Cryptista
| Cryptista | |
|---|---|
| |
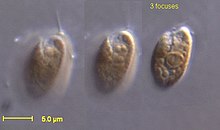
| Rhodomonas salina, a cryptophyte | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota
|
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | Cryptista Adl et al., 2018 [Cavalier-Smith 1989, 2018][1]
|
| Phyla & Classes | |
| |
Cryptista is a clade of algae-like eukaryotes. It is sometimes placed along with Haptista in the group Hacrobia, within the kingdom Chromista.[2] However, in 2016, a broad phylogenomic study found that cryptists fall within the group Archaeplastida, while haptophytes are closely related to the SAR supergroup.[3][4]
Taxonomy[]
Based on studies done by Cavalier-Smith, Chao & Lewis 2015[5][6]
- Corbihelia
- Phylum Tedersoo 2017 [Endohelia Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Class Endohelea Cavalier-Smith 2012
- Phylum Tedersoo 2017 [Endohelia Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Clade Cryptista s.s.
- Phylum Tedersoo 2017
- Class Palpitea Cavalier-Smith 2012
- Clade Rollomonadia Cavalier-Smith 2013 stat. nov.
- Phylum Okamoto & Inouye 2005 [Leucocrypta Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Class Leucocryptea Cavalier-Smith 2004[7] [Kathablepharidea (sic) Okamoto & Inouye 2005; Kathablepharidophyceae]
- Phylum Cryptophyta Pascher 1913 em. Adl et al. 2012 (Cryptomonada Cavalier-Smith 2004 sta. n.]
- Class Goniomonadea Cavalier-Smith 1993
- Class Cryptophyceae Fritsch 1937
- Phylum Okamoto & Inouye 2005 [Leucocrypta Cavalier-Smith 2015]
- Phylum Tedersoo 2017
References[]
- ^ Adl, Sina M.; Bass, David; Lane, Christopher E.; Lukeš, Julius; Schoch, Conrad L.; Smirnov, Alexey; Agatha, Sabine; Berney, Cedric; Brown, Matthew W. (2018-09-26). "Revisions to the Classification, Nomenclature, and Diversity of Eukaryotes". The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 66 (1): 4–119. doi:10.1111/jeu.12691. ISSN 1550-7408. PMC 6492006. PMID 30257078.
- ^ Ruggiero, Michael A.; Gordon, Dennis P.; Orrell, Thomas M.; Bailly, Nicolas; Bourgoin, Thierry; Brusca, Richard C.; Cavalier-Smith, Thomas; Guiry, Michael D.; Kirk, Paul M. (2015-04-29). "A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms". PLOS ONE. 10 (4): e0119248. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1019248R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119248. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4418965. PMID 25923521.
- ^ Burki F; Kaplan M; Tikhonenkov DV; Zlatogursky V; Minh BQ; Radaykina LV; Smirnov A; Mylnikov AP; Keeling PJ (2016), "Untangling the early diversification of eukaryotes: a phylogenomic study of the evolutionary origins of Centrohelida, Haptophyta and Cryptista.", Proc Biol Sci, 283 (1823): 20152802, doi:10.1098/rspb.2015.2802, PMC 4795036, PMID 26817772
- ^ Burki, F; Inagaki, Y; Bråte, J; Archibald, J.; Keeling, P.; Cavalier-Smith, T; Sakaguchi, M; Hashimoto, T; Horak, A; Kumar, S; Klaveness, D; Jakobsen, K.S; Pawlowski, J; Shalchian-Tabrizi, K (2009). "Large-scale phylogenomic analyses reveal that two enigmatic protist lineages, Telonemia and Centroheliozoa, are related to photosynthetic chromalveolates" (Free full text). Genome Biology and Evolution. 1: 231–8. doi:10.1093/gbe/evp022. PMC 2817417. PMID 20333193.
- ^ Cavalier-Smith; Chao; Lewis (2015), "Multiple origins of Heliozoa from flagellate ancestors: New cryptist subphylum Corbihelia, superclass Corbistoma, and monophyly of Haptista, Cryptista, Hacrobia and Chromista", Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 93: 331–362, doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2015.07.004, PMID 26234272
- ^ Tedersoo, Leho (2017), "Proposal for practical multi-kingdom classification of eukaryotes based on monophyly and comparable divergence time criteria", bioRxiv, 2017, doi:10.1101/240929, S2CID 90691603
- ^ "Katablepharids".
External links[]
| Wikispecies has information related to Cryptista. |
Categories:
- Cryptista
- Infrakingdoms
- Taxa named by Thomas Cavalier-Smith
- Hacrobia stubs