Archaeol
Archaeol is one of the main core membrane lipids of archaea, one of the three domains of life. One of the key features that distinguishes archaea from bacteria and eukarya is their membrane lipids, where archaeol plays an important role. Because of this, archaeol is also broadly used as a biomarker for ancient archaea, especially methanogens, activity.[1]
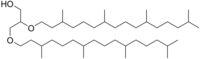
Archaeol is generally composed by linking two phytanyl chains to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of a glycerol molecule. The highly branched side chains are speculated to account for the very low permeability of archaeol-based membrane, which may be one of the key adaptations of archaea to extreme environments.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3-Bis(3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadecoxy)propan-1-ol
| |
| Other names
Archaeol lipid; 2,3-Di-O-phytanyl-sn-glycerol; 2,3-Bis[(3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadecyl)oxy]-1-propanol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| MeSH | archaeol+lipid |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C43H88O3 | |
| Molar mass | 653.174 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Chemistry[]
Archaeol is a diether lipid commonly found in archaea. Standard archaeol is 2,3-di-O-phytanyl-sn-glycerol, with two phytanyl chains binding to the position of sn-2 and sn-3 of glycerol by ether bonds. The 2,3-sn-glycerol structure and ether bond linkage are two key differences of archaea lipids from those of bacteria and eukarya that use 1,2-sn-glycerol, and mostly, ester bonds.[2] Natural archaeol has 3R, 7R, 11R configurations for the three chiral centers in the isoprenoid chains. There are four structural variations, contributing to the complexity of the membrane lipids in function and properties. The two phytanyl chains can form a 36-member ring to yield macrocyclic archaeol. Hydroxylated archaeol has phytanyl chains hydroxylated at the first tertiary carbon atom, while sesterterpanyl archaeol have the phytanyl side chains with C25 sesterterpanyl chains, substituting at C2 of glycerol or at both carbons. Unsaturated archaeol, with the same carbon skeleton as standard archaeol but one or multiple double bonds in the phytanyl side chains is also discovered.[3]
Two archaeol molecules can undergo head-to-head linkage to form caldarchaeol (one typical glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether, GDGT), one of the most common tetraether lipid in archaea.







Biological role and synthesis[]
Biological role[]
Archaeol has been found in all analyzed archaea so far, at least trace amount. It represents 100% of the diether core lipids in most neutrophilic halophiles[3] and sulfur-dependent thermophiles (though their most core lipids are tetraether lipids). Methanogens contain hydroxyarchaeol and macrocyclic other than the standard archaeol, and sesterterpanyl-chain-containing archaeol is characteristic of alkaliphilic extreme halophiles. It is noteworthy that tetraether lipids are also widely present in archaea.[2]
Liposomes (a spherical vesicle having at least at least one lipid bilayer) of lipids from archaea typically demonstrate extremely low permeability for molecules and ions, even including protons. The ion permeability induced by ionophores (ion transporters across the membranes) are also quite low, and only comparable to that of egg phosphatidylcholine (a very common biological membrane component) at 37˚C when the temperature rises up to c.a. 70˚C.[4][5] Compared to bacteria and eukarya, the isoprenoid side chains of archaeol are highly branched. This structural difference is believed lower the permeability of archaea over the whole growth temperature range which enables archaea to adapt to extreme environments.[6]
Synthesis process[]
Archaeol is usually found as phospholipid in archaea cells. The synthetic pathway of fully saturated archaeol phospholipid proceeds as follows: the synthesis of isoprenoid side chains by head-to-tail linkage of isoprenes, ether linkage to glycerol-1-phosphate backbone, CDP archaeol formation, polar head group attachment and saturation of double bonds. Following this, tetraether lipids may be synthesized afterwards by dimerization reaction via a head-to-head linkage.[7]
Archaea feature different biosynthetic pathways of isoprenoid chains compared to bacteria and eukarya. The precursors for isoprenoid are C5 units isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are universal for all three domains of life. Generally, the two compounds are synthesized in bacteria via 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate/1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate pathway (MEP/DOXP pathway), and are synthesized via mevalonate (MVA) pathway in most eukarya. The synthesis of IPP and DMAPP in archaea follows an alternate MVA pathway which differs from the classic MVA pathway in the last three steps and shares the remaining four steps.[7]
Ether lipids in bacteria[]
Though archaeol, featuring the ether linkage between isoprenoid chain to glycerol, has been considered as a cogent biomarker for archaea, ether membrane lipids have also been discovered in some aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, including lipids with one ester bond and one ether bond to alkyl chains. Many strictly anoxic bacteria and a few aerobic species contain plasmalogens (Pla), which has an alkyl chain bound to sn-1 position of the glycerol via a vinyl-ether bond. Similar to archaea, these lipids are thought to increase the resistivity of bacteria to adverse environments. More stunning is the discovery of nonisoprenoid dialkyl glycerol diether lipids(DGD) and branched dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids (brGDGT), which are formed, in the similar way to archaeol, by binding alkyls chains (but not isoprenoid chains) to glycerol molecules via ether linkage. It's highly notable that these lipids are only different from archaea ether lipids in the side chains and binding positions on the glycerol. DGD is reported in thermophilic bacteria, a few mesophilic bacteria and aggregating myxobacteria.[8][9]
Used as a lipid biomarker[]
Archaeol in the sediments typically originates from the hydrolysis of archaea membrane phospholipids during diagenesis. Due to its high preservation potential, it is often detected and used by organic geochemists as a biomarker for archaea activity, especially for methanogen biomass and activity. As a methanogen proxy, it is used by Michinari Sunamura et al. to directly measure the methanogens in the sediments of Tokyo Bay,[10] and also used by Katie L. H. Lim et al. as an indicator of methanogenesis in water-saturated soils.[11] C. A. McCartney et al. used it as a proxy for methane production in cattle.[12]
In the meantime, it's also used to help understand ancient biogeochemistry. It was used as a biomarker by Richard D. Pancost et al. in order to reconstruct the Holocene biogeochemistry in ombrotrophic peatlands.[13] A pilot study led by Ian D. Bull et al. also used archaeol as a biomarker to reveal the differences between fermenting digestive systems in foregut and hindgut of ancient herbivorous mammals.[14]
Additionally, because of different degradation kinetics of intact archaeol and caldarchaeol, the ratio of archaeol to caldarchaeol was proposed as a salinity proxy in highland lakes, providing a tool for paleosalinity studies.[15]
Archaeol can also get hydrolyzed in some cases, with its side chains preserved as phytane or pristane, depending on the redox conditions.[16]
Measurement[]
To analyze archaeol, lipids are commonly extracted via the traditional Bligh-Dyer procedure,[17] usually followed by fractionation (by thin layer or column chromatography) and derivatization. Kazuhiro Demizu et al.[18]and Sadami Ohtsubo et al.[19] proposed similar processes involving acid Bligh and Dyer extraction, acid treatment and derivatization, with the core lipids finally being subjected to chromatography.
To determine the concentration of archaeol present in a sample, chromatography technologies are commonly employed, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC),[18][19][20] gas chromatography (GC),[21] and supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC),[22][23] with mass spectrometry (MS) often applied to aid the identification.
See also[]
- Diacylglycerol
- Caldarchaeol
- id:Archaeol
References[]
- ^ Edited by Ricardo Cavicchioli (2007), Archaea, Washington, DC: ASM Press, ISBN 978-1-55581-391-8, OCLC 172964654CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Koga, Y Nishihara, M Morii, H Akagawa-Matsushita, M (1993). "Ether polar lipids of methanogenic bacteria: structures, comparative aspects, and biosyntheses". Microbiological Reviews. 57 (1): 164–82. doi:10.1128/MMBR.57.1.164-182.1993. OCLC 680443863. PMC 372904. PMID 8464404.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gambacorta, A.; Gliozzi, A.; De Rosa, M. (1995). "Archaeal lipids and their biotechnological applications". World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 11 (1): 115–131. doi:10.1007/BF00339140. PMID 24414415.
- ^ Yamauchi, Kiyoshi; Doi, Kuniyuki; Kinoshita, Masayoshi; Kii, Fumiko; Fukuda, Hideki (October 1992). "Archaebacterial lipid models: highly salt-tolerant membranes from 1,2-diphytanylglycero-3-phosphocholine". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1110 (2): 171–177. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(92)90355-p. ISSN 0005-2736. PMID 1390846.
- ^ Yamauchi, Kiyoshi; Doi, Kumiyuki; Yoshida, Yoichi; Kinoshita, Masayoshi (March 1993). "Archaebacterial lipids: highly proton-impermeable membranes from 1,2-diphytanyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocoline". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes. 1146 (2): 178–182. doi:10.1016/0005-2736(93)90353-2. ISSN 0005-2736. PMID 8383997.
- ^ Koga, Yosuke (2012). "Thermal Adaptation of the Archaeal and Bacterial Lipid Membranes". Archaea. 2012: 789652. doi:10.1155/2012/789652. ISSN 1472-3646. PMC 3426160. PMID 22927779.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jain, Samta (2014). "Biosynthesis of archaeal membrane ether lipids". Frontiers in Microbiology. 5: 641. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00641. PMC 4244643. PMID 25505460.
- ^ Grossi, Vincent; Mollex, Damien; Vinçon-Laugier, Arnauld; Hakil, Florence; Pacton, Muriel; Cravo-Laureau, Cristiana (2015). "Mono- and Dialkyl Glycerol Ether Lipids in Anaerobic Bacteria: Biosynthetic Insights from the Mesophilic Sulfate Reducer Desulfatibacillum alkenivorans PF2803T". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 81 (9): 3157–3168. doi:10.1128/AEM.03794-14. PMC 4393425. PMID 25724965.
- ^ Lorenzen, Wolfram; Ahrendt, Tilman; Bozhüyük, Kenan A J; Bode, Helge B (2014-05-11). "A multifunctional enzyme is involved in bacterial ether lipid biosynthesis". Nature Chemical Biology. 10 (6): 425–427. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1526. ISSN 1552-4450. PMID 24814673.
- ^ Sunamura, Michinari; Koga, Yosuke; Ohwada, Kouichi (1999-11-01). "Biomass Measurement of Methanogens in the Sediments of Tokyo Bay Using Archaeol Lipids". Marine Biotechnology. 1 (6): 562–568. doi:10.1007/PL00011811. ISSN 1436-2228. PMID 10612681.
- ^ Lim, Katie L. H.; Pancost, Richard D.; Hornibrook, Edward R. C.; Maxfield, Peter J.; Evershed, Richard P. (2012). "Archaeol: An Indicator of Methanogenesis in Water-Saturated Soils". Archaea. 2012: 896727. doi:10.1155/2012/896727. ISSN 1472-3646. PMC 3512251. PMID 23226972.
- ^ Dewhurst, R. J.; Yan, T.; Bull, I. D.; McCartney, C. A. (2013-02-01). "Assessment of archaeol as a molecular proxy for methane production in cattle". Journal of Dairy Science. 96 (2): 1211–1217. doi:10.3168/jds.2012-6042. ISSN 0022-0302. PMID 23261373.
- ^ Pancost, Richard D.; McClymont, Erin L.; Bingham, Elizabeth M.; Roberts, Zoë; Charman, Dan J.; Hornibrook, Edward R.C.; Blundell, Anthony; Chambers, Frank M.; Lim, Katie L.H. (November 2011). "Archaeol as a methanogen biomarker in ombrotrophic bogs". Organic Geochemistry. 42 (10): 1279–1287. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.07.003.
- ^ Gill, Fiona L.; Dewhurst, Richard J.; Dungait, Jennifer A.J.; Evershed, Richard P.; Ives, Luke; Li, Cheng-Sen; Pancost, Richard D.; Sullivan, Martin; Bera, Subir (May 2010). "Archaeol – a biomarker for foregut fermentation in modern and ancient herbivorous mammals?". Organic Geochemistry. 41 (5): 467–472. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2010.02.001.
- ^ Wang, Huanye; Liu, Weiguo; Zhang, Chuanlun L.; Jiang, Hongchen; Dong, Hailiang; Lu, Hongxuan; Wang, Jinxiang (January 2013). "Assessing the ratio of archaeol to caldarchaeol as a salinity proxy in highland lakes on the northeastern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau". Organic Geochemistry. 54: 69–77. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.09.011.
- ^ Rowland, S.J. (Jan 1990). "Production of acyclic isoprenoid hydrocarbons by laboratory maturation of methanogenic bacteria". Organic Geochemistry. 15 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(90)90181-x. ISSN 0146-6380.
- ^ Bligh, E. G.; Dyer, W. J. (August 1959). "A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology. 37 (8): 911–917. doi:10.1139/o59-099. ISSN 0576-5544. PMID 13671378. S2CID 7311923.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Demizu, Kazuhiro; Ohtsubo, Sadami; Kohno, Shuhei; Miura, Isao; Nishihara, Masateru; Koga, Yosuke (1992). "Quantitative determination of methanogenic cells based on analysis of ether-linked glycerolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography". Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering. 73 (2): 135–139. doi:10.1016/0922-338x(92)90553-7. ISSN 0922-338X.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ohtsubo, S (May 1993). "A sensitive method for quantification of aceticlastic methanogens and estimation of total methanogenic cells in natural environments based on an analysis of ether-linked glycerolipids". FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 12 (1): 39–50. doi:10.1016/0168-6496(93)90023-z. ISSN 0168-6496.
- ^ Martz, Robert F.; Sebacher, Daniel I.; White, David C. (February 1983). "Biomass measurement of methane forming bacteria in environmental samples". Journal of Microbiological Methods. 1 (1): 53–61. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(83)90007-6. ISSN 0167-7012. PMID 11540801.
- ^ Smith, G.C.; Floodgate, G.D. (October 1992). "A chemical method for estimating methanogenic biomass". Continental Shelf Research. 12 (10): 1187–1196. Bibcode:1992CSR....12.1187S. doi:10.1016/0278-4343(92)90078-x. ISSN 0278-4343.
- ^ Holzer, Gunther U.; Kelly, Patrick J.; Jones, William J. (July 1988). "Analysis of lipids from a hydrothermal vent methanogen and associated vent sediment by supercritical fluid chromatography". Journal of Microbiological Methods. 8 (3): 161–173. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(88)90017-6. ISSN 0167-7012.
- ^ King, Jerry (2002-01-22), "Supercritical Fluid Technology for Lipid Extraction, Fractionation, and Reactions", Lipid Biotechnology, CRC Press, doi:10.1201/9780203908198.ch34, ISBN 9780824706197
- Lipids
- Ethers