Bifascicular block
| Bifascicular block | |
|---|---|
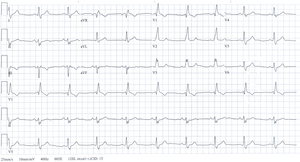 | |
| bifascicular block on an electrocardiogram | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
Bifascicular block is a conduction abnormality in the heart where two of the three main fascicles of the His/Purkinje system are blocked.
Most commonly, it refers to a combination of right bundle branch block (RBBB) and either left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) or left posterior fascicular block (LPFB), with the former being more common.[1]
Some authors consider left bundle branch block (LBBB) to be a technical bifascicular block, since the block occurs above the bifurcation of the left anterior and left posterior fascicles of the left bundle branch.[citation needed]
Diagnosis[]
This section is empty. You can help by . (September 2017) |
Treatment[]
In those with bifascicular block and no symptoms, little with respect to treatment is needed. In those with syncope, a pacemaker is recommended.[citation needed]
References[]
- ^ "Lesson VI - ECG Conduction Abnormalities". Archived from the original on 16 January 2009. Retrieved 2009-01-07.
External links[]
| Classification |
|---|
Categories:
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Circulatory disease stubs