Geography of Georgia (U.S. state)

| |||
| Map of Georgia eleven | Area | ||
| Total | 153,870 km2 (59,410 sq mi) | ||
| Land | 149,976 km2 (57,906 sq mi) | ||
| Water | 854 sq mi (2,210 km2)[1] | ||
| Latitude | 30° 35′ N to 35° N | ||
| Longitude | 80° 50′ W to 85° 36′ W | ||
| Borders | |||
| Florida | state | ||
| South Carolina | state | ||
| Alabama | state | ||
| Tennessee | state | ||
| North Carolina | state | ||
| Coastlines | 100 miles[2] | ||
The geography of Georgia describes a state in the Southeastern United States in North America. The Golden Isles of Georgia lie off the coast of the state. The main geographical features include mountains such as the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians in the northwest, the Blue Ridge Mountains in the northeast, the Piedmont plateau in the central portion of the state and Coastal Plain in the south. The highest area in Georgia is Brasstown Bald which is 1,458 m (4,784 ft) above sea level, while the lowest is at sea level, at the Atlantic Ocean. Georgia is located at approximately 33° N 83.5° W. The state has a total area of 154,077 km2 (59,489 sq mi) and the geographic center is located in Twiggs County.[3]
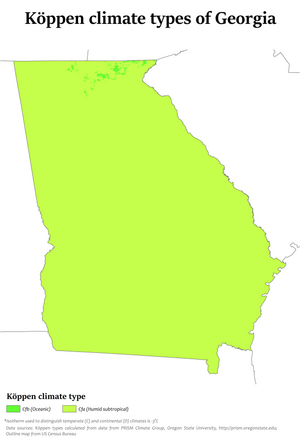
Georgia has primarily a humid subtropical climate with hot and humid summers, except at the highest elevations. Georgia's subtropical climate depends on latitude and how close an area is to the Atlantic Ocean or the Gulf of Mexico. The state's weather is mostly moderate, but Georgia has occasional extreme weather. The highest temperature ever recorded is 112 °F (44.4 °C) and the lowest is -17 °F (-27.2 °C).[4] Georgia is vulnerable to hurricanes, though the coast rarely experiences a direct hurricane strike.
Georgia has 500 cities in 159 counties with 13 congressional districts. 149 of the 159 in the state are governed by a committee of around three to eleven commissioners while the other 10 are overseen by a single commissioner.[5] Most of the 536 cities are governed by a mayor-council system. Georgia has almost eight million acres (32,000 km2) of prime farmland while over 60% of the land is made up of pine forests. Georgia has 70,150 miles (112,900 km) of streams and rivers, 425,000 acres (1,720 km2) of lakes, and approximately 4,500,000 acres (18,000 km2) of freshwater wetlands. Manganese, iron, copper, among and other minerals make up the natural resources of the state.
Physical geography[]
There are five major geographical regions of Georgia. They are the Appalachian Plateau region, the Ridge and Valley region, the Blue Ridge region, the Piedmont region, and the Coastal Plain region.
The Appalachian Plateau region is the southern portion of the Appalachian Plateau that stretches from New York through Georgia and west into Alabama.
The Ridge and Valley region lies in the northwestern portion of the state.[6] The area was formed due to extreme folding and faulting events. This folding and faulting created a series of ridges and valleys that vary in "height, width and geological materials".[7] It consists of limestone, sandstone, chert, mudstone and shale as well as many other types of rocks. Much of the land in the area is heavily forested as forests cover almost half of the region.[8]
The Blue Ridge region of Georgia is situated in the northeast of the state just north of the Piedmont.[6] The mountain peaks in the Blue Ridge, which are among the highest in the state, average between two thousand and five thousand feet.[7] It includes igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary geology; the main types of rocks in the area are gneiss, slate and saprolite. The soils of the Broad Basin are mostly loamy or clayey Ultiso.[8] The Blue Ridge consists primarily of Precambrian metamorphic rocks, and the landscape has relatively high relief.
The Piedmont region consists of Paleozoic metamorphic and igneous rocks, and the landscape has relatively low relief. The Piedmont is the second largest region of Georgia, and it has 3 water systems: the Chattahoochee River, West Point Lake, and Lake Sidney Lanier. The rocks of the Piedmont are made up of Precambrian and Paleozoic metamorphic and igneous rocks and the soils are of a finer texture than those found on the coastal plain. Some specific types of rock in the Piedmont are schist, gneiss, and phyllite among others.[8] Georgia's coastal plain is made up of sedimentary rock dating from the Late Cretaceous to Holocene periods.[9] The primary natural mineral resource in the area is kaolin.[10]
The Coastal Plain region is the largest and includes portions of the Atlantic coastal plain and the Gulf of Mexico Coastal Plain. The Atlantic Coastal Plain and Gulf of Mexico Coastal Plain consist of sediments and sedimentary rocks that range in age from Cretaceous to Present. The boundary between the Piedmont Region and the Coastal Plain Region is the Fall Line. The Sandhills or Carolina Sandhills is a 10–35 mi (16–56 km) wide region within the Atlantic Coastal Plain province, along the inland margin of this province.[11] The Satilla River is in the Atlantic Coastal Plain. Alapaha River, Suwanee River, and the Flint and Chattahoochee rivers flow through the Gulf Coastal Plain and the Florida Panhandle into the Gulf of Mexico. Lake Seminole is a reservoir at the confluence of the Chattahoochee and Flint rivers on the Georgia–Florida border.
Geologic History[]
The oldest known rocks found in Georgia are from the Precambrian Proterozoic Era and are about 1 to 1.34 billion years old. They are found in the Piedmont Plateau and Blue Ridge mountain regions. Approximately 1 billion years ago a metamorphic change occurred during an event called the Grenville Orogeny and caused the rocks, which were originally sediment, to compress into a form of rock called gneiss due to heat and pressure. Around 630 million years ago the Grenville mountains began to erode carrying sediments from streams to the sea. The gneiss formed from these sediments created the marble, metaconglomerate, phyllite, quartzite, schist, and slate found in the Blue Ridge and Piedmont areas.
Three separate orogeny events impacted the eastern portion of North America during the Paleozoic. From these orogeny came folding, faulting, and igneous intrusions in the Piedmont, the Blue Ridge, the Valley and Ridge and the Appalachian Plateau.[12]
Georgia Mountains Region[]

The Georgia Mountains Region are part of the Blue Ridge Mountains and begin in the northeast corner of Georgia. Brasstown Bald, the highest mountain in Georgia at 4,784 feet (1,458 m) above mean sea level,[13] is part of the chain and sits in an area known as Wolfpen Ridge.[14] Other mountains in Georgia include Rabun Bald, Arabia Mountain, Big Bald Mountain, Black Mountain, and Blood Mountain.
Stone Mountain, located in Stone Mountain, Georgia is a well-known mountain that has an elevation of 1,683 feet (513 m) amsl from its summit and 825 feet (251.5 m) above the surrounding plateau. The mountain is known for its geology and also for its enormous bas-relief depicting three Confederate leaders: Jefferson Davis, Robert E. Lee and Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson. The bas-relief is the largest in the world.[15]
Rivers and lakes[]
Several major rivers run through the state of Georgia. Some of them are the Flint River, Towaliga River, Ocmulgee River, Etowah River, Altamaha River, Savannah River, the Suwannee River. The Chattahoochee River is Georgia's longest, at 436 miles (702 km).[16] The river begins in the Blue Ridge Mountains just below Brasstown Bald and ends at Lake Seminole in the southwesternmost corner of Georgia where it creates a boundary between Alabama and Florida.[17]
Lake Lanier is the largest lake in Georgia[18] followed by Lake Oconee as the second largest.[19] Lake Lanier is 26 miles (42 km) long and covers approximately 47 miles (76 km) of riverbed[20] Lake Oconee is 20 miles (32 km) long and about a mile wide.[19] Other lakes in the state include Lake Acworth, Lake Allatoona, Lake Blackshear, Jackson Lake (Georgia), West Point Lake, High Falls, Lake Seminole, Lake Chatuge and Walter F. George Lake.
Islands[]

Georgia has fourteen barrier islands off of its coast. Four of these islands are known as The Golden Isles. The largest of these islands is Cumberland Island in Camden County.[21] The island is uninhabited and is only accessible by boat. Some of the next largest islands are St. Simon's Island in Glynn County as the second largest;[22] Ossabaw Island, twenty miles (32 km) south of Savannah, is the third largest of the islands and Sapelo Island, sixty miles south of Savannah, is the fourth.[23][24] The smallest of the islands is Jekyll Island in Glynn County.[25]
Climate[]

The majority of Georgia has primarily a humid subtropical climate tempered somewhat by occasional polar air masses in the winter. Hot and humid summers are typical, except at the highest elevations. The entire state, including the north Georgia mountains, receives moderate to heavy precipitation, which varies from 45 inches (1143 mm) in central Georgia[26] to approximately 75 inches (1905 mm) around the Northeast part of the state.[27] The degree to which the weather of a certain area of Georgia is subtropical depends not just on the latitude, but also on how close it is to the Atlantic Ocean or Gulf of Mexico and the altitude. This is especially true in the mountainous areas in the northern part of the state, which are further away from ocean waters and can be up to 4500 feet (1350 m) or higher above sea level.
In spite of having moderate weather compared to many other states, Georgia has occasional extreme weather. The highest temperature ever recorded is 112 °F (44.4 °C),[28] while the lowest ever recorded is -17 °F (-27.2 °C).[4] Georgia is one of the leading states in incidents of tornadoes. The areas closest to the Florida border get the same small F0 and F1 tornadoes associated with summer afternoon thunderstorms. However, it is very uncommon for tornadoes to become severe (over F3). As it is on the Atlantic coast, Georgia is also vulnerable to hurricanes, although the Georgia coastline only rarely experiences a direct hurricane strike. More common are hurricanes which strike the Florida panhandle, weaken over land, and bring strong tropical storm winds and heavy rain to the Georgia interior, as well as hurricanes that come close to the Georgia coastline, brushing the coast on their recurvature on the way up to hit the Carolinas.
In 2006 and 2007, however, Georgia has had severe droughts, especially in 2007. Temperatures over 100 degrees have been recorded.
Climate change[]
Climate change in Georgia encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. state of Georgia.
Studies show that Georgia is among a string of "Deep South" states that will experience the worst effects of climate change,[29][30] with effects including "more severe floods and drought", and higher water levels "eroding beaches, submerging low lands, and exacerbating coastal flooding".[31]
The United States Environmental Protection Agency states: "In the coming decades, Georgia will become warmer, and the state will probably experience more severe floods and drought. Even today, more rain is falling in heavy downpours, and sea level is rising about one inch every decade. ... Like other southeastern states, Georgia has warmed less than most of the nation during the last century. But during the next few decades, the changing climate is likely to harm livestock, increase the number of unpleasantly hot days, and increase the risk of heat stroke and other heat-related illnesses".[31]Political and human geography[]

Georgia is made up of more than 500 cities[32] in 159 counties within 13 congressional districts. The map to the right shows the county boundaries for all 159 counties in Georgia.
149 of the 159 counties in the state are governed by a committee made of between three and eleven commissioners[5] while the other 10 counties are overseen by a single commissioner. All commissioners are elected by the voters of their county for terms that range between two and six years with most counties having terms lasting four years. Serving members wield both executive and legislative power in their county.
Most of the 536 cities in Georgia are governed by a mayor-council system. All municipalities in the state are considered cities. There are no lesser incorporations such as towns, villages, or boroughs. Most basic public services rendered outside of the cities are provided by the counties.
Natural resources[]
Agriculture and water[]
Georgia has almost eight million acres (32,000 km2) of prime farmland while over 60% of the land is made up of pine forests.[33] Due to the great number of forested areas in the state Georgia produces more lumber and pulpwood than any other state east of the Mississippi river; from these forests come 74.4 percent of the rasins and turpentines (naval stores) produced in the United States, and over half of the world's supply.[33] Both the agricultural areas and the waters of Georgia have created a thriving environment for hunting, fishing and game.[33] The state of Georgia has much in the way of agricultural resources. Among these resources are potato.
Georgia has 70,150 miles (112,900 km) of streams and rivers, 425,000 acres (1,720 km2) of lakes, and approximately 4,500,000 acres (18,000 km2) of freshwater wetlands.[33]
Geological resources[]
The geological resources of Georgia include many types of minerals, manganese, iron ore, copper, coal, oil, clays, stone, kaolin, sand and gravel.[8]
See also[]
Geologic map of Georgia
References[]
- ^ wetstates.html, Accessed October 4, 2007
- ^ Georgia.org, Accessed October 7, 2007
- ^ USGS.gov, Accessed May 25, 2007
- ^ Jump up to: a b Each state's low temperature record USA Today, last updated August 2006
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Government of Georgia Archived 2008-06-26 at the Wayback Machine, Accessed June 24, 2008
- ^ Jump up to: a b State Flags Flowers Birds Symbols and Emblems State Quarters Geography and Maps Newspapers History and Economy for the 50 States, Accessed June 20, 2008
- ^ Jump up to: a b The University of Georgia (UGA) Georgia Overview, Accessed June 20, 2008
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Georgia Ecoregion Descriptions, Accessed November 23, 2007
- ^ A Tapestry of Time and Terrain: The Coastal Plain Archived 2009-05-06 at the Wayback Machine, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Kaolin, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Swezey, C.S., Fitzwater, B.A., Whittecar, G.R., Mahan, S.A., Garrity, C.P., Aleman Gonzalez, W.B., and Dobbs, K.M., 2016, "The Carolina Sandhills: Quaternary eolian sand sheets and dunes along the updip margin of the Atlantic Coastal Plain province, southeastern United States": Quaternary Research, v. 86, p. 271-286; www.cambridge.org/core/journals/quaternary-research
- ^ New Georgia Encyclopedia: Geologic History of Georgia: Overview Accessed, May 22, 2007
- ^ Georgia's Named Summits Accessed October 3, 2007
- ^ Georgia Summits Above 4,000 Feet Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine Accessed October 3, 2007
- ^ Stone Mountain georgia.gov Archived 2008-04-22 at the Wayback Machine, Accessed June 23, 2008
- ^ Carl Vinson Institute of Government Chattahoochee River, Accessed September 27, 2007
- ^ The Natural History of the Chattahoochee River, Accessed June 24, 2008
- ^ Dawson County Outdoor Recreation Archived 2008-06-21 at the Wayback Machine, Accessed June 23, 2008
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lake Oconee Georgia "Great Waters", Accessed June 23, 2008
- ^ Lake Lanier, Accessed June 24, 2008
- ^ Cumberland Island, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ St. Simon's Island, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Ossabaw Island Accessed, November 25, 2007
- ^ Sapelo Island, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Jekyll Island, Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Monthly Averages for Macon, GA The Weather Channel.
- ^ Monthly Averages for Clayton, GA The Weather Channel.
- ^ Each state's high temperature record USA Today, last updated August 2006.
- ^ Meyer, Robinson (June 29, 2017). "The American South Will Bear the Worst of Climate Change's Costs". The Atlantic.
- ^ Wood, Ada (November 15, 2018). "Georgia will face danger from climate change". The Signal.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "What Climate Change Means for Georgia" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. August 2016.
- ^ Government and Laws of Georgia: Overview Accessed November 25, 2007
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Georgia's Natural Resources, Accessed November 26, 2007
- Geography of Georgia (U.S. state)

