Middle cardiac vein
This section needs expansion. You can help by . (May 2012) |
| Middle cardiac vein | |
|---|---|
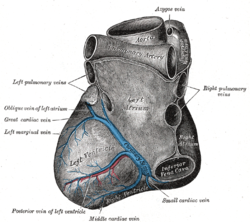 Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart. (Middle cardiac vein labeled at bottom.) | |
 ARTERIES: RCA = right coronary AB = atrial branches SANB = sinuatrial nodal RMA = right marginal LCA = left coronary CB = circumflex branch LAD/AIB = anterior interventricular LMA = left marginal PIA/PDA = posterior descending AVN = atrioventricular nodal VEINS: SCV = small cardiac ACV = anterior cardiac AIV/GCV = great cardiac MCV = middle cardiac CS = coronary sinus | |
| Details | |
| Drains to | Coronary sinus |
| Artery | Posterior interventricular artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Vena cardiaca media, vena cordis media |
| TA98 | A12.3.01.009 |
| TA2 | 4165 |
| FMA | 4713 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The middle cardiac vein commences at the apex of the heart; ascends in the posterior longitudinal sulcus, and ends in the coronary sinus near its right extremity.
Structure[]
Variation[]
The middle cardiac vein has a constant location on the surface of the ventricles.[1]
Clinical significance[]
The middle cardiac vein is useful for epicardial access to the inferior side of the ventricles.[2]
References[]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 642 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 642 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Worley, Seth J. (2017-01-01), Ellenbogen, Kenneth A.; Wilkoff, Bruce L.; Kay, G. Neal; Lau, Chu-Pak (eds.), "30 - Coronary Sinus Lead Implantation", Clinical Cardiac Pacing, Defibrillation and Resynchronization Therapy (Fifth Edition), Elsevier, pp. 739–834, ISBN 978-0-323-37804-8, retrieved 2021-01-08
- ^ Issa, Ziad F.; Miller, John M.; Zipes, Douglas P. (2012-01-01), Issa, Ziad F.; Miller, John M.; Zipes, Douglas P. (eds.), "Chapter 27 - Epicardial Ventricular Tachycardia", Clinical Arrhythmology and Electrophysiology: A Companion to Braunwald's Heart Disease (Second Edition), Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 608–617, ISBN 978-1-4557-1274-8, retrieved 2021-01-08
External links[]
- Anatomy figure: 20:04-05 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Posterior view of the heart."
Categories:
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Veins of the torso
- Cardiovascular system stubs