Constitutional carry
In the United States, the term constitutional carry, also called permitless carry,[1] unrestricted carry,[2] or Vermont carry,[3] refers to the legal carrying of a handgun, either openly or concealed, without a license or permit.[4][5][3] The phrase does not typically refer to the unrestricted carrying of a long gun, a knife, or other weapons. The scope and applicability of constitutional carry may vary by state.[6]
The phrase "constitutional carry" reflects the view that the Second Amendment to the U.S. Constitution does not abide restrictions on gun rights, including the right to carry or bear arms.
The U.S. Supreme Court had never extensively interpreted the Second Amendment until the landmark case District of Columbia v. Heller in 2008.[7] Prior to this, a tapestry of different and sometimes conflicting laws about carrying firearms developed across the nation.[8] In deciding the case, the Court found that self-defense was a "...central component of the 2nd Amendment" and D.C.'s handgun ban was invalidated. The Court further stated that some state or local gun controls are allowed. The Heller case was extended by the Supreme Court in the 2010 decision McDonald v. Chicago, which held that the 2nd and 14th Amendments to the U.S. Constitution were "fully incorporated" and thus the right to "...keep and bear arms applies to the states and not 'in a watered-down version' but 'fully applicable'...," and limits state and local governments in passing laws that restrict this individual and fundamental right to "...keep and bear arms," for self-defense.
All of the state laws described below operate in the context of federal regulation regarding the transfer and sale of firearms. Firearms and ammunition are subject to taxation as well.
U.S. jurisdictions that have constitutional carry[]

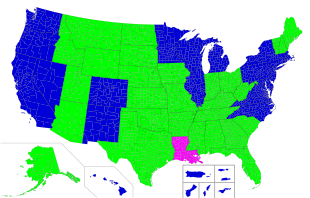


As of June 16, 2021, Alaska, Arizona, Arkansas, Idaho, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, New Hampshire, North Dakota (residents only; concealed carry only), Oklahoma, South Dakota, Tennessee (handguns only), Texas (effective September 1, 2021), Utah, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wyoming do not require a permit to carry a loaded concealed firearm for any person of age who is not prohibited from owning a firearm. Permitless carry in North Dakota is applicable to residents only; nonresidents must have a permit to carry a handgun concealed or openly. Permitless concealed carry in Mississippi only covers certain manners of carrying. Permitless carry in Oklahoma applies to both residents and nonresidents 21+ as well as 18+ nonresidents who can carry without a permit in their home state. All aforementioned jurisdictions do not require a permit to openly carry either except for North Dakota and certain localities in Missouri.
On July 26, 2014, Washington, D.C. became a permitless carry jurisdiction for a few days when its ban on carrying a handgun was ruled unconstitutional, and the ruling was not stayed.[9] The ruling said that any resident who had a legally registered handgun could carry it without a permit and nonresidents without felony convictions could carry as well. The ruling was then stayed on July 29, 2014.[10][11][12][13]
In June 2015, following victory in a class-action suit brought by "Damas de la Segunda Enmienda" Ladies of the Second Amendment (an affiliate of the Second Amendment Foundation) the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico's carry and licensing regulations were struck down, eliminating the requirement to obtain a permit.[14][15] On October 31, 2016, The Supreme Court of Puerto Rico denied a motion for reconsideration of a previous Court of Appeals decision that had found the Weapons Act to be constitutional.[16]
Vermont does not have any provision for issue of concealed-carry licenses, as none has ever been necessary. As such, Vermont residents wishing to carry handguns in other states must acquire a license from a state which is valid in their destination. All other constitutional carry states previously had concealed-carry license requirements prior to adoption of unrestricted carry laws, and continue to issue licenses on a shall-issue basis for the purposes of inter-state reciprocity (allowing residents of the state to travel to other states with a concealed weapon, abiding by that state's law).
Alaska[]
On June 11, 2003, Alaska governor Frank Murkowski signed House Bill 102 into law (effective September 9, 2003), making Alaska the first state to rescind its requirement for a concealed carry permit.[17] The bill eliminated the crime of simply carrying a concealed weapon by changing the definition of the crime. The section of law that describes the first instance of "misconduct involving weapons in the 5th degree" now requires that a person must either fail to inform a law enforcement officer of the weapon upon contact, fail to allow the law enforcement officer to secure the weapon (or to properly secure the weapon him/herself) upon contact, or if at another person's home, fail to obtain permission from a resident to have a concealed weapon on the premises. No permit is required to open carry or conceal carry for both residents and nonresidents. Open carry is 16+ and concealed carry is 21+.[18]
Arizona[]
On April 16, 2010, Arizona governor Jan Brewer signed Senate Bill 1108 into law (effective July 29, 2010).[19][20] The law eliminated the requirement to obtain a permit to carry a concealed weapon in Arizona for U.S. citizens or U.S residents 21 and older. The process to obtain a permit was left in place so that Arizona residents could still obtain permits in order to carry concealed in other states or to carry in a restaurant or bar that serves alcohol.[21] This extends to both Arizona residents and nonresidents with no permit required to open carry at 18 and none required to concealed carry 21 and up.
Arkansas[]
Prior to August 16, 2013, Arkansas law (§ 5-73-120) prohibited "...carrying a weapon...with a purpose to employ the handgun, knife, or club as a weapon against a person." Among other exceptions, Arkansas law allowed a defense to the charge of carrying of a weapon if "[t]he person is on a journey..." but did not define what constituted a "journey." Another defense permitted an individual to carry a concealed weapon if the person had a valid concealed weapons license.[22] This provision was generally interpreted to prohibit open carry.
On August 16, 2013, Arkansas enacted Act 746.[22] This act made two major changes. First, it statutorily defined a "journey" as "...travel beyond the county in which a person lives..." Because traveling on a journey is one of the defenses to § 5-73-120, a plain reading of the statute would indicate that the prohibition against carrying a weapon would now apply only to a person traveling within their home county. Second, it modified § 5-73-120 to prohibit "...carrying a weapon...with a purpose to attempt to unlawfully employ the handgun, knife, or club as a weapon against a person." Various firearms groups interpreted this provision to require that the state must now prove that a person actually intends to use a weapon to commit a crime; and without proving this intent, possession of weapons, whether openly or concealed, is now legal.[23]
However, some confusion still existed. On July 8, 2013, Arkansas Attorney General Dustin McDaniel issued an opinion stating that Act 746 did not authorize open carry.[24] On August 18, 2015, Arkansas Attorney General Leslie Rutledge issued a different opinion, saying that open carry of a weapon following Act 746's passage is now generally legal, provided that the person has no intent to unlawfully employ said weapon. Rutledge also opined that, while mere possession of a loaded handgun was formerly sufficient to establish "intent to employ" it as a weapon, such possession is now no longer sufficient to convict someone under § 5-73-120. Rather, the state must now additionally prove intent to unlawfully use the weapon. However, Rutledge also opined that concealed carry generally remains illegal without a permit. Because Act 746 did not remove or modify the other sections of Arkansas law pertaining to issuing concealed weapons permits, she concluded that possession of a concealed weapon without a permit could be construed as meeting the "unlawful purpose" requirement.[25] However, various firearms groups disputed this opinion and argued that, because § 5-73-120 (and specifically subsection (a)) permits unlicensed open carry, the same legal logic would dictate that concealed carry without a permit would also be legal.[23] Further adding to the confusion was the fact that Act 746 changed the list of § 5-73-120 exceptions, including possession while on a journey and possession of a concealed handgun with a concealed handgun permit, from a list of "affirmative defenses" to a list of "permissible circumstances." Rutledge noted in her opinion that such change could be construed as creating a "non-exhaustive list of circumstances under which it is permissible to carry a handgun," thereby permitting a person to assert additional circumstances not spelled out in the statute. She also noted that future legislation would be the best solution to clear up the confusion that Act 746 has caused.[25]
On October 17, 2018, the Arkansas Court of Appeals issued a ruling that clarified that the mere carrying of a handgun is not a crime by itself absent a purpose to attempt to unlawfully employ the handgun as a weapon against a person, and any ambiguity would be found in favor of the defendant per the rule of lenity.[26] This effectively ends the dispute on the legality of permitless carry in Arkansas and allows for the unlicensed open carry and concealed carry of a weapon.[27]
Idaho[]
As of July 1, 2020, HB 516 extended the law to be applicable to all U.S. citizens and active military members.[28] Prior permitless carry (SB 1389) was limited to Idaho residents and active military members from July 1, 2016 to July 1, 2020.[citation needed] The minimum age was lowered from 21 to 18 on July 1, 2019 while within city limits (minimum age was already 18 outside city limits)[29][30] and allows for any weapon, not just handguns.[31] Before July 1, 2016, permitless concealed carry was allowed only outside city limits with only permitless open carry being legal statewide. Now both open and concealed carry without a permit is allowed for residents and nonresidents 18+ statewide.
Iowa[]
On March 17, 2021, the Iowa House of Representatives passed HF 756, 60–37. The Iowa Senate passed the bill on March 22, 2021, 31–17. Among other provisions, it removes the requirement for a permit to carry a firearm concealed or to carry a firearm openly within city limits. Governor Kim Reynolds signed the bill on April 2, 2021, and it took effect on July 1, 2021.[32]
Kansas[]
SB45 was introduced in the Kansas Senate in early 2015. The bill initially passed the Senate 31-7 on February 26. The bill was sent to the House, amended, and passed 85–39 on March 25. The Senate then concurred, passing the amended bill 31-8 (also on March 25). On April 2, the bill was signed by Governor Sam Brownback (effective July 1, 2015), establishing constitutional carry in Kansas.[33][34] Can carry concealed at 21 years old or older and open carry at 18 years or older without a permit for both residents and nonresidents.[35]
Kansas issues licenses to carry concealed handguns on a shall-issue basis. As of April 2015, over 87,000 current permits are issued.[36][37] Kansas will continue to issue permits so that Kansas residents may carry in other states that accept Kansas concealed carry permits.[34]
Kentucky[]
On February 14, 2019, the Kentucky Senate passed SB150 by a vote of 29–8. It then passed the Kentucky House of Representatives on March 1, 2019, by a vote of 60–37.[38] On March 11, 2019, Governor Matt Bevin signed the bill into law (effective June 27, 2019). It allows residents and nonresidents who are 21 years old or older who are otherwise able to lawfully possess a firearm, to carry concealed firearms (or any other deadly weapon) without a permit. Open carry without a permit for both residents and nonresidents 18 years old or older was already legal as guaranteed by the State Constitution.
Maine[]
In 2015, LD 652 was a constitutional carry bill that was under consideration by the Maine Legislature. It had 17 co-sponsors in the Senate and 79 co-sponsors in the House.[39] LD 652 was signed into law by Governor Paul LePage on July 8, 2015 (effective October 15, 2015), applying to both residents and nonresidents with no permit being required at 18+ for open carry and none required for concealed carry for 21+.[40]
Mississippi[]
In 2013, the Unlicensed Open Carry Bill was passed to clarify that no permit was needed to open carry at the age of 18+ and was clarified by the Mississippi Supreme Court that the Right to Open Carry was guaranteed by the Mississippi State Constitution. As of July 1, 2015, the concealed carry law was amended to say "no license shall be required under this section for a loaded or unloaded pistol or revolver carried in a purse, handbag, satchel, other similar bag or briefcase or fully enclosed case."[41] On April 15, 2016, the law was further expanded to include belt and shoulder holsters and sheaths.[42][43] This effectively allows for constitutional carry in Mississippi for residents and nonresidents age 18 and up. However, some forms of concealed carrying would still require a permit (e.g. Mexican carry[Note 1] or concealed in an ankle holster).
Missouri[]
SB 656 allows for permitless concealed carry for anyone who may lawfully own a gun. The bill was passed by the legislature in 2016, but Governor Nixon vetoed it on June 27, 2016. The legislature reconvened for the veto-override session on September 14, 2016. The Senate voted to override the veto with a 24 – 6 vote (23 required) and the House followed through shortly thereafter with a 112 – 41 vote (109 required). No permit is needed for open carry or concealed carry and applies to both residents and nonresidents. While no permit is required for either form of carrying, only concealed carry falls fully under state-preemption. Therefore, unlicensed open carry can still be restricted by local city ordinances unless one possesses a concealed carry permit, thus exempting them from local open carry restrictions. The law went into effect on January 1, 2017.[44]
Montana[]
On February 18, 2021, Montana Governor Greg Gianforte signed HB 102 into law, which allows residents and nonresidents 18 or older to concealed carry a firearm throughout the state without a permit. Permitless open carry was already legal. HB 102 also removed a number of Montana's "gun-free" zones, which previously prohibited carrying a firearm in select locations throughout the state. HB 102 takes effect immediately, save one provision altering the law on carrying a handgun on college and university grounds, which will go into effect June 1, 2021.[45][46][47] This law makes Montana the 18th state to allow permitless carry of a firearm for anyone 18+.[48] Previously, permitless concealed carry was allowed if a person was outside the official boundaries of a city or town or the confines of a logging, lumbering, mining, or railroad camp or who is lawfully engaged in hunting, fishing, trapping, camping, hiking, backpacking, farming, ranching, or other outdoor activity in which weapons are often carried for recreation or protection.[49]
Previously, HB 271 was introduced in 2011 to allow constitutional carry. The bill passed the House with a vote of 55–45 and passed the Senate with a vote of 29–21.[50][51] It was vetoed by then-Governor Brian Schweitzer on May 10, 2011,[52] and was unable to gather the necessary two-thirds majority to overturn the veto.[53]
HB 298 was introduced in the 2015 legislative session, which would have legalized firearms carry statewide for all persons who are not prohibited from possessing a firearm. The bill passed the House 56-43 and the Senate 28-21 but was later vetoed by Governor Steve Bullock.[54][55][56]
New Hampshire[]
In early 2017, several senators and representatives introduced New Hampshire Senate Bill 12, which proposed removing the requirement for a license to carry a loaded concealed handgun. The bill also proposed extending the minimum license period from four years to five years, removing the discretionary "suitable person" language from the Pistol/Revolver License law, and directing the state police to pursue reciprocity agreements.[57][58] On January 19, it was passed by the New Hampshire Senate by a vote of 13 – 10.[59] Governor Chris Sununu, who took office in January 2017, expressed support for this bill after the Senate vote, stating, "I am pleased that the State Senate today voted to advance common-sense legislation in support of a citizen’s fundamental right to carry a firearm, joining neighboring states throughout the region and across the country."[60] On February 9, it was passed by the New Hampshire House by a vote of 200 – 97.[61] Governor Sununu signed the bill into law on February 22, 2017, and it became effective immediately. Thus, no permit is required for open carry or concealed carry of handguns; and this applies to both residents and nonresidents over the age of 18.[62]
Previously, carrying a concealed handgun unloaded was legal without a license. A New Hampshire Supreme Court decision in 2013 clarified that the law did not prohibit carrying a concealed handgun if it is unloaded (no round is chambered).[63]
North Dakota (residents only; concealed carry only)[]
On March 23, 2017, North Dakota Governor Doug Burgum signed House Bill 1169 (effective August 1, 2017).[64] Under its provisions, people carrying concealed without a concealed weapons license will need to carry a form of state-issued photo ID, must be a North Dakota resident for at least 30 days (originally 1 year), must have had a state-issued ID for 1 year, must inform police about their handgun upon contact, and must not otherwise be prohibited from possessing a firearm by law. Minimum age is 18. Open carry of a loaded handgun will still require a permit, but no permit is required to open carry an unloaded handgun; one is allowed to possess a loaded magazine as long as it is not inserted into the gun. Carrying in a vehicle was originally thought of as requiring a permit, but Attorney General Wayne Stenehjem issued an opinion interpreting the law as allowing for constitutional carry within vehicles.[65] This was codified in 2019.[66] Nonresidents are required to have a resident permit recognized by North Dakota to carry openly or concealed.
Oklahoma[]
On February 27, 2019, Oklahoma Governor Kevin Stitt signed House Bill 2597 (effective November 1, 2019),[67] which will allow both residents and nonresidents 21+ (or 18+ and in the military) to open or concealed carry without a permit. Oklahoma's existing reciprocity also recognizes any concealed carry license issued both as resident and nonresident as well as the permitless carry of other states, so if one is a nonresident and 18+ and their state allows open carry or concealed carry without a permit, they may carry in that fashion so long as they have valid ID proving they are a resident of that state.[68]
South Dakota[]
On January 22, 2019, the South Dakota Senate passed SB 47 by a vote of 23–11. It then passed the House of Representatives on January 29, 2019, by a vote of 47–23.[69] Governor Kristi Noem signed SB 47 on January 31, 2019 (effective July 1, 2019).[70] This change in the law removes the requirement of a permit to concealed carry a handgun for residents and nonresidents 18+. Open carry was already legal without a permit.
Tennessee (handguns only)[]
On March 18, 2021, the Tennessee Senate passed Senate Bill 765, 23–9. On March 29, 2021, the Tennessee House of Representatives passed the bill, 64–29.[71] Governor Bill Lee signed the bill on April 8, 2021. The law, which took effect July 1, 2021, allows for both open and concealed carrying of handguns by any unprohibited person 21 and older without a permit as well as for military members ages 18 to 20. It does not apply to long guns, a point of contention among gun rights activists.[72]
Texas[]
On April 19, 2021, the Texas House approved HB1927. The Texas Senate approved an amended version on May 5. The House chose to reject the Senate changes and a conference committee was formed. The compromise version was then approved by the House on May 23 and the Senate on May 24. The bill was sent to Texas Governor Greg Abbott on May 28 and he signed it into law on June 16, 2021. The bill will take effect on September 1, 2021.[73] The new law allows the carrying of a handgun without a license, openly or concealed, as long as one is 21 years or older, legally able to possess a handgun, and has not been convicted in the last five years of misdemeanor bodily assault causing injury, deadly conduct, terroristic threat, or disorderly conduct (display or discharge) of a firearm. Open carry requires a holster. Carrying long guns without a license was already legal.[74][75]
Utah[]
In 2021, HB60 passed the legislature and Governor Spencer Cox signed the bill into law on February 12, 2021.[76][77][78] It took effect May 5, 2021. It allows for permitless carry, both openly and concealed, for adults over the age of 21. Adults in Utah ages 18–20 are allowed to concealed carry with a provisional permit or open carry without a permit if unloaded – two actions away from firing.[Note 2]
Previously, in 2013, HB76 was passed by a two-thirds majority in both the state House and the state Senate, but Governor Gary Herbert subsequently vetoed the bill, stating that the existing gun laws did not restrict one's ability to acquire a concealed carry permit, and "we're not the wild and woolly west."[79][80][81] Other attempts had been made to renew the efforts, but had failed because then-Governor Herbert had stated he would veto the effort.[82]
Vermont[]
For many decades, the only state to allow "constitutional carry" of a handgun (i.e., without any government permit) was Vermont. From the formation of the 13 original states, "constitutional carry" was the law in all states until the 19th century. By the 20th century, all states except Vermont had enacted concealed carry bans, with the exemption in most states for those citizens with a permit.[citation needed] Due to wording in its state constitution and decisions made by the state courts, Vermont has never been able to have a restriction on the method of how one could carry a firearm, and thus, in this regard, Vermont stood entirely separate from the rest of the United States for quite some time. No permit is required (or offered) for open carry and concealed carry, and this applies to both residents and nonresidents 16+ who can legally own a firearm.[83][84] Because of this, constitutional carry is still sometimes referred to as "Vermont carry."[3]
West Virginia[]
HB 4145 was passed by the House on February 8, 2016, and Senate on February 22, 2016, but vetoed by Governor Earl Ray Tomblin on March 3, 2016. The House then voted to override the veto on March 4, 2016, and the Senate voted to override on March 5, 2016. The law took effect on May 24, 2016. No permit is needed to open carry for residents and nonresidents 18+ and for concealed carry for residents and nonresidents 21+. Residents and nonresidents may carry concealed if between 18–21 with a permit.[85][86][87][88]
Wyoming[]
On March 2, 2011, Governor Matt Mead signed legislation to allow constitutional carry for residents of the state, effective July 1, 2011.[89][90] On April 6, 2021, Governor Mark Gordon signed a bill allowing constitutional carry for residents of other states, effective July 1, 2021.[91] Under the law, United States citizens and lawful permanent residents age 21 or older may carry concealed or openly without a permit. People under 21 must have a valid concealed carry permit from a jurisdiction that Wyoming recognizes if they wish to carry concealed, or can open carry without a permit.
Wyoming is similar to Vermont in that the police may not disarm a citizen just because they "feel" it's necessary.[92]
U.S. states that have a limited form of permitless concealed carry[]
Certain states may have a limited form of permitless carry, restricted based on one or more of the following: a person's location, the loaded/unloaded state of the firearm, or the specific persons who may carry without a permit. As of July 3, 2021, three of these states are Illinois, New Mexico and Washington.
Illinois (Non-resident, Unloaded and fully enclosed weapon)[]
In 1996, the Fourth District Illinois Appellate Court ruled that an unloaded handgun carried in a purse did not meet the definition of unlawful use of a weapon per se due to being fully enclosed and possessed in conjunction with a FOID card if an Illinois resident. Following this ruling, a movement started in the early 2000s dubbed Fanny Pack Carry, where proponents carried unloaded handguns in fanny packs to protest the state's outright ban on carrying loaded firearms.[93] This resulted in several arrests, but ultimately every criminal prosecution failed[94] and resulted in one successful wrongful arrest lawsuit.[95]
In 2009 the Supreme Court of Illinois ruled that any object that fully encloses a handgun and fastens closed in any form or manner legally constitutes a "case" per se under Illinois Law.
Following this in 2011 before the passage of Conceal Carry in Illinois, the Illinois Department of Natural Resources published a brochure which stated that to transport a firearm on one's person, one only has to meet three conditions:
- Unloaded
- Enclosed in a case
- Possessed in conjunction with an Illinois FOID.[96]
The Illinois State Police reaffirmed this in a 2012 brochure that states that a person may have a firearm upon their person as long as it's unloaded and enclosed in a case.[97]
Non-residents of Illinois are specifically exempted from the requirement to have a FOID Card while carrying an unloaded firearm enclosed in a case.
New Mexico (unloaded weapon)[]
Under New Mexico law, no permit is needed for open carry for anyone 19+ but a concealed handgun license is required for concealed carry when the weapon is both loaded and concealed, and the individual carrying is on foot. It is legal to carry an unloaded firearm.
Washington (outdoor recreational activities)[]
Washington allows for open carry without a permit, and concealed carry without a permit when a person is hiking, hunting, fishing, camping, horseback riding, or performing some other lawful outdoor recreational activity, so long as it is reasonable to assume that they are performing that activity or traveling to or from the activity.[98]
Ages to carry without a permit[]
| State | Open | Concealed |
|---|---|---|
| Alaska | 16 | 21 |
| Arizona | 18 | 21 |
| Arkansas | 19 | 19 |
| Idaho | 18 | 18 |
| Iowa | 21 | 21 |
| Kansas | 18 | 21 |
| Kentucky | 18 | 21 |
| Maine | 18 | 21 |
| Mississippi | 18 | 18 |
| Missouri | 18 | 18 |
| Montana | 18 | 18 |
| New Hampshire | 18 | 18 |
| North Dakota | N/A | 18 |
| Oklahoma | 21 | 21 |
| South Dakota | 18 | 18 |
| Tennessee | 21 | 21 |
| Texas | 21 | 21 |
| Utah | 21 | 21 |
| Vermont | 16 | 16 |
| West Virginia | 18 | 21 |
| Wyoming | 18 | 21 |
See also[]
- Concealed carry in the United States
- Gun laws in the United States (federal)
- Gun laws in the United States (by state)
- Open carry in the United States
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ "Kansas: Permitless Carry Bill to Receive Vote Tomorrow on Senate Floor". NRA-ILA. February 25, 2015. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ^ Schiller, Henry J.; Matos, Miguel A.; Zielinski, Martin D.; Bailey, Kent R.; Hernandez, Matthew C.; Hamill, Mark E. (January 1, 2019). "State Level Firearm Concealed-Carry Legislation and Rates of Homicide and Other Violent Crime". Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 228 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2018.08.694. ISSN 1072-7515. PMID 30359832.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Maine lawmaker submits 'Constitutional Carry' bill". Bangor Daily News. February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ^ "Arizona to allow concealed weapons without permit". Fox News. Associated Press. April 16, 2010. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ^ Gehrke, Robert (February 24, 2011). "'Constitutional Carry' law stalls in committee". The Salt Lake Tribune. Archived from the original on February 27, 2015. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ^ NRA-ILA. "NRA Advisory Notice Concerning North Dakota Permitless Carry Law". Retrieved August 5, 2017.
- ^ Louisiana Law Review (April 1, 2010). "District of Columbia v. Heller: The Second Amendment Shoots One Down".
- ^ Congressional Research Service (September 7, 2016). "Post-Heller Second Amendment Jurisprudence" (PDF).
- ^ "Palmer v. DC" (PDF).
- ^ Williams, Martin Weil, Clarence; Zauzmer, Julie (July 26, 2014). "Federal judge declares D.C. ban on carrying handguns in public unconstitutional". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Kopel, David (July 28, 2014). "Licensed handgun carry now legal in District of Columbia: Palmer v. DC". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "DC Chief of Police Order in response to concealed carry ruling". Scribd. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ Marimow, Ann E.; Hermann, Peter (July 29, 2014). "Judge puts D.C. handgun ruling on hold". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "Judge's ruling threatens upheaval of Puerto Rico gun laws". Guns.com. June 22, 2015. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "SAF LAUDS PUERTO RICO COURT VICTORY FOR GUN RIGHTS". Second Amendment Foundation. Retrieved March 28, 2016.
- ^ "Tribunal Supremo reitera constitucionalidad de la Ley de Armas". Departamento de Justicia de Puerto Rico. November 1, 2016. Retrieved January 19, 2017.
- ^ "Bill History Action for 23rd Legislature (Bill HB 102)". The Alaska State Legislature. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ "HB0102Z (Enrolled HB 102)" (PDF). The Alaska State Legislature. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ Sakal, Mike (July 23, 2010). "Concealed weapons permit, training requirement ends Thursday". East Valley Tribune. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ Paul Davenport; Jonathan Cooper (June 16, 2010). "Arizona Gun Law: Concealed Weapons Allowed Without Permit Under New Law". Huffington Post. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ Rau, Alia Beard (April 16, 2010). "Arizona to allow concealed weapons without permit". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Act 746" (PDF).
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Archived copy". Archived from the original on October 5, 2015. Retrieved March 5, 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on April 1, 2015. Retrieved January 7, 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Archived copy". Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 8, 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Jamie Taff v. State of Arkansas" (PDF).
- ^ "Gun laws in Arkansas" (PDF).
- ^ "HOUSE BILL 516 – Idaho State Legislature". Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ^ "Idaho Expands Constitutional Carry Laws". Guns.com. April 4, 2019. Retrieved April 4, 2019.
- ^ "HOUSE BILL 206 – Idaho State Legislature". Retrieved April 30, 2019.
- ^ "HOUSE BILL 199 – Idaho State Legislature". Retrieved April 30, 2019.
- ^ Gruber-Miller, Stephen. "Iowa Gov. Kim Reynolds signs gun law allowing permitless handgun carry, purchase". Des Moines Register. Retrieved April 2, 2021.
- ^ "SB 45". Kansas Legislature. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lowry, Bryan (April 2, 2015). "Brownback signs bill that allows permit-free concealed carry of guns in Kansas". Kansas City Star. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- ^ "Kansas gun laws" (PDF).
- ^ "Kansas Passes Constitutional Carry". April 3, 2015.
- ^ "Kansas Personal and Family Protection Act K.S.A. 75-7c01 et seq" (PDF). Kansas Attorney General. January 2015. Retrieved March 5, 2015.
- ^ "19RS SB 150". apps.legislature.ky.gov. Retrieved March 6, 2019.
- ^ "Maine: "Constitutional Carry" Introduced in the Pinetree State". NRA-ILA Institute for Legislative Action. NRA-ILA. February 27, 2015. Retrieved March 3, 2015.
- ^ "Maine Governor LePage signs NRA-backed bill for Permitless carry". NRA-ILA Institute for Legislative Action. NRA-ILA. July 8, 2015. Retrieved July 8, 2015.
- ^ "SB2394 (As Sent to Governor) – 2015 Regular Session".
- ^ NRA-ILA. "NRA-ILA Mississippi: Gov. Phil Bryant Signs NRA-Backed Permitless Carry Bill & Other Pro-Second Amendment Measures into Law!". NRA-ILA. Retrieved April 16, 2016.
- ^ WLOX Staff. "Gov. Bryant signs Church Protection Act". www.wdam.com. Archived from the original on April 16, 2016. Retrieved April 16, 2016.
- ^ NRA-ILA. "NRA-ILA | Missourians Celebrate a Win for Self-Defense Rights on Wednesday". Retrieved September 15, 2016.
- ^ Dietrich, Eric (February 18, 2021). "Gianforte signs 'constitutional carry' gun bill". Montana Free Press. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ Samuels, Iris (February 18, 2021). "Montana relaxes gun restrictions, allows guns on campuses". Associated Press. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ Riley, John (February 18, 2021). "Guns coming to campus: Permitless concealed carry of firearms now legal in Montana". Missoulacurrent.com. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ NRA-ILA; Association, National Rifle. "NRA-ILA | Constitutional Carry Passes in Montana". NRA-ILA. Retrieved February 18, 2021.
- ^ "45-8-317. Exceptions". Montana Code Annotated 2014. Montana Legislature.
- ^ "Senate endorses looser concealed carry law". KULR-8. March 27, 2001. Archived from the original on April 2, 2011. Retrieved March 29, 2011.
- ^ http://www.mtstandard.com/news/state-and-regional/article_91af16b9-41a4-58aa-ab65-126c61a2b789.html. Retrieved September 27, 2011. Missing or empty
|title=(help)[dead link] - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 16, 2011. Retrieved July 4, 2011.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ [1] Archived September 22, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Montana Legislature Detailed Bill Information". Montana Legislative Branch. Retrieved March 3, 2015.
- ^ "House Bill No. 298" (PDF). Montana Legislative Branch. Retrieved March 3, 2015.
- ^ Inbody, Kristen (March 27, 2015). "Gun bills meet no votes, vetos". Great Falls Tribune. Retrieved April 8, 2015.
- ^ "NH SB12 2017 Regular Session". LegiScan. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ "Bill Text NH SB12 2017 Regular Session Introduced". LegiScan. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ Solomon, Dave (January 19, 2017). "Senate OKs 'concealed carry' without a permit for firearms". New Hampshire Union Leader. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ "Governor Chris Sununu Statement on State Senate Vote to Pass Constitutional Carry Legislation". Office of the Governor of New Hampshire. State of New Hampshire. January 19, 2017. Retrieved January 19, 2017.
- ^ Tuohy, Dan (February 9, 2017). "House passes repeal of 'concealed carry' gun license law". New Hampshire Union Leader. Retrieved February 9, 2017.
- ^ "Gov. Sununu signs concealed carry bill into law". WMUR. February 22, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ Grossmith, Pat (August 7, 2013). "Court tells Manchester police a 'loaded gun' must have bullets in it". New Hampshire Union Leader. Retrieved September 3, 2013.
- ^ "Burgum signs "constitutional carry" bill into law | North Dakota Office of the Governor". www.governor.nd.gov. Archived from the original on May 27, 2019. Retrieved June 29, 2019.
- ^ NRA-ILA. "NRA-ILA | North Dakota: Ruling Issued Approving Constitutional Carry in Vehicles". NRA-ILA. Retrieved December 17, 2017.
- ^ "North Dakota Bill Actions: HB 1042". www.legis.nd.gov. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- ^ World, Barbara Hoberock Tulsa. "'Constitutional carry' becomes first legislation signed into law by Gov. Kevin Stitt". Tulsa World. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- ^ "Reciprocal Agreement Authority". www.oscn.net. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- ^ "SDLRC – 2019 Senate Bill 47". sdlegislature.gov. Retrieved January 29, 2019.
- ^ KSFY. "Gov. Kristi Noem signs 'constitutional carry' bill into law". www.ksfy.com. Retrieved February 1, 2019.
- ^ "Tennessee SB0765 | 2021-2022 | 112th General Assembly". LegiScan. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ "Tennessee constitutional carry bill brings GOP infighting". archive.is. July 25, 2021. Retrieved July 25, 2021.
- ^ "Texas HB1927 | 2021-2022 | 87th Legislature". LegiScan. Retrieved June 18, 2021.
- ^ Sparber, Sami (June 16, 2021). "Texans can carry handguns without a license or training starting Sept. 1, after Gov. Greg Abbott signs permitless carry bill into law". The Texas Tribune. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ "HB 1927: Constitutional Carry FAQ | GOA Texas". Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ "Bill removing concealed weapon permit rule signed into law". AP NEWS. February 13, 2021.
- ^ Ruiz, Michael (February 12, 2021). "Utah Gov. Spencer Cox signs law allowing concealed carry without a permit". Fox News.
- ^ "Gov. Spencer Cox signs bill to eliminate requirement of permit to carry concealed gun". The Salt Lake Tribune.
- ^ "Herbert vetoes controversial gun carry bill". March 22, 2013.
- ^ "Gov. Gary Herbert vetoes 'constitutional carry' bill". March 22, 2013.
- ^ "Lawmaker resurrects push for 'constitutional carry' bill". January 23, 2017.
- ^ "Republican lawmakers say no 'constitutional carry' gun bill in 2018". utahpolicy.com. Retrieved January 8, 2021.
- ^ Cooke, Charles (June 24, 2014). "Vermont: Safe and Happy and Armed to the Teeth". National Review. National Review. Retrieved March 3, 2015.
- ^ "The Vermont Constitution". USConstitution.net. Retrieved March 3, 2015.
- ^ "West Virginia Concealed Carry". www.wvcdl.org. Archived from the original on January 29, 2017. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- ^ "Bill Status – Complete Bill History". www.legis.state.wv.us. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
- ^ NRA-ILA. "NRA-ILA | West Virginia: Legislature Overrides Tomblin's Veto of Permitless Carry Legislation". NRA-ILA. Retrieved March 5, 2016.
- ^ "Bill To Authorize Satellite Casinos Dies in West Virginia Senate Finance Committee". theintelligencer.net. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- ^ "Wyoming House approves concealed carry bill". Laramie Boomerang. Retrieved February 26, 2011.
- ^ "Wyoming governor signs concealed gun bill". Casper Star-Tribune. Associated Press. March 2, 2011. Retrieved March 3, 2011.
- ^ https://oilcity.news/wyoming/legislature/2021/04/07/wyoming-to-allow-nonresidents-to-conceal-carry-without-a-permit-starting-july-1/
- ^ "Combat vet sues over Wyoming traffic stop". The Billings Gazette. Associated Press.
- ^ Higgins, Michael (November 28, 2000). "Owners Say Law Lets Them Tote Guns in Fanny Packs". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- ^ "Gun-Rights Advocates Win Victory in Chicago Court". The Crime Report. May 18, 2004. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- ^ Gregory, Ted (June 3, 2004). "Dupage Pays for Handgun Arrest". Chicago Tribune. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- ^ "Transport Your Firearm Legally" (PDF). Illinois Department of Natural Resources. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- ^ "Transport your Firearm Legally" (PDF). Illinois State Police PDF rehosted by illinoisconcealcarryllc.com. September 1, 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 18, 2018. Retrieved April 22, 2018.
- ^ "Firearms FAQ | Washington State". www.atg.wa.gov. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- Licenses
- Gun politics in the United States
- Self-defense
- United States firearms law
