Economist
The examples and perspective in this article deal primarily with the English-speaking world and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (May 2015) |
| Part of a series on |
| Economics |
|---|
|
An economist is a practitioner in the social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this field there are many sub-fields, ranging from the broad philosophical theories to the focused study of minutiae within specific markets, macroeconomic analysis, microeconomic analysis or financial statement analysis, involving analytical methods and tools such as econometrics, statistics, economics computational models, financial economics, mathematical finance and mathematical economics.
Professions[]


Economists work in many fields including academia, government and in the private sector, where they may also "...study data and statistics in order to spot trends in economic activity, economic confidence levels, and consumer attitudes. They assess this information using advanced methods in statistical analysis, mathematics, computer programming [and] they make recommendations about ways to improve the efficiency of a system or take advantage of trends as they begin."[1]
In contrast to regulated professions such as engineering, law or medicine, there is not a legally required educational requirement or license for economists. In academia, most economists have a Ph.D. degree in Economics.[citation needed] In the U.S. Government, on the other hand, a person can be hired as an economist provided that they have a degree that included or was supplemented by 21 semester hours in economics and three hours in statistics, accounting, or calculus.[2]
A professional working inside of one of many fields of economics or having an academic degree in this subject is often considered to be an economist.[3] In addition to government and academia, economists are also employed in banking, finance, accountancy, commerce, marketing, business administration, lobbying and non- or not-for profit organizations.[4]
Politicians often consult economists before enacting economic policy. Many statesmen have academic degrees in economics.
By country[]
Economics graduates are employable in varying degrees depending on the regional economic scenario and labour market conditions at the time for a given country. Apart from the specific understanding of the subject, employers value the skills of numeracy and analysis, the ability to communicate and the capacity to grasp broad issues which the graduates acquire at the university or college. Whilst only a few[quantify] economics graduates may be expected to become professional economists,[citation needed] many find it a base for entry into a career in finance – including accounting, insurance, tax and banking, or management;[citation needed] see financial analyst. A number of economics graduates from around the world have been successful in obtaining employment in a variety of major national and international firms in the financial and commercial sectors, and in manufacturing, retailing and IT, as well as in the public sector – for example, in the health and education sectors, or in government and politics. Small numbers[quantify][citation needed] go on to undertake postgraduate studies, either in economics, research, teacher training or further qualifications in specialist areas.
Brazil[]
In Brazil, unlike most countries in the world where the profession is not regulated, the profession of Economist is regulated by Law. 1411 of August 13, 1951. The professional designation of economist, according to the said law, is exclusive to the bachelors in economics graduates in Brazil.[5]
United States[]
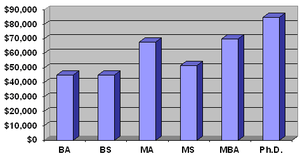
According to the United States Department of Labor, there were about 15,000 non-academic economists in the United States in 2008, with a median salary of roughly $83,000 the top ten percent earning more than $147,040 annually.[7] Nearly 135 colleges and universities[8][verification needed] grant around 900 new Ph.D.s every year. Incomes are highest for those in the private sector, followed by the federal government, with academia paying the lowest incomes. As of January 2013, PayScale.com showed Ph.D. economists' salary ranges as follows: all Ph.D. economists, $61,000 to $160,000; Ph.D. corporate economists, $71,000 to $207,000; economics full professors, $89,000 to $137,000; economics associate professors, $59,000 to $156,000, and economics assistant professors, $72,000 to $100,000.[6]
United Kingdom[]
The largest single professional grouping of economists in the UK are the more than 1000 members of the Government Economic Service, who work in 30 government departments and agencies.[citation needed]
Analysis of destination surveys for economics graduates from a number of selected top schools of economics in the United Kingdom (ranging from Newcastle University to the London School of Economics), shows nearly 80 percent in employment six months after graduation – with a wide range of roles and employers, including regional, national and international organisations, across many sectors.[citation needed] This figure compares very favourably with the national picture, with 64 percent of economics graduates in employment.[citation needed]
Notable economists[]
Some current well-known economists include:
- B. R. Ambedkar, who was an Indian scholar, jurist, economist, politician and social reformer. The Reserve Bank of India was conceptualized in accordance with the guidelines presented by Ambedkar to the Hilton Young Commission (also known as Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance) based on his book, The Problem of the Rupee – Its Origin and Its Solution.
- Amartya Sen (b. 1933), Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate and professor at Harvard University.
- Kenneth Arrow, Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate and professor at Stanford University.
- Robert Aumann (b. 1930), Israeli-American mathematician, Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics in 2005
- Ben Bernanke, Chairman of the Federal Reserve from 2006 to 2014.
- Esther Duflo, Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate and professor at MIT
- John Maynard Keynes, English economist well known for forming the basis of Keynesian economics
- Milton Friedman, Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate.
- Claudia Goldin, professor at Harvard University
- Alan Greenspan, Chairman of the Federal Reserve from 1987 to 2006.
- James Heckman, 2000 Nobel Prize winner and Professor at University of Chicago; most cited economist as of 2018.
- Glenn Hubbard, Dean of the Columbia University Graduate School of Business; Chair of the Council of Economic Advisers from 2001 to 2003.
- Thomas M. Humphrey, American economist and historian of economic thought.
- Paul Krugman, a 2008 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate, a public intellectual, and an advocate of modern liberal policies.
- Greg Mankiw, American macroeconomist, academic economist, public intellectual, Chair of the Council of Economic Advisers from 2003 to 2005.
- Joseph Stiglitz, 2001 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics winner, critic of inequality and the governance of globalization, and former World Bank Chief Economist.
- Dambisa Moyo, a Zambian-born international economist and author who analyzes the macroeconomy and global affairs.
- Thomas Sowell, American economist and social theorist, Senior Fellow at the Hoover Institution.
- Robert Lucas Jr., 1995 Nobel Prize in Economics winner.
- Carmen Reinhart, member of American Economic Association, 2018, King Juan Carlos Prize in Economics winner
- William Forsyth Sharpe, 1990 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences winner
- Christopher Antoniou Pissarides, 2010 the Nobel Prize in Economics.
- Arthur Laffer, 2019 Presidential Medal of Freedom winner
- Jeffrey Sachs, Professor of Sustainable Development at Columbia's School of International and Public Affairs, 2015 Blue Planet Prize awarded
- Vusal Gasimli, Azerbaijani economist and public intellectual, author of Geo-Economics
- Ludwig von Mises, Austrian economist and philosopher, author of Human Action.
- Friedrich Hayek, Austrian economist, Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences laureate and author of The Road to Serfdom.
- Adam Smith, Scottish economist and philosopher. Known as father of economics.
See also[]
References[]
Citations[]
- ^ Economist
- ^ "Economist Series, 0110: U.S. Office of Personnel Management".
- ^ "Economists". U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Retrieved 2017-02-02.
- ^ "Economics Jobs and Economist Jobs - Econ-Jobs.com".
- ^ "Guia do mercado de trabalho do economista CORECON". Retrieved 2018-01-14.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Pay Scale, US income of Economists". Retrieved 2013-01-14.
- ^ US Bureau of Labor, Occupational Outlook Handbook Archived April 30, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Subscription Application".
Sources[]
- Mark Blaug and Howard R. Vane (1983, 2003 4th ed.). . Table of Contents links. Cheltenham & Edward Elgar Pub.
- Pressman, Steven, 2006. Fifty Major Economists. Routledge,
- Robert Sobel, 1980. The Worldly Economists .
External links[]
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Economist |
![]() The dictionary definition of economist at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of economist at Wiktionary
- Economics occupations
- Social science occupations
- Economists