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 15, 2017. Retrieved November 7, 2018.
Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway is located .... on the former rail bed of the former Washington and Old Dominion Railroad.
(2) "Trail in Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway" (PDF). Alexandria Bike Map. City of Alexandria, Virginia, government. Retrieved November 7, 2018. Archived October 17, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) Coordinates of trail in Mount Jefferson Park and Greenway: 38°49′55″N 77°03′27″W / 38.8319285°N 77.0573918°W - ^ 1900 map of Del Ray and St. Elmo showing Alexandria Junction and Washington & Ohio Junction in Ness, Leland (2008). "St. Asaph Racetrack historical marker" (PDF). Del Ray and the Town of Potomac: Del Ray Interpretive Signs. City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 7, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Ness, Leland (2008). "The Bluemont Line historical marker" (PDF). Del Ray and the Town of Potomac: Del Ray Interpretive Signs. City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 17, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Del Ray and the Town of Potomac: Del Ray Interpretive Signs". City of Alexandria, Virginia. 2008. Archived from the original on March 31, 2017. Retrieved January 23, 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Locations and partial texts of markers: alsdmf (May 19, 2010). "Del Ray Interpretive Markers". Retrieved January 23, 2016 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Crossroads of Transportation historic marker, with maps showing Alexandria Junction, Alexandria Canal and nearby railroads and roads" (PDF). City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 22, 2018. Retrieved October 22, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 2" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on December 26, 2018.
- ^ Ness, Leland (2008). "The Electric Railway historical marker" (PDF). Del Ray and the Town of Potomac: Del Ray Interpretive Signs. City of Alexandria, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 17, 2017. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Johnson, Bert, Arlington County Manager (1967). A History of the Boundaries of Arlington County, Virginia (2nd ed.). Office of the County Manager, Arlington, Virginia. p. 1., describes the Arlington boundary in the area of the Cowdon station as: ".... westwardly, in general along the line of Four Mile Run, without regard to its meanders, intersecting the south right-of-way line of the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad, then 1,858.44 feet to where the center line of Shirlington Road intersects the said south right-of-way line; thence south and slightly east to the center line of Quaker Lane, ....". The Cowdon station was in Arlington County, between the railroad right-of-way's intersection with Four Mile Run and the right of way's intersection with the center line of Shirlington Road. The station was north of the railroad's south right-of-way line.
- ^ "Map 17: Arlington (mileage marker 0)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on August 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Liebertz, John (2016). Map of Alexandria County, Virginia, for the Virginia Title Company, 1900 (PDF). A Guide to the African American Heritage of Arlington County (2nd ed.). Historic Preservation Program: Department of Community Planning, Housing and Development, Government of Arlington County, Virginia. p. 25. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 7, 2016. Retrieved October 7, 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af "Historical marker(s) in Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Markers series". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 13, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 3" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "Map 16: Arlington (mileage markers 0 to 2.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved July 20, 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 4" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. "Glencarlyn Station" marker. Located northwest of Arlington Boulevard (U.S. Route 50) bridge over W&OD Trail and Four Mile Run and southwest of W&OD Trail at former site of station.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps": Bluemont Junction Wye" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The District Title Insurance Company (1942). "Plate 21". Property Atlas of Arlington County 1943: Virginia. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Franklin Survey Company. LCCN map44000008. Archived from the original on May 26, 2019. Retrieved May 26, 2019 – via Historic Map Works: Residential Genealogy. Contains map of Bluemont Junction.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h "Map 15: Falls Church (mileage markers 3 to 5.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 5" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ ""Brandymore Castle" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 16, 2012. Retrieved August 23, 2010. Erected by the Arlington County, Virginia, government 0.4 miles (0.6 km) west of the former site of the Fostoria Station.
- ^ Swain, Craig (March 13, 2021). ""East Falls Church Station" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 13, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (March 13, 2021). ""East Falls Church" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 13, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021. Erected by the Arlington County, Virginia, government 0.1 miles (0.2 km) east of the former site of the Falls Church (East Falls Church) Station.
- ^ Iekel, John F. "A History of East Falls Church" (PDF). East Falls Church History: Train Stations. Arlington-East Falls Church Civic Association. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Map 14: Falls Church (mileage markers 5.6 to 8.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 6" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 7" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Map 13: Vienna (mileage markers 9 to 11.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 8" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "Map 12: Vienna (mileage markers 12 to 14)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on February 3, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Wood, Rebekah K. (May 3, 2002). "Vienna Depot: Description and Historical Significance: Vienna, Virginia. Prepared for the nomination of the Vienna Depot to the National Register of Historic Places". Washington & Old Dominion Railroad, 1847 to 1968: A Photographic History, by Paul McCray. Retrieved September 14, 2010. Archived January 22, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 9" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 10" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Map 11: Reston (mileage markers 14.5 to 17)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on February 3, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 11" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Map 10: Herndon-Reston (mileage markers 17.5 to 20)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 12" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Vetter
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 13" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Map 9: Herndon (mileage markers 20.5 to 22.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 17, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 14" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Map 8: Sterling (mileage markers 23 to 25)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Identified as Smiths in 1916 list of stations in Harwood, p. 140 and in August 25, 1940, W&OD Railroad timetable; no station at this location in "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 15" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Identified as Normans in 1916 list of stations in Harwood, p. 140 and in August 25, 1940, W&OD Railroad timetable. Identified as Smith's Station in "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 15" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Map 7: Ashburn (mileage markers 25.5 to 28)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Tracks Into History" marker in W&OD Trail rest stop located 0.1 mile northwest of crossing of Smith's Switch Road and W&OD Trail.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 16" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ ""Ashburn Station" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on May 29, 2016. Retrieved September 25, 2016.
When the Alexandra, Loudoun & Hampshire Railroad (later the W&OD) arrived in 1860, the aptly named crossroads of Farmwell became one of the many rail stops that served agrarian Loudoun County. In 1896, after an ash tree caught fire and supposedly burned for a week, Farmwell changed its name to Ashburn
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Map 6: Quarry Overlook (mileage markers 28.5 to 30.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ ""Belmont" historical marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 12, 2012. Retrieved August 19, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Map 5: Leesburg (mileage markers 31.5 to 34)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 19" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Map 4: Leesburg (mileage markers 34.5 to 37)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on March 9, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 21" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Map 3: Paeonian Springs (mileage markers 37 to 40)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on August 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 22" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Map 2: Vienna (mileage markers 40 to 42.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on August 7, 2011. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 23" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Map 1: Purcellville (mileage markers 43 to 44.5)". Map of the W&OD. The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on September 10, 2010. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- ^ "Interstate Commerce Commission (July 1, 1916). "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Map No. 24" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 28, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Washington and Old Dominion Railway: Right of Way Maps. Map 8" (PDF). 1911. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 15, 2020. Retrieved February 15, 2020.
- ^ "Washington and Old Dominion Railway: Right of Way Maps. Map 5" (PDF). 1911. p. 6. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 15, 2020. Retrieved February 15, 2020.
- ^ "Washington and Old Dominion Railway: Right of Way Maps. Map 1" (PDF). 1911. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 15, 2020. Retrieved February 15, 2020.
- ^ (1) Harwood, p. 107.
(2) Information sheet on interior wall of Bluemont Junction caboose, September 2012. - ^ "Northern Virginia Model Railroaders, Inc". Vienna, Virginia: Northern Virginia Model Railroaders, Inc. Archived from the original on August 9, 2018. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (July 2, 2007). "Vienna Station" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Vienna Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 27, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "Vienna Station". W&OD Railroad Regional Park. lifewithjohn.net. February 17, 2013. Archived from the original (photograph) on October 13, 2018. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (November 19, 2009). "Sunset Hills Station Today" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Sunset Hills Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 26, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ Lep, Dave. "Sunset Hills Station" (photograph). Facebook. Retrieved April 29, 2021.
in Reston
- ^ "Sunset Hills station" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ "The Herndon Historical Society". Herndon, Virginia: Herndon Historical Society. Archived from the original on August 13, 2018. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ Prats, J.J. (photographer) (March 10, 2006). "The Station" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Herndon Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 27, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "Undated historical images of Herndon Depot". Herndon, Virginia: Herndon Historical Society. Archived from the original on February 21, 2020. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ "Market Station, Leesburg, Virginia". Archived from the original on November 18, 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Properties: Market Station". Metro Management Services, LLC. Archived from the original on May 22, 2013. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ "A Few Words About Us". Fire Works Pizza. Leesburg, Virginia: Fire Works Pizza. 2012. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 9, 2017.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (January 26, 2008). "The Relocated Freight Depot" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Leesburg Freight Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 23, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ ""The Depot" marker". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Datatbase. Archived from the original on March 12, 2012. Retrieved November 18, 2011.
It was moved two blocks to Market Station in 1984.
- ^ Swain (photographer), Craig (August 25, 2007). "Marker in front of the Shelter Along the Trail" (photograph). Photograph number 2 in "Paeonian Springs Station" marker. HMdb: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
- ^ "A relocated passenger shelter (formerly at Clarks Gap; now at Paeonian Springs" (photograph). Exploring the W&OD Rail Trail. MidAtlanticDayTrips.com. August 2, 2017. Archived from the original on December 29, 2019. Retrieved December 29, 2019.
- ^ (1) McCray, Paul. "Paeonian Springs Station". Washington & Old Dominion Railroad 1847 to 1968: A Photographic History. Paul McCray. Archived from the original on October 3, 2013. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
The Paeonian Springs Station was located approximately where the small passenger shelter now sits next to the trail in the community of Paeonian Springs. The shelter was originally located at Clarks Gap and was built from pieces of the larger, demolished Clarks Gap station.
.
(2) Swain, Craig (August 25, 2007). "Marker in front of the Shelter Along the Trail" (photograph). HMdb: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2019." showing passenger shelter and "Additional comment" dated January 29, 2008, in Swain, Craig. "Paeonian Springs Station marker". HMdb: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on July 18, 2011. Retrieved December 29, 2019.In 2006, the shelter along the trail at the site of the former Paeonian Springs station contained on its rear wall a sheet of paper within a plastic cover. The sheet described the history of the shelter. The sheet stated that the Washington & Old Dominion Railroad constructed the shelter at the site of the Clarkes Gap station on Dry Mill Road after the Clarkes Gap station burned down. According to the sheet, a railroad employee who lived in Paeonian Springs preserved the shelter. The sheet further stated that the employee's family had donated the shelter to the Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority.
- ^ "Hamilton station" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (January 3, 2010). "Hamilton Station" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Hamilton Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 22, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ Gibson, Kevin (photographer) (March 29, 2020). "Hamilton Station" (photograph). Facebook. Retrieved April 29, 2021.
- ^ "Train Station Steering & Oversight Committee". Town of Purcellville, Virginia. Archived from the original on April 6, 2012. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "Loudoun Visitors Center in Purcellville: Wine Tastings & Information". Loudoun Convention & Visitors Association (Visit Loudoun). 2012. Archived from the original on March 14, 2016. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (October 3, 2009). "Purcellville Station Today" (photograph). Photograph number 4 in "Purcellville Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 26, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (October 3, 2009). "Markers in front of the Train Station" (photograph). Photograph number 3 in "Purcellville Station" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 26, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "Purcellville Train Station". Town of Purcellville, Virginia. Archived from the original (interior photographs) on October 13, 2018. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- ^ "History of the Purcellville Preservation Association". Purcellville Preservation Association. Ashley Cyber Services. Archived from the original on October 20, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "W&OD; Railroad Station, 1997". Our Town: Tour Stop 28: Train Station. Town of Round Hill, Virginia, government. Archived from the original on February 5, 2012.
- ^ Stewart, Kevin (July 15, 2014). "Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Depot - Round Hill VA" (photograph). Retrieved February 8, 2020 – via Flickr. Archived February 8, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Wahl, Scott (photographer) (2019). "Paeonian Springs station" (photograph). Facebook. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ Wahl, Scott (photographer) (April 28, 2019). "Round Hill Freight House" (photograph). Facebook. Retrieved April 30, 2021.
- ^ "Bridge abutment on Russell Road" (photograph). WashCycle. Archived from the original on December 29, 2019. Retrieved February 8, 2020.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (January 22, 2010). "Bridge Abutments" (photograph). Photograph number 5 in "Terror by the Tracks" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 26, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (November 22, 2009). "Bridge over Difficult Run" (photograph). Photograph number 4 in "Strategic Junction: Hunter Mill Road and the AL&H Railroad" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "W&OD Trail bridge over Broad Run" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (August 11, 2007). "Goose Creek Bridge" (photograph). Photograph number 4 in "Diesel Trains on the W&OD" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on May 23, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2011.
- ^ "W&OD Trail bridge over Goose Creek" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ "W&OD Trail bridge over Syclolin Creek" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on March 14, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (August 3, 2007). "Close Up of the Bridge, East Side" (photograph). Photograph number 4 in "Clarkes Gap" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on October 22, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2021.
- ^ "Stone arch culvert under unnamed stream west of Simpson Circle in Paeonian Springs" (photograph). Yosemite. The Geocities Gallery: a restorativland project. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (November 22, 2009). "Floor of Electric Substation". Photograph number 5 in "Bluemont Junction" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015. Retrieved December 25, 2015.
- ^ "Bluemont Junction Park". Arlington County, Virginia: Arlington County Department of Parks and Recreation. Archived from the original on October 13, 2018. Retrieved October 13, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Bluemont Junction Park". Arlington County, Virginia: Arlington County Department of Parks and Recreation. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
- ^ (1) Liebertz, John (Arlington County Historic Preservation Planner). Arlington County Register of Historic Places: Historic District Designation Form: Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle (PDF). Government of Arlington County, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 12, 2021. Retrieved March 12, 2021.
(2) "Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle". Projects & Planning. Government of Arlington County, Virginia. 2021. Archived from the original on March 12, 2021. Retrieved March 12, 2021. - ^ Kotok, Alan (April 3, 2007). "Overgrown W&OD railroad trestle, Arlington, Virginia". Photostream. Flickr. Archived from the original on May 11, 2017. Retrieved April 17, 2016.
- ^ (1) Liebertz, John (Arlington County Historic Preservation Planner). Arlington County Register of Historic Places: Historic District Designation Form: Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle (PDF). Government of Arlington County, Virginia. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 12, 2021. Retrieved March 12, 2021.
(2) Rothstein, Ethan (June 6, 2014). "Part of W&OD Railroad Torn Down for Storage Facility". ARLnow. Archived from the original on June 13, 2014. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
(3) Sullivan, Patricia (June 11, 2014). "Landowner removes remnants of Arlington's industrial past for self-storage units". Local. The Washington Post. Archived from the original on June 11, 2018. Retrieved June 11, 2018.
(3) Rothstein, Ethan (June 13, 2014). "W&OD Trestle Could Get Historic Designation". ARLnow. Archived from the original on June 16, 2014. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
(4) County Manager, Arlington County, Virginia (September 12, 2014). "Board Report: Historic District Designation of and Design Guidelines for Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle, located on the southern side of the Washington & Old Dominion (W&OD) Trail near the southwestern corner of Lee Highway and Fairfax Drive, adjacent to the northern property line of 6873 Lee Highway, and which district boundary shall include only the trestle structure itself in the portion of the parcel identified as RPC #11-065-001". County Board Agenda Item 50: Meeting of September 20, 2014. Government of Arlington County, Virginia. Archived from the original on October 28, 2018. Retrieved October 28, 2018.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
(5) Fisette, Jay, Chair, Arlington County Board (September 20, 2014). "Approval of agenda item number 50 (p. 27): Historic District Designation of and Design Guidelines for Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle, located on the southern side of the Washington & Old Dominion (W&OD) Trail near the southwestern corner of Lee Highway and Fairfax Drive, adjacent to the northern property line of 6873 Lee Highway, and which district boundary shall include only the trestle structure itself in the portion of the parcel identified as RPC #11-065-001" (PDF). Minutes of Arlington County Board meeting of September 20, 2014: Consent Items (Items 1-53). Government of Arlington County, Virginia. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 5, 2021. Retrieved February 5, 2021.
(6) "Benjamin Elliott's Coal Trestle". Projects & Planning. Government of Arlington County, Virginia. 2021. Archived from the original on March 12, 2021. Retrieved March 12, 2021. - ^ Swain, Craig (photographer) (January 26, 2008). "Stationmaster's House". Photograph number 2 in "Stationmaster's House" marker. HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Archived from the original on December 27, 2015. Retrieved December 25, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Photographs of the front and the inside of the Stationmaster's House". Leesburg, Virginia: Leesburg Cigar & Pipe. Archived from the original on October 18, 2013. Retrieved January 5, 2013.
- ^ "W&OD Railroad Station, 1997". Our Town: Tour Stop 28: Train Station: Main Street. Round Hill, Virginia: Round Hill Town Office. Archived from the original on February 5, 2012. Retrieved April 17, 2016.
- ^ Coordinates of trail connecting Russell Road and Landover Street, Alexandria: 38°50′13″N 77°03′48″W / 38.836967°N 77.063266°W
- ^ Coordinates of section of Mount Vernon Trail adjacent to Norfolk Southern Railway spur: 38°48′56″N 77°02′20″W / 38.815507°N 77.038979°W
- ^ Locations of stations from distances along railroad route from Interstate Commerce Commission. "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018. and Harwood, pp. 139 and 141.
- ^ Side of tracks from Interstate Commerce Commission. "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 2" (PDF). W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Rosslyn Station historical marker located at site of Bluemont Junction station of Washington and Old Dominion Railroad. See: Washington and Old Dominion Railroad#Stations
- ^ Jump up to: a b Albee, Carrie E.; Trieschmann, Laura V. (EHT Traceries. Inc.) (November 2002). "Maywood Historic District" (PDF). National Register of Historic Places: Registration Form. Virginia Department of Historic Resources. p. 65 (Section 8). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 12, 2018. Retrieved November 12, 2018. and Accompanying map
- ^ Jump up to: a b Albee, Carrie E.; Trieschmann, Laura V. (EHT Traceries. Inc.) (November 2002). "Maywood Historic District" (PDF). National Register of Historic Places: Registration Form. Virginia Department of Historic Resources. p. 50 (Section 8). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 12, 2018. Retrieved November 12, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 3" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History: W&OD Railroad Maps. NOVA Parks. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 10, 2018. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Albee, Carrie E.; Trieschmann, Laura V. (EHT Traceries. Inc.) (November 2002). "Maywood Historic District" (PDF). National Register of Historic Places: Registration Form. Virginia Department of Historic Resources. pp. 59–60 (Section 8). Archived (PDF) from the original on November 12, 2018. Retrieved November 12, 2018.
- ^ 1929 topographic map of Washington, D.C., the city of Alexandria, Alexandria County, Falls Church and northeastern Fairfax County, showing the location of the Lee Heights station on the W&OD Railway's Great Falls Division: "Washington and Vicinity: Maryland: District of Columbia: Virginia". Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior: United States Geological Survey. 1929. LCCN 87693006. OCLC 15653164. Retrieved July 24, 2020 – via Library of Congress.
- ^ Harwood, p. 141.
- ^ "Old Dominion Citizens' Association Neighborhood Conservation Plan" (PDF). Government of Arlington County, Virginia. pp. 8–10. Retrieved January 27, 2021.
- ^ Note: Rixey station in undated photo Archived June 12, 2017, at the Wayback Machine was on southwest side of tracks, east of N. Glebe Road (Coordinates: 38°54′14″N 77°07′41″W / 38.903779°N 77.128192°W.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 4" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 5" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Coalition for the Capital Crescent Trail. "The Georgetown Branch Railroad". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database (photographed by Tom Fuchs, Greenbelt, MD, 2006-01-21). Archived from the original on September 27, 2015. Retrieved January 1, 2012. Description of planned Baltimore and Ohio (B&O) Railroad branch in Virginia.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 6" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 7" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 8" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- ^ Harwood, pp. 101, 106.
(2) Williams, pp. 107, 131. - ^ (1) "Bluemont Junction Caboose". Arlington County, Virginia: Arlington County Department of Parks and Recreation. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
(2) "Bluemont Junction Park". Arlington County, Virginia: Arlington County Department of Parks and Recreation. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 13, 2021.
(3) "Events Set for Third Annual Arlington Neighborhood Day". News Release. Arlington County, Virginia government. October 16, 1999. Archived from the original on September 28, 2013. Retrieved March 4, 2013.Several park events have been planned as well, including dedication of the Bluemont Junction Caboose and Railroad Display at Bluemont Park ....
(4) Coordinates of caboose at Bluemont Junction:38°52′23″N 77°07′57″W / 38.87306°N 77.132564°W
(3) Coordinates of intersection of Bluemont Junction Trail and Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Trail: 38°52′19″N 77°07′56″W / 38.8718317°N 77.1321047°W - ^ Copy of Southern Railway records in album inside Bluemont Junction caboose.
- ^ Locations of stations from distances along railroad route in Harwood, p. 139.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Harwood, p. 139.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Washington and Old Dominion Railroad timetable dated August 25, 1940
- ^ Coordinates of Lacey Car Barn historical marker: 38°52′56″N 77°07′00″W / 38.8821931°N 77.1165401°W
- ^ Coordinates of I-66 between Lee Highway and Washington Boulevard: 38°53′20″N 77°06′41″W / 38.888851°N 77.11128°W
- ^ Coordinates of Bluemont Junction Trail: 38°52′25″N 77°07′30″W / 38.873582°N 77.124992°W
- ^ Coordinates of Custis Trail between Lee Highway and Washington Boulevard: 38°53′36″N 77°06′04″W / 38.893204°N 77.101101°W
- ^ Coordinates of Bluemont Junction Park: 38°52′32″N 77°07′23″W / 38.8756158°N 77.1231866°W
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Rolling Stock of the Utah State Railroad Museum: Cargill 6751: SW1". Utah State Railroad Museum: Spencer S. & Dolores Doré Eccles Rail Center. Ogden, Utah: Ogden Union Station. 2018. Archived from the original (photograph) on September 3, 2018. Retrieved October 31, 2018.
This locomotive began life as Baltimore & Ohio 213, and later became B&O 8413. It was sold to Arco Petroleum in Carson, California, and renumbered 8417, then later Arco 6971. Sold to General American Tank Car (GATX) in Colton, California, keeping the same number. Cargill purchased the unit from Western Railway Supply, a used equipment dealer, and moved it to Ogden in August 1993 for use at the company’s Globe Mill. In 2010 it was replaced by a Trackmobile, and Cargill donated it to the museum. It was delivered on May 21, 2011, free of charge thanks to Utah Central and Union Pacific. It is one of the first SW1s to be built, and when sold to the B&O was classified as an NS1.
While out of service at the elevator, vandals stripped the wiring from the traction motors, as well as from inside the cab which remained unlocked. Cargill funded the complete repainting and restoration of the locomotive to operation. Painting was completed in November 2011. Located on Track 1. - ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Harwood, p. 137.
- ^ Van Cleve, Jeff (July 4, 1996). "Cargill 6751" (photograph). RR Picture Archives.net. Ogden, Utah. Retrieved December 20, 2013. Archived October 29, 2018, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Pictures of CRGX 6751" (photographs). RR Picture Archives.net. November 27, 2020. Retrieved November 27, 2020. Archived November 27, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ (1) "Cargill EMD SW1 #6751" (photograph). Utah State Railroad Museum Locomotives. Retrieved June 7, 2019. Archived June 7, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) "Cargill EMD SW1 #6751" (photograph). rgusmrail.com. March 1, 2019. Retrieved June 7, 2019.This SW1 unit was built by EMD in 1940 as #213 for the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad. The unit was subsequently renumbered BO #8413. It was sold to Arco Petroleum at Carson, CA, where it was renumbered #6971. It next went to the locomotive leasing company General American Transportation Corporation at Colton, CA. After the lease expired, the unit was stored at the GATX facility until it was sold through the dealer, Western Railway Supply, to Cargill. It moved to the Horizon Milling Company in Ogden in mid August 1993 and was repainted, lettered and renumbered #6751. It was replaced by a Trackmobile in 2010. Donated to the Utah State Railroad Museum in April 2011, it was moved to Union Station on 21st May 2011.
Archived June 7, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) Daniels, Roger (June 27, 2020). "CRGX 6751(SW1)" (photograph). RR Picture Archives.net. Ogden, Utah. Retrieved November 27, 2020. Archived November 27, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. - ^ (1) Kerr, James (November 20, 2009). "Columbia & Reading ALCO S2 CORY 2-26" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Frank Sahd Salvage Center, Columbia, Pennsylvania. Retrieved January 28, 2014. Archived February 3, 2014, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) k41361 (February 24, 2010). "Columbia & Reading S2.AVI" (video). Retrieved June 29, 2016. Video of CORY 2-26 crossing Route 262 in Columbia, Pennsylvania. Archived June 29, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) "Columbia & Reading Railway No. 2-26" (photograph). Green Initiatives. Columbia, Pennsylvania: Sahd Metal Recycling. Retrieved December 20, 2013. Archived September 27, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
(4) Walker, Craig (September 27, 2013). "Columbia & Reading ALCO S2 CORY 2-26" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Columbia, Pennsylvania. Retrieved January 28, 2014.Tucked away in a scrap yard in Columbia, Pennsylvania, is Columbia & Reading S2 2-26. This 1946-built Alco has put in the miles for a number of railroads, starting with the Chesapeake & Ohio (#5015, then #9165) followed by stints as GEX 106, FCIN 106, PVRR 27, CCCR 27 and JCNX 27.
Archived 2015-06-04 at the Wayback Machine.
(5) "Pictures of CORY 2-26" (photographs). Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved December 23, 2017. Archived December 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(6) Central PA Locos (April 26, 2014). "CORY 2-26" (photographs). Pictures of CORY 2-26. Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved May 25, 2015. Archived May 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
(7) Darnell, Tim (July 28, 2016). "CORY 2-26" (photograph). Pictures of CORY 2-26. Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved January 27, 2017. Archived January 27, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(8) Painter, Kevin (October 27, 2017). "CORY 2-26(S2)" (photograph). Pictures of CORY 2-26. Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved December 23, 2017. Archived December 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(9) Painter, Kevin (February 13, 2019). "CORY 2-26(S2)" (photograph). Pictures of CORY 2-26. Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved June 7, 2019. Archived June 7, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
(10) "HD Columbia and Reading ALCO S2 2 26 around Columbia,PA" (video). Alex Gillespie Rail Productions. February 14, 2019. Retrieved November 27, 2020 – via YouTube. (9:38 minutes)
(11) Painter, Kevin (January 21, 2020). "CORY 2-26 (S2)" (photograph). Pictures of CORY 2-26. Columbia, Pennsylvania: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved November 27, 2020. Archived November 27, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. - ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 131, 137.
(2) 1941 and 1946 photographs of W&OD 47: Harwood, pp. 83, 88. - ^ Jump up to: a b c "GE 44-Ton Number 30" (photographs). Number 30. The Fonda Johnstown & Gloversville Railroad. Retrieved June 29, 2016. Photographs of the former W&OD 47 as FJGRR 30, on the Great Western Railway of Colorado and as BJRY 44. Archived August 8, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Zygmunt, Chris (June 8, 2012). "BJRY 44" (photograph). LocoPhotos: Comprehensive Locomotive Archiving. Burlington, Iowa: Jack Hilton. Archived from the original on September 18, 2014. Retrieved September 17, 2014.
Lineage: ex GWR 44, ex Cargill, ex FJG 30, ex WOD 47
- ^ Jump up to: a b (1) Zygmunt, Chris (June 8, 2012). "Burlington Junction Railway No. 44 (with 2013-02-24 comment by Jack M. Jakeman: "This was the locomotive that the railroad was started with.")" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Burlington, Iowa. Retrieved December 20, 2013. Archived December 21, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) Zygmunt, Chris (June 8, 2012). "BJRY 44" (photograph). LocoPhotos: Comprehensive Locomotive Archiving. Burlington, Iowa: Jack Hilton. Archived from the original on September 18, 2014. Retrieved September 17, 2014.Lineage: ex GWR 44, ex Cargill, ex FJG 30, ex WOD 47
(3) "Profiles of Railroads Operating in Iowa". Rail System Plan: Appendix A. Ames, Iowa: Iowa Department of Transportation. Retrieved September 17, 2014. Archived February 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine. - ^ (1) Lewis, Edward A. (1996). Burlington Junction Railway. American Shoreline Railway Guide (5th ed.). Waukesha, Wisconsin: Kalmbach Publishing Company. p. 53. ISBN 0890242909. LCCN 96215170. OCLC 35286187. Retrieved December 23, 2017 – via Google Books.
(2) Miller, Gerry; Sink, Tom; Zygmunt, Chris (June 8, 2012). "Photographs of BJRY 44" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Burlington and West Burlington, Iowa. Retrieved December 17, 2014. Archived October 30, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) Rumbut, Kris (September 11, 2014). "BJRY 44" (photograph). Pictures of BJRY 44. Burlington, Iowa: RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved May 25, 2015. Archived May 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
(4) Mackey, Dan (August 5, 2018). "BRJY 44" (photograph). Burlington, Iowa: Flickr. Archived from the original on June 7, 2019. Retrieved June 7, 2019.
(5) Zygmunt, Chris (June 8, 2012). "BJRY 44" (photograph). LocoPhotos: Comprehensive Locomotive Archiving. Burlington, Iowa: Jack Hilton. Archived from the original on September 18, 2014. Retrieved September 17, 2014.Lineage: ex GWR 44, ex Cargill, ex FJG 30, ex WOD 47
- ^ (1) Harwood, pp. 68, 135.
(2) Blake, Henry W.; Bozell, Harold V., eds. (June 25, 1921). "Manufacturers and the Markets: Rolling Stock". Electric Railway Journal. New York: McGraw-Hill Company, Inc. 57 (28): 917. ISSN 0095-9715. OCLC 2021289. Retrieved September 28, 2017 – via Google Books. Description of 50-ton Baldwin-Westinghouse electric locomotive purchased by the Mononghahela Valley Traction Company, Fairmont, West Virginia, circa 1921 and similar to W&OD 50.
(3) 1922 and 1940 photographs of W&OD 50: Harwood, p. 71.
(4) Rice, Leonard. "W&OD electric freight locomotive 50 in the Rosslyn shop yard" (photograph). Archived December 24, 2013, at the Wayback Machine. In McCray, Paul. "Washington & Old Dominion Railroad, 1847 to 1968: A Photographic History". Retrieved December 2, 2015. Archived December 10, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
(5) Guillaudeu, 2013, p. 114. "This photograph from March 25, 1944, is one of the last images of Locomotive No. 50 in use on the W&OD Railroad. ... (Photograph by Leonard W. Rice.)" - ^ Jump up to: a b Harwood, p. 135.
- ^ (1) Harper, James P. (April 7, 1947). "Washington & Old Dominion 50 at Cedar Rapids, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) Ross, Don (September 25, 1954). "CR&IC 58 at Cedar Rapids, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived 2012-10-23 at the Wayback Machine.(3) - ^ (1) Harwood, p. 135.
(2) Ross, Don (March 1960). "Kansas City Kaw Valley 507 at Bonner Springs, KS" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) McDowell, Mark (May 1, 1960). "Motor 507 switching Lone Star Cement, 1960" (photograph). Pictures of KVW 507. Bonner Springs, Kansas: RR Pictures Archives.net. Retrieved November 2, 2020. Archived November 2, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. - ^ (1) the_trainman407 (July 14, 2012). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. AGP Ethanol Plant, Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
Iowa traction number 50 is a 50-ton steeplecab, built by Baldwin-Westinghouse in 1920 as Washington & Old Dominion Number 50. It was acquired by the Cedar Rapids & Iowa City in 1947, was rebuilt and renumbered number 58. In 1955 it was sold to the Kansas City-Kaw Valley Railroad and became their number 507. Finally, in 1962 it was sold to the Iowa Terminal and renumbered 53, later becoming IATR 50. The unit is seen here switching out Mason City's AGP plant
Archived December 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) "Iowa Traction Railway Locomotive Roster". Iowa Traction Railway. American-Rails.com. 2020. Retrieved November 2, 2020.Builder: Baldwin-Westinghouse; Model Type: Steeple Cab; Road Number: 50; Notes: Built as Washington & Old Dominion #50 in October, 1920. Acquired by the Cedar Rapids & Iowa City (Crandic) in 1947 as #58 and sold again to the Kansas City Kaw Valley Railroad (KCKV) in 1955 as #507. Finally, it was purchased by the Iowa Terminal in 1962, and renumbered #50 a year later.
Archived September 20, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
(3) Ross, Don (October 22, 1962). "Iowa Terminal RR 50 at Mason City, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 22, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(4) Schneider, Lynn (June 28, 1980). "Iowa Terminal RR 50 at Mason City, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(5) Rueber, James (May 24, 1986). "IAT 50 at Mason City, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(6) Menge, George (September 3, 1992). "IATR 50 at Emery, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 22, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(7) Richards, John (December 2001). "Iowa Traction RR 50 at Mason City, IA" (photograph). Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived October 23, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
(8) Blaszczyk, Andrew (September 24, 2008). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved September 18, 2014. Archived September 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine.
(9) R., Ryan; R., Jim (March 15, 2010). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved December 21, 2017. Archived December 21, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(10) "Pictures of IATR 50" (photograph). RR Pictures Archive.net. Retrieved May 25, 2015. Archived May 25, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
(11) "Pictures with BLW Serial No 53784 in them: Locomotive IATR 50 (Steeple Cab)" (photographs). RR Pictures Archive.Net. Retrieved May 25, 2015. Archived September 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
(12) Guillaudeu, 2013, p. 115 Photograph legend: "A railfan pretends to operate the Class B Baldwin-Westinghouse Locomotive No. 50 on September 20, 2009, where it is still in use on the Iowa Traction Railroad, almost 90 years after it was finished, in February 1921." - ^ Videos of IATR 50 in operation:
(1) jfreelan1964 (September 16, 2010). "Iowa Traction Empty Gondola Movement" (video). Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via YouTube. (14:39 minutes)
(2) jfreelan1964 (September 16, 2010). "Iowa Traction Scrap Metal Arrives at the UP Interchange" (video). Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via YouTube. (12:04 minutes)
(3) Chicagojoe28 (July 31, 2015). "Iowa Traction RR: The Last Electrified freight in the US" (video). Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via YouTube. (10:40 minutes)
(4) airailimages (August 1, 2015). "Iowa Traction Action - 27 July 2015" (video). Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via YouTube. (4:42 minutes)
(5) jfreelan1964 (February 3, 2017). "Iowa Traction Railway Winter 2016" (video). Retrieved December 21, 2017 – via YouTube. (23:49 minutes) - ^ (1) "Progressive Rail acquires Iowa Traction Railroad". ProgressiveRailroading.com. October 16, 2012. Retrieved November 13, 2012. Archived December 22, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) "Freight Tariff IATR 9001" (PDF). Iowa Traction Railway Company. October 4, 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 22, 2013. Retrieved December 20, 2013.
(3) Nelson, Jacob (June 3, 2013). "IATR 50" (photograph). RR Pictures Archives.net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved February 6, 2016. Archived February 6, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
(4) Terry, Jeff (January 29, 2014). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. CP Interchange, Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved September 18, 2014.Iowa Traction 50 shoves four hoppers back to the CP interchange track near Clear Lake Junction.
Archived September 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine.
(5) Schumann, John (December 6, 2015). "IATR 50" (photograph). RR Pictures Archives.net. Clear Lake, Iowa. Retrieved March 30, 2016. Archived March 30, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
(6) Smith, Nick (June 21, 2016). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. IATR AGP Elevator Lead, Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved January 27, 2017.Iowa Traction RR IATR 50 is tied down at Mason City on the main outside the UP interlocking. IATR built for the Washington & Old Dominion in 1920 and spent time on the Cedar Rapids & Iowa City and the Kansas City Kaw Valley & Western RR before coming to Mason City.
Archived January 27, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(7) Guillaudeu and McCray, 2016, pp. 85, 90-93.
(8) Ebright, Dick (June 24, 2017). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. AGProcessing spur, Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved September 27, 2017.IATR #50, seen here on the spur to the AGP soybean facility, was built by Baldwin in 1920; 97 years old and still in revenue service.
Archived September 27, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(9) mtnclimberjoe (August 18, 2017). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. AGP Facility, Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved December 23, 2017.The Iowa Traction railroad uses BLW steeple cab electric number 50 to shove a large cut of covered hoppers into the AGP corn processing facility in Mason City, Iowa.
Archived December 23, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
(10) mtnclimberjoe (August 18, 2017). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Mason City, Iowa. Archived from the original on February 14, 2019. Retrieved February 14, 2018.The Iowa Traction has just finished switching out the Renewable Energy Group ethanol facility and heads east with a big cut of tank cars.
(11) Leach, Paul (April 12, 2018). "IATR 50 (Steeple Cab)" (photograph). RR Picture Archives.net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved June 13, 2018.Preparing to move grain cars
Archived June 14, 2018, at the Wayback Machine.
(12) Junges, Olaf (August 29, 2018). "IATR 50". RR Picture Archives.net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved June 14, 2018.Heavy action day with 3 (!) Steeple Caps on duty.
Archived February 14, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
(13) Williams, Craig (March 11, 2019). "IATR 50" (photograph). RailPictures.Net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved June 6, 2019. Archived June 6, 2019, at the Wayback Machine.
(14) Leach, Paul (March 15, 2019). "IATR 50 (Steeple Cab)" (photograph). RR Picture Archives.net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved June 6, 2019.Working at the interchange
Archived June 6, 2019, at the Wayback Machine. - ^ (1) POTB 101 (October 17, 2020). "Iowa Traction 50" (photograph). Mason City, Iowa: Railroadforums.com. Retrieved November 2, 2020. Archived November 2, 2020, at the Wayback Machine.
(2) Leach, Paul (December 21, 2020). "IATR 50 (Steeple Cab)" (photograph). RR Picture Archives.net. Mason City, Iowa. Retrieved January 22, 2021.Tied down for the day
Archived January 22, 2021, at the Wayback Machine.
References[]
- Guillaudeu, David A.; Foreword by McCray, Paul E. (2013). Washington & Old Dominion Railroad. Images of Rail. Charleston, South Carolina: Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 9780738597928. OCLC 811603181. Retrieved November 13, 2016 – via Google Books.
- Guillaudeu, David A.; McCray, Paul E. (2016). Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Revisited. Images of Rail. Charleston, South Carolina: Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 9781467116381. OCLC 944086523. Retrieved November 13, 2016 – via Google Books.
- Harwood, Herbert H., Jr. (April 2000). Rails to the Blue Ridge: The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad, 1847 – 1968 (3rd ed.). Fairfax Station, Virginia: Northern Virginia Parks Authority. ISBN 0615114539. LCCN 77104382. OCLC 44685168.
- In Appendix K of Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority - Pre-filed Direct Testimony of Mr. Hafner, Mr. Mcray and Mr. Simmons, November 30, 2005 (Parts 4 and 5), Case No. PUE-2005-00018, Virginia State Corporation Commission. Obtained in "Case Docket Search". Virginia State Corporation Commission. Retrieved September 28, 2017. Archived September 28, 2017.
- Interstate Commerce Commission. "W&OD Railway 1916 ICC Valuation Maps". Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- King, W.E. (1934-07-19). Index map showing Washington & Old Dominion Railway's line abandoned in relation to other railroads and common carriers in lower left corner of "GF&OD Railroad 1916 ICC Valuation Map No. 3" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Regional Park: W&OD Railroad Maps. Northern Virginia Regional Park Authority: Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park. July 1, 1916. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 8, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2015.
- "Map of the W&OD". The Friends of the Washington & Old Dominion Trail. Archived from the original on November 24, 2010. Retrieved September 29, 2010.
- Vetter, Peggy D (2000). "The W&OD Railroad is Heart of Herndon for 120 Years". The Observer. Herndon, VA: The Herndon Publishing Company, Inc. Archived from the original on August 7, 2008. Retrieved January 17, 2010. (A detailed history of the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad.)
- Washington and Old Dominion Railway (1911). "W&OD Railway Track Plats". Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park: History: W&OD Railroad Maps. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original on November 10, 2018. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- Williams, Ames W. (1989). The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad. Arlington, Virginia: Arlington Historical Society. ISBN 0926984004. OCLC 20461397.
Further reading[]
- Glakas, Barbara. "The Rail Comes to Herndon: The Evolution of the WO&D Railroad" (PDF). Herndon, Virginia: Herndon Historical Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- Mauro, Chuck. "How the Railroad Came to Herndon" (PDF). Herndon, Virginia: Herndon Historical Society. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 24, 2019. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- Tennyson, E.L. (1984). "The History of Arlington's Electric Railways" (PDF). The Arlington Historical Magazine. Arlington County, Virginia: Arlington Historical Society. 7 (4). Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- Williams, Ames W. (1966). "The Washington and Old Dominion Railroad". Records of the Columbia Historical Society. Washington, D.C.: Columbia Historical Society. 66: 231–276. JSTOR 40067258. Retrieved June 11, 2021 – via JSTOR.
Videos[]
- Crockett, Bob. "W&OD 1939" (video). Video uploaded by Paul McCray on January 17, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2012 – via YouTube. (4:03 minutes). Video filmed in 1939 from Rosslyn to Difficult Run Bridge west of Vienna.
- "W&OD Railroad in action" (video). greenwayheightshistory.com. Retrieved December 29, 2019. Video filmed in 1939 at various points along the W&OD Railroad. (2:52 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (December 18, 2011). "Frank Tosh Interview about the W&OD Railroad" (video). Retrieved October 29, 2012 – via YouTube. (52:08 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (December 19, 2011). "Interview with W&OD Train Driver Douglas Lee and Brakeman Randolph Shutts Part 1" (video). Retrieved October 29, 2012 – via YouTube. (50:10 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (December 19, 2011). "Interview with W&OD Train Driver Douglas Lee and Brakeman Randolph Shutts Part 2" (video). Retrieved January 7, 2015 – via YouTube. (48:14 minutes)
- Mudd, Roger (January 4, 2012). "The Civil War on the W&OD Trail - Herndon" (video). Fairfax County, Virginia, Government Television. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (4:21 minutes)
- Mudd, Roger (January 4, 2012). "The Civil War on the W&OD in Vienna, VA" (video). Fairfax County, Virginia, Government Television. Retrieved October 28, 2012 – via YouTube. (3:10 minutes). 1861 Civil War skirmish on the Alexandria, Loudoun and Hampshire Railroad in Vienna.
- McCray, Paul (February 23, 2012). "Paul McCray W&OD Presentation 2-23-2012" (video). Reston Museum, Reston, Virginia. Retrieved June 11, 2021 – via YouTube. (4:23 minutes)
- "Mosby's Raid at downtown Herndon, Virginia - March 9, 2013" (video). Herndon, Virginia: HCTV. May 9, 2013. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube.
Civil War reenactment held near Herndon's historic W&OD Depot Museum commemorating the 150th anniversary of John S. Mosby's Herndon Station Raid, March 17, 1863.
(13:44 minutes) - McCray, Paul (September 26, 2020). "The W&OD Railroad Begins" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (6:18 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (October 5, 2020). "The W&OD Railroad: After the Civil War" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (6:20 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (October 25, 2020). "Great Falls & Old Dominion Railroad and the W&OD Railway" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (10:32 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (November 5, 2020). "The End of the W&OD Railroad" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (9:05 minutes)
- "Melvin Partlow Talks About Riding the Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Cars in Ashburn" (video). NOVA History Remembered. December 13, 2020. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (1:12 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (March 19, 2021). "Evans Autorailer and The Arlington & Fairfax Auto Railroad" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (5:56 minutes)
- McCray, Paul (May 2, 2021). "Strike on the Washington & Old Dominion Railway1916...Union Action Gains National Attention" (video). NOVA History Remembered. Retrieved June 9, 2021 – via YouTube. (11:31 minutes)
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Washington and Old Dominion Railroad. |
| ( • help)
|
- "Washington and Old Dominion Railroad Markers series". HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved August 18, 2010. Photographs and descriptions of markers describing the history of the W&OD Railroad.
- Haring, O. Edwards, ed. (1903). "Barcroft News". Barcroft, Virginia. (Articles about Bluemont Branch of Southern Railway):
- Crowded Trains. Vol. 1, No. 3 (1903-07-05).
- Klemroth, E.H. (1903-06-25), Letter to the editor. Vol. 1, No. 3 (1903-07-05).
- Bearing Fruit. Vol. 1, No. 4 (1903-07-19).
- The R.-H. W.. Vol. 1, No. 4 (1903-07-19).
- Talk Is Cheap. Vol. 1, No. 6 (1903-08-16).
- Where They Belong. Vol. 1, No. 6 (1903-08-16).
- A Grain of Comfort. Vol. 1, No. 7 (1903-09-14).
- Newslets. Vol. 1, No. 7 (1903-09-14).
- A Step Forward. Vol. 1, No. 7 (1903-09-28).
- Who Can Tell Us. Vol. 1, No. 8 (1903-09-14).
- New Schedule. Vol. 1, No. 9 (1903-09-28).
- New Schedule. Vol. 1, No. 10 (1903-10-12).
- The Bridge Monopoly. Vol. 1, No. 11 (1903-10-26).
- Considerate. Vol. 1, No. 11 (1903-10-26).
- Newsletts. Vol. 1, No. 13 (1903-11-23).
- In "The 1903 Barcroft News". Arlington County, Virginia: Barcroft School and Civic League. August 11, 2008. Archived from the original on September 4, 2011. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- "Historical Background: Old Dominion Drive Notable Facts (Formerly the Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad)". greenwayheightshistory.com. Eloise Lorenze. Archived from the original on December 30, 2019. Retrieved December 30, 2019. Photographs of stations, tickets and promotional materials about the Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad and the Great Falls Division of the Washington & Old Dominion Railway.
- McCray, Paul. "Washington & Old Dominion Railroad, 1847 to 1968: A Photographic History". Retrieved June 28, 2010. Website describing the history of the W&OD Railroad. Archived March 13, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
- Ross, Don. "Washington & Old Dominion Ry". Don's Rail Photos. Don Ross Group. Archived from the original on April 4, 2013. Retrieved September 18, 2014.
- Washington and Old Dominion Railway (October 1, 1912). "Rules and Regulations for the Government of Employees of the Washington and Old Dominion Railway" (PDF). Washington & Old Dominion Railroad Regional Park: History. NOVA Parks. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 10, 2018. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- Historic Great Falls of Potomac: Scenic Beauty Around Great Falls and Picturesque—Waterfalls Reached by the Washington, Great Falls and Old Dominion Railroad. Advertisement in "Industrial and Historical Sketch of Fairfax County, Virginia". Fairfax County Board of Supervisors. 1907. p. 92. Retrieved April 10, 2021 – via Google Books.
- American companies established in 1936
- Defunct Virginia railroads
- Predecessors of the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
- Railway companies established in 1936
- Railway companies disestablished in 1968
- Transportation in Arlington County, Virginia
- Transportation in Fairfax County, Virginia
- Transportation in Loudoun County, Virginia







