Complex system
 |
| Complex systems |
|---|
| Topics |
A complex system is a system composed of many components which may interact with each other. Examples of complex systems are Earth's global climate, organisms, the human brain, infrastructure such as power grid, transportation or communication systems, social and economic organizations (like cities), an ecosystem, a living cell, and ultimately the entire universe.
Complex systems are systems whose behavior is intrinsically difficult to model due to the dependencies, competitions, relationships, or other types of interactions between their parts or between a given system and its environment. Systems that are "complex" have distinct properties that arise from these relationships, such as nonlinearity, emergence, spontaneous order, adaptation, and feedback loops, among others. Because such systems appear in a wide variety of fields, the commonalities among them have become the topic of their independent area of research. In many cases, it is useful to represent such a system as a network where the nodes represent the components and links to their interactions.
The term complex systems often refers to the study of complex systems, which is an approach to science that investigates how relationships between a system's parts give rise to its collective behaviors and how the system interacts and forms relationships with its environment.[1] The study of complex systems regards collective, or system-wide, behaviors as the fundamental object of study; for this reason, complex systems can be understood as an alternative paradigm to reductionism, which attempts to explain systems in terms of their constituent parts and the individual interactions between them.
As an interdisciplinary domain, complex systems draws contributions from many different fields, such as the study of self-organization and critical phenomena from physics, that of spontaneous order from the social sciences, chaos from mathematics, adaptation from biology, and many others. Complex systems is therefore often used as a broad term encompassing a research approach to problems in many diverse disciplines, including statistical physics, information theory, nonlinear dynamics, anthropology, computer science, meteorology, sociology, economics, psychology, and biology.
Key concepts[]
Systems[]

Complex systems are chiefly concerned with the behaviors and properties of systems. A system, broadly defined, is a set of entities that, through their interactions, relationships, or dependencies, form a unified whole. It is always defined in terms of its boundary, which determines the entities that are or are not part of the system. Entities lying outside the system then become part of the system's environment.
A system can exhibit properties that produce behaviors which are distinct from the properties and behaviors of its parts; these system-wide or global properties and behaviors are characteristics of how the system interacts with or appears to its environment, or of how its parts behave (say, in response to external stimuli) by virtue of being within the system. The notion of behavior implies that the study of systems is also concerned with processes that take place over time (or, in mathematics, some other phase space parameterization). Because of their broad, interdisciplinary applicability, systems concepts play a central role in complex systems.
As a field of study, a complex system is a subset of systems theory. General systems theory focuses similarly on the collective behaviors of interacting entities, but it studies a much broader class of systems, including non-complex systems where traditional reductionist approaches may remain viable. Indeed, systems theory seeks to explore and describe all classes of systems, and the invention of categories that are useful to researchers across widely varying fields is one of the systems theory's main objectives.
As it relates to complex systems, systems theory contributes an emphasis on the way relationships and dependencies between a system's parts can determine system-wide properties. It also contributes to the interdisciplinary perspective of the study of complex systems: the notion that shared properties link systems across disciplines, justifying the pursuit of modeling approaches applicable to complex systems wherever they appear. Specific concepts important to complex systems, such as emergence, feedback loops, and adaptation, also originate in systems theory.
Complexity[]
"Systems exhibit complexity" means that their behaviors cannot be easily inferred from their properties. Any modeling approach that ignores such difficulties or characterizes them as noise, then, will necessarily produce models that are neither accurate nor useful. As yet no fully general theory of complex systems has emerged for addressing these problems, so researchers must solve them in domain-specific contexts. Researchers in complex systems address these problems by viewing the chief task of modeling to be capturing, rather than reducing, the complexity of their respective systems of interest.
While no generally accepted exact definition of complexity exists yet, there are many archetypal examples of complexity. Systems can be complex if, for instance, they have chaotic behavior (behavior that exhibits extreme sensitivity to initial conditions, among other properties), or if they have emergent properties (properties that are not apparent from their components in isolation but which result from the relationships and dependencies they form when placed together in a system), or if they are computationally intractable to model (if they depend on a number of parameters that grows too rapidly with respect to the size of the system).
Networks[]
The interacting components of a complex system form a network, which is a collection of discrete objects and relationships between them, usually depicted as a graph of vertices connected by edges. Networks can describe the relationships between individuals within an organization, between logic gates in a circuit, between genes in gene regulatory networks, or between any other set of related entities.
Networks often describe the sources of complexity in complex systems. Studying complex systems as networks, therefore, enables many useful applications of graph theory and network science. Many complex systems, for example, are also complex networks, which have properties such as phase transitions and power-law degree distributions that readily lend themselves to emergent or chaotic behavior. The fact that the number of edges in a complete graph grows quadratically in the number of vertices sheds additional light on the source of complexity in large networks: as a network grows, the number of relationships between entities quickly dwarfs the number of entities in the network.
Nonlinearity[]

Complex systems often have nonlinear behavior, meaning they may respond in different ways to the same input depending on their state or context. In mathematics and physics, nonlinearity describes systems in which a change in the size of the input does not produce a proportional change in the size of the output. For a given change in input, such systems may yield significantly greater than or less than proportional changes in output, or even no output at all, depending on the current state of the system or its parameter values.
Of particular interest to complex systems are nonlinear dynamical systems, which are systems of differential equations that have one or more nonlinear terms. Some nonlinear dynamical systems, such as the Lorenz system, can produce a mathematical phenomenon known as chaos. Chaos, as it applies to complex systems, refers to the sensitive dependence on initial conditions, or "butterfly effect", that a complex system can exhibit. In such a system, small changes to initial conditions can lead to dramatically different outcomes. Chaotic behavior can, therefore, be extremely hard to model numerically, because small rounding errors at an intermediate stage of computation can cause the model to generate completely inaccurate output. Furthermore, if a complex system returns to a state similar to one it held previously, it may behave completely differently in response to the same stimuli, so chaos also poses challenges for extrapolating from experience.
Emergence[]

Another common feature of complex systems is the presence of emergent behaviors and properties: these are traits of a system that are not apparent from its components in isolation but which result from the interactions, dependencies, or relationships they form when placed together in a system. Emergence broadly describes the appearance of such behaviors and properties, and has applications to systems studied in both the social and physical sciences. While emergence is often used to refer only to the appearance of unplanned organized behavior in a complex system, emergence can also refer to the breakdown of an organization; it describes any phenomena which are difficult or even impossible to predict from the smaller entities that make up the system.
One example of a complex system whose emergent properties have been studied extensively is cellular automata. In a cellular automaton, a grid of cells, each having one of the finitely many states, evolves according to a simple set of rules. These rules guide the "interactions" of each cell with its neighbors. Although the rules are only defined locally, they have been shown capable of producing globally interesting behavior, for example in Conway's Game of Life.
Spontaneous order and self-organization[]
When emergence describes the appearance of unplanned order, it is spontaneous order (in the social sciences) or self-organization (in physical sciences). Spontaneous order can be seen in herd behavior, whereby a group of individuals coordinates their actions without centralized planning. Self-organization can be seen in the global symmetry of certain crystals, for instance the apparent radial symmetry of snowflakes, which arises from purely local attractive and repulsive forces both between water molecules and their surrounding environment.
Adaptation[]
Complex adaptive systems are special cases of complex systems that are adaptive in that they have the capacity to change and learn from experience. Examples of complex adaptive systems include the stock market, social insect and ant colonies, the biosphere and the ecosystem, the brain and the immune system, the cell and the developing embryo, the cities, manufacturing businesses and any human social group-based endeavor in a cultural and social system such as political parties or communities.[3]
Features[]
Complex systems may have the following features:[4]
- Cascading failures
- Due to the strong coupling between components in complex systems, a failure in one or more components can lead to cascading failures which may have catastrophic consequences on the functioning of the system.[5] Localized attack may lead to cascading failures and abrupt collapse in spatial networks.[6]
- Complex systems may be open
- Complex systems are usually open systems — that is, they exist in a thermodynamic gradient and dissipate energy. In other words, complex systems are frequently far from energetic equilibrium: but despite this flux, there may be ,[7] see synergetics.
- Complex systems may exhibit critical transitions

- Critical transitions are abrupt shifts in the state of ecosystems, the climate, financial systems or other complex systems that may occur when changing conditions pass a critical or bifurcation point.[9][10][11][12] The 'direction of critical slowing down' in a system's state space may be indicative of a system's future state after such transitions when delayed negative feedbacks leading to oscillatory or other complex dynamics are weak.[8]
- Complex systems may have a memory
- Recovery from a critical transition may require more than a simple return to the conditions at which a transition occurred, a phenomenon called hysteresis. The history of a complex system may thus be important. Because complex systems are dynamical systems they change over time, and prior states may have an influence on present states.[13] Interacting systems may have complex hysteresis of many transitions.[14] An example of hysteresis has been observed in urban traffic. [15]
- Complex systems may be nested
- The components of a complex system may themselves be complex systems. For example, an economy is made up of organisations, which are made up of people, which are made up of cells - all of which are complex systems. The arrangement of interactions within complex bipartite networks may be nested as well. More specifically, bipartite ecological and organisational networks of mutually beneficial interactions were found to have a nested structure.[16][17] This structure promotes indirect facilitation and a system's capacity to persist under increasingly harsh circumstances as well as the potential for large-scale systemic regime shifts.[18][19]
- Dynamic network of multiplicity
- As well as coupling rules, the dynamic network of a complex system is important. Small-world or scale-free networks[20][21][22] which have many local interactions and a smaller number of inter-area connections are often employed. Natural complex systems often exhibit such topologies. In the human cortex for example, we see dense local connectivity and a few very long axon projections between regions inside the cortex and to other brain regions.
- May produce emergent phenomena
- Complex systems may exhibit behaviors that are emergent, which is to say that while the results may be sufficiently determined by the activity of the systems' basic constituents, they may have properties that can only be studied at a higher level. For example, the termites in a mound have physiology, biochemistry and biological development that are at one level of analysis, but their social behavior and mound building is a property that emerges from the collection of termites and needs to be analyzed at a different level.
- Relationships are non-linear
- In practical terms, this means a small perturbation may cause a large effect (see butterfly effect), a proportional effect, or even no effect at all. In linear systems, the effect is always directly proportional to cause. See nonlinearity.
- Relationships contain feedback loops
- Both negative (damping) and positive (amplifying) feedback are always found in complex systems. The effects of an element's behavior are fed back in such a way that the element itself is altered.
History[]

Although arguably, humans have been studying complex systems for thousands of years, the modern scientific study of complex systems is relatively young in comparison to established fields of science such as physics and chemistry. The history of the scientific study of these systems follows several different research trends.
In the area of mathematics, arguably the largest contribution to the study of complex systems was the discovery of chaos in deterministic systems, a feature of certain dynamical systems that is strongly related to nonlinearity.[24] The study of neural networks was also integral in advancing the mathematics needed to study complex systems.
The notion of self-organizing systems is tied with work in nonequilibrium thermodynamics, including that pioneered by chemist and Nobel laureate Ilya Prigogine in his study of dissipative structures. Even older is the work by Hartree-Fock on the quantum chemistry equations and later calculations of the structure of molecules which can be regarded as one of the earliest examples of emergence and emergent wholes in science.
One complex system containing humans is the classical political economy of the Scottish Enlightenment, later developed by the Austrian school of economics, which argues that order in market systems is spontaneous (or emergent) in that it is the result of human action, but not the execution of any human design.[25][26]
Upon this, the Austrian school developed from the 19th to the early 20th century the economic calculation problem, along with the concept of dispersed knowledge, which were to fuel debates against the then-dominant Keynesian economics. This debate would notably lead economists, politicians, and other parties to explore the question of computational complexity.[citation needed]
A pioneer in the field, and inspired by Karl Popper's and Warren Weaver's works, Nobel prize economist and philosopher Friedrich Hayek dedicated much of his work, from early to the late 20th century, to the study of complex phenomena,[27] not constraining his work to human economies but venturing into other fields such as psychology,[28] biology and cybernetics. Cybernetician Gregory Bateson played a key role in establishing the connection between anthropology and systems theory; he recognized that the interactive parts of cultures function much like ecosystems.
While the explicit study of complex systems dates at least to the 1970s,[29] the first research institute focused on complex systems, the Santa Fe Institute, was founded in 1984.[30][31] Early Santa Fe Institute participants included physics Nobel laureates Murray Gell-Mann and Philip Anderson, economics Nobel laureate Kenneth Arrow, and Manhattan Project scientists George Cowan and Herb Anderson.[32] Today, there are over 50 institutes and research centers focusing on complex systems.[citation needed]
Since the late 1990s, the interest of mathematical physicists in researching economic phenomena has been on the rise. The proliferation of cross-disciplinary research with the application of solutions originated from the physics epistemology has entailed a gradual paradigm shift in the theoretical articulations and methodological approaches in economics, primarily in financial economics. The development has resulted in the emergence of a new branch of discipline, namely “econophysics,” which is broadly defined as a cross-discipline that applies statistical physics methodologies which are mostly based on the complex systems theory and the chaos theory for economics analysis.[33]
Applications[]
Complexity in practice[]
The traditional approach to dealing with complexity is to reduce or constrain it. Typically, this involves compartmentalization: dividing a large system into separate parts. Organizations, for instance, divide their work into departments that each deal with separate issues. Engineering systems are often designed using modular components. However, modular designs become susceptible to failure when issues arise that bridge the divisions.
Complexity management[]
As projects and acquisitions become increasingly complex, companies and governments are challenged to find effective ways to manage mega-acquisitions such as the Army Future Combat Systems. Acquisitions such as the FCS rely on a web of interrelated parts which interact unpredictably. As acquisitions become more network-centric and complex, businesses will be forced to find ways to manage complexity while governments will be challenged to provide effective governance to ensure flexibility and resiliency.[34]
Complexity economics[]
Over the last decades, within the emerging field of complexity economics, new predictive tools have been developed to explain economic growth. Such is the case with the models built by the Santa Fe Institute in 1989 and the more recent economic complexity index (ECI), introduced by the MIT physicist Cesar A. Hidalgo and the Harvard economist Ricardo Hausmann. Based on the ECI, Hausmann, Hidalgo and their team of The Observatory of Economic Complexity have .[citation needed]
Complexity and education[]
Focusing on issues of student persistence with their studies, Forsman, Moll and Linder explore the "viability of using complexity science as a frame to extend methodological applications for physics education research", finding that "framing a social network analysis within a complexity science perspective offers a new and powerful applicability across a broad range of PER topics".[35]
Complexity and modeling[]
One of Friedrich Hayek's main contributions to early complexity theory is his distinction between the human capacity to predict the behavior of simple systems and its capacity to predict the behavior of complex systems through modeling. He believed that economics and the sciences of complex phenomena in general, which in his view included biology, psychology, and so on, could not be modeled after the sciences that deal with essentially simple phenomena like physics.[36] Hayek would notably explain that complex phenomena, through modeling, can only allow pattern predictions, compared with the precise predictions that can be made out of non-complex phenomena.[37]
Complexity and chaos theory[]
Complexity theory is rooted in chaos theory, which in turn has its origins more than a century ago in the work of the French mathematician Henri Poincaré. Chaos is sometimes viewed as extremely complicated information, rather than as an absence of order.[38] Chaotic systems remain deterministic, though their long-term behavior can be difficult to predict with any accuracy. With perfect knowledge of the initial conditions and the relevant equations describing the chaotic system's behavior, one can theoretically make perfectly accurate predictions of the system, though in practice this is impossible to do with arbitrary accuracy. Ilya Prigogine argued[39] that complexity is non-deterministic and gives no way whatsoever to precisely predict the future.[40]
The emergence of complexity theory shows a domain between deterministic order and randomness which is complex.[41] This is referred to as the "edge of chaos".[42]
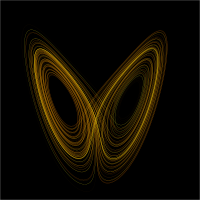
When one analyzes complex systems, sensitivity to initial conditions, for example, is not an issue as important as it is within chaos theory, in which it prevails. As stated by Colander,[43] the study of complexity is the opposite of the study of chaos. Complexity is about how a huge number of extremely complicated and dynamic sets of relationships can generate some simple behavioral patterns, whereas chaotic behavior, in the sense of deterministic chaos, is the result of a relatively small number of non-linear interactions.[41]
Therefore, the main difference between chaotic systems and complex systems is their history.[44] Chaotic systems do not rely on their history as complex ones do. Chaotic behavior pushes a system in equilibrium into chaotic order, which means, in other words, out of what we traditionally define as 'order'.[clarification needed] On the other hand, complex systems evolve far from equilibrium at the edge of chaos. They evolve at a critical state built up by a history of irreversible and unexpected events, which physicist Murray Gell-Mann called "an accumulation of frozen accidents".[45] In a sense chaotic systems can be regarded as a subset of complex systems distinguished precisely by this absence of historical dependence. Many real complex systems are, in practice and over long but finite periods, robust. However, they do possess the potential for radical qualitative change of kind whilst retaining systemic integrity. Metamorphosis serves as perhaps more than a metaphor for such transformations.
Complexity and network science[]
A complex system is usually composed of many components and their interactions. Such a system can be represented by a network where nodes represent the components and links represent their interactions.[22][46][47][48] For example, the Internet can be represented as a network composed of nodes (computers) and links (direct connections between computers), and the resilience of the Internet to failures has been studied using percolation theory, a form of complex systems analysis.[49] The failure and recovery of these networks is an open area of research.[13] Other examples of complex networks include social networks, financial institution interdependencies,[50] traffic systems,[51][52] airline networks,[53] biological networks, and climate networks.[54] Finally, entire networks often interact in a complex manner; if an individual complex system can be represented as a network, then interacting complex systems can be modeled as networks of networks with dynamic properties.[55][14]
One of the main reasons for high vulnerability of a network is their central control, i.e., a node which is disconnected from the cluster is usually regraded as failed. A percolation approach to generate and study decentralized systems is by using reinforced nodes that have their own support and redundancy links.[56] Network science has been found useful to better understand the complexity of earth systems.[57][58]
Notable scholars[]
- Robert McCormick Adams
- Christopher Alexander
- Philip Anderson
- Kenneth Arrow
- Robert Axelrod
- W. Brian Arthur
- Per Bak
- Yaneer Bar-Yam
- Albert-Laszlo Barabasi
- Gregory Bateson
- Ludwig von Bertalanffy
- Alexander Bogdanov
- Samuel Bowles
- Guido Caldarelli
- Paul Cilliers
- Walter Clemens, Jr.
- James P. Crutchfield
- Chris Danforth
- Peter Sheridan Dodds
- Brian Enquist
- Joshua Epstein
- Doyne Farmer
- Jay Forrester
- Nigel R. Franks
- Murray Gell-Mann
- Nigel Goldenfeld
- Vittorio Guidano
- James Hartle
- F. A. Hayek
- John Holland
- Alfred Hubler
- Arthur Iberall
- Stuart Kauffman
- J. A. Scott Kelso
- David Krakauer
- Ellen Levy
- Robert May
- Melanie Mitchell
- Cris Moore
- Edgar Morin
- Harold Morowitz
- Scott Page
- Luciano Pietronero
- David Pines
- Vladimir Pokrovskii
- Ilya Prigogine
- Sidney Redner
- Jerry Sabloff
- Cosma Shalizi
- Herbert Simon
- Dave Snowden
- Sergei Starostin
- Steven Strogatz
- Alessandro Vespignani
- Andreas Wagner
- Duncan Watts
- Geoffrey West
- Stephen Wolfram
- David Wolpert
See also[]
|
|
|
|
References[]
- ^ Bar-Yam, Yaneer (2002). "General Features of Complex Systems" (PDF). Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ^ Daniel Dennett (1995), Darwin's Dangerous Idea, Penguin Books, London, ISBN 978-0-14-016734-4, ISBN 0-14-016734-X
- ^ Skrimizea, Eirini; Haniotou, Helene; Parra, Constanza (2019). "On the 'complexity turn' in planning: An adaptive rationale to navigate spaces and times of uncertainty". Planning Theory. 18: 122–142. doi:10.1177/1473095218780515. S2CID 149578797.
- ^ Alan Randall (2011). Risk and Precaution. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139494793.
- ^ S. V. Buldyrev; R. Parshani; G. Paul; H. E. Stanley; S. Havlin (2010). "Catastrophic cascade of failures in interdependent networks". Nature. 464 (7291): 1025–8. arXiv:0907.1182. Bibcode:2010Natur.464.1025B. doi:10.1038/nature08932. PMID 20393559. S2CID 1836955.
- ^ Berezin, Yehiel; Bashan, Amir; Danziger, Michael M.; Li, Daqing; Havlin, Shlomo (2015). "Localized attacks on spatially embedded networks with dependencies". Scientific Reports. 5 (1): 8934. Bibcode:2015NatSR...5E8934B. doi:10.1038/srep08934. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4355725. PMID 25757572.
- ^ Pokrovskii, Vladimir (2021). Thermodynamics of Complex Systems: Principles and applications. IOP Publishing, Bristol, UK. Bibcode:2020tcsp.book.....P.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lever, J. Jelle; Leemput, Ingrid A.; Weinans, Els; Quax, Rick; Dakos, Vasilis; Nes, Egbert H.; Bascompte, Jordi; Scheffer, Marten (2020). "Foreseeing the future of mutualistic communities beyond collapse". Ecology Letters. 23 (1): 2–15. doi:10.1111/ele.13401. PMC 6916369. PMID 31707763.
- ^ Scheffer, Marten; Carpenter, Steve; Foley, Jonathan A.; Folke, Carl; Walker, Brian (October 2001). "Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems". Nature. 413 (6856): 591–596. Bibcode:2001Natur.413..591S. doi:10.1038/35098000. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 11595939. S2CID 8001853.
- ^ Scheffer, Marten (26 July 2009). Critical transitions in nature and society. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691122045.
- ^ Scheffer, Marten; Bascompte, Jordi; Brock, William A.; Brovkin, Victor; Carpenter, Stephen R.; Dakos, Vasilis; Held, Hermann; van Nes, Egbert H.; Rietkerk, Max; Sugihara, George (September 2009). "Early-warning signals for critical transitions". Nature. 461 (7260): 53–59. Bibcode:2009Natur.461...53S. doi:10.1038/nature08227. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 19727193. S2CID 4001553.
- ^ Scheffer, Marten; Carpenter, Stephen R.; Lenton, Timothy M.; Bascompte, Jordi; Brock, William; Dakos, Vasilis; Koppel, Johan van de; Leemput, Ingrid A. van de; Levin, Simon A.; Nes, Egbert H. van; Pascual, Mercedes; Vandermeer, John (19 October 2012). "Anticipating Critical Transitions". Science. 338 (6105): 344–348. Bibcode:2012Sci...338..344S. doi:10.1126/science.1225244. hdl:11370/92048055-b183-4f26-9aea-e98caa7473ce. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 23087241. S2CID 4005516. Archived from the original on 24 June 2020. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Majdandzic, Antonio; Podobnik, Boris; Buldyrev, Sergey V.; Kenett, Dror Y.; Havlin, Shlomo; Eugene Stanley, H. (2013). "Spontaneous recovery in dynamical networks". Nature Physics. 10 (1): 34–38. Bibcode:2014NatPh..10...34M. doi:10.1038/nphys2819. ISSN 1745-2473. S2CID 18876614.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Majdandzic, Antonio; Braunstein, Lidia A.; Curme, Chester; Vodenska, Irena; Levy-Carciente, Sary; Eugene Stanley, H.; Havlin, Shlomo (2016). "Multiple tipping points and optimal repairing in interacting networks". Nature Communications. 7: 10850. arXiv:1502.00244. Bibcode:2016NatCo...710850M. doi:10.1038/ncomms10850. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 4773515. PMID 26926803.
- ^ Guanwen Zeng, Jianxi Gao, Louis Shekhtman, Shengmin Guo, Weifeng Lv, Jianjun Wu, Hao Liu, Orr Levy, Daqing Li, Ziyou Gao, H Eugene Stanley, Shlomo Havlin (2020). "Multiple metastable network states in urban traffic". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (30): 17528–17534. doi:10.1073/pnas.1907493117. PMC 7395445. PMID 32661171.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Bascompte, J.; Jordano, P.; Melian, C. J.; Olesen, J. M. (24 July 2003). "The nested assembly of plant-animal mutualistic networks". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (16): 9383–9387. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.9383B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1633576100. PMC 170927. PMID 12881488.
- ^ Saavedra, Serguei; Reed-Tsochas, Felix; Uzzi, Brian (January 2009). "A simple model of bipartite cooperation for ecological and organizational networks". Nature. 457 (7228): 463–466. Bibcode:2009Natur.457..463S. doi:10.1038/nature07532. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 19052545. S2CID 769167.
- ^ Bastolla, Ugo; Fortuna, Miguel A.; Pascual-García, Alberto; Ferrera, Antonio; Luque, Bartolo; Bascompte, Jordi (April 2009). "The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity". Nature. 458 (7241): 1018–1020. Bibcode:2009Natur.458.1018B. doi:10.1038/nature07950. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 19396144. S2CID 4395634.
- ^ Lever, J. Jelle; Nes, Egbert H. van; Scheffer, Marten; Bascompte, Jordi (2014). "The sudden collapse of pollinator communities". Ecology Letters. 17 (3): 350–359. doi:10.1111/ele.12236. hdl:10261/91808. ISSN 1461-0248. PMID 24386999.
- ^ A. L. Barab´asi, R. Albert (2002). "Statistical mechanics of complex networks". Reviews of Modern Physics. 74 (1): 47–94. arXiv:cond-mat/0106096. Bibcode:2002RvMP...74...47A. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.242.4753. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.74.47. S2CID 60545.
- ^ M. Newman (2010). Networks: An Introduction. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-920665-0.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Reuven Cohen, Shlomo Havlin (2010). Complex Networks: Structure, Robustness and Function. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-84156-6.
- ^ "complexity map castellani map of complexity science, complexity theory, complexity science, complexity, brian castellani, durham sociology complexity". www.art-sciencefactory.com.
- ^ "History of Complex Systems". Archived from the original on November 23, 2007.
- ^ Ferguson, Adam (1767). An Essay on the History of Civil Society. London: T. Cadell. Part the Third, Section II, p. 205.
- ^ Friedrich Hayek, "The Results of Human Action but Not of Human Design" in New Studies in Philosophy, Politics, Economics, Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1978, pp. 96–105.
- ^ Bruce J. Caldwell, Popper and Hayek: Who influenced whom? Archived 2018-12-11 at the Wayback Machine, Karl Popper 2002 Centenary Congress, 2002.
- ^ Friedrich von Hayek, The Sensory Order: An Inquiry into the Foundations of Theoretical Psychology, The University of Chicago Press, 1952.
- ^ Vemuri, V. (1978). Modeling of Complex Systems: An Introduction. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0127165509.
- ^ Ledford, H (2015). "How to solve the world's biggest problems". Nature. 525 (7569): 308–311. Bibcode:2015Natur.525..308L. doi:10.1038/525308a. PMID 26381968.
- ^ "History | Santa Fe Institute". www.santafe.edu. Archived from the original on 2019-04-03. Retrieved 2018-05-17.
- ^ Waldrop, M. M. (1993). Complexity: The emerging science at the edge of order and chaos. Simon and Schuster.
- ^ Ho, Y. J.; Ruiz Estrada, M. A; Yap, S. F. (2016). "The evolution of complex systems theory and the advancement of econophysics methods in the study of stock market crashes". Labuan Bulletin of International Business & Finance. 14: 68–83.
- ^ "CSIS paper: "Organizing for a Complex World: The Way Ahead" (PDF).
- ^ Forsman, Jonas; Moll, Rachel; Linder, Cedric (2014). "Extending the theoretical framing for physics education research: An illustrative application of complexity science". Physical Review Special Topics: Physics Education Research. 10 (2): 020122. Bibcode:2014PRPER..10b0122F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevSTPER.10.020122. hdl:10613/2583.
- ^ "Reason Magazine - The Road from Serfdom". Archived from the original on 2007-03-10. Retrieved 2017-09-22.
- ^ "The Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel 1974". NobelPrize.org.
- ^ Hayles, N. K. (1991). Chaos Bound: Orderly Disorder in Contemporary Literature and Science. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY.
- ^ Prigogine, I. (1997). The End of Certainty, The Free Press, New York.
- ^ See also D. Carfì (2008). "Superpositions in Prigogine approach to irreversibility". AAPP: Physical, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences. 86 (1): 1–13..
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cilliers, P. (1998). Complexity and Postmodernism: Understanding Complex Systems, Routledge, London.
- ^ Per Bak (1996). How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organized Criticality, Copernicus, New York, U.S.
- ^ Colander, D. (2000). The Complexity Vision and the Teaching of Economics, E. Elgar, Northampton, Massachusetts.
- ^ Buchanan, M. (2000). Ubiquity : Why catastrophes happen, three river press, New-York.
- ^ Gell-Mann, M. (1995). What is Complexity? Complexity 1/1, 16-19
- ^ Dorogovtsev, S.N.; Mendes, J.F.F. (2003). Evolution of Networks. Adv. Phys. 51. p. 1079. arXiv:cond-mat/0106144. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198515906.001.0001. ISBN 9780198515906.
- ^ Fortunato, Santo (2011). "Reuven Cohen and Shlomo Havlin: Complex Networks". Journal of Statistical Physics. 142 (3): 640–641. Bibcode:2011JSP...142..640F. doi:10.1007/s10955-011-0129-7. ISSN 0022-4715. S2CID 121892672.
- ^ Newman, Mark (2010). Networks. doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199206650.001.0001. ISBN 9780199206650.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Cohen, Reuven; Erez, Keren; ben-Avraham, Daniel; Havlin, Shlomo (2001). "Cohen, Erez, ben-Avraham, and Havlin Reply". Physical Review Letters. 87 (21): 219802. Bibcode:2001PhRvL..87u9802C. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.219802. ISSN 0031-9007.
- ^ Battiston, Stefano; Caldarelli, Guido; May, Robert M.; Roukny, tarik; Stiglitz, Joseph E. (2016-09-06). "The price of complexity in financial networks". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (36): 10031–10036. Bibcode:2016PNAS..11310031B. doi:10.1073/pnas.1521573113. PMC 5018742. PMID 27555583.
- ^ Li, Daqing; Fu, Bowen; Wang, Yunpeng; Lu, Guangquan; Berezin, Yehiel; Stanley, H. Eugene; Havlin, Shlomo (2015-01-20). "Percolation transition in dynamical traffic network with evolving critical bottlenecks". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (3): 669–672. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112..669L. doi:10.1073/pnas.1419185112. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4311803. PMID 25552558.
- ^ Limiao Zhang, Guanwen Zeng; Daqing Li, Hai-Jun Huang; H Eugene Stanley, Shlomo Havlin (2019). "Scale-free resilience of real traffic jams". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (18): 8673–8678. arXiv:1804.11047. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116.8673Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.1814982116. PMC 6500150. PMID 30979803.
- ^ Barrat, A.; Barthelemy, M.; Pastor-Satorras, R.; Vespignani, A. (2004). "The architecture of complex weighted networks". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 101 (11): 3747–3752. arXiv:cond-mat/0311416. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.3747B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400087101. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 374315. PMID 15007165.
- ^ Yamasaki, K.; Gozolchiani, A.; Havlin, S. (2008). "Climate Networks around the Globe are Significantly Affected by El Niño". Physical Review Letters. 100 (22): 228501. Bibcode:2008PhRvL.100v8501Y. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.228501. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 18643467. S2CID 9268697.
- ^ Gao, Jianxi; Buldyrev, Sergey V.; Stanley, H. Eugene; Havlin, Shlomo (2011). "Networks formed from interdependent networks" (PDF). Nature Physics. 8 (1): 40–48. Bibcode:2012NatPh...8...40G. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.379.8214. doi:10.1038/nphys2180. ISSN 1745-2473.
- ^ X. Yuan, Y. Hu, H.E. Stanley, S. Havlin (2017). "Eradicating catastrophic collapse in interdependent networks via reinforced nodes". PNAS. 114 (13): 3311–3315. arXiv:1605.04217. Bibcode:2017PNAS..114.3311Y. doi:10.1073/pnas.1621369114. PMC 5380073. PMID 28289204.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ J Fan, J Meng, J Ludescher, X Chen, Y Ashkenazy, J Kurths, S Havlin, Hans Joachim Schellnhuber (2021). "Statistical physics approaches to the complex Earth system". Physics Reports. 896: 1–84. arXiv:2009.04918. Bibcode:2021PhR...896....1F. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2020.09.005. PMC 7532523. PMID 33041465.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ A. Gozolchiani, K. Yamasaki, S. Havlin (2011). "The Emergence of El-Nino as an Autonomous Component in the Climate Network". Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (14): 148501. arXiv:1010.2605. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.148501. PMID 22107243. S2CID 1062870.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading[]
- Complexity Explained.
- L.A.N. Amaral and J.M. Ottino, Complex networks — augmenting the framework for the study of complex system, 2004.
- Chu, D.; Strand, R.; Fjelland, R. (2003). "Theories of complexity". Complexity. 8 (3): 19–30. Bibcode:2003Cmplx...8c..19C. doi:10.1002/cplx.10059.
- Walter Clemens, Jr., Complexity Science and World Affairs, SUNY Press, 2013.
- Gell-Mann, Murray (1995). "Let's Call It Plectics". Complexity. 1 (5): 3–5. Bibcode:1996Cmplx...1e...3G. doi:10.1002/cplx.6130010502.
- A. Gogolin, A. Nersesyan and A. Tsvelik, Theory of strongly correlated systems , Cambridge University Press, 1999.
- Nigel Goldenfeld and Leo P. Kadanoff, Simple Lessons from Complexity, 1999
- Kelly, K. (1995). Out of Control, Perseus Books Group.
- Syed M. Mehmud (2011), A Healthcare Exchange Complexity Model
- Preiser-Kapeller, Johannes, "Calculating Byzantium. Social Network Analysis and Complexity Sciences as tools for the exploration of medieval social dynamics". August 2010
- Donald Snooks, Graeme (2008). "A general theory of complex living systems: Exploring the demand side of dynamics". Complexity. 13 (6): 12–20. Bibcode:2008Cmplx..13f..12S. doi:10.1002/cplx.20225.
- Stefan Thurner, Peter Klimek, Rudolf Hanel: Introduction to the Theory of Complex Systems, Oxford University Press, 2018, ISBN 978-0198821939
- SFI @30, Foundations & Frontiers[permanent dead link] (2014).
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Complex systems. |
| Look up complex systems in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- "The Open Agent-Based Modeling Consortium".
- "Complexity Science Focus".
- "Santa Fe Institute".
- "The Center for the Study of Complex Systems, Univ. of Michigan Ann Arbor".
- "INDECS". (Interdisciplinary Description of Complex Systems)
- "Introduction to Complexity - Free online course by Melanie Mitchell". Archived from the original on 2018-08-30. Retrieved 2018-08-29.
- Jessie Henshaw (October 24, 2013). "Complex Systems". Encyclopedia of Earth.
- Introduction to complex systems-short course by Shlomo Havlin
- Complex systems in scholarpedia.
- Complex Systems Society
- Complexity Science Hub Vienna
- (Australian) Complex systems research network.
- Complex Systems Modeling based on Luis M. Rocha, 1999.
- CRM Complex systems research group
- The Center for Complex Systems Research, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
- FuturICT — Exploring and Managing our Future
- Complex dynamics
- Complex systems theory
- Cybernetics
- Emergence
- Systems theory
- Systems science
- Mathematical modeling