Bay of Quinte


The Bay of Quinte (/ˈkwɪnti/) is a long, narrow bay shaped like the letter "Z" on the northern shore of Lake Ontario in the province of Ontario, Canada. It is just west of the head of the Saint Lawrence River that drains the Great Lakes into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It is located about 200 kilometres (120 mi) east of Toronto and 350 kilometres (220 mi) west of Montreal.
The name "Quinte" is derived from "Kenté", which was the name of an early French Catholic mission located on the north shore of what is now Prince Edward County.[1] Officially, in the Mohawk language, the community is called "Kenhtè:ke", which means "the place of the bay". The Cayuga name is Tayęda:ne:gęˀ or Detgayę:da:negęˀ, "land of two logs."[2][3]
The Bay, as it is known locally, provides some of the best trophy walleye angling in North America as well as most sport fish common to the great lakes. The bay is subject to algal blooms in late summer. Zebra mussels as well as the other invasive species found in the Great Lakes are present.
The Quinte area played a vital role in bootlegging during Prohibition in the United States, with large volumes of liquor being produced in the area, and shipped via boat on the bay to Lake Ontario finally arriving in New York State where it was distributed. Illegal sales of liquor accounted for many fortunes in and around Belleville.
Tourism in the area is significant, especially in the summer months due to the Bay of Quinte and its fishing, local golf courses, provincial parks, and wineries.
Geography[]
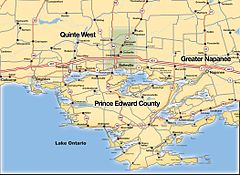
The northern side of the bay is defined by Ontario's mainland, while the southern side follows the shore of the Prince Edward County headland. Beginning in the east with the outlet to Lake Ontario, the bay runs west-southwest for 25 kilometres (16 mi) to Picton (although this section is also called Adolphus Reach), where it turns north-northwest for another 20 kilometres (12 mi) as far as Deseronto. From there it turns south-southwest again for another 40 kilometres (25 mi), running past Big Island on the south and Belleville on the north. The width of the bay rarely exceeds two kilometres (1.2 mi). The bay ends at Trenton (Quinte West) and the Trent River, both also on the north side. The Murray Canal has been cut through the "Carrying Place", the few kilometres separating the end of the bay and Lake Ontario on the west side. The Trent River is part of the Trent-Severn Waterway, a canal connecting Lake Ontario to Lake Simcoe and then Georgian Bay on Lake Huron.
There are several sub-bays off the Bay of Quinte, including Hay Bay, Big Bay, and Muscote Bay.
Quinte Region[]
Quinte is also a region comprising several communities situated along the Bay of Quinte, including Belleville, which is the largest city in the Quinte Region, and represents a midpoint between Montreal, Ottawa, and Toronto.
The Greater Bay of Quinte area includes the municipalities of Brighton, Quinte West, Belleville, Prince Edward County, and Greater Napanee as well as the Native Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory. Overall population of the area exceeds 200,000.[4]
Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte[]
The Mohawks of the Bay of Quinte (Kenhtè:ke Kanyen'kehá:ka)[3] on traditional Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory. Their reserve Band number 244, their current land base, is 73 km2 (18,000 acres) on the Bay of Quinte in southeastern Ontario east of Belleville and immediately to the west of Deseronto.[3]
The community takes its name from a variant spelling of Mohawk leader Joseph Brant's traditional Mohawk name, Thayendanegea (standardized spelling Thayentiné:ken), which means 'two pieces of fire wood beside each other'.[5] Officially, in the Mohawk language, the community is called "Kenhtè:ke" (Tyendinaga), which means "on the bay", and was the birthplace of Tekanawí:ta. The Cayuga name is Tyendinaga, Tayęda:ne:gęˀ or Detgayę:da:negęˀ, "land of two logs."[2]
Communities[]
- Belleville
- Quinte West
- Brighton
- Shannonville
- Napanee
- Deseronto
- Tyendinaga Mohawk Territory
- Ameliasburgh
- Picton
- Carrying Place
Education[]
The Quinte Region, specifically the City of Belleville, is home to . Other post-secondary schools in the region include Maxwell College of Advanced Technology, CDI College, and Quinte Literacy. Secondary schools in the region include Albert College (private school) and Sir James Whitney (a school for the deaf and severely hearing-impaired).
Industry and employment[]
The Quinte Region is home to a large number of national and international food processing manufacturers. Quinte also houses a large number of industries in the plastics & packaging sector, transportation sector, logistics sector and advanced manufacturing sector, including the following (just a few of over 350 industries located in the Bay of Quinte Region) :
- Essroc Canada a division of Italcementi
- Stream—Contact centre
- Autosystems Division of Decoma International—Automotive parts (lighting)
- Halla Climate Control Canada Ltd.—Automotive parts
- Procter and Gamble Inc.—Feminine hygiene products
- Kellogg—Breakfast cereal manufacturer
- Nestle Canada Inc.—Frozen and dry mix food service products
- Trenton Cold Storage Group Inc.—Refrigerated warehousing and distribution. Custom co-packing
- Parmalat Canada—Black Diamond Cheese Division—Cheese manufacturing and packaging
- Avaya—A telecommunications research and product development centre, providing customers worldwide with advanced communications and networking systems, and creating next-generation internet telephony solutions.
- Research Casting International—Canadian company specializing in moulding and casting for the production of museum exhibits
- Cooney Transport Ltd.—Trucking company
- Wellington Mushroom Farm / Highline Produce—Mushroom farm
- Domtech—Copper wiring
- ClearWater Design Canoe and Kayak—Boat manufacturer
- The SAB Group of Companies Limited—Consumer goods company
- Mapco Plastics—Biodegradable plastic packaging manufacturer[6]
- Citipack Distribution—Cash and carry[6]
- Babars Bazaar—International commodity trading[6]
- Jobsters Staffing—Staffing agency
Images[]

Picnic on the Bay in August 1909
The Bay of Quinte at night, with a view of CFB Trenton.
References[]
- ^ Great Canadian Lakes, Lake Ontario - Saving Souls in Kente Archived March 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved: 2010-04-15
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cayuga: Our Oral Legacy - Home. Cayuga Digital Dictionary". Archived from the original on 2012-03-26. Retrieved 2012-05-27.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Bruce Elliott Johansen; Barbara Alice Mann (2000). Encyclopedia of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois Confederacy). Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-313-30880-2. Retrieved 11 December 2011.
- ^ Demographics of the greater Bay of Quinte region Archived July 15, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Retrieved: 2010-04-19
- ^ Isaac, Ruth et al. A Spelling Worldist of Six Nations Mohawk. Brantford: The Woodland Indian Cultural-Educational Centre, 1986. Print
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Cameron, Alana (June 7, 2021). "Company moving to Quinte West". Quinte News. Retrieved July 23, 2021.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bay of Quinte. |
- Central Ontario
- Bays of Ontario
- Bays of Lake Ontario


