Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation
Brihan Mumbai Municipal Corporation | |
|---|---|
 Seal of the Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai | |
| Type | |
| Type | Municipal Corporation |
| History | |
| Founded | 1888 |
| Leadership | |
Mayor | Kishori Pednekar (SHS) |
Deputy Mayor | Suhas Wadkar (SHS) |
Municipal Commissioner | I. S. Chahal, IAS |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 227 |
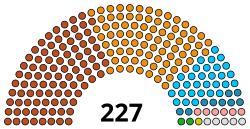 | |
Political groups | Government:115
BJP: 107 seats
MNS: 8 seats
Opposition:106 SS: 65 seats
INC: 33 seats
NCP: 8 seats
Others: AIMIM: 2 seats
SP: 6 seats |
| Elections | |
Last election | February 2017 |
Next election | 2022 |
| Motto | |
| यतो धर्मस्ततो जय: (Sanskrit) Where there is Righteousness, there shall be Victory | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Municipal Corporation Building, Mumbai | |
| Website | |
| portal | |
The Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai (MCGM; Marathi: बृहन्मुंबई महानगरपालिका, IAST: bṛhanmuṃbaī mahānagarapālikā),[1] formerly known as the Bombay Municipal Corporation, is the governing civic body of Mumbai, the capital city of Maharashtra. It is India's richest municipal corporation.[2][3] The MCGM's annual budget exceeds that of some of India's smaller states. It was established under the Bombay Municipal Corporation Act 1888.[4] MCGM is responsible for the civic infrastructure and administration of the city and some suburbs.
Administration[]
The MCGM is headed by an IAS officer who serves as Municipal Commissioner, wielding executive power. A quinquennial election is held to elect corporators, who are responsible for basic civic infrastructure and enforcing duty. The Mayor, usually from the majority party, serves as head of the house. As of June 2008, all administrative business in the MCGM was conducted in Marathi, a decision that sparked controversy,[5] following which the BMC eased its stance and began accepting forms in English.[6]
| Mayor | Kishori Pednekar[7] | 22 November 2019 |
| Deputy Mayor | Suhas Wadkar | 22 November 2019 |
| Municipal Commissioner | Iqbal Singh Chahal[8] | 8 May 2020 |
Legislature[]
As of 2017, the MCGM's legislature, also known as the Corporation Council, consisted of 227 members. 2017 was the first time 31 candidates contested from a single ward (164). Raghvendra Singh was the youngest independent candidate at age 21.[citation needed] MCGM is one of the richest municipal corporations in Asia.[9]
References[]
- ^ "Welcome to The Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai". Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation. Archived from the original on 24 February 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- ^ "BMC to open green channel for octroi". Financialexpress.com. 3 September 2007. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ "Gold & beautiful, News - Cover Story". Mumbai Mirror. Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2010.
- ^ "BMC-Act-1888.pdf" (PDF). Retrieved 12 January 2013.
- ^ "From today. MCGM will do business only in Marathi". The Times of India. 25 June 2008. Archived from the original on 11 August 2011. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ "BMC drops only marathi clause, to accept forms in english". Hindustan Times. 28 January 2012.
- ^ "Shiv Sena leader Kishori Pednekar elected Mayor of BMC". DDNews.Gov.in. Retrieved 29 November 2019.
- ^ "BMC Commissioner Praveen Pardeshi Replaced; Iqbal Chahal Becomes The New Commissioner Of Mumbai". MumbaiLive. Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- ^ Mishra, Sohit (21 February 2017). "BMC Elections 2017: Complete fact sheet of Asia's richest civic corporation". India.com. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
- Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation
- 1888 establishments in India
- Organizations established in 1888