Arboreol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
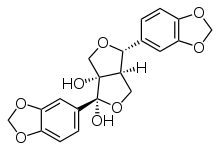
| IUPAC name
(1R,4R,6aR)-1,4-Bis(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)dihydro-1H,3H-furo[3,4-c]furan-1,6a(6H)-diol
| |
| Other names
(7β,7'α,8α,8'α)-3,4:3',4'-bis(methylenedioxy)-7,9':7',9-diepoxylignane-7,8-diol
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H18O8 | |
| Molar mass | 386.35 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Arboreol is an epoxylignan.
Arboreol can be transformed by acid catalysis into gmelanone.[2]
References[]
- ^ Buckingham, John (2 December 1993). Dictionary of Natural Products. CRC Press. p. 481. ISBN 978-0-412-46620-5.
- ^ Acid catalysed rearrangements of arboreol: A biomimetic synthesis of gmelanone. L. Ramachandra Row and Reveru Ventkateswarlu, Tetrahedron Letters, 1980, Volume 21, Issue 30, Pages 2919–2922, doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)78645-X
External links[]
| Look up arboreol in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Categories:
- Lignans
- Benzodioxoles
- Aromatic compound stubs