Euronest Parliamentary Assembly
 | |
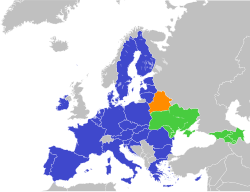 European Union member states Non-EU members Suspended members | |
| Formation | 2011 |
|---|---|
| Type | Economic and political cooperation organization |
| Location |
|
Membership | 5 plus 27 European Parliament members |
| Website | |
The Euronest Parliamentary Assembly is the inter-parliamentary forum in which members of the European Parliament and the national parliaments of Ukraine, Moldova, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia[1] participate and forge closer political and economic ties with the European Union.[2][3] It was established in 2011 by the European Commission as a component of the Eastern Partnership. After the elections in Belarus in 2010 were declared as flawed by the OSCE, the membership of Belarus in Euronest was automatically suspended. Belarus is welcome to re-join the Assembly once political requirements have been fulfilled.[4] In 2015, Azerbaijan's membership was suspended due to the European Union's criticism of human rights abuses by the government. In September 2016, it was announced that Azerbaijan would take the necessary steps towards restoring ties.[5] As of 2017, the combined population of Euronest members (excluding Belarus and European Union members) stands at 61,927,521 people.
Member states[]
In addition to the 27 member states of the European Parliament, 4 Eastern European states participate:
 Armenia
Armenia Georgia
Georgia Moldova
Moldova Ukraine
Ukraine
Suspended members[]
 Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Belarus
Belarus
Plenary meetings[]
The Euronest Parliamentary Assembly meets once a year. Meeting locations alternate between an Eastern European Partner country and one of the European Parliament places of work (Brussels, Luxembourg or Strasbourg):
| Session | Date | Host Country | Host City |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | September 2011 | France | Strasbourg |
| II | April 2012 | Azerbaijan | Baku |
| III | May 2013 | Belgium | Brussels |
| IV | March 2015 | Armenia | Yerevan |
| V | March 2016 | Belgium | Brussels |
| VI | October 2017 | Ukraine | Kyiv |
| VII | June 2018 | Belgium | Brussels |
| VIII | December 2019 | Georgia | Tbilisi |
| – | 2020 | Cancelled due to the COVID-19 pandemic | – |
| IX | April 2021 | Belgium | Brussels |
| X | 2022 | TBD | TBD |
EU integration[]
Members of Euronest have been regarded as belonging to the "European family". All members are part of the European Neighbourhood Policy and each maintain various degrees of integration with the EU. Some members of Euronest such as Ukraine and Georgia are actively seeking eventual EU membership and wish to forge closer ties with the EU. Other states such as Armenia and Moldova cooperate with both the European Union and the Russian-led Eurasian Union. While Azerbaijan and Belarus have been questioned about their European perspectives due to human rights abuses and lack of freedom of speech.
EU membership perspective[]
In December 2019, following the eighth plenary meeting held in Tbilisi, a resolution was passed by all members of the Euronest Parliamentary Assembly. The resolution outlines various EU integration goals to be achieved by 2030. The resolution highlights the importance of the Eastern Partnership program and how the initiative supports the six EU associated countries in letting them move more rapidly with reform implementation and deeper political and economic integration with the EU.[6]
The resolution also confirms the successes of the EU Enlargement Policy and its transformative power on Central and Eastern European countries in their development from post-totalitarian regulated economies to European style democracies and that future enlargement shall spread these successes to the Eastern Partnership countries willing to join the EU. The resolution affirms that the process of EU enlargement is open to Eastern Partnership member states and that future enlargement of the EU will be mutually beneficial for both the EU and Eastern Partnership members.[7]
Furthermore, the resolution endorses continuing progressive reforms and harmonization with EU standards, promoting European values and human rights and establishing visa free travel to the EU's Schengen Area for Eastern Partnership members.
The resolution praised the achievements made by Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine in signing Association Agreements and a Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area with the EU. Similarly, the resolution endorsed the progress made in Armenia following the 2018 Velvet Revolution. The resolution stated that, "Armenia is the only country in Europe to transition from being a hybrid regime in 2017 to a democracy in 2018" and that the ratification of a new Comprehensive and Enhanced Partnership Agreement (CEPA) by the Armenian Parliament in April 2018 is considered evidence of a strategically reinforced partnership between Armenia and EU. The resolution coined the term "Trio + 1" which represents the three Association Agreements established with Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine, as well as, the CEPA established with Armenia. The resolution calls for promoting further integration efforts between the EU and the "Trio + 1" group over the next decade.[8]
The resolution also acknowledges the potential threat that Russia may have in destabilizing these countries and preventing them from achieving European unity.[9]
See also[]
- Armenia–European Union relations
- Association Trio
- Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations
- Community of Democratic Choice
- Council of Europe
- Deep and Comprehensive Free Trade Area
- Euro-Mediterranean Parliamentary Assembly - Euronest counterpart for the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership of the ENP
- Eastern Europe
- Eastern European Group
- Eastern Partnership
- European integration
- Eurosphere
- Eurovoc
- Future enlargement of the European Union
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
- Politics of Europe
- Post-Soviet states
- TRACECA
References[]
- ^ "Members". EuroNest Parliamentary Assembly
- ^ "Initial Agreement Reached To Establish Parliamentary Assembly Of European Parliament's Eastern Neighbors". Archived from the original on 2011-06-15.
- ^ European Parliament decision of 6 May 2009 on the number of interparliamentary delegations, delegations to joint parliamentary committees, delegations to parliamentary cooperation committees and multilateral Parliamentary Assemblies
- ^ "Initial Agreement Reached To Establish Parliamentary Assembly Of European Parliament's Eastern Neighbors". Archived from the original on 2015-06-16. Retrieved 2017-03-01.
- ^ "EU Azer".
- ^ "The future of the Trio Plus Strategy 2030: building a future of Eastern Partnership" (PDF).
- ^ "The future of the Trio Plus Strategy 2030: building a future of Eastern Partnership" (PDF).
- ^ "The future of the Trio Plus Strategy 2030: building a future of Eastern Partnership" (PDF).
- ^ "The future of the Trio Plus Strategy 2030: building a future of Eastern Partnership" (PDF).
External links[]
- Euronest Parliamentary Assembly web site
- Delegation to the Euronest Parliamentary Assembly (European Parliament)
- Delegation to the Euronest Parliamentary Assembly[permanent dead link] (ALDE Group)
- Video: Euronest - how it works (EuroparlTV)
- Parliamentary assemblies
- European Union and third organisations
- International organizations based in Europe
- European integration
- Pan-Europeanism

