40th Canadian Parliament
| 40th Parliament of Canada | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Minority parliament | |||
| November 18, 2008 – March 26, 2011 | |||
 | |||
| Parliament leaders | |||
| Prime Minister (cabinet) | Rt. Hon. Stephen Harper (28th Canadian Ministry) February 6, 2006 – November 4, 2015 | ||
| Leader of the Opposition | Hon. Stéphane Dion December 2, 2006 – December 10, 2008 | ||
| Hon. Michael Ignatieff December 10, 2008 – May 2, 2011 | |||
| Party caucuses | |||
| Government | Conservative Party | ||
| Opposition | Liberal Party | ||
| Recognized | Bloc Québécois | ||
| New Democratic Party | |||
| Unrecognized | Progressive Conservative* | ||
| * Only in the Senate. | |||
| House of Commons | |||
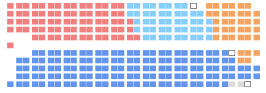 Seating arrangements of the House of Commons | |||
| Speaker of the Commons | Hon. Peter Milliken January 29, 2001 – June 2, 2011 | ||
| Government House Leader | Hon. Jay Hill October 3, 2008 – August 6, 2010 | ||
| Hon. John Baird August 6, 2010 – May 2, 2011 | |||
| Opposition House Leader | Hon. Ralph Goodale February 10, 2006 – September 10, 2010 | ||
| David McGuinty September 10, 2010 – May 26, 2011 | |||
| Members | 308 seats MP seats List of members | ||
| Senate | |||
 Seating arrangements of the Senate | |||
| Speaker of the Senate | Hon. Noël A. Kinsella February 8, 2006 – November 26, 2014 | ||
| Government Senate Leader | Hon. Marjory LeBreton February 6, 2006 - July 14, 2013 | ||
| Opposition Senate Leader | Hon. Jim Cowan November 3, 2008 – November 5, 2015 | ||
| Senators | 105 seats senator seats List of senators | ||
| Sessions | |||
| 1st Session November 18, 2008 – December 4, 2008 | |||
| 2nd Session January 26, 2009 – December 30, 2009 | |||
| 3rd Session March 3, 2010 – March 26, 2011 | |||
| |||
The 40th Canadian Parliament was in session from November 18, 2008 to March 26, 2011. It was the last Parliament of the longest-running minority government in Canadian history that began with the previous Parliament. The membership of its House of Commons was determined by the results of the 2008 federal election held on October 14, 2008. Its first session was then prorogued by the Governor General on December 4, 2008, at the request of Prime Minister Stephen Harper, who was facing a likely no-confidence motion and a coalition agreement between the Liberal party and the New Democratic Party with the support of the Bloc Québécois (2008–2009 Canadian parliamentary dispute). Of the 308 MPs elected at the October 14, 2008 general election, 64 were new to Parliament and three sat in Parliaments previous to the 39th: John Duncan, Jack Harris and Roger Pomerleau.
There were three sessions of the 40th Parliament. On March 25, 2011, the House of Commons passed a Liberal motion of non-confidence by a vote of 156 to 145, finding the Conservative Cabinet in contempt of parliament, an unprecedented finding in Canadian and Commonwealth parliamentary history.[1] On March 26, 2011, Prime Minister Stephen Harper subsequently asked Governor General David Johnston to dissolve parliament and issue a writ of election.[2]
Party standings[]
The party standings as of the election, and at dissolution, were as follows:
| Affiliation | House Members | Senate Members | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 Election Results[3] |
At Dissolution | On Election Day 2008[4] |
At Dissolution | ||
| Conservative | 143 | 143 | 21 | 52 | |
| Liberal | 77 | 77 | 58 | 46 | |
| Bloc Québécois | 49 | 47 | 0 | 0 | |
| New Democratic | 37 | 36 | 0 | 0 | |
| Independent | 2[5] | 1[6] | 5[7] | 2[8] | |
| Senate Progressive Conservative Caucus | 0 | 0 | 3[9] | 2[10] | |
| Independent Conservative | 0 | 1[11] | 0 | 0 | |
| Independent Liberal | 0 | 0 | 1[12] | 0 | |
| Independent New Democrat | 0 | 0 | 1[13] | 0 | |
| Total members | 308 | 305 | 89 | 102 | |
| Vacant | 0 | 3 | 16 | 3 | |
| Total seats | 308 | 105 | |||
Resignations and by-elections[]
NDP MP Dawn Black resigned her seat of New Westminster—Coquitlam effective April 13, 2009, to run (successfully) in the provincial riding of New Westminster in the 2009 British Columbia general election.[14] The NDP's Fin Donnelly won the seat left vacant by Black in a by-election on November 9, 2009.[15]
Independent MP Bill Casey resigned his seat of Cumberland—Colchester—Musquodoboit Valley effective April 30, 2009, to accept a job as the Nova Scotia Department of Intergovernmental Affairs' senior representative in Ottawa. He was a former Conservative who voted against the 2007 budget, claiming that it broke the Atlantic Accord with his province and Newfoundland and Labrador, and was subsequently expelled from the Conservative caucus.[16] Scott Armstrong, the Conservative candidate, won the by-election for this seat on November 9, 2009.[15]
Bloc Québécois MP Paul Crête resigned his seat of Montmagny—L'Islet—Kamouraska—Rivière-du-Loup on May 21, 2009, to run in a provincial by-election in Rivière-du-Loup. Conservative Bernard Généreux won the November 9, 2009 by-election for this seat.[15]
Bloc Québécois MP Réal Ménard resigned his seat of Hochelaga on September 16, 2009, to run in Montreal's municipal elections.[17] On November 9, 2009, Daniel Paillé won this seat for the Bloc in a by-election.[15]
New Democratic Party MP Judy Wasylycia-Leis (Winnipeg North) resigned from the House on April 30, 2010, to run (unsuccessfully) for the mayoralty of Winnipeg.[18] Liberal Kevin Lamoureux won the by-election to replace her on November 29, 2010.[19]
Liberal MP Maurizio Bevilacqua (Vaughan) resigned from the House effective August 25, 2010 to successfully run for mayor in Vaughan.[20] Conservative Julian Fantino won the November 29, 2010 by-election to replace him.[19]
Conservative MP Inky Mark (Dauphin—Swan River—Marquette) resigned from the House effective September 15, 2010 to run for mayor in Dauphin.[21] Robert Sopuck held the seat for the Conservatives in a by-election held on November 29, 2010.[19]
Bloc Québécois MP Jean-Yves Roy resigned from the House effective October 22, 2010,[22] followed by Conservative MP Jay Hill effective October 25, 2010.[23] Conservative MP Jim Prentice resigned from the House effective November 14, 2010 to take a position with CIBC.[24] By-elections in these three ridings were not scheduled prior to the issue of the writ for the 41st general election.
1st session and prorogation[]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2016) |
The first session of the 40th parliament opened on November 18, 2008, after Prime Minister Stephen Harper and the Conservatives won a slightly stronger minority government in the 2008 election. With a new government in session, Finance Minister Jim Flaherty tabled a fiscal update nine days later. Among other things, the update cut government spending, suspended the ability of civil servants to strike, sold off some Crown assets, and eliminated existing political party subsidies. This fiscal update was rejected by the opposition, and became a catalyst for talks of a coalition government. Stéphane Dion of the Liberal Party and Jack Layton of the New Democratic Party, signed an accord stating that in the event that the government lost the confidence of the house, they would form a coalition with the support of Gilles Duceppe and the Bloc Québécois, if asked to do so by the Governor General of Canada Michaëlle Jean. However, Stephen Harper delayed the vote of non-confidence scheduled for December 1, and the Governor General prorogued parliament on Harper's advice on December 4, 2008, until January 26, 2009.
After prorogation, calls came from within the Liberal Party for Dion to resign immediately. Dion initially scheduled his resignation for the party's leadership convention in May 2009, but on December 8, 2008, he announced that he would step down upon the selection of an interim leader. After the withdrawal of Bob Rae and Dominic LeBlanc from the 2009 leadership race, Michael Ignatieff became the only leadership candidate, and therefore was appointed interim leader of the Liberals and the opposition on December 10, 2008.
2nd Session and prorogation[]
The Governor-in-Council recalled parliament on January 26, 2009. Its first business (after the Throne Speech) was to present the federal budget, which included a large deficit. After negotiations with new opposition leader Michael Ignatieff, the government promised to present regular updates on the stimulus budget, and the Liberals and Conservatives joined to pass the budget and keep the Conservative government in power. The Conservative government made crime a major focus of the session. The Conservatives reintroduced their former mandatory minimums bill, known as Bill C-15.[25]


On December 30, 2009, Prime Minister Stephen Harper announced that he would advise the Governor General to prorogue parliament during the 2010 Winter Olympics, until March 3, 2010. He telephoned Governor General Michaëlle Jean to ask her permission to end the parliamentary session and Jean signed the proclamation later that day.[26][27] According to Harper's spokesman, he sought his second prorogation to consult with Canadians about the economy.[26] In an interview with CBC News, Prince Edward Island Liberal member of parliament Wayne Easter accused the Prime Minister of "shutting democracy down".[28][29] The second prorogation in a year also received some international criticism as being not very democratic.[30]
In response to the prorogation, demonstrations took place on January 23, 2010, in over 60 Canadian cities, and at least four cities in other countries. The protests attracted thousands of participants, many who had joined a group on Facebook.[31][32]
Senate appointments[]
The Senate of Canada has seen new members appointed in blocs of 18, 9, and 5; all were appointed to the Conservative caucus. The balance of power shifted for the first time on August 27, 2009, when the Liberal caucus was reduced to holding a plurality of 52 seats. On January 29, 2010, the balance shifted again as five vacancies were filled by appointed Conservatives, giving them a plurality of 51, with the Liberals holding the next-highest number of seats at 49. The Conservatives achieved an absolute majority when Don Meredith and Larry Smith were appointed on December 20, 2010. After dissolution, Smith and Fabian Manning resigned to run in the 2011 election. That reduced the Conservative caucus to 52, but they retained a majority of sitting senators as there were 50 senators of other parties and 3 vacancies.
Honorary Senators[]
The Senate of Canada posthumously awarded the title of Honorary Senator during the 40th Parliament to five pioneering women known as The Famous Five.[33]
| Emily Murphy |
| Henrietta Muir Edwards |
| Nellie McClung |
| Irene Parlby |
| Louise McKinney |
Members[]
Committees[]
House[]
- Standing Committee on Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development
- Standing Committee on Access to Information, Privacy and Ethics
- Standing Committee on Agriculture and Agri-Food
- Standing Committee on Canadian Heritage
- Standing Committee on Citizenship and Immigration
- Standing Committee on Environment and Sustainable Development
- Standing Committee on Finance
- Standing Committee on Fisheries and Oceans
- Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs and International Development
- Standing Committee on Government Operations and Estimates
- Standing Committee on Health
- Standing Committee on Human Resources, Skills and Social Development and the Status of Persons with Disabilities
- Standing Committee on Industry, Science and Technology
- Standing Committee on International Trade
- Standing Committee on Justice and Human Rights
- Standing Committee on National Defence
- Standing Committee on Natural Resources
- Standing Committee on Official Languages
- Standing Committee on Procedure and House Affairs[34]
- Standing Committee on Public Accounts
- Standing Committee on Public Safety and National Security
- Standing Committee on the Status of Women
- Standing Committee on Transport, Infrastructure and Communities
- Standing Committee on Veterans Affairs[35]
Senate[]
- Standing Committee on Aboriginal Peoples
- Standing Committee on Agriculture and Forestry
- Standing Committee on Banking, Trade and Commerce
- Standing Committee on Conflict of Interest for Seniors
- Standing Committee on Energy, the Environment and Natural Resources
- Standing Committee on Fisheries and Oceans
- Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs and International Trade
- Standing Committee on Human Rights
- Standing Committee on Internal Economy, Budgets and Administration
- Standing Committee on Legal and Constitutional Affairs
- Standing Committee on National Finance
- Standing Committee on National Security and Defence
- Standing Committee on Official Languages
- Standing Committee on Rules, Procedures and the Rights of Parliament
- Standing Committee on Social Affairs, Science and Technology
- Standing Committee on Transport and Communications
Joint Committees[]
Officeholders[]
Speakers[]
- Senate: Noël Kinsella, Conservative Senator for New Brunswick.
- House of Commons: Peter Milliken, the Liberal member for Kingston and the Islands.
Other Chair occupants[]
Senate
- Speaker pro tempore of the Canadian Senate:
- Rose-Marie Losier-Cool, Liberal Senator from New Brunswick (until March 2, 2010)
- Donald H. Oliver, Conservative Senator for Nova Scotia (from March 4, 2010)
House of Commons
- House of Commons Deputy Speaker and Chair of Committees of the Whole: Andrew Scheer, Conservative member for Regina—Qu'Appelle
- Deputy Chair of Committees of the Whole: Denise Savoie, NDP member for Victoria
- Assistant Deputy Chair of Committees of the Whole: Barry Devolin, Conservative member for Haliburton—Kawartha Lakes—Brock
Leaders[]
- Prime Minister of Canada: Rt. Hon. Stephen Harper (Conservative)
- Leader of the Opposition (Liberal):
- Hon. Stéphane Dion (until December 9, 2008)
- Hon. Michael Ignatieff (acting from December 10, 2008, permanent from May 2, 2009)
- Bloc Québécois leader: Gilles Duceppe
- New Democratic Party leader: Hon. Jack Layton
Floor leaders[]
Senate
- Leader of the Government in the Senate: Hon. Marjory LeBreton
- Leader of the Opposition in the Senate: Jim Cowan
House of Commons
- Government House Leader:
- Hon. Jay Hill (until Aug 6, 2010)
- Hon. John Baird (from Aug 6, 2010)
- Opposition House Leader:
- Hon. Ralph Goodale (until Sept 9, 2010)
- David McGuinty (from Sept 8, 2010)
- Bloc Québécois House Leader: Pierre Paquette
- New Democratic Party House Leader: Libby Davies
Whips[]
Senate
- Government Whip in the Senate:
- Terry Stratton (until Dec 31, 2009)
- Consiglio Di Nino (from Jan 1, 2010)
- Deputy Government Whip in the Senate: Stephen Greene
- Opposition Whip in the Senate: Jim Munson
- Deputy Opposition Whip in the Senate: Elizabeth Hubley
House of Commons
- Chief Government Whip: Hon. Gordon O'Connor
- Deputy Government Whip: Harold Albrecht
- Official Opposition Whip:
- Rodger Cuzner (until Sept 10, 2010)
- Marcel Proulx (from Sept 10, 2010)
- Bloc Québécois Whip:
- Michel Guimond (until June 22, 2010)
- Claude DeBellefeuille (from June 23, 2010)
- New Democratic Party Whip: Yvon Godin
Shadow cabinets[]
- Official Opposition Shadow Cabinet of the 40th Parliament of Canada
- Bloc Québécois Shadow Cabinet of the 40th Parliament of Canada
- New Democratic Party Shadow Cabinet of the 40th Parliament of Canada
By-elections[]
| By-election | Date | Incumbent | Party | Winner | Party | Cause | Retained | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vaughan | November 29, 2010 | Maurizio Bevilacqua | Liberal | Julian Fantino | Conservative | Resigned to run for Mayor of Vaughan | No | ||
| Dauphin—Swan River—Marquette | November 29, 2010 | Inky Mark | Conservative | Robert Sopuck | Conservative | Resigned to run for Mayor of Dauphin | Yes | ||
| Winnipeg North | November 29, 2010 | Judy Wasylycia-Leis | New Democratic | Kevin Lamoureux | Liberal | Resigned to run for Mayor of Winnipeg | No | ||
| Cumberland—Colchester—Musquodoboit Valley | November 9, 2009 | Bill Casey | Independent | Scott Armstrong | Conservative | Resigned to accept appointment with Nova Scotia's Department of Intergovernmental Affairs | No | ||
| Hochelaga | November 9, 2009 | Réal Ménard | Bloc Québécois | Daniel Paillé | Bloc Québécois | Resigned to run for Montreal City Council | Yes | ||
| Montmagny—L'Islet—Kamouraska—Rivière-du-Loup | November 9, 2009 | Paul Crête | Bloc Québécois | Bernard Généreux | Conservative | Resigned to enter provincial politics | No | ||
| New Westminster—Coquitlam | November 9, 2009 | Dawn Black | New Democratic | Fin Donnelly | New Democratic | Resigned to enter provincial politics | Yes | ||
References[]
- ^ Bruce Cheadle (March 25, 2011). "Harper government topples on contempt motion, triggering May election". The Canadian Press; CTV news. Retrieved March 26, 2011.
- ^ CBC News (March 25, 2011). "MPs gather for historic vote". CBC. Archived from the original on March 28, 2011. Retrieved March 25, 2011.
- ^ "Canada Votes 2008 - Overall Results". CBC News.
- ^ Members of the Canadian Senate are appointed by the Governor General on the advice of the Prime Minister and remain as Senators until the age of 75, even if the House of Commons has been dissolved or an election has been called.
- ^ André Arthur and Bill Casey.
- ^ André Arthur
- ^ Anne Cools, Michael Pitfield, Marcel Prud'homme, Jean-Claude Rivest, Mira Spivak.
- ^ Anne Cools, Jean-Claude Rivest.
- ^ Elaine McCoy, Lowell Murray, Norman Atkins
- ^ Elaine McCoy, Lowell Murray
- ^ Helena Guergis— CBC News (April 9, 2010). "Guergis to sit outside Tory caucus". CBC. Archived from the original on April 11, 2010. Retrieved April 9, 2010.
- ^ Raymond Lavigne sat as a Liberal, but was not officially part of the Liberal caucus.
- ^ Lillian Dyck.
- ^ "NDP MP to seek provincial seat in B.C.". cbc.ca, March 7, 2009.
- ^ a b c d "Conservatives win 2 byelections, 1 at Bloc's expense". cbc.ca, November 10, 2009.
- ^ Tory MP ejected from caucus after budget vote, CBC.ca, June 5, 2007.
- ^ "Bloc MP runs for municipal politics". CTV News, June 25, 2009.
- ^ "NDP’s Judy Wasylycia-Leis calls it quits". The Globe and Mail, April 27, 2010.
- ^ a b c "Fantino wins Vaughan for Tories; Liberals take Manitoba by-election". The Globe and Mail, November 30, 2010.
- ^ Maurizio Bevilacqua moves closer to Vaughan mayor’s seat. The National Post, August 25, 2010.
- ^ "Inky hopes to make a Mark as mayor again". Winnipeg Free Press, August 17, 2010.
- ^ "Jean-Yves Roy quitte la politique". Radio-Canada, October 22, 2010.
- ^ "Hill set to resign on Oct. 25: CP". Prince George Citizen, October 4, 2010.
- ^ "Prentice resigns seat; earliest byelection Jan. 3. Calgary Herald, November 17, 2010. p. A4
- ^ "House Government Bill - C-15, First Reading (40-2)". Retrieved December 25, 2016.
- ^ a b CBC News (December 31, 2009). "PM shuts down Parliament until March". CBC. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- ^ Richard J. Brennan (January 2, 2010). "Critics say anger is growing over PM's 'imperial' style". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved January 2, 2010.
- ^ POV, CBC News (December 30, 2009). "Parliament prorogued: Necessary move or undemocratic?". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on January 2, 2010. Retrieved July 5, 2012.
- ^ "PM 'shutting democracy down', says Easter". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. December 31, 2009. Archived from the original on January 3, 2010. Retrieved January 1, 2010.
- ^ "Harper goes prorogue". January 7, 2010. Retrieved December 25, 2016 – via The Economist.
- ^ "Thousands protest Parliament's suspension". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. January 23, 2010. Archived from the original on January 26, 2010. Retrieved January 24, 2010.
- ^ Delacourt, Susan; Richard J. Brennan (January 5, 2010). "Grassroots fury greets shuttered Parliament". Toronto Star. Archived from the original on January 8, 2010. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^ "'Famous 5' named honorary senators". CBC News. October 10, 2009.
- ^ "House of Commons Committees - PROC - ARCHIVE (40-1)". Parliament of Canada. Retrieved March 27, 2012.
- ^ "House of Commons Committees - PROC (40-1)". Parliament of Canada. Retrieved March 27, 2012.
- ^ "Senate Committees Homepage". Retrieved December 25, 2016.
External links[]
| Wikinews has related news: |
![]() Media related to Protests against the prorogation of the 40th Parliament of Canada at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Protests against the prorogation of the 40th Parliament of Canada at Wikimedia Commons
- 40th Canadian Parliament
- 2008 establishments in Canada
- 2011 disestablishments in Canada
- Stephen Harper
- Minority governments