Antigonid dynasty
Antigonids Antigonid Empire Ἀντιγονίδαι Antigonidai | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 306 BC–168 BC | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
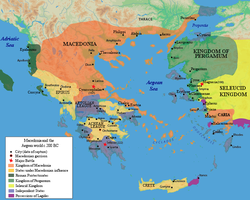 Antigonid Empire c. 200 BC | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Pella (until 167 BC) | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Greek | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Greek / Hellenistic | ||||||||||||
| Government | Hellenistic monarchy | ||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||
• 306 BC – 301 BC | Antigonus I Monophthalmus | ||||||||||||
• 179 BC – 168 BC | Perseus of Macedon | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Hellenistic | ||||||||||||
• Established | 306 BC | ||||||||||||
• Defeat by Rome | 168 BC | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Antigonid dynasty (/ænˈtɪɡoʊnɪd/; Greek: Ἀντιγονίδαι) was a dynasty of Hellenistic kings descended from Alexander the Great's general Antigonus I Monophthalmus ("the One-eyed") that ruled mainly in Macedonia.
History[]
Succeeding the Antipatrid dynasty in much of Macedonia, Antigonus ruled mostly over Asia Minor and northern Syria. His attempts to take control of the whole of Alexander's empire led to his defeat and death at the Battle of Ipsus in 301 BC. Antigonus's son Demetrius I Poliorcetes survived the battle, and managed to seize control of Macedon itself a few years later, but eventually lost his throne, dying as a prisoner of Seleucus I Nicator. After a period of confusion, Demetrius's son Antigonus II Gonatas was able to establish the family's control over the old Kingdom of Macedon, as well as over most of the Greek city-states, by 276 BC.[2]
Legacy[]
It was one of four dynasties established by Alexander's successors, the others being the Seleucid dynasty, Ptolemaic dynasty and Attalid dynasty. The last scion of the dynasty, Perseus of Macedon, who reigned between 179 and 168 BC, proved unable to stop the advancing Roman legions and Macedon's defeat at the Battle of Pydna signaled the end of the dynasty.[3]
Dynasty[]
The ruling members of the Antigonid dynasty were:
| King | Reign (BC) | Consort(s) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antigonus I Monophthalmus (Western Asian Antigonid kingdom) | 306–301 BC | Stratonice | One of Alexander the Great's top generals; a major participant in the so-called "funeral games" following that king's death. |
| Demetrius I Poliorcetes (Macedon, Cicilia) | 294–287 BC | Phila Ptolemais Deïdameia Lanassa ?Eurydice ?Unnamed Illyrian woman |
Son of Antigonus I Monophthalmus. Demetrius' wife Phila was a daughter of Antipater, and ancestor of all subsequent Antigonid kings of Macedon, except Antigonus III Doson, through her son Antigonus II Gonatas. Antigonus III Doson was descended from the marriage of Demetrius and Ptolemais, who was a daughter of Ptolemy I Soter and mother of Doson's father, Demetrius the Fair, the ephemeral King of Cyrene. Deïdameia was a daughter of Aeacides of Epirus and sister of Pyrrhus, she had one son, Alexander, by Demetrius. Demetrius had a further two sons, Demetrius the Thin and Corrhagus, the former by an unnamed Illyrian woman, the latter by a woman named Eurydice. Demetrius I Poliorcetes was the first Antigonid king of Macedon. |
| Antigonus II Gonatas (Macedon) | 276–239 BC | Phila | Son of Demetrius Poliorcetes and Phila, grandson of Antigonus I Monophthalmus. His wife, Phila, was the daughter of his sister, Stratonice. Only one known legitimate child, Demetrius II Aetolicus. |
| Demetrius the Fair (Cyrene) | c. 250 BC | Olympias of Larissa Berenice II |
Son of Demetrius I Poliorcetes and Ptolemaïs. Father of Antigonus III Doson and, apparently, Echecrates by Olympias. |
| Demetrius II Aetolicus (Macedon) | 239–229 BC | Stratonice of Macedon Phthia of Epirus Nicaea of Corinth Chryseis |
Son of Antigonus II and Phila. Stratonice of Macedon was a daughter of Antiochus I Soter and Stratonice. Phthia of Epirus was a daughter of Alexander II of Epirus and Olympias II of Epirus. Nicaea of Corinth was the widow of Demetrius' cousin, Alexander of Corinth. Chryseis was a former captive of Demetrius.[4] Only known son, Philip by Chryseis, also had a daughter by Stratonice of Macedon, Apama III. |
| Antigonus III Doson (Macedon) | 229–221 BC | Chryseis | Son of Demetrius the Fair and Olympias of Larissa. Children unknown. |
 Philip V (Macedon) |
221–179 BC | Polycratia of Argos | Son of Demetrius II and Chryseis.[4] At least four children: Perseus of Macedon, Apame, Demetrius and Philippus. |
 Perseus (Macedon) |
179–168 BC (died 166 BC) |
Laodice V | The last ruler of Macedon. Laodice V was a daughter of the Seleucid king, Seleucus IV Philopator. At least two sons, Philip and Alexander. |
The Greek rebel against Rome and last King of Macedonia, Andriscus, claimed to be the son of Perseus.
Family tree of Antigonids[]
| Derdas III | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derdas III archon of Elimiotis | Machatas of Elimeia satrap of India | Phila of Elimeia | Philip II king of Macedonia 359-336 BC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Philip | wife | Periandros of Pella | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demetrius | Stratonice daughter of Corrhaeus | Antigonus I Monophthalmus king of Macedonia 306-301 BC | Ptolemy | Marsyas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.Phila daughter of Antipater 2.Eurydice of Athens 3.Deidamia I of Epirus daughter of Aeacides of Epirus | Demetrius I Poliorketes king of Macedon 294-288 BC | 4.Lanassa daughter of Agathocles of Syracuse 5.Ptolemais daughter of Ptolemy I of Egypt | Philip prince | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) Stratonice of Syria ∞ 1.Seleucus I Nicator 2.Antiochus I Soter | (1) Antigonus II Gonatas king of Macedon 277-274, 272-239 BC | Phila daughter of Seleucus I Nicator | (5) Demetrius the Fair king of Cyrene 250-249 BC | 1.Olympias of Larissa 2.Berenice II daughter of Magas king of Cyrene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2) 1.Stratonice of Macedon | Demetrius II Aetolicus king of Macedonia 239-229 BC | 2.Nicaea of Corinth 3.Phthia daughter of Alexander II of Epirus 4.Chryseis | (1) Antigonus III Doson king of Macedon 229-221 BC | Echecrates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prusias I of Bithynia | (1) Apama III | (4) Philip V king of Macedon 221-179 BC | Polycratia of Argos | Antigonos | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prusias II of Bithynia king of Bithynia | Apame IV | (illeg.) Perseus king of Macedon 179-168 BC | Laodice V daughter of Seleucus IV Philopator | Demetrius prince | Philippus prince | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alexander prince | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coin gallery[]
|
See also[]
- List of kings of Macedon
References[]
- ^ Taagepera, Rein (1979). "Size and Duration of Empires: Growth-Decline Curves, 600 B.C. to 600 A.D.". Social Science History. 3 (3/4): 121. doi:10.2307/1170959. JSTOR 1170959.
- ^ J. Spielvogel, Jackson (2005). Western Civilization: Volume I: To 1715. Thomson Wadsworth. pp. 89–90. ISBN 0-534-64603-4.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica, Antigonid dynasty, 2008, O.Ed. "But Perseus' failure to deploy his full resources brought about his defeat (168) at Pydna in Macedonia and signaled the end of the dynasty."
- ^ Jump up to: a b Eusebius, Chronicle 1.237-8; Syncellus Chronicle 535.19
Further reading[]
| Library resources about Antigonid dynasty |
- Adams, Winthrop Lindsay. 2010. "Alexander's Successors to 221 BC." In A Companion to Ancient Macedonia. Edited by Joseph Roisman and Ian Worthington, 208–224. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Anson, Edward M. 2014. Alexander's Heirs: The Age of the Successors. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Edson, Charles F. 1934. "The Antigonids, Heracles, and Beroia." Harvard Studies in Classical Philology 45:213–246.
- O'Neil, James L. 2003. "The Ethnic Origins of the Friends of the Antigonid Kings of Macedon." The Classical Quarterly 53, no. 2: 510–22. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3556219.
- Antigonid dynasty
- Antigonid Macedonia
- Ancient Macedonian dynasties
- 3rd century BC in Macedonia (ancient kingdom)
- 2nd century BC in Macedonia (ancient kingdom)
- 300s BC establishments
- 306 BC
- 4th-century BC establishments
- 2nd-century BC disestablishments
- 168 BC




