Dexelvucitabine
This article does not cite any sources. (March 2015) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
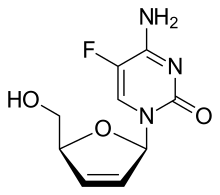
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Amino-5-fluoro-1-[(2R,5S)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-1-yl]pyrimidin-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names
Reverset
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H10FN3O3 | |
| Molar mass | 227.195 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dexelvucitabine is a failed experimental agent for the management of HIV infection. Dexelvucitabine is a cytidine nucleoside analog and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. It was found to inhibit HIV-1 replication in vitro and during Phase II clinical trials, it was found to decrease mean viral load in patients with HIV.[medical citation needed]
On April 3, 2006, Pharmasset and Incyte, the pharmaceutical companies developing dexelvucitabine announced the decision to cease further trials and development of the drug due to an increased incidence of grade 4 hyperlipasemia (an excess of the pancreatic enzyme, lipase) in a phase II trial.[citation needed]
Categories:
- Abandoned drugs
- Dihydrofurans
- Nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors
- Organofluorides
- Pyrimidones
- Hydroxymethyl compounds
- Antiinfective agent stubs