Anterior cardiac veins
| Anterior cardiac veins | |
|---|---|
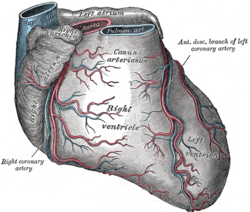 Sternocostal surface of heart.(Anterior cardiac veins not labeled, but visible at left.) | |
 Arteries: RCA = right coronary AB = atrial branches SANB = sinuatrial nodal RMA = right marginal LCA = left coronary CB = circumflex branch LAD/AIB = anterior interventricular LMA = left marginal PIA/PDA = posterior descending AVN = atrioventricular nodal Veins: SCV = small cardiac ACV = anterior cardiac AIV/GCV = great cardiac MCV = middle cardiac CS = coronary sinus | |
| Details | |
| Drains to | Right atrium |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Venae cardiacae anteriores, venae ventriculi dextri anteriores |
| TA98 | A12.3.01.012 |
| TA2 | 4168 |
| FMA | 71567 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior cardiac veins (or anterior veins of right ventricle) comprise a variable number of small vessels, usually between two and five, which collect blood from the front of the right ventricle and open into the right atrium; the right marginal vein frequently opens into the right atrium,[1] and is therefore sometimes regarded as belonging to this group.
Unlike most cardiac veins, they do not end in the coronary sinus. Instead, these veins drain directly into the anterior wall of the right atrium.
References[]
- ^ Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Limited. pp. 994–1023. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9.
External links[]
Categories:
- Veins of the torso
- Cardiovascular system stubs