Flavonoid
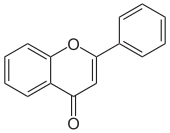

Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word flavus, meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.[1]
Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen).[1][2] This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature,[3][4] they can be classified into:
- flavonoids or bioflavonoids
- isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure
- neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure
The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols).[1] This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non-ketone polyhydroxy polyphenol compounds, which are more specifically termed flavanoids. The three cycles or heterocycles in the flavonoid backbone are generally called ring A, B, and C.[2] Ring A usually shows a phloroglucinol substitution pattern.
History[]
In the 1930s, Albert Szent-Györgyi and other scientists discovered that Vitamin C alone was not as effective as the crude yellow extract from oranges, lemons or paprika. They attributed the increased activity of this extract to the other substances in this mixture, which they referred to as "citrin" (referring to citrus) or "Vitamin P" (a reference to its effect on reducing the permeability of capillaries). The substances in question (hesperidin, eriodictyol, hesperidin methyl chalcone and neohesperidin) were however later shown not to fulfil the criteria of a vitamin,[5] so that this term is now obsolete.[6]
Biosynthesis[]
Flavonoids are secondary metabolites synthesized mainly by plants. The general structure of flavonoids is a 15-carbon skeleton, containing 2 benzene rings connected by a 3-carbon linking chain.[1] Therefore, they are depicted as C6-C3-C6 compounds. Depending on the chemical structure, degree of oxidation, and unsaturation of the linking chain (C3), flavonoids can be classified into different groups, such as anthocyanidins, chalcones, flavonols, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, flavanonols, flavones, and isoflavonoids.[1] Furthermore, flavonoids can be found in plants in glycoside-bound and free aglycone forms. The glycoside-bound form is the most common flavone and flavonol form consumed in the diet.[1]
Functions of flavonoids in plants[]
Flavonoids are widely distributed in plants, fulfilling many functions.[1] Flavonoids are the most important plant pigments for flower coloration, producing yellow or red/blue pigmentation in petals designed to attract pollinator animals. In higher plants, flavonoids are involved in UV filtration, symbiotic nitrogen fixation, and floral pigmentation. They may also act as chemical messengers, physiological regulators, and cell cycle inhibitors. Flavonoids secreted by the root of their host plant help Rhizobia in the infection stage of their symbiotic relationship with legumes like peas, beans, clover, and soy. Rhizobia living in soil are able to sense the flavonoids and this triggers the secretion of Nod factors, which in turn are recognized by the host plant and can lead to root hair deformation and several cellular responses such as ion fluxes and the formation of a root nodule. In addition, some flavonoids have inhibitory activity against organisms that cause plant diseases, e.g. Fusarium oxysporum.[7]
Subgroups[]
Over 5000 naturally occurring flavonoids have been characterized from various plants. They have been classified according to their chemical structure, and are usually subdivided into the following subgroups (for further reading see[8]):
Anthocyanidins[]

Anthocyanidins are the aglycones of anthocyanins; they use the flavylium (2-phenylchromenylium) ion skeleton.[1]
- Examples: Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Petunidin
Anthoxanthins[]
Anthoxanthins are divided into two groups:[9]
| Group | Skeleton | Examples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Functional groups | Structural formula | |||
| 3-hydroxyl | 2,3-dihydro | ||||
| Flavone | 2-phenylchromen-4-one | ✗ | ✗ | 
|
Luteolin, Apigenin, Tangeritin |
| Flavonol or 3-hydroxyflavone |
3-hydroxy-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ✓ | ✗ | 
|
Quercetin, Kaempferol, Myricetin, Fisetin, Galangin, Isorhamnetin, Pachypodol, Rhamnazin, Pyranoflavonols, Furanoflavonols, |
Flavanones[]
| Group | Skeleton | Examples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Functional groups | Structural formula | |||
| 3-hydroxyl | 2,3-dihydro | ||||
| Flavanone | 2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ✗ | ✓ | 
|
Hesperetin, Naringenin, Eriodictyol, Homoeriodictyol |
Flavanonols[]
| Group | Skeleton | Examples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Functional groups | Structural formula | |||
| 3-hydroxyl | 2,3-dihydro | ||||
| Flavanonol or 3-Hydroxyflavanone or 2,3-dihydroflavonol |
3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one | ✓ | ✓ | 
|
Taxifolin (or Dihydroquercetin), Dihydrokaempferol |
Flavans[]
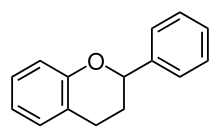
Include flavan-3-ols (flavanols), flavan-4-ols and flavan-3,4-diols.
| Skeleton | Name |
|---|---|

|
Flavan-3-ol (flavanol) |
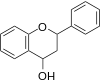
|
Flavan-4-ol |

|
Flavan-3,4-diol (leucoanthocyanidin) |
- Flavan-3-ols (flavanols)
- Flavan-3-ols use the 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-ol skeleton
- Examples: Catechin (C), Gallocatechin (GC), (Cg), (GCg), Epicatechins (Epicatechin (EC)), Epigallocatechin (EGC), Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECg), Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCg)
- Examples: Theaflavin-3-gallate, , Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate
- Thearubigin
- Proanthocyanidins are dimers, trimers, oligomers, or polymers of the flavanols
Isoflavonoids[]
- Isoflavonoids
- Isoflavones use the 3-phenylchromen-4-one skeleton (with no hydroxyl group substitution on carbon at position 2)
- Isoflavanes
- Isoflavandiols
- Isoflavenes
- Coumestans
- Pterocarpans
Dietary sources[]



Flavonoids (specifically flavanoids such as the catechins) are "the most common group of polyphenolic compounds in the human diet and are found ubiquitously in plants".[1][10] Flavonols, the original bioflavonoids such as quercetin, are also found ubiquitously, but in lesser quantities. The widespread distribution of flavonoids, their variety and their relatively low toxicity compared to other active plant compounds (for instance alkaloids) mean that many animals, including humans, ingest significant quantities in their diet.[1] Foods with a high flavonoid content include parsley,[11] onions,[11] blueberries and other berries,[11] black tea,[11] green tea and oolong tea,[11] bananas, all citrus fruits, Ginkgo biloba, red wine, sea-buckthorns, buckwheat,[12] and dark chocolate with a cocoa content of 70% or greater.
Parsley[]
Parsley, both fresh and dried, contains flavones.[11]
Blueberries[]
Blueberries are a dietary source of anthocyanidins.[11][13]
Black tea[]
Black tea is a rich source of dietary flavan-3-ols.[11]
Citrus[]
The citrus flavonoids include hesperidin (a glycoside of the flavanone hesperetin), quercitrin, rutin (two glycosides of the flavonol quercetin), and the flavone tangeritin. The flavonoids are much less concentrated in the pulp than in the peels (for example, 165 vs. 1156 mg/100g in pulp vs. peel of satsuma mandarin, and 164 vs 804 mg/100g in pulp vs. peel of clementine).[14]
Wine[]
Cocoa[]
Flavonoids exist naturally in cocoa, but because they can be bitter, they are often removed from chocolate, even dark chocolate.[15] Although flavonoids are present in milk chocolate, milk may interfere with their absorption;[16] however this conclusion has been questioned.[17]
Peanut[]
Peanut (red) skin contains significant polyphenol content, including flavonoids.[18][19]
| Food source | Flavones | Flavonols | Flavanones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red onion | 0 | 4 - 100 | 0 |
| Parsley, fresh | 24 - 634 | 8 - 10 | 0 |
| Thyme, fresh | 56 | 0 | 0 |
| Lemon juice, fresh | 0 | 0 - 2 | 2 - 175 |
Unit: mg/100g[1]
Dietary intake[]
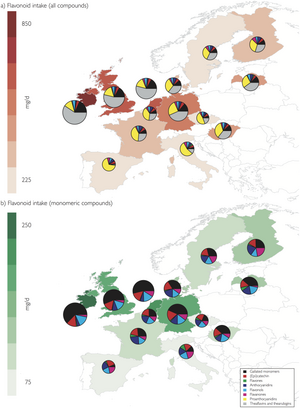
Food composition data for flavonoids were provided by the USDA database on flavonoids.[11] In the United States NHANES survey, mean flavonoid intake was 190 mg/d in adults, with flavan-3-ols as the main contributor.[21] In the European Union, based on data from EFSA, mean flavonoid intake was 140 mg/d, although there were considerable differences among individual countries.[20] The main type of flavonoids consumed in the EU and USA were flavan-3-ols (80% for USA adults), mainly from tea or cocoa in chocolate, while intake of other flavonoids was considerably lower.[1][20][21]

Research[]
Neither the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) nor the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved any health claim for flavonoids or approved any flavonoids as prescription drugs.[1][22][23][24] The U.S. FDA has warned numerous dietary supplement companies about illegal advertising and misleading health claims.[25][26]
Metabolism and excretion[]
Flavonoids are poorly absorbed in the human body (less than 5%), then are quickly metabolized into smaller fragments with unknown properties, and rapidly excreted.[1][24][27][28] Flavonoids have negligible antioxidant activity in the body, and the increase in antioxidant capacity of blood seen after consumption of flavonoid-rich foods is not caused directly by flavonoids, but by production of uric acid resulting from flavonoid depolymerization and excretion.[1] Microbial metabolism is a major contributor to the overall metabolism of dietary flavonoids.[1][29] The effect of habitual flavonoid intake on the human gut microbiome is unknown.[1][30]
Inflammation[]
Inflammation has been implicated as a possible origin of numerous local and systemic diseases, such as cancer,[31] cardiovascular disorders,[32] diabetes mellitus,[33] and celiac disease.[34] There is no clinical evidence that dietary flavonoids affect any of these diseases.[1]
Cancer[]
Clinical studies investigating the relationship between flavonoid consumption and cancer prevention or development are conflicting for most types of cancer, probably because most human studies have weak designs, such as a small sample size.[1][35] There is little evidence to indicate that dietary flavonoids affect human cancer risk in general, but observational studies and clinical trials on hormone-dependent cancers (breast and prostate) have shown benefits.[1]
A recent review has suggested that dietary intake of flavonoids is associated with a reduced risk of different types of cancer, including gastric, breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer.[36]
Cardiovascular diseases[]
Although no significant association has been found between flavan-3-ol intake and cardiovascular disease mortality, clinical trials have shown improved endothelial function and reduced blood pressure (with a few studies showing inconsistent results).[1] Reviews of cohort studies in 2013 found that the studies had too many limitations to determine a possible relationship between increased flavonoid intake and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease, although a trend for an inverse relationship existed.[1][37]
In vitro[]
Laboratory studies on isolated cells or cell cultures in vitro indicate that flavonoids may selectively inhibit kinases, but in vivo results could differ because of low bioavailability.[1]
Synthesis, detection, quantification, and semi-synthetic alterations[]
Color spectrum[]
Flavonoid synthesis in plants is induced by light color spectrums at both high and low energy radiations. Low energy radiations are accepted by phytochrome, while high energy radiations are accepted by carotenoids, flavins, cryptochromes in addition to phytochromes. The photomorphogenic process of phytochrome-mediated flavonoid biosynthesis has been observed in Amaranthus, barley, maize, Sorghum and turnip. Red light promotes flavonoid synthesis.[38]
Availability through microorganisms[]
Several recent research articles have demonstrated the efficient production of flavonoid molecules from genetically engineered microorganisms.[39][40][41] and the project [42][43] aims to provide a cost-effective alternative to current flavonoid production breaking down their complex biosynthetic pathways into standardized specific parts, which can be transferred to engineered microorganisms within Synthetic Microbial Consortia to promote flavonoid assembly through distributed catalysis.
Tests for detection[]
- Shinoda test
Four pieces of magnesium filings are added to the ethanolic extract followed by few drops of concentrated hydrochloric acid. A pink or red colour indicates the presence of flavonoid.[44] Colours varying from orange to red indicated flavones, red to crimson indicated flavonoids, crimson to magenta indicated flavonones.
- Sodium hydroxide test
About 5 mg of the compound is dissolved in water, warmed, and filtered. 10% aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to 2 ml of this solution. This produces a yellow coloration. A change in color from yellow to colorless on addition of dilute hydrochloric acid is an indication for the presence of flavonoids.[45]
- p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde test
A colorimetric assay based upon the reaction of A-rings with the chromogen p-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde (DMACA) has been developed for flavanoids in beer that can be compared with the vanillin procedure.[46]
Quantification[]
Lamaison and Carnet have designed a test for the determination of the total flavonoid content of a sample (AlCI3 method). After proper mixing of the sample and the reagent, the mixture is incubated for ten minutes at ambient temperature and the absorbance of the solution is read at 440 nm. Flavonoid content is expressed in mg/g of quercetin.[47]
Semi-synthetic alterations[]
Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase can be used to catalyze the regioselective acylation of flavonoids.[48]
See also[]
- Phytochemical
- List of antioxidants in food
- List of phytochemicals in food
- Phytochemistry
- Secondary metabolites
- Homoisoflavonoids, related chemicals with a 16 carbons skeleton
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Delage B (November 2015). "Flavonoids". Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon. Retrieved 2021-01-26.
- ^ Jump up to: a b de Souza Farias SA, da Costa KS, Martins JB (April 2021). "Analysis of Conformational, Structural, Magnetic, and Electronic Properties Related to Antioxidant Activity: Revisiting Flavan, Anthocyanidin, Flavanone, Flavonol, Isoflavone, Flavone, and Flavan-3-ol". ACS Omega. 6 (13): 8908–8918. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c06156. PMC 8028018. PMID 33842761.
- ^ McNaught AD, Wilkinson A (1997), IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (2nd ed.), Oxford: Blackwell Scientific, doi:10.1351/goldbook.F02424, ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7
- ^ Nič M, Jirát J, Košata B, Jenkins A, McNaught A, eds. (2009). "Flavonoids (isoflavonoids and neoflavonoids)". The Gold Book. doi:10.1351/goldbook. ISBN 978-0-9678550-9-7. Retrieved 16 September 2012.
- ^ Vitamins and Hormones. Academic Press. 1949. ISBN 978-0-08-086604-8.
- ^ Clemetson, Alan B. (2018-01-10). Vitamin C: Volume I. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-351-08601-1.
- ^ Galeotti F, Barile E, Curir P, Dolci M, Lanzotti V (2008). "Flavonoids from carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) and their antifungal activity". Phytochemistry Letters. 1: 44–48. doi:10.1016/j.phytol.2007.10.001.
- ^ Ververidis F, Trantas E, Douglas C, Vollmer G, Kretzschmar G, Panopoulos N (October 2007). "Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health". Biotechnology Journal. 2 (10): 1214–34. doi:10.1002/biot.200700084. PMID 17935117. S2CID 24986941.
- ^ Isolation of a UDP-glucose: Flavonoid 5-O-glucosyltransferase gene and expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.). Da Qiu Zhao, Chen Xia Han, Jin Tao Ge and Jun Tao, Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 15 November 2012, Volume 15, Number 6, doi:10.2225/vol15-issue6-fulltext-7
- ^ Spencer JP (May 2008). "Flavonoids: modulators of brain function?". The British Journal of Nutrition. 99 E Suppl 1 (E-S1): ES60-77. doi:10.1017/S0007114508965776. PMID 18503736.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i USDA’s Database on the Flavonoid Content
- ^ Oomah BD, Mazza G (1996). "Flavonoids and Antioxidative Activities in Buckwheat". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 44 (7): 1746–1750. doi:10.1021/jf9508357.
- ^ Ayoub M, de Camargo AC, Shahidi F (April 2016). "Antioxidants and bioactivities of free, esterified and insoluble-bound phenolics from berry seed meals". Food Chemistry. 197 (Pt A): 221–32. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.107. PMID 26616944.
- ^ Levaj B; others (2009). "Determination of flavonoids in pulp and peel of mandarin fruits (table 1)" (PDF). Agriculturae Conspectus Scientificus. 74 (3): 223.
- ^ The Lancet (December 2007). "The devil in the dark chocolate". Lancet. 370 (9605): 2070. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61873-X. PMID 18156011. S2CID 41271401.
- ^ Serafini M, Bugianesi R, Maiani G, Valtuena S, De Santis S, Crozier A (August 2003). "Plasma antioxidants from chocolate" (PDF). Nature. 424 (6952): 1013. Bibcode:2003Natur.424.1013S. doi:10.1038/4241013a. PMID 12944955. S2CID 4381941.
- ^ Roura E, Andrés-Lacueva C, Estruch R, Mata-Bilbao ML, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Waterhouse AL, Lamuela-Raventós RM (2007). "Milk does not affect the bioavailability of cocoa powder flavonoid in healthy human". Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism. 51 (6): 493–8. doi:10.1159/000111473. PMID 18032884. S2CID 25993668.[permanent dead link]
- ^ de Camargo AC, Regitano-d'Arce MA, Gallo CR, Shahidi F (2015). "Gamma-irradiation induced changes in microbiological status, phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of peanut skin". Journal of Functional Foods. 12: 129–143. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2014.10.034.
- ^ Chukwumah Y, Walker LT, Verghese M (November 2009). "Peanut skin color: a biomarker for total polyphenolic content and antioxidative capacities of peanut cultivars". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 10 (11): 4941–52. doi:10.3390/ijms10114941. PMC 2808014. PMID 20087468.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Vogiatzoglou A, Mulligan AA, Lentjes MA, Luben RN, Spencer JP, Schroeter H, et al. (2015). "Flavonoid intake in European adults (18 to 64 years)". PLOS ONE. 10 (5): e0128132. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1028132V. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0128132. PMC 4444122. PMID 26010916.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Chun OK, Chung SJ, Song WO (May 2007). "Estimated dietary flavonoid intake and major food sources of U.S. adults". The Journal of Nutrition. 137 (5): 1244–52. doi:10.1093/jn/137.5.1244. PMID 17449588.
- ^ "FDA approved drug products". US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 8 November 2013.
- ^ "Health Claims Meeting Significant Scientific Agreement". US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 8 November 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) (2010). "Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to various food(s)/food constituent(s) and protection of cells from premature aging, antioxidant activity, antioxidant content and antioxidant properties, and protection of DNA, proteins and lipids from oxidative damage pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/20061". EFSA Journal. 8 (2): 1489. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1489.
- ^ "Inspections, Compliance, Enforcement, and Criminal Investigations (Flavonoid Sciences)". US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 8 November 2013.
- ^ "Inspections, Compliance, Enforcement, and Criminal Investigations (Unilever, Inc.)". US Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 25 October 2013.
- ^ Lotito SB, Frei B (December 2006). "Consumption of flavonoid-rich foods and increased plasma antioxidant capacity in humans: cause, consequence, or epiphenomenon?". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 41 (12): 1727–46. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.04.033. PMID 17157175.
- ^ Williams RJ, Spencer JP, Rice-Evans C (April 2004). "Flavonoids: antioxidants or signalling molecules?". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 36 (7): 838–49. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.001. PMID 15019969.
- ^ Hidalgo M, Oruna-Concha MJ, Kolida S, Walton GE, Kallithraka S, Spencer JP, de Pascual-Teresa S (April 2012). "Metabolism of anthocyanins by human gut microflora and their influence on gut bacterial growth". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 60 (15): 3882–90. doi:10.1021/jf3002153. PMID 22439618.
- ^ Ivey KL, Chan AT, Izard J, Cassidy A, Rogers GB, Rimm EB (September 2019). "Role of Dietary Flavonoid Compounds in Driving Patterns of Microbial Community Assembly". mBio. 10 (5). doi:10.1128/mBio.01205-19. PMC 6759757. PMID 31551328.
- ^ Ravishankar D, Rajora AK, Greco F, Osborn HM (December 2013). "Flavonoids as prospective compounds for anti-cancer therapy". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 45 (12): 2821–31. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.10.004. PMID 24128857.
- ^ Manach C, Mazur A, Scalbert A (February 2005). "Polyphenols and prevention of cardiovascular diseases". Current Opinion in Lipidology. 16 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1097/00041433-200502000-00013. PMID 15650567. S2CID 794383.
- ^ Babu PV, Liu D, Gilbert ER (November 2013). "Recent advances in understanding the anti-diabetic actions of dietary flavonoids". The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 24 (11): 1777–89. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.06.003. PMC 3821977. PMID 24029069.
- ^ Ferretti G, Bacchetti T, Masciangelo S, Saturni L (April 2012). "Celiac disease, inflammation and oxidative damage: a nutrigenetic approach". Nutrients. 4 (4): 243–57. doi:10.3390/nu4040243. PMC 3347005. PMID 22606367.
- ^ Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI (2012). "Flavonoids and cancer prevention: a review of the evidence". Journal of Nutrition in Gerontology and Geriatrics. 31 (3): 206–38. doi:10.1080/21551197.2012.702534. PMID 22888839. S2CID 205960210.
- ^ Rodríguez-García C, Sánchez-Quesada C, J Gaforio J (May 2019). "Dietary Flavonoids as Cancer Chemopreventive Agents: An Updated Review of Human Studies". Antioxidants. 8 (5): 137. doi:10.3390/antiox8050137. PMC 6562590. PMID 31109072.
- ^ Wang X, Ouyang YY, Liu J, Zhao G (January 2014). "Flavonoid intake and risk of CVD: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies". The British Journal of Nutrition. 111 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1017/S000711451300278X. PMID 23953879.
- ^ Sinha RK (2004-01-01). Modern Plant Physiology. CRC Press. p. 457. ISBN 9780849317149.
- ^ Hwang EI, Kaneko M, Ohnishi Y, Horinouchi S (May 2003). "Production of plant-specific flavanones by Escherichia coli containing an artificial gene cluster". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 69 (5): 2699–706. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.5.2699-2706.2003. PMC 154558. PMID 12732539.
- ^ Trantas E, Panopoulos N, Ververidis F (November 2009). "Metabolic engineering of the complete pathway leading to heterologous biosynthesis of various flavonoids and stilbenoids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae". Metabolic Engineering. 11 (6): 355–66. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2009.07.004. PMID 19631278.
- ^ Ververidis F, Trantas E, Douglas C, Vollmer G, Kretzschmar G, Panopoulos N (October 2007). "Biotechnology of flavonoids and other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products. Part II: Reconstruction of multienzyme pathways in plants and microbes". Biotechnology Journal. 2 (10): 1235–49. doi:10.1002/biot.200700184. PMID 17935118. S2CID 5805643.
- ^ "SynBio4Flav | boosting the standardization of high complexity synthetic biological parts". synbio4flav.eu. Retrieved 2020-11-16.
- ^ "Synthetic microbial consortia-based platform for flavonoids production using synthetic biology | H2020 | European Commission".
- ^ Yisa, Jonathan (2009). "Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity Of Scoparia Dulcis and Nymphaea Lotus". Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 3 (4): 3975–3979. Archived from the original on 2013-10-17.
- ^ Bello IA, Ndukwe GI, Audu OT, Habila JD (October 2011). "A bioactive flavonoid from Pavetta crassipes K. Schum". Organic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 1 (1): 14. doi:10.1186/2191-2858-1-14. PMC 3305906. PMID 22373191.
- ^ Delcour JA (1985). "A New Colourimetric Assay for Flavanoids in Pilsner Beers". Journal of the Institute of Brewing. 91: 37–40. doi:10.1002/j.2050-0416.1985.tb04303.x.
- ^ Lamaison, JL; Carnet, A (1991). "Teneurs en principaux flavonoides des fleurs de Cratageus monogyna Jacq et de Cratageus Laevigata (Poiret D.C) en Fonction de la vegetation". Plantes Medicinales Phytotherapie. 25: 12–16.
- ^ Passicos E, Santarelli X, Coulon D (July 2004). "Regioselective acylation of flavonoids catalyzed by immobilized Candida antarctica lipase under reduced pressure". Biotechnology Letters. 26 (13): 1073–6. doi:10.1023/B:BILE.0000032967.23282.15. PMID 15218382. S2CID 26716150.
Further reading[]
- Andersen ØM, Markham KR (2006). 'Flavonoids: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Applications. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-0-8493-2021-7.
- Grotewold E (2006). The science of flavonoids. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-74550-3.
- Harborne JB (1967). Comparative Biochemistry of the Flavonoids.
- l.a.g (1971). "The systematic identification of flavonoids". Journal of Molecular Structure. 10 (2): 320. doi:10.1016/0022-2860(71)87109-0.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flavonoids. |
Databases[]
- Flavonoids
- Nutrients
- Nutrition
- Flavonoid antioxidants