1952 United States presidential election
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2021) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
531 members of the Electoral College 266 electoral votes needed to win | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 63.3%[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
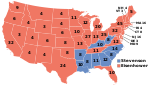
  Presidential election results map. Red denotes states won by Eisenhower/Nixon, blue denotes those won by Stevenson/Sparkman. Numbers indicate the number of electoral votes allotted to each state. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1952 United States presidential election was the 42nd quadrennial presidential election. It was held on Tuesday, November 4, 1952. Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower won a landslide victory over Democrat Adlai Stevenson, ending a string of Democratic Party wins that stretched back to 1932.
Stevenson emerged victorious on the third presidential ballot of the 1952 Democratic National Convention, defeating Kefauver, Senator Richard Russell Jr. of Georgia, and other candidates. The Republican nomination was primarily contested by Eisenhower, a general who was widely popular for his leadership in World War II, and conservative Senator Robert A. Taft of Ohio. With the support of Thomas E. Dewey and other party leaders, Eisenhower narrowly prevailed over Taft at the 1952 Republican National Convention with Richard Nixon, a young senator from California, as his running mate. In the first televised presidential campaign Eisenhower, in sharp contrast to Stevenson, was charismatic and very well known.[4]
Republicans attacked Truman's handling of the Korean War and the broader Cold War, and alleged that Soviet spies had infiltrated the U.S. government. Democrats faulted Eisenhower for failing to condemn Republican Senator Joe McCarthy and other reactionary Republicans who they alleged had engaged in reckless and unwarranted attacks, while Stevenson tried to separate himself from the unpopular Truman administration, instead campaigning on the popularity of the New Deal and stoking fears of another Great Depression under a Republican administration.
Eisenhower retained his enormous popularity from the war, as seen in his campaign slogan "I Like Ike". Eisenhower's popularity and Truman's unpopularity led to a Republican victory, and Eisenhower won 55.18% of the popular vote, carrying every state outside of the South, as well as Virginia, Tennessee, Florida, and Texas, states that had almost always voted for Democrats since the end of Reconstruction.
Republicans also won control of both houses of Congress.
Nominees[]
Republican Party[]

 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dwight D. Eisenhower | Richard Nixon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| President of Columbia University (1948–1953) Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) (1951–1952) |
U.S. Senator from California (1950–1953) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Senator
Robert A. Taft
from Ohio
Former Governor
Harold Stassen
of Minnesota
Governor
Earl Warren
of California
General of the Army Douglas MacArthur, from New York
The fight for the Republican nomination was between General Dwight D. Eisenhower, who became the candidate of the party's moderate eastern establishment; Senator Robert A. Taft from Ohio, the longtime leader of the Republican Party's conservative wing; Governor Earl Warren of California, who appealed to Western delegates and independent voters; and former Governor Harold Stassen of Minnesota, who still had a base of support in the Midwest.
The moderate Eastern Republicans were led by New York governor Thomas E. Dewey, the party's presidential nominee in 1944 and 1948. The moderates tended to be interventionists who felt that the country needed to fight the Cold War overseas and confront the Soviet Union in Eurasia. They were also willing to accept most aspects of the social welfare state created by the New Deal in the 1930s. The moderates were also concerned with ending the Republicans' losing streak in presidential elections; they felt that the popular Eisenhower had the best chance of beating the Democrats. For this reason, Dewey declined the notion of a third run for president despite his large amount of support within the party. The GOP had been out of power for 20 years, and the sentiment that a proper two-party system needed to be reestablished was strong. It was also felt that a Republican Party in control of the White House would have more incentive to rein in unpopular demagogues such as Wisconsin senator Joseph McCarthy.
The conservative Republicans, led by Taft, were based in the Midwest and parts of the South. The Midwest was a bastion of conservatism and isolationist sentiment. Dislike of Europeans, in particular Great Britain, was common, and there was a widespread feeling that the British manipulated American foreign policy and were eager to kowtow to the Soviet Union, although attitudes were beginning to change among the younger generation who had fought in World War II. Taft had unsuccessfully sought the Republican nomination in the 1940 and 1948 presidential elections, losing both times to moderate candidates from New York (Wilkie and Dewey). At the age of 63, Taft felt that this was his last chance to run for president, so his friends and supporters worked diligently on his behalf.
Warren, although highly popular in California, refused to campaign in the presidential primaries and thus limited his chances of winning the nomination. He did retain the support of the California delegation, and his supporters hoped that, in the event of an Eisenhower–Taft deadlock, Warren might emerge as a compromise candidate.
After being persuaded to run, Eisenhower scored a major victory in the New Hampshire primary, when his supporters wrote his name onto the ballot, giving him an upset victory over Taft. However, from there until the Republican National Convention, the primaries were divided fairly evenly between the two, and by the time the convention opened, the race for the nomination was still too close to call. Taft won the Nebraska, Wisconsin, Illinois and South Dakota primaries, while Eisenhower won in New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts and Oregon. Stassen and Warren only won their home states of Minnesota and California respectively, which effectively ended their chances of earning the nomination. General Douglas MacArthur also won the support of ten delegates from various states (mostly Oregon), but had made it clear from early in the race that he had no interest in being nominated.
Republican Convention[]
When the 1952 Republican National Convention opened in Chicago, most political experts rated Taft and Eisenhower as neck-and-neck in the delegate vote totals. Eisenhower's managers, led by Dewey and Massachusetts senator Henry Cabot Lodge Jr., accused Taft of "stealing" delegate votes in Southern states such as Texas and Georgia. They claimed that Taft's leaders in these states had unfairly denied delegate spots to Eisenhower supporters and put Taft delegates in their place. Lodge and Dewey proposed to evict the pro-Taft delegates in these states and replace them with pro-Eisenhower delegates; they called this proposal "Fair Play". Although Taft and his supporters angrily denied this charge, the convention voted to support Fair Play 658 to 548, and Taft lost many Southern delegates. Eisenhower's chances were boosted when several uncommitted state delegations, such as Michigan and Pennsylvania, decided to support him, and also when Stassen released his delegates and asked them to support Eisenhower. The removal of many pro-Taft Southern delegates and the support of the uncommitted states decided the nomination in Eisenhower's favor.
However, the convention was among the most bitter and emotional in American history. When Senator Everett Dirksen from Illinois, a Taft supporter, pointed at Dewey on the convention floor during a speech and accused him of leading the Republicans "down the road to defeat," mixed boos and cheers rang out from the delegates, and there were even fistfights between some Taft and Eisenhower delegates.
In the end, Eisenhower narrowly defeated Taft on the first ballot. To heal the wounds caused by the battle, he visited Taft's hotel suite and met with him. Taft issued a brief statement congratulating Eisenhower on his victory, but he was bitter about the accusation that he had stolen delegates and he withheld his active support for Eisenhower for several weeks after the convention. In September 1952, Taft and Eisenhower met again at Morningside Heights in New York City, where Taft promised to actively support Eisenhower in exchange for the fulfillment of a number of requests. These included a demand that Eisenhower would offer Taft's followers a fair share of patronage positions if he went on to win the election and that Eisenhower would agree to balance the federal budget and "fight creeping domestic socialism in every field." Eisenhower agreed to the terms, and Taft campaigned assiduously for the Republican ticket.[5] In fact, Eisenhower and Taft agreed on most domestic issues; their disagreements were primarily on foreign policy.[6]
Though there were initial suggestions that Warren could earn the party's vice-presidential slot for the second successive election if he withdrew and endorsed Eisenhower, he ultimately chose not to do so. Eisenhower wished to award the VP nod to Stassen, who had endorsed Eisenhower and held generally similar political positions. However, the party bosses wanted to find a running mate who could mollify Taft's supporters, as the schism between the moderate and conservative wings was so severe that it was feared that the conservatives may run Taft as a third-party candidate.
Eisenhower had apparently given little thought to choosing his running mate. When asked, he replied that he assumed the convention would pick someone. The spot ultimately fell to the young California senator Richard Nixon, who was viewed as a centrist. Nixon was known as an aggressive campaigner and a fierce anti-communist, but as one who shied away from some of the more extreme ideas of the party's right wing, including isolationism and dismantling the New Deal. Most historians[who?] now believe that Eisenhower's nomination was the result his perceived electability against the Democrats; most of the delegates were conservatives who would probably have supported Taft if they felt that he could have won the general election.
Despite not earning the presidential or vice-presidential nomination, Warren would subsequently be appointed as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court in October 1953, while Stassen would hold various positions within Eisenhower's administration.
The balloting at the Republican convention went as follows:[7]
| Presidential Balloting, RNC 1952 | ||
| Ballot | 1st Before Shifts | 1st After Shifts |
|---|---|---|
| Dwight D. Eisenhower | 595 | 845 |
| Robert A. Taft | 500 | 280 |
| Earl Warren | 81 | 77 |
| Harold Stassen | 20 | 0 |
| Douglas MacArthur | 10 | 4 |
Democratic Party[]
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adlai Stevenson | John Sparkman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| for President | for Vice President | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31st Governor of Illinois (1949–1953) |
U.S. Senator from Alabama (1946–1979) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Campaign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Vice President
Alben W. Barkley
Senator Hubert Humphrey from Minnesota

Senator Estes Kefauver from Tennessee

Senator Robert S. Kerr from Oklahoma

Senator Richard Russell, Jr. from Georgia

President Harry S. Truman from Missouri
The expected candidate for the Democratic nomination was incumbent President Harry S. Truman. Since the newly passed 22nd Amendment did not apply to whoever was president at the time of its passage, he was eligible to run again. But Truman entered 1952 with his popularity plummeting, according to polls. The bloody and indecisive Korean War was dragging into its third year, Senator Joseph McCarthy's anti-Communist crusade was stirring public fears of an encroaching "Red Menace", and the disclosure of widespread corruption among federal employees (including some high-level members of Truman's administration) left Truman at a low political ebb. Polls showed that he had a 66% disapproval rating, a record only matched decades later by Richard Nixon and surpassed by George W. Bush.[8]

Truman's main opponent was populist Tennessee Senator Estes Kefauver, who had chaired a nationally televised investigation of organized crime in 1951 and was known as a crusader against crime and corruption. The Gallup poll of February 15 showed Truman's weakness: nationally Truman was the choice of only 36% of Democrats, compared with 21% for Kefauver. Among independent voters, however, Truman had only 18% while Kefauver led with 36%. In the New Hampshire primary, Kefauver upset Truman, winning 19,800 votes to Truman's 15,927 and capturing all eight delegates. Kefauver graciously said that he did not consider his victory "a repudiation of Administration policies, but a desire...for new ideas and personalities." Stung by this setback, Truman announced March 29 that he would not seek re-election (however, Truman insisted in his memoirs that he had decided not to run for reelection well before his defeat by Kefauver).
With Truman's withdrawal, Kefauver became the front-runner for the nomination, and he won most of the primaries. Other primary winners were Senator Hubert Humphrey, who won his home state of Minnesota, while Senator Richard Russell Jr. from Georgia won the Florida primary and U.S. diplomat W. Averell Harriman won West Virginia. However, most states still chose their delegates to the Democratic Convention via state conventions, which meant that the party bosses – especially the mayors and governors of large Northern and Midwestern states and cities – were able to choose the Democratic nominee. These bosses (including Truman) strongly disliked Kefauver; his investigations of organized crime had revealed connections between Mafia figures and many of the big-city Democratic political organizations.[9] The party bosses thus viewed Kefauver as a maverick who could not be trusted, and they refused to support him for the nomination.[9]
Instead, with Truman taking the initiative, they began to search for other, more acceptable, candidates. However, most of the other candidates had a major weakness. Richard Russell had much Southern support, but his support of racial segregation and opposition to civil rights for Southern blacks led many liberal Northern and Midwestern delegates to reject him.[9] Truman favored W. Averell Harriman of New York, but he had never held an elective office and was inexperienced in politics. Truman next turned to his vice-president, Alben W. Barkley, but at 74 he was rejected as being too old by labor union leaders. Other minor or favorite son candidates included Oklahoma Senator Robert S. Kerr, Governor Paul A. Dever of Massachusetts, Senator Hubert Humphrey from Minnesota, and Senator J. William Fulbright from Arkansas.
One candidate soon emerged who seemingly had few political weaknesses: Governor Adlai Stevenson of Illinois. The grandson of former vice-president Adlai E. Stevenson, he came from a distinguished family in Illinois and was well known as a gifted orator, intellectual, and political moderate. In the spring of 1952, Truman tried to convince Stevenson to take the presidential nomination, but Stevenson refused, stating that he wanted to run for re-election as Governor of Illinois. Yet Stevenson never completely took himself out of the race, and as the convention approached, many party bosses, as well as normally apolitical citizens, hoped that he could be "drafted" to run.
Democratic Convention[]
The 1952 Democratic National Convention was held in Chicago in the same coliseum the Republicans had gathered in several weeks earlier. Since the convention was being held in his home state, Governor Stevenson – who still proclaimed that he was not a presidential candidate – was asked to give the welcoming address to the delegates. He proceeded to give a witty and stirring address that led his supporters to begin a renewed round of efforts to nominate him, despite his protests. After meeting with Jacob Arvey, the "boss" of the Illinois delegation, Stevenson finally agreed to enter his name as a candidate for the nomination. The party bosses from other large Northern and Midwestern states quickly joined in support. Kefauver led on the first ballot, but had far fewer votes than necessary to win. Stevenson gradually gained strength until he was nominated on the third ballot.
After the delegates nominated Stevenson, the convention then turned to selecting a vice-presidential nominee. After narrowing it down to Senators John Sparkman, and A. S. Mike Monroney, President Truman and a small group of political insiders chose Sparkman, a conservative and segregationist from Alabama, for the nomination. The convention largely complied and nominated Sparkman as Stevenson's running mate. He was chosen because of his Southern identity and conservative record; party leaders hoped this factor would create a balanced ticket.
Sparkman remained in the Senate until his retirement in 1978.
General election[]
Campaign issues[]
The Eisenhower campaign was one of the first presidential campaigns to make a major, concerted effort to win the female vote. Many of his radio and television commercials discussed topics such as education, inflation, ending the war in Korea, and other issues that were thought to appeal to women. The Eisenhower campaign made extensive use of female campaign workers. These workers made phone calls to likely Eisenhower voters, distributed "Ike" buttons and leaflets, and threw parties to build support for the GOP ticket in their neighborhoods. On election day, Eisenhower won a solid majority of the female vote.[10]
Eisenhower campaigned by attacking "Korea, Communism, and Corruption"—that is, what the Republicans regarded as the failures of the outgoing Truman administration to deal with these issues.[11] The Eisenhower campaign accused the administration of "neglecting Latin America" and thus "leading them into the arms of wily Communist agents waiting to exploit local misery and capitalize on any opening to communize the Americas."[12] Charges that Soviet spies had infiltrated the government plagued the Truman Administration and also became a "major campaign issue" for Eisenhower.[13] The Republicans blamed the Democrats for the military's failure to be fully prepared to fight in Korea; they accused the Democrats of harboring communist spies within the federal government; and they blasted the Truman Administration for the numbers of officials who had been accused of various crimes.
Stevenson hoped to exploit the rift between the conservative Taft Republicans and the moderate Eisenhower Republicans.[14] In a speech in Baltimore, Stevenson said, "The GOP elephant has two heads nowadays, and I can't tell from day to day who's driving the poor beast, Senator Taft or the General. I doubt that America will entrust its future, its hopes, to the master of a house divided against itself."[14] Stevenson, Truman, and other Democrats campaigning that fall also criticized Senator Joseph McCarthy and other right-wing Republicans for what they believed were reckless and unwarranted attacks and congressional investigations into leading government officials and public servants.[15] In a Salt Lake City speech Stevenson stated that right-wing Republicans were "quick with accusations, with defamatory hints and whispering campaigns when they see a chance to scare or silence those with whom they disagree. Rudely, carelessly, they invade the field of thought, of conscience, which belongs to God, and not to Senators...McCarthy and men like him can say almost anything, and if my opponent's conscience permits, he can try to help all of them get reelected."[15] Stevenson said that right-wing attacks on government officials such as General George Marshall, who had served Truman as Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense, reflected a "middle of the gutter approach" to politics.[16] President Truman repeatedly criticized Senator McCarthy's character and temperament, and called on Eisenhower to repudiate him.[17] Stevenson ridiculed right-wing Republicans "who hunt Communists in the Bureau of Wildlife and Fisheries while hesitating to aid the gallant men and women who are resisting the real thing in the front lines of Europe and Asia...They are finally the men who seemingly believe that we can confound the Kremlin by frightening ourselves to death."[18] In return, Senator McCarthy often jokingly confused the names Adlai and Alger, the first name of convicted Soviet spy Alger Hiss, by stating "Alger, I mean Adlai..." in his speeches.[19] McCarthy, in response to Stevenson's criticisms, also stated during the campaign that he would like to get on the Stevenson campaign trail "with a club and make a good and loyal American" out of Stevenson.[16]

Neither Stevenson nor Sparkman had been a part of the Truman administration and they largely ignored its record, preferring to hark back to the Roosevelt's New Deal achievements while warning of against a repetition of the Hoover depression. Historian Herbert Parmet says that although Stevenson:
- tried to separate his campaign from Truman's record, his efforts failed to dispel the widespread recognition that, for a divided America, torn by paranoia and unable to understand what had disrupted the anticipated tranquility of the postwar world, the time for change had really arrived. Neither Stevenson nor anyone else could have dissuaded the electorate from its desire to repudiate 'Trumanism.'[20]
Campaign[]

Many Democrats were particularly upset when Eisenhower, on a scheduled campaign swing through Wisconsin, decided not to give a speech he had written criticizing McCarthy's methods, and then allowed himself to be photographed shaking hands with McCarthy as if he supported him. Truman, formerly friends with Eisenhower, never forgot what he saw as a betrayal; he had previously thought Eisenhower would make a good president, but said, "he has betrayed almost everything I thought he stood for."[21]
Eisenhower retained his enormous personal popularity from his leading role in World War II, and huge crowds turned out to see him around the nation. His campaign slogan, "I Like Ike," was one of the most popular in American history. Stevenson attracted the support of the young, emergent postwar intellectual class; however, Eisenhower was seen as more appealing to Main Street. Stevenson was ridiculed in some quarters as too effeminate to be president, the staunchly conservative New York Daily News called him "Adelaide" Stevenson, even though he had a reputation as a ladies' man (having been divorced in 1949 and remaining single throughout 1952).
Nixon scandal and "Checkers speech"[]
A notable event of the 1952 campaign concerned a scandal that emerged when Richard Nixon, Eisenhower's running mate, was accused by several newspapers of receiving $18,000 in undeclared "gifts" from wealthy donors. In reality, contributions were by design only from early supporters and limited to $1,000, with full accountability. Nixon, who had been accusing the Democrats of hiding crooks, suddenly found himself on the defensive. Eisenhower and his aides considered dropping Nixon from the ticket and picking another running mate.


Eisenhower, who barely knew Nixon, waffled and refused to comment on the incident. Nixon saved his political career, however, with a dramatic half-hour speech, the "Checkers speech," on live television. In this speech, Nixon denied the charges against him, gave a detailed account of his modest financial assets, and offered a glowing assessment of Eisenhower's candidacy. The highlight of the speech came when Nixon stated that a supporter had given his daughters a gift – a dog named "Checkers" – and that he would not return it, because his daughters loved it. The "Checkers speech" led hundreds of thousands of citizens nationwide to wire the Republican National Committee urging the Republican Party to keep Nixon on the ticket, and Eisenhower stayed with him.
Despite the red-baiting of the right wing of the GOP, the campaign on the whole was conducted with a considerable degree of dignity and Stevenson was seen as reinvigorating a Democratic Party that had become exhausted after 20 years in power and refreshing its appeal with younger voters. He accused Eisenhower of silently tolerating Joseph McCarthy's excesses. Stevenson went before the American Legion, a bastion of hardline conservatism, and boldly declared that there was nothing patriotic or American about what Joseph McCarthy was doing.
Even with the dignified nature of the campaign, the dislike between the two candidates was visible; Stevenson criticized Eisenhower's non-condemnation of McCarthy and use of television spots, and Eisenhower, while he had initially respected Stevenson, in time came to view him as simply another career politician, something he strongly disliked.
Television[]
The 1952 election campaign was the first one to make use of the new medium of television, in part thanks to the efforts of Rosser Reeves, the head of the , a leading advertising firm. Reeves had initially proposed a series of radio spots to Thomas Dewey in the 1948 campaign, but Dewey considered them undignified, and Reeves maintained that Dewey might have won the election had he been slightly more open-minded.
Studying Douglas MacArthur's keynote speech at the Republican convention in July, Reeves believed that the general's words were "powerful", but "unfocused" and "all over the map". Eisenhower's public speeches were even worse, he was unable to make his point to the voting public in a clear, intelligible manner. Reeves felt that Eisenhower needed to condense his message down to a few simple, easily digestible slogans.
Eisenhower at first also fared poorly on television and had a difficult time appearing relaxed and at ease on camera. The TV lighting was not flattering and it made him look old and unattractive, in particular his forehead tended to glisten under the lights. Eisenhower became upset when CBS correspondent Dave Schoenbrun pointed this out and suggested he try altering his poses to make his forehead less noticeable and also apply makeup so it would not shine from the lighting. Eventually, he gave in and agreed to these modifications. Reeves also wanted Eisenhower to not wear his eyeglasses on camera in order to look younger, but he could not read the prompter board without them, so Reeves devised a large, handwritten signboard.
Reeves's TV work, although pioneering, was the subject of considerable criticism on the grounds that he was attempting to sell a presidential candidate to the public in the same manner that one might sell a car or a brand of toothpaste. (Liberal journalist Marya Mannes mocked the approach with this ditty: "Eisenhower hits the spot/One full general, that's a lot/Feeling sluggish, feeling sick?/Take a dose of Ike and Dick!/Philip Morris, Lucky Strike/Alka Seltzer, I like Ike!")[22] For his part, Stevenson would have nothing to do with TV at all and condemned Eisenhower's use of the medium, calling it "selling the presidency like cereal". He himself made a point of the fact that he did not watch or even own a television, nor did many members of his inner circle.
Both campaigns made use of television ads. A notable ad for Eisenhower was an issue-free, feel-good animated cartoon with a soundtrack song by Irving Berlin called "I Like Ike." For the first time, a presidential candidate's personal medical history was released publicly, as were partial versions of his financial histories, because of the issues raised in Nixon's speech.[23] Near the end of the campaign, Eisenhower, in a major speech, announced that if he won the election he would go to Korea to see if he could end the war. His great military prestige, combined with the public's weariness with the conflict, gave Eisenhower the final boost he needed to win.
Throughout the entire campaign, Eisenhower led in all opinion polls, and by wide margins in most of them.
Citizens for Eisenhower[]
To circumvent the local Republican Party apparatus mostly controlled by Taft supporters, the Eisenhower forces created a nationwide network of grass-roots clubs, "Citizens for Eisenhower." Independents and Democrats were welcome, as the group specialized in canvassing neighborhoods and holding small group meetings. Citizens for Eisenhower hoped to revitalize the GOP by expanding its activist ranks and by supporting moderate and internationalist policies. It did not endorse candidates other than Eisenhower. However Eisenhower paid it little attention after he won, and it failed to maintain its impressive starting momentum. Instead it energized the conservative Republicans, leading finally to the Barry Goldwater campaign of 1964. Long-time Republican activists viewed the newcomers with suspicion and hostility. More significantly, activism in support of Eisenhower did not translate into enthusiasm for the party cause.[24]
Results[]
On election day, Eisenhower won a decisive victory, winning over 55% of the popular vote and carrying thirty-nine of the forty-eight states. Stevenson did not win a single state north of the Mason–Dixon line or west of Arkansas, whilst Eisenhower took three Southern states that the Republicans had won only once since Reconstruction: Virginia, Florida, and Texas. Despite the Republican win in Florida, this remains the last time to date a Democrat has won Collier County before southwestern Florida was turned into a growing Sun Belt Republican stronghold, and is also the last time a Democrat has won Aiken County, South Carolina, before the "Solid South" would collapse in the wake of the Civil Rights Movement.[25] 1952 is also, however, the last time a Republican won Yolo County, California, or Native American Rolette County, North Dakota, and the last until Donald Trump in 2016 that the Republicans won Pacific County, Washington, or Swift County, Minnesota.[25] This was the last time the Republicans won Missouri until 1968. It is also the last time that a Republican won the election without Kentucky. Stevenson's 700-vote win was the smallest percentage margin in any state since Woodrow Wilson won New Hampshire by fifty-six votes in 1916.
This election was the first in which a computer (the UNIVAC I) was used to predict the results; it came within 3.5% of Eisenhower's popular vote tally, and four votes of his electoral vote total.[26]
| Presidential candidate | Party | Home state | Popular vote | Electoral vote |
Running mate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | Percentage | Vice-presidential candidate | Home state | Electoral vote | ||||
| Dwight David Eisenhower | Republican | New York | 34,075,529 | 55.18% | 442 | Richard Milhous Nixon | California | 442 |
| Adlai Ewing Stevenson II | Democratic | Illinois | 27,375,090 | 44.33% | 89 | John Jackson Sparkman | Alabama | 89 |
| Vincent Hallinan | Progressive | California | 140,746 | 0.23% | 0 | Charlotta Amanda Spears Bass | New York | 0 |
| Stuart Hamblen | Prohibition | Texas | 73,412 | 0.12% | 0 | Enoch Arden Holtwick | Illinois | 0 |
| Eric Hass | Socialist Labor | New York | 30,406 | 0.05% | 0 | Stephen Emery | New York | 0 |
| Darlington Hoopes | Socialist | Pennsylvania | 20,203 | 0.03% | 0 | Samuel Herman Friedman | New York | 0 |
| Douglas MacArthur | Constitution | Arkansas | 17,205 | 0.03% | 0 | Harry Flood Byrd Sr. | Virginia | 0 |
| Farrell Dobbs | Socialist Workers | Minnesota | 10,312 | 0.02% | 0 | Myra Tanner Weiss | California | 0 |
| Other | 9,039 | 0.02% | — | Other | — | |||
| Total | 61,751,942 | 100% | 531 | 531 | ||||
| Needed to win | 266 | 266 | ||||||
Source (Popular Vote): Leip, David. "1952 Presidential Election Results". Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved September 16, 2012.Source (Electoral Vote): "Electoral College Box Scores 1789–1996". National Archives and Records Administration. Retrieved August 1, 2005.


Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote
Results by state[]
| States/districts won by Stevenson/Sparkman |
| States/districts won by Eisenhower/Nixon |
| Dwight D. Eisenhower Republican |
Adlai Stevenson Democratic |
Vincent Hallinan Progressive |
Stuart Hamblen Prohibition |
Eric Hass Socialist Labor |
Margin | State Total | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | electoral votes |
# | % | # | |
| Alabama | 11 | 149,231 | 35.02 | – | 275,075 | 64.55 | 11 | – | – | – | 1,814 | 0.43 | – | – | – | – | -125,844 | -29.53 | 426,120 | AL |
| Arizona | 4 | 152,042 | 58.35 | 4 | 108,528 | 41.65 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 43,514 | 16.70 | 260,570 | AZ |
| Arkansas | 8 | 177,155 | 43.76 | – | 226,300 | 55.90 | 8 | – | – | – | 886 | 0.22 | – | 1 | 0.00 | – | -49,145 | -12.14 | 404,800 | AR |
| California | 32 | 3,035,587 | 56.83 | 32 | 2,257,646 | 42.27 | – | 24,692 | 0.46 | – | 16,117 | 0.30 | – | 273 | 0.01 | – | 777,941 | 14.56 | 5,341,603 | CA |
| Colorado | 6 | 379,782 | 60.27 | 6 | 245,504 | 38.96 | – | 1,919 | 0.30 | – | – | – | – | 352 | 0.06 | – | 134,278 | 21.31 | 630,103 | CO |
| Connecticut | 8 | 611,012 | 55.70 | 8 | 481,649 | 43.91 | – | 1,466 | 0.13 | – | – | – | – | 535 | 0.05 | – | 129,363 | 11.79 | 1,096,911 | CT |
| Delaware | 3 | 90,059 | 51.75 | 3 | 83,315 | 47.88 | – | 155 | 0.09 | – | 234 | 0.13 | – | 242 | 0.14 | – | 6,744 | 3.88 | 174,025 | DE |
| Florida | 10 | 544,036 | 54.99 | 10 | 444,950 | 44.97 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 99,086 | 10.02 | 989,337 | FL |
| Georgia | 12 | 198,979 | 30.34 | – | 456,823 | 69.66 | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -257,844 | -39.32 | 655,803 | GA |
| Idaho | 4 | 180,707 | 65.42 | 4 | 95,081 | 34.42 | – | 443 | 0.16 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 85,626 | 31.00 | 276,231 | ID |
| Illinois | 27 | 2,457,327 | 54.84 | 27 | 2,013,920 | 44.94 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 9,363 | 0.21 | – | 443,407 | 9.90 | 4,481,058 | IL |
| Indiana | 13 | 1,136,259 | 58.11 | 13 | 801,530 | 40.99 | – | 1,222 | 0.06 | – | 15,335 | 0.78 | – | 979 | 0.05 | – | 334,729 | 17.12 | 1,955,325 | IN |
| Iowa | 10 | 808,906 | 63.75 | 10 | 451,513 | 35.59 | – | 5,085 | 0.40 | – | 2,882 | 0.23 | – | 139 | 0.01 | – | 357,393 | 28.17 | 1,268,773 | IA |
| Kansas | 8 | 616,302 | 68.77 | 8 | 273,296 | 30.50 | – | – | – | – | 6,038 | 0.67 | – | – | – | – | 343,006 | 38.27 | 896,166 | KS |
| Kentucky | 10 | 495,029 | 49.84 | – | 495,729 | 49.91 | 10 | 336 | 0.03 | – | 1,161 | 0.12 | – | 893 | 0.09 | – | -700 | -0.07 | 993,148 | KY |
| Louisiana | 10 | 306,925 | 47.08 | – | 345,027 | 52.92 | 10 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -38,102 | -5.84 | 651,952 | LA |
| Maine | 5 | 232,353 | 66.05 | 5 | 118,806 | 33.77 | – | 332 | 0.09 | – | – | – | – | 156 | 0.04 | – | 113,547 | 32.28 | 351,786 | ME |
| Maryland | 9 | 499,424 | 55.36 | 9 | 395,337 | 43.83 | – | 7,313 | 0.81 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 104,087 | 11.54 | 902,074 | MD |
| Massachusetts | 16 | 1,292,325 | 54.22 | 16 | 1,083,525 | 45.46 | – | 4,636 | 0.19 | – | 886 | 0.04 | – | 1,957 | 0.08 | – | 208,800 | 8.76 | 2,383,398 | MA |
| Michigan | 20 | 1,551,529 | 55.44 | 20 | 1,230,657 | 43.97 | – | 3,922 | 0.14 | – | 10,331 | 0.37 | – | 1,495 | 0.05 | – | 320,872 | 11.47 | 2,798,592 | MI |
| Minnesota | 11 | 763,211 | 55.33 | 11 | 608,458 | 44.11 | – | 2,666 | 0.19 | – | 2,147 | 0.16 | – | 2,383 | 0.17 | – | 154,753 | 11.22 | 1,379,483 | MN |
| Mississippi | 8 | 112,966 | 39.56 | – | 172,566 | 60.44 | 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -59,600 | -20.87 | 285,532 | MS |
| Missouri | 13 | 959,429 | 50.71 | 13 | 929,830 | 49.14 | – | 987 | 0.05 | – | 885 | 0.05 | – | 169 | 0.01 | – | 29,599 | 1.56 | 1,892,062 | MO |
| Montana | 4 | 157,394 | 59.39 | 4 | 106,213 | 40.07 | – | 723 | 0.27 | – | 548 | 0.21 | – | – | – | – | 51,181 | 19.31 | 265,037 | MT |
| Nebraska | 6 | 421,603 | 69.15 | 6 | 188,057 | 30.85 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 233,546 | 38.31 | 609,660 | NE |
| Nevada | 3 | 50,502 | 61.45 | 3 | 31,688 | 38.55 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 18,814 | 22.89 | 82,190 | NV |
| New Hampshire | 4 | 166,287 | 60.92 | 4 | 106,663 | 39.08 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 59,624 | 21.84 | 272,950 | NH |
| New Jersey | 16 | 1,374,613 | 56.81 | 16 | 1,015,902 | 41.99 | – | 5,589 | 0.23 | – | 989 | 0.04 | – | 5,815 | 0.24 | – | 358,711 | 14.83 | 2,419,554 | NJ |
| New Mexico | 4 | 132,170 | 55.39 | 4 | 105,661 | 44.28 | – | 225 | 0.09 | – | 297 | 0.12 | – | 35 | 0.01 | – | 26,509 | 11.11 | 238,608 | NM |
| New York | 45 | 3,952,815 | 55.45 | 45 | 3,104,601 | 43.55 | – | 64,211 | 0.90 | – | – | – | – | 1,560 | 0.02 | – | 848,214 | 11.90 | 7,128,241 | NY |
| North Carolina | 14 | 558,107 | 46.09 | – | 652,803 | 53.91 | 14 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -94,696 | -7.82 | 1,210,910 | NC |
| North Dakota | 4 | 191,712 | 70.97 | 4 | 76,694 | 28.39 | – | 344 | 0.13 | – | 302 | 0.11 | – | – | – | – | 115,018 | 42.58 | 270,127 | ND |
| Ohio | 25 | 2,100,391 | 56.76 | 25 | 1,600,367 | 43.24 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 500,024 | 13.51 | 3,700,758 | OH |
| Oklahoma | 8 | 518,045 | 54.59 | 8 | 430,939 | 45.41 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 87,106 | 9.18 | 948,984 | OK |
| Oregon | 6 | 420,815 | 60.54 | 6 | 270,579 | 38.93 | – | 3,665 | 0.53 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 150,236 | 21.61 | 695,059 | OR |
| Pennsylvania | 32 | 2,415,789 | 52.74 | 32 | 2,146,269 | 46.85 | – | 4,222 | 0.09 | – | 8,951 | 0.20 | – | 1,377 | 0.03 | – | 269,520 | 5.88 | 4,580,969 | PA |
| Rhode Island | 4 | 210,935 | 50.89 | 4 | 203,293 | 49.05 | – | 187 | 0.05 | – | – | – | – | 83 | 0.02 | – | 7,642 | 1.84 | 414,498 | RI |
| South Carolina | 8 | 168,082 | 49.28 | – | 173,004 | 50.72 | 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -4,922 | -1.44 | 341,086 | SC |
| South Dakota | 4 | 203,857 | 69.27 | 4 | 90,426 | 30.73 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 113,431 | 38.54 | 294,283 | SD |
| Tennessee | 11 | 446,147 | 49.99 | 11 | 443,710 | 49.71 | – | 885 | 0.10 | – | 1,432 | 0.16 | – | – | – | – | 2,437 | 0.27 | 892,553 | TN |
| Texas | 24 | 1,102,878 | 53.13 | 24 | 969,228 | 46.69 | – | 294 | 0.01 | – | 1,983 | 0.10 | – | – | – | – | 133,650 | 6.44 | 2,075,946 | TX |
| Utah | 4 | 194,190 | 58.93 | 4 | 135,364 | 41.07 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 58,826 | 17.85 | 329,554 | UT |
| Vermont | 3 | 109,717 | 71.45 | 3 | 43,355 | 28.23 | – | 282 | 0.18 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 66,362 | 43.22 | 153,557 | VT |
| Virginia | 12 | 349,037 | 56.32 | 12 | 268,677 | 43.36 | – | 311 | 0.05 | – | – | – | – | 1,160 | 0.19 | – | 80,360 | 12.97 | 619,689 | VA |
| Washington | 9 | 599,107 | 54.33 | 9 | 492,845 | 44.69 | – | 2,460 | 0.22 | – | – | – | – | 633 | 0.06 | – | 106,262 | 9.64 | 1,102,708 | WA |
| West Virginia | 8 | 419,970 | 48.08 | – | 453,578 | 51.92 | 8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | -33,608 | -3.85 | 873,548 | WV |
| Wisconsin | 12 | 979,744 | 60.95 | 12 | 622,175 | 38.71 | – | 2,174 | 0.14 | – | – | – | – | 770 | 0.05 | – | 357,569 | 22.25 | 1,607,370 | WI |
| Wyoming | 3 | 81,047 | 62.71 | 3 | 47,934 | 37.09 | – | – | – | – | 194 | 0.15 | – | 36 | 0.03 | – | 33,113 | 25.62 | 129,251 | WY |
| TOTALS: | 531 | 34,075,529 | 55.18 | 442 | 27,375,090 | 44.33 | 89 | 140,746 | 0.23 | – | 73,412 | 0.12 | – | 30,406 | 0.05 | – | 6,700,439 | 10.85 | 61,751,942 | US |
Close states[]
Election results in these states were within one percentage point (21 electoral votes):
- Kentucky, 0.07% (700 votes)
- Tennessee, 0.27% (2,437 votes)
Election results in these states were within five percentage points (36 electoral votes):
- South Carolina, 1.44% (4,922 votes)
- Missouri, 1.56% (29,599 votes)
- Rhode Island, 1.84% (7,642 votes)
- West Virginia, 3.85% (33,608 votes)
- Delaware, 3.88% (6,744 votes)
Election results in these states were between five and ten percentage points (140 electoral votes):
- Louisiana, 5.84% (38,102 votes)
- Pennsylvania, 5.88% (269,520 votes)
- Texas, 6.44% (133,650 votes)
- North Carolina, 7.82% (94,696 votes)
- Massachusetts, 8.76% (208,800 votes)
- Oklahoma, 9.18% (87,106 votes)
- Washington, 9.64% (106,262 votes)
- Illinois, 9.90% (443,407 votes)
Tipping point state:
- Michigan, 11.47% (320,872 votes)
Statistics[]
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Republican)
- Plaquemines Parish, Louisiana 92.97%
- Gillespie County, Texas 92.29%
- McIntosh County, North Dakota 90.89%
- Campbell County, South Dakota 90.14%
- Kenedy County, Texas 88.52%
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Democratic)
- Greene County, North Carolina 94.12%
- Hart County, Georgia 94.08%
- Treutlen County, Georgia 93.34%
- Martin County, North Carolina 92.98%
- Walton County, Georgia 91.89%
See also[]
- 1952 United States House of Representatives elections
- 1952 United States Senate elections
- History of the United States (1945–1964)
- First inauguration of Dwight D. Eisenhower
References[]
- ^ "Voter Turnout in Presidential Elections". The American Presidency Project. UC Santa Barbara.
- ^ Sabato, Larry; Ernst, Howard (2006). "Presidential Election 1952". Encyclopedia of American Political Parties and Elections. Facts on File. p. 354. ISBN 9781438109947. Retrieved November 16, 2016.
Eisenhower, born in Texas, considered a resident of New York, and headquartered at the time in Paris, finally decided to run for the Republican nomination...
- ^ "The Presidents". uselectionatlas.org. David Leip. Retrieved January 3, 2009.
- ^ James C. Davies, "Charisma in the 1952 Campaign." American Political Science Review 48#4 (1954): 1083-102. online.
- ^ (Patterson, pp. 575-578)
- ^ (Patterson, pp. 591-592)
- ^ (Richard C. Bain and Judith H. Parris, Convention Decisions and Voting Records, pp. 280-286)
- ^ Page, Susan (April 22, 2008). "Disapproval of Bush breaks record". USA Today. Retrieved April 23, 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c (McKeever, p. 186)
- ^ "1952: The Election of a Military Hero". The Press and the Presidency. Kennesaw State University, Department of Political Science & International Affairs. August 31, 2001. Archived from the original on April 20, 2009. Retrieved November 20, 2008.
- ^ Robert North Roberts; Scott John Hammond; Valerie A. Sulfaro (2012). Presidential Campaigns, Slogans, Issues, and Platforms. ABC-CLIO. p. 255. ISBN 9780313380921.
- ^ Smith, Peter H. (2007) [1996]. Talons of the Eagle: Dynamics of U.S. – Latin American Relations (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press, USA. p. 392.
- ^ Time: "The Corruption Issue: A Pandora's Box," September 24, 1956, accessed November 18, 2010
- ^ Jump up to: a b (Abels, p. 192)
- ^ Jump up to: a b (Halberstam, p. 234)
- ^ Jump up to: a b (Halberstam, p. 235)
- ^ (McCullough, p. 911)
- ^ (Halberstam, p. 236)
- ^ (McKeever, p. 237)
- ^ Quoted in Chester J. Pach, ed. (2017). A Companion to Dwight D. Eisenhower. Wiley. p. 136. ISBN 9781119027331.
- ^ Gibbs, Nancy (November 10, 2008). "When New President Meets Old, It's Not Always Pretty". Time. Archived from the original on November 11, 2008.
- ^ "Executives - Are you afraid to say 'I don't know?'".
- ^ TIME: "National Affairs: Public Accounting," October 27, 1952, accessed November 18, 2010
- ^ Mason, Robert (2013). "Citizens for Eisenhower and the Republican Party, 1951–1965" (PDF). The Historical Journal. 56 (2): 513–536. doi:10.1017/S0018246X12000593. S2CID 54894636.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sullivan, Robert David; 'How the Red and Blue Map Evolved Over the Past Century'; America Magazine in The National Catholic Review; June 29, 2016
- ^ UNIVAC: the troubled life of America's first computer arstechnica.com. Retrieved February 9, 2012.
- ^ "1952 Presidential General Election Data – National". Retrieved March 18, 2013.
- ^ "1952 Presidential General Election Data – National". Retrieved March 18, 2013.
Further reading[]
- Ambrose, Stephen E. Eisenhower. Vol. I. Soldier, General of the Army, President Elect 1890–1952 (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1983), pp 550–572.
- Blake, David Haven. Liking Ike: Eisenhower, Advertising, and the Rise of Celebrity Politics (Oxford UP, 2016). xvi, 281 pp.
- Boomhower, Ray E. "All the Way with Adlai: John Bartlow Martin and the 1952 Adlai Stevenson Campaign." Journal of the Illinois State Historical Society 111#3 (2018): 67–102 online.
- Bowen, Michael. The roots of modern conservatism: Dewey, Taft, and the battle for the soul of the Republican party (2011)
- Converse, Philip E., Warren E. Miller, Donald E. Stokes, Angus Campbell. The American Voter (1964) the classic political science study of voters in 1952 and 1956
- David, Paul Theodore (1954). Presidential nominating politics in 1952. 5 vol of details on each region
- Davies, Gareth, and Julian E. Zelizer, eds. America at the Ballot Box: Elections and Political History (2015) pp. 167–83, role of television.
- Davies, James C. "Charisma in the 1952 Campaign." American Political Science Review 48#4 (1954): 1083–102. doi:10.2307/1951012. online.
- Divine, Robert A. (1974). Foreign Policy and U.S. Presidential Elections, 1952–1960. New York, New Viewpoints.
- Donaldson, Gary. When America Liked Ike: How Moderates Won the 1952 Presidential Election and Reshaped American Politics (2016) 137pp.
- Grant, Philip A. "Eisenhower and the 1952 Republican Invasion of the South: The Case of Virginia." Presidential Studies Quarterly 20#2 (1990): 285–93. online.
- Greene, John Robert. I Like Ike: The Presidential Election of 1952 (2017) excerpt
- Halberstam, David. The Fifties. (New York: Fawcett Columbine, 1993) online
- Hyman, Herbert H. and Paul B. Sheatsley. "The political appeal of President Eisenhower", Public Opinion Quarterly, 17 (1953–54), pp. 443–60 online
- McCullough, David. Truman. New York: Simon & Schuster. (1992)
- McKeever, Porter (1991). Adlai Stevenson: his life and legacy.
- Martin, John Bartlow. Adlai Stevenson of Illinois (1976) vol 1 covers his campaign in depth
- Medhurst, Martin J. "Text and Context in the 1952 Presidential Campaign: Eisenhower's 'I Shall Go to Korea' Speech." Presidential Studies Quarterly 30.3 (2000): 464–484. online
- Murphy, John M. "Civic republicanism in the modern age: Adlai Stevenson in the 1952 presidential campaign." Quarterly Journal of Speech (1994) 80#3 pp 313–328.
- Parmet, Herbert S. Eisenhower and the American crusades (1972) online
- Patterson, James T. (1972). Mr. Republican: a biography of Robert A. Taft. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (HMH). ISBN 9780395139387.
- Pickett, William B. (2000). Eisenhower Decides to Run: Presidential Politics and Cold War Strategy. Chicago: Ivan R. Dee. ISBN 1-56-663787-2. OCLC 43953970.
- Smith, Jean Edward. Eisenhower in War and Peace (2012) pp. 498–549 ISBN 978-1-4000-6693-3
- Strong, Donald S. "The presidential election in the South, 1952." Journal of Politics 17.3 (1955): 343–389. online
Primary sources[]
- Gallup, George H., ed. (1972). The Gallup Poll: Public Opinion, 1935–1971. 3 vols. Random House. ISBN 9780394472706.
- Chester, Edward W A guide to political platforms (1977) online
- Porter, Kirk H. and Donald Bruce Johnson, eds. National party platforms, 1840–1964 (1965) online 1840–1956
External links[]
- Newsreel on Eisenhower campaign
- 1952 popular vote by counties
- 1952 State-by-state Popular vote
- The Decision Not to Run in 1952, an excerpt from a Truman biography from a University of Virginia
- How close was the 1952 election? — Michael Sheppard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- The Living Room Candidate: Presidential Campaign Commercials: 1952
- Eisenhower's 1952 presidential campaign, Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library
- Election of 1952 in Counting the Votes
- "Project X" episode 5 of The Last Archive by Jill Lepore (premiered 11 June 2020)
- "It's a Free Country". Time Magazine. September 1, 1952. Archived from the original on January 15, 2009. Retrieved May 6, 2008.
- 1952 United States presidential election
- Presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Richard Nixon