1800 United States presidential election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
138 members of the Electoral College 70 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 32.3%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
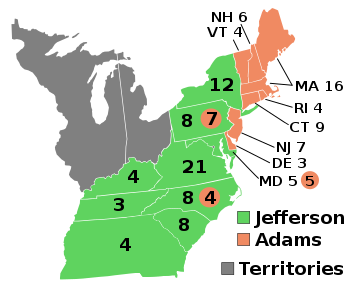 Presidential election results map. Green denotes states won by Jefferson and burnt orange denotes states won by Adams. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes cast by each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1801 contingent U.S. presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
16 state delegations of the House of Representatives 9 state votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1800 United States presidential election was the fourth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from October 31 to December 3, 1800. In what is sometimes referred to as the "Revolution of 1800",[2][3] Vice President Thomas Jefferson of the Democratic-Republican Party defeated incumbent President John Adams of the Federalist Party. The election was a political realignment that ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican leadership.
Adams had narrowly defeated Jefferson in the 1796 election. Under the rules of the electoral system in place before the 1804 ratification of the 12th Amendment, each member of the Electoral College cast two votes, with no distinction made between electoral votes for president and electoral votes for vice president. As Jefferson received the second-most votes in 1796, he was elected vice president. In 1800, unlike in 1796, both parties formally nominated tickets. The Democratic-Republicans nominated a ticket consisting of Jefferson and Aaron Burr, while the Federalists nominated a ticket consisting of Adams and Charles C. Pinckney. Each party formed a plan by which one of their respective electors would vote for a third candidate or abstain so that its preferred presidential candidate (Adams for the Federalists and Jefferson for the Democratic-Republicans) would win one more vote than the party's other nominee.[citation needed]
The chief political issues revolved around the fallout from the French Revolution and the Quasi-War. The Federalists favored a strong central government and close relations with Great Britain. The Democratic-Republicans favored decentralization to the state governments, and the party attacked the taxes the Federalists imposed. The Democratic-Republicans also denounced the Alien and Sedition Acts, which the Federalists had passed to make it harder for immigrants to become citizens and to restrict statements critical of the federal government. The Democratic-Republicans were well organized at the state and local levels, but the Federalists were disorganized and suffered a bitter split between their two major leaders, Adams and Alexander Hamilton. According to historian John Ferling, the jockeying for electoral votes, regional divisions, and the propaganda smear campaigns created by both parties made the election recognizably modern.[4]
At the end of a long and bitter campaign, Jefferson and Burr each won 73 electoral votes, Adams won 65, and Pinckney won 64. The Federalists swept New England, the Democratic-Republicans dominated the South, and the parties split the Mid-Atlantic states of New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
The Democratic-Republicans' failure to execute their plan to award Jefferson one more vote than Burr resulted in a tie, which necessitated a contingent election in the House of Representatives. Under the terms laid out in the Constitution, the outgoing House of Representatives chose between Jefferson and Burr. Burr was accused of campaigning for the presidency himself in the contingent election despite being a member of Jefferson's party. Each state delegation cast one vote, and a victory in the contingent election required one candidate to win a majority of the state delegations. Neither Burr nor Jefferson was able to win on the first 35 ballots of the contingent election, as most Federalist representatives backed Burr and all Democratic-Republican representatives backed Jefferson. Hamilton favored Jefferson over Burr, and he convinced several Federalists to switch their support to Jefferson, giving Jefferson a victory on the 36th ballot. Jefferson became the second incumbent vice president to be elected president.
Candidates[]
Both parties used congressional nominating caucuses to formally nominate tickets for the first time. The Federalists nominated a ticket consisting of incumbent President John Adams of Massachusetts and Charles Cotesworth Pinckney of South Carolina. Pinckney had fought in the American Revolutionary War and later served as the minister to France. The Democratic-Republicans nominated a ticket consisting of Vice President Thomas Jefferson of Virginia and former Senator Aaron Burr of New York. Jefferson had been the runner-up in the previous election and had co-founded the party with James Madison and others, while Burr was popular in the electorally important state of New York.[5]
Federalist candidates[]

President
John Adams
from Massachusetts
Former
Minister to France
Charles C.
Pinckney
from South Carolina
Democratic-Republican candidates[]

Vice President
Thomas Jefferson
from Virginia
Former
U.S. Senator
Aaron Burr
from New York
General election[]
Campaign[]
While the 1800 election was a re-match of the 1796 election, it ushered in a new type of American politics, a two-party republic and acrimonious campaigning behind the scenes and through the press. On top of this, the election pitted the "larger than life" Adams and Jefferson, who were formerly close allies turned political enemies.[6]
The campaign was bitter and characterized by slander and personal attacks on both sides. Federalists spread rumors that the Democratic-Republicans were radical atheists[7] who would ruin the country (based on the Democratic-Republican support for the French Revolution). In 1798, George Washington had complained "that you could as soon scrub the blackamoor white, as to change the principles of a professed Democrat; and that he will leave nothing unattempted to overturn the Government of this Country".[8] Meanwhile, the Democratic-Republicans accused Federalists of subverting republican principles with the Alien and Sedition Acts, some of which were later declared unconstitutional after their expiration by the Supreme Court, and relying for their support on foreign immigrants; they also accused Federalists of favoring Britain and the other coalition countries in their war with France in order to promote aristocratic, anti-democratic values.[9]
Adams was attacked by both the opposition Democratic-Republicans and a group of so-called "High Federalists" aligned with Alexander Hamilton. The Democratic-Republicans felt that the Adams foreign policy was too favorable toward Britain; feared that the new army called up for the Quasi-War would oppress the people; opposed new taxes to pay for war; and attacked the Alien and Sedition Acts as violations of states' rights and the Constitution. "High Federalists" considered Adams too moderate and would have preferred the leadership of Alexander Hamilton instead.[10]
Hamilton had apparently grown impatient with Adams and wanted a new president who was more receptive to his goals. During Washington's presidency, Hamilton had been able to influence the federal response to the Whiskey Rebellion (which threatened the government's power to tax citizens). When Washington announced that he would not seek a third term, Adams was widely recognized by the Federalists as next-in-line.[citation needed]
Hamilton appears to have hoped in 1796 that his influence within an Adams administration would be as great as or greater than in Washington's. By 1800, Hamilton had come to realize that Adams was too independent and thought the Federalist vice presidential candidate, Charles Cotesworth Pinckney of South Carolina, more suited to serving Hamilton's interests. In his third sabotage attempt toward Adams,[11] Hamilton quietly schemed to elect Pinckney to the presidency. Given Pinckney's lack of political experience, he would have been expected to be open to Hamilton's influence. However, Hamilton's plan backfired and hurt the Federalist party, particularly after one of his letters, a scathing criticism of Adams that was fifty-four pages long,[12] fell into the hands of a Democratic-Republican and soon after became public. It embarrassed Adams and damaged Hamilton's efforts on behalf of Pinckney,[4] not to mention speeding Hamilton's own political decline.[12]
The contemporarily unorthodox public campaigning methods employed in 1800 were first employed by Jefferson's running mate and campaign manager, Aaron Burr, who is credited by some historians with inventing the modern electioneering process.[13]
Selection method changes[]
Partisans on both sides sought any advantage they could find. In several states, this included changing the process of selecting electors to ensure the desired result. In Georgia, Democratic-Republican legislators replaced the popular vote with selection by the state legislature.[citation needed] Federalist legislators did the same in Massachusetts and New Hampshire. This may have had some unintended consequences in Massachusetts, where the makeup of the delegation to the House of Representatives changed from 12 Federalists and 2 Democratic-Republicans to 8 Federalists and 6 Democratic-Republicans, perhaps the result of backlash on the part of the electorate.[citation needed] Pennsylvania also switched to legislative choice, but this resulted in an almost evenly split set of electors. Virginia switched from electoral districts to winner-take-all, a move that probably switched one or two votes out of the Federalist column.[citation needed]
Voting[]

Because each state could choose its own election day in 1800, voting lasted from April to October. In April, Burr's mobilization of the vote in New York City succeeded in reversing the Federalist majority in the state legislature to provide decisive support for the Democratic-Republican ticket.[citation needed] With the two parties tied 63–63 in the Electoral College in the autumn of 1800, the last state to vote, South Carolina, chose eight Democratic-Republicans to award the election to Jefferson and Burr.
Under the United States Constitution as it then stood, each elector cast two votes, and the candidate with a majority of the votes was elected president, with the vice presidency going to the runner-up. The Federalists therefore arranged for one of their electors to vote for John Jay rather than for Pinckney. The Democratic-Republicans had a similar plan to have one of their electors cast a vote for another candidate instead of Burr but failed to execute it,[why?] thus all of the Democratic-Republican electors cast their votes for both Jefferson and Burr, 73 in all for each of them. According to a provision of the United States Constitution, a tie in a case of this type had to be resolved by the House of Representatives, with each state casting one vote. Although the congressional election of 1800 turned over majority control of the House of Representatives to the Democratic-Republicans by 68 seats to 38,[14] the presidential election had to be decided by the outgoing House that had been elected in the congressional election of 1798 (at that time, the new presidential and congressional terms all started on March 4 of the year after a national election). In the outgoing House, the Federalists retained a majority of 60 seats to 46.[14][4]
Disputes[]
Defective certificate[]
When the electoral ballots were opened and counted on February 11, 1801, it turned out that the certificate of election from Georgia was defective: while it was clear that the electors had cast their votes for Jefferson and Burr, the certificate did not take the constitutionally mandated form of a "List of all the Persons voted for, and of the Number of Votes for each".[15] Vice President Jefferson, who was counting the votes in his role as President of the Senate, immediately counted the votes from Georgia as votes for Jefferson and Burr, and no objections were raised.[15]
If the disputed Georgia ballots were rejected on these technicalities, Jefferson and Burr would have been left with 69 votes each, or one short of the 70 votes required for a majority, meaning a contingent election would have been required between the top five finishers (Jefferson, Burr, incumbent president John Adams, Charles C. Pickney and John Jay) in the House of Representatives. With these votes, the total number of votes for Jefferson and Burr was 73, which gave them a majority of the total, but they were tied.[15]
Results[]
Jefferson and Burr carried every state that had supported the Democratic-Republicans in 1796, made gains in Maryland, and picked up Burr's home state of New York. In the six states choosing electors by some form of popular vote, they won a landslide over Adams and Pinckney, polling 15,846 more votes than the Federalist ticket. Adams made gains in Pennsylvania and North Carolina, but these votes were not enough to offset the Democratic-Republican gains elsewhere. Of the 155 counties and independent cities making returns, Jefferson and Burr won in 115 (74.19%), whereas the Adams ticket carried 40 (25.81%). This was the last time that Vermont voted for the Federalists, and the last time a Federalist won electoral votes from Pennsylvania.

| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote(a), (b), (c) | Electoral vote | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | ||||
| Thomas Jefferson | Democratic-Republican | Virginia | 45,467 | 60.5% | 73 |
| Aaron Burr | Democratic-Republican | New York | — | — | 73 |
| John Adams (incumbent) | Federalist | Massachusetts | 29,621 | 39.4% | 65 |
| Charles Cotesworth Pinckney | Federalist | South Carolina | — | — | 64 |
| John Jay | Federalist | New York | — | — | 1 |
| Other(d) | 54 | 0.1% | 0 | ||
| Total | 75,142 | 100.0% | 276 | ||
| Needed to win | 70 | ||||
Source (Popular Vote): A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns 1787-1825[16]
Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved July 30, 2005.
(a) Votes for Federalist electors have been assigned to John Adams and votes for Democratic-Republican electors have been assigned to Thomas Jefferson.
(b) Only 6 of the 16 states chose electors by any form of popular vote.
(c) Those states that did choose electors by popular vote had widely varying restrictions on suffrage via property requirements.
(d) Eight votes were cast for electors pledged to both Adams and Jefferson; 46 votes were cast for electors of unknown affiliation.
Electoral College vote by state[]
| State | Electoral votes |
TJ | AB | JA | CP | JJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connecticut | 9 | — | — | 9 | 9 | — |
| 3 | — | — | 3 | 3 | — | |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | — | — | — | |
| 4 | 4 | 4 | — | — | — | |
| 10 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | — | |
| 16 | — | — | 16 | 16 | — | |
| 6 | — | — | 6 | 6 | — | |
| New Jersey | 7 | — | — | 7 | 7 | — |
| New York | 12 | 12 | 12 | — | — | — |
| 12 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | — | |
| Pennsylvania | 15 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 7 | — |
| 4 | — | — | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| South Carolina | 8 | 8 | 8 | — | — | — |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | — | — | — | |
| Vermont | 4 | — | — | 4 | 4 | — |
| 21 | 21 | 21 | — | — | — | |
| TOTAL | 138 | 73 | 73 | 65 | 64 | 1 |
| TO WIN | 70 | |||||
Source: "Tally of Electoral Votes for the 1800 Presidential Election, February 11, 1801". The Center for Legislative Archives. National Archives. August 15, 2016. Retrieved February 15, 2018.
Results by state[]
Of the 16 states that took part in the 1800 election, six (Kentucky, Maryland, North Carolina, Rhode Island, Tennessee, and Virginia) used some kind of popular vote. In Rhode Island and Virginia, voters elected their state's entire Electoral College delegation at large; Kentucky, Maryland, North Carolina, and Tennessee all used some variation of single-member districts. In the rest, electors were chosen by the state legislature. Popular vote records for several states are incomplete, and the returns from Kentucky and Tennessee appear to have been lost. Below are the surviving popular vote figures as published in A New Nation Votes.
| Thomas Jefferson Democratic-Republican |
John Adams Federalist |
Margin | State total | Citation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | Electoral votes |
# | % | # | |
| Connecticut | 9 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 9 | — | — | [17] | |||
| 3 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 3 | — | — | [18] | ||||
| 4 | No popular vote | 4 | No popular vote | — | — | — | |||||
| [a] | 4 | 75 | 63.03 | 4 | no ballots | — | 75 | 63.03 | 119 | [19] | |
| [b] | 10 | 10,638 | 51.35 | 5 | 10,068 | 48.60 | 5 | 570 | 2.75 | 20,716 | [20] |
| 16 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 16 | — | — | [21] | ||||
| 6 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 6 | — | — | [22] | ||||
| New Jersey | 7 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 7 | — | — | [23] | |||
| New York | 12 | No popular vote | 12 | No popular vote | — | — | — | [24] | |||
| [c] | 12 | 11,593 | 51.26 | 8 | 11,025 | 48.75 | 4 | 568 | 2.52 | 22,618 | [25] |
| Pennsylvania | 15 | No popular vote | 8 | No popular vote | 7 | — | — | [26] | |||
| 4 | 2,159 | 47.85 | — | 2,353 | 52.15 | 4 | -194 | -4.30 | 4,512 | [27] | |
| South Carolina | 8 | No popular vote | 8 | No popular vote | — | — | — | [28] | |||
| [d] | 3 | No data | 3 | No data | — | No data | No data | [29] | |||
| Vermont | 4 | No popular vote | — | No popular vote | 4 | — | — | [30] | |||
| 21 | 21,002 | 77.28 | 21 | 6,175 | 22.72 | — | 14,827 | 54.56 | 27,177 | [31] | |
| TOTALS | 138 | 45,467 | 60.51 | 73 | 29,621 | 39.42 | 65 | 15,846 | 21.09 | 75,142 | |
| TO WIN | 70 | ||||||||||
District results[]
Kentucky, Maryland, North Carolina, and Tennessee chose each of their electors from specially-drawn single-member districts, the results from which are as follows.
| Thomas Jefferson Democratic-Republican |
John Adams Federalist |
Margin | District total | Citation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | # | % | # | % | # | % | # | |
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [32] | ||||
| [a] | 75 | 63.03 | No data | 75 | 63.03 | 119 | [33] | |
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [34] | ||||
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [35] | ||||
| 68 | 5.75 | 1,114 | 94.25 | -1,046 | -88.50 | 1,182 | [36] | |
| [e] | 789 | 31.98 | 1,669 | 67.65 | -880 | -35.67 | 2,467 | [37] |
| 1,724 | 45.27 | 2,084 | 54.73 | -360 | -9.46 | 3,808 | [38] | |
| 1,351 | 50.17 | 1,342 | 49.83 | 9 | 0.34 | 2,693 | [39] | |
| 2,379 | 75.45 | 774 | 24.55 | 1,605 | 50.90 | 3,153 | [40] | |
| 1,640 | 87.00 | 245 | 13.00 | 1,395 | 74.00 | 1,885 | [41] | |
| 1,031 | 58.15 | 742 | 41.85 | 289 | 16.32 | 1,773 | [42] | |
| 1,022 | 67.55 | 491 | 32.45 | 531 | 35.10 | 1,513 | [43] | |
| 629 | 44.61 | 781 | 55.39 | -152 | -10.78 | 1,410 | [44] | |
| [f] | 5 | 0.60 | 826 | 99.40 | -821 | -98.8 | 831 | [45] |
| [c] | No data | No data | No data | No data | [46] | |||
| 1,035 | 44.02 | 1,316 | 55.98 | -281 | -11.96 | 2,351 | [47] | |
| 299 | 12.32 | 2,128 | 87.68 | -1,829 | -75.36 | 2,427 | [48] | |
| 1,344 | 63.61 | 769 | 36.39 | 575 | 27.22 | 2,113 | [49] | |
| 1,374 | 73.95 | 484 | 26.05 | 890 | 47.90 | 1,858 | [50] | |
| 1,134 | 54.89 | 932 | 45.11 | 202 | 9.78 | 2,066 | [51] | |
| 715 | 50.49 | 701 | 49.51 | 14 | 0.98 | 1,416 | [52] | |
| 1,319 | 63.87 | 746 | 36.13 | 573 | 27.74 | 2,065 | [53] | |
| 1,322 | 53.63 | 1,143 | 46.37 | 179 | 7.26 | 2,465 | [54] | |
| 1,010 | 43.11 | 1,333 | 56.89 | -323 | -13.78 | 2,343 | [55] | |
| 1,340 | 79.86 | 338 | 20.14 | 1,002 | 59.72 | 1,678 | [56] | |
| 701 | 38.18 | 1,135 | 61.82 | -434 | -23.64 | 1,836 | [57] | |
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [58] | ||||
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [59] | ||||
| No data | No data | No data | No data | [60] | ||||
Close states and districts[]
States and districts where the margin of victory was under 1%:
- Maryland's 4th electoral district, 0.34% (9 votes)
- North Carolina's Northampton electoral district, 0.98% (14 votes)
States and districts where the margin of victory was under 5%:
- Rhode Island, 4.06% (194 votes)
States and districts where the margin of victory was under 10%:
- North Carolina's Rockingham electoral district, 7.26% (179 votes)
- Maryland's 3rd electoral district, 9.46% (360 votes)
- North Carolina's New Bern electoral district, 9.78% (202 votes)
1801 contingent election[]

In February 1801, the members of the House of Representatives balloted as states to determine whether Jefferson or Burr would become president. There were sixteen states, each with one vote; an absolute majority of nine was required for victory. It was the outgoing House of Representatives, controlled by the Federalist Party, that was charged with electing the new president. Jefferson was the great enemy of the Federalists, and a faction of Federalist representatives tried to block him and elect Burr. Most Federalists voted for Burr, giving Burr six of the eight states controlled by Federalists. The seven delegations controlled by Democratic-Republicans all voted for Jefferson, and Georgia's sole Federalist representative also voted for him, giving him eight states. The Vermont delegation was evenly split and cast a blank ballot. The remaining state, Maryland, had five Federalist representatives to three Democratic-Republicans; one of its Federalist representatives voted for Jefferson, forcing that state delegation also to cast a blank ballot.[61]
Publicly, Burr remained quiet between mid-December 1800 and mid-February 1801, when the electoral votes were counted. Behind the scenes, he faced mounting pressure from within the party to step aside if he and Jefferson should tie in electoral votes. However, there was confusion as to whether or not Burr could simply concede the presidency to Jefferson and become vice-president, or whether he would have been forced to withdraw entirely and allow one of the Federalist candidates to become vice-president, as the Constitution was unclear on the matter. Regardless, he refused to disavow the presidency, writing in December 1800 to Representative Samuel Smith (R-MD) that he would not "engage to resign" if chosen president, adding that the question was "unnecessary, unreasonable and impertinent." Rumors circulated that Representative James A. Bayard (F-DE) had—purportedly in Burr's name—approached Smith and Edward Livingston (R-NY) with offers of political appointments if they voted for Burr.[62]
True or not, House Republicans, who from the start of the 1800 campaign viewed Jefferson as their candidate for president and Burr for vice president, faced two abhorrent possible outcomes when the House met to vote: the Federalists could engineer a victory for Burr; or the Federalists could refuse to break the deadlock, leaving Federalist Secretary of State John Marshall as Acting President.[63] Neither came to pass however, chiefly due to Hamilton's energetic opposition to Burr. Hamilton embarked on a frenzied letter-writing campaign to get Federalist Representatives to switch votes.[64] He urged the Federalists to support Jefferson because he was "by far not so dangerous a man" as Burr; in short, he would much rather have someone with wrong principles than someone devoid of any.[12]
From February 11 to 17, the House cast a total of 35 ballots; each time eight state delegations voted for Jefferson, one short of the necessary majority of nine.
On February 17, on the 36th ballot, Bayard changed his vote from Burr to no selection,[4] joined by his allies in Maryland and Vermont.[65] This changed the Maryland and Vermont votes from no selection to Jefferson, giving him the votes of 10 states and the presidency. The four representatives present from South Carolina, all Federalists, also changed their 3–1 selection of Burr to four abstentions.
Due to the experiences of this and the previous election, sentiment for a new way of selecting the President and Vice-President rose significantly, resulting in the 12th Amendment.
Results[]
| February 11–17, 1801 – 1st through 35th ballots | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thomas Jefferson | 8 | 50.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aaron Burr | 6 | 37.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Divided | 2 | 12.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total votes: | 16 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Votes necessary: | 9 | >50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| February 17, 1801 – 36th ballot | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Candidate | Votes | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thomas Jefferson | 10 | 62.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aaron Burr | 4 | 25.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Blank | 2 | 12.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total votes: | 16 | 100 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Votes necessary: | 9 | >50 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(a) The votes of the representatives is typical and may have fluctuated from ballot to ballot, but the result for each state did not change.
(b) Even though Georgia had two representatives apportioned, one seat was vacant due to the death of James Jones.
(c) Even though South Carolina had six representatives apportioned, Thomas Sumter was absent due to illness, and Abraham Nott departed for South Carolina between the first and final ballots.
Electoral College selection[]
The Constitution, in Article II, Section 1, provided that the state legislatures should decide the manner in which their electors were chosen. Different state legislatures chose different methods:[70]
| Method of choosing electors | State(s) |
|---|---|
| State is divided into electoral districts, with one Elector chosen per district by the voters of that district |
|
| Each Elector chosen by voters statewide |
|
|
Tennessee |
| Each Elector appointed by state legislature | (all other states)
|
In popular culture[]
The election's story and the eventual reconciliation between Jefferson and Adams was also retold in a second-season episode of Comedy Central's Drunk History, with Jerry O'Connell portraying Jefferson and Joe Lo Truglio as Adams.
In Hamilton, a 2015 musical by Lin Manuel Miranda, the contest between Jefferson and Burr is recounted in "The Election of 1800." The song focuses on Alexander Hamilton's role in deciding the outcome of the 1801 contingent election. In the musical, John Adams's unpopularity means the real choice is between Jefferson and Burr, with Hamilton's "endorsement" tipping the scales in Jefferson's favor. Historians have criticized the musical for overstating Hamilton's importance to the outcome, as well as inflating the proportions of Jefferson's victory. It implies Hamilton's support for Jefferson over Burr was the catalyst for the Burr-Hamilton duel, when in fact the duel was provoked by Hamilton's statements about Burr in the 1804 New York gubernatorial election.[71]
The story of the 1801 contingent election between Burr and Jefferson is told in Gore Vidal's 1973 novel Burr.
See also[]
- First inauguration of Thomas Jefferson
- Bibliography of Thomas Jefferson
- 1800 and 1801 United States House of Representatives elections
- 1800 and 1801 United States Senate elections
- History of the United States (1789–1849)
- Stephen Simpson (writer) (editor of the Aurora, a Philadelphia newspaper Jefferson credited for his victory in 1800)
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b The complete returns for appear to have been lost. Partial returns from the 2nd district of Kentucky show 44 votes for an elector of unknown affiliation.
- ^ Eight votes were cast in Maryland for electors pledged to both John Adams and Thomas Jefferson; two votes were cast for electors of unknown affiliation.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Results from the Edenton district appear to have been lost. The district chose an elector who voted for Thomas Jefferson and Aaron Burr.
- ^ The returns appear to have been lost.
- ^ Eight votes were cast for electors pledged to both Jefferson and Adams; one vote was cast for an elector of unknown affiliation.
- ^ One vote was cast for an elector of unknown affiliation.
References[]
Primary references[]
- Annals of the Congress of the United States, Washington, D.C.: Gales and Seaton, 1834–1856, pp. 10:1028–1033
- "A Historical Analysis of the Electoral College". The Green Papers. Retrieved March 20, 2005.
Inline references[]
- ^ "National General Election VEP Turnout Rates, 1789-Present". United States Election Project. CQ Press.
- ^ "Thomas Jefferson: The Revolution of 1800". PBS. Retrieved April 23, 2012.
- ^ "A Revolution of 1800 After All: The Political Culture of the Earlier Early Republic and the Origins of American Democracy". Jeffrey L. Pasley University of Missouri-Columbia. Retrieved April 23, 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Ferling (2004)
- ^ Deskins, Donald Richard; Walton, Hanes; Puckett, Sherman (2010). Presidential Elections, 1789-2008: County, State, and National Mapping of Election Data. University of Michigan Press. pp. 33–34.
- ^ Lepore, Jill (September 9, 2007). "Party Time for a Young America". The New Yorker.
- ^ Lily, Rothman (2016). Everything you need to ace American history in one big fat notebook. Workman Publishing Co., Inc. ISBN 978-0-7611-6083-0.
- ^ Mintz, S. (2003). "Gilder Lehrman Document Number: GLC 581". Digital History. Archived from the original on October 6, 2006. Retrieved September 20, 2006.
- ^ Buel (1972)
- ^ Sisson, Dan, 1937- (September 15, 2014). The American revolution of 1800 : how Jefferson rescued democracy from tyranny and faction and what this means today. Hartmann, Thom, 1951- (40th anniversary ed.). San Francisco. ISBN 978-1-60994-986-0. OCLC 886106713.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ McCullough (2001)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Chernow (2004)
- ^ "The Election of 1800 - American History - Thomas Jefferson, John Adams". lehrmaninstitute.org.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives* 1789–Present". Office of the Historian, House of United States House of Representatives. Retrieved February 1, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bruce Ackerman and David Fontana, "How Jefferson Counted Himself In," The Atlantic, March 2004. See also: Bruce Ackerman and David Fontana, "Thomas Jefferson Counts Himself into the Presidency," (2004), 90 Virginia Law Review 551-643.
- ^ "A New Nation Votes". elections.lib.tufts.edu.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Connecticut 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Delaware 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Kentucky 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Massachusetts 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "New Hampshire 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "New Jersey 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "New York 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Pennsylvania 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Rhode Island 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "South Carolina 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Tennessee 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Vermont 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Virginia 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Kentucky 1800 Electoral College, District 1". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Kentucky 1800 Electoral College, District 2". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Kentucky 1800 Electoral College, District 3". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Kentucky 1800 Electoral College, District 4". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 1". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 2". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 3". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 4". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 5". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 6". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 7". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 8". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 9". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Maryland 1800 Electoral College, District 10". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Edenton District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Edgecombe District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Fayetteville District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Hilsborough District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Morgan District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, New Bern District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Northampton District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Raleigh District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Rockingham District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Salisbury District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Warren District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "North Carolina 1800 Electoral College, Wilmington District". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Tennessee 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Tennessee 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Lampi, Philip. "Tennessee 1800 Electoral College". A New Nation Votes. Tufts University. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- ^ Ferling 2004, pp. 175–196.
- ^ Van Bergen, Jennifer (Spring 2003). "Aaron Burr and the Electoral Tie of 1801:Strict Constitutional Construction" (PDF). The Cardozo Public Law, Policy & Ethics Journal. 1 (1): 91–130. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 22, 2018. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
- ^ Colvin, Nathan L.; Foley, Edward B. (2010). "The Twelfth Amendment: A Constitutional Ticking Time Bomb". University of Miami Law Review. 64 (2): 475–534. Retrieved July 21, 2018.
- ^ Roberts (2008)
- ^ Noel Campbell and Marcus Witcher, "Political entrepreneurship: Jefferson, Bayard, and the election of 1800." Journal of Entrepreneurship and Public Policy 4.3 (2015): 298-312.
- ^ "10 Annals of Cong. 1024–1033 (1801)". A Century of Lawmaking for a New Nation: U.S. Congressional Documents and Debates, 1774–1875. Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
- ^ "US President House Run-off (Contingent Election, 1801): Race Details". ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
- ^ "Election of a President". The national intelligencer and Washington advertiser. Washington, D.C. February 13, 1801. Retrieved August 28, 2019 – via Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers, Library of Congress.
- ^ "On Tuesday". The national intelligencer and Washington advertiser. Washington, D.C. February 18, 1801. Retrieved August 28, 2019 – via Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers, Library of Congress.
- ^ "The Electoral Count for the Presidential Election of 1789". The Papers of George Washington. Archived from the original on September 14, 2013. Retrieved May 4, 2005.
- ^ McCarthy, Bill (July 3, 2020). "PolitiFact: Fact-checking 'Hamilton' the musical". Tampa Bay Times. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
Bibliography[]
- Ben-Atar, Doron; Oberg, Barbara B., eds. (1999), Federalists Reconsidered, University of Virginia Press, ISBN 978-0-8139-1863-1
- Pasley, Jeffrey L.; et al., eds. (2004), Beyond the Founders: New Approaches to the Political History of the Early American Republic, University of North Carolina Press, ISBN 978-0-8078-5558-4
- Beard, Charles A. (1915), The Economic Origins of Jeffersonian Democracy, ISBN 978-1-146-80267-3
- Bowling, Kenneth R.; Kennon, Donald R. (2005), Establishing Congress: The Removal to Washington, D.C., and the Election of 1800, Ohio University Press, ISBN 978-0-8214-1619-8
- Buel, Richard (1972), Securing the Revolution: Ideology in American Politics, 1789–1815
- Chambers, William Nisbet (1963), Political Parties in a New Nation: The American Experience, 1776–1809
- Chernow, Ron (2005), Alexander Hamilton, Penguin, ISBN 978-0-14-303475-9
- (1965), The Making of the American Party System 1789 to 1809
- Der Linden, Frank Van. (2000) "The Turning Point: Jefferson's Battle for the Presidency." (Washington D.C.: Robert B. Luce).
- Dunn, Susan (2004), Jefferson's second revolution: The Election Crisis of 1800 and the Triumph of Republicanism, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN 978-0-618-13164-8
- Elkins, Stanley; McKitrick, Eric (1995), The Age of Federalism
- Ferling, John (2004). Adams vs. Jefferson: The Tumultuous Election of 1800. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195167719.
- Fischer, David Hackett (1965), The Revolution of American Conservatism: The Federalist Party in the Era of Jeffersonian Democracy
- Freeman, Joanne B. (2001), Affairs of Honor: National Politics in the New Republic
- Freeman, Joanne B. (1999), "The election of 1800: a study in the logic of political change", Yale Law Journal, 108 (8): 1959–1994, doi:10.2307/797378, JSTOR 797378
- Goodman, Paul (1967), "The First American Party System", in Chambers, William Nisbet; Burnham, Walter Dean (eds.), The American Party Systems: Stages of Political Development, pp. 56–89
- Hofstadter, Richard (1970), The Idea of a Party System
- Kennedy, Roger G. (2000), Burr, Hamilton, and Jefferson: A Study in Character, Oxford University Press
- McCullough, David (2001), John Adams
- Horn, James P. P.; Lewis, Jan Ellen; Onuf, Peter S. (2002), The Revolution of 1800: Democracy, Race, and the New Republic
- Miller, John C. (1959), Alexander Hamilton: Portrait in Paradox
- Roberts, Cokie (2008), Ladies of Liberty
- Schachner, Nathan (1961), Aaron Burr: A Biography
- Schlesinger, Arthur Meier, ed. (1986), History of American Presidential Elections, 1789-1984, 1, essay and primary sources on 1800.
- Sharp, James Roger. The Deadlocked Election of 1800: Jefferson, Burr, and the Union in the Balance (University Press of Kansas; 2010) 239 pages;
- Wills, Garry (2003), "Negro President": Jefferson and the Slave Power, Houghton Mifflin Co., pp. 47–89, ISBN 0-618-34398-9 ... also listed (in at least one source) as from Mariner Books (Boston) in 2004
- Weisberger, Bernard A. (2000) "America Afire: Jefferson, Adams, and the Revolutionary Election of 1800" (New York: William Morrow).
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to United States presidential election, 1800. |
- 1800 U.S. Presidential Election at VoteArchive.com Extant popular vote data and county-by-county maps for four states
- Vote Archive: County-level results for Maryland
- Vote Archive: County-level results for North Carolina
- Vote Archive: County-level results for Rhode Island
- Vote Archive: County-level results for Virginia
- Presidential Election of 1800: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Documentary Timeline 1787-1800 Lesson plans from NEH
- A New Nation Votes: American Election Returns 1787-1825
- Overview at Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections
- Booknotes interview with Bernard Weisberger on America Afire: Jefferson, Adams, and the First Contested Election, February 25, 2001.
- Booknotes interview with John Ferling on Adams vs. Jefferson: The Tumultuous Election of 1800, October 3, 2004.
- Election of 1800 in Counting the Votes Archived September 30, 2019, at the Wayback Machine
- 1800 United States presidential election
- Presidency of Thomas Jefferson
- Thomas Jefferson
- John Adams
- Aaron Burr






