History of Cuba
| History of Cuba |
|---|
 |
| Governorate of Cuba (1511–1519) |
| Viceroyalty of New Spain (1535–1821) |
| Captaincy General of Cuba (1607–1898) |
|
|
| US Military Government (1898–1902) |
| Republic of Cuba (1902–1959) |
|
|
| Republic of Cuba (1959–) |
|
|
| Timeline |
|
|
| Topical |
|
|
|
The history of Cuba is characterized by dependence on outside powers—Spain, the US, and the USSR. The island of Cuba was inhabited by various Amerindian cultures prior to the arrival of the Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus in 1492. After his arrival on a Spanish expedition, Spain conquered Cuba and appointed Spanish governors to rule in Havana. The administrators in Cuba were subject to the Viceroy of New Spain and the local authorities in Hispaniola. In 1762–63, Havana was briefly occupied by Britain, before being returned to Spain in exchange for Florida. A series of rebellions between 1868 and 1898, led by Dominican General Máximo Gómez, failed to end Spanish rule and claimed the lives of hundreds of thousands of Cubans. However, the Spanish–American War resulted in a Spanish withdrawal from the island in 1898, and following three-and-a-half years of subsequent US military rule,[1] Cuba gained formal independence in 1902.[2]
In the years following its independence, the Cuban republic saw significant economic development, but also political corruption and a succession of despotic leaders, culminating in the overthrow of the dictator Fulgencio Batista by the 26th of July Movement, led by Fidel Castro, during the 1953–1959 Cuban Revolution.[3] The new government aligned with the Soviet Union and embraced communism.[a] In the early 1960s, Castro's regime withstood invasion (April 1961), faced nuclear Armageddon (October 1962),[b] and experienced a civil war (October 1960) that included Dominican support for regime opponents.[c] Following the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia (1968), Castro publicly declared Cuba's support. His speech marked the start of Cuba's complete absorption into the Eastern Bloc.[8] By the mid-1970s, little would remain of Cuba's political or economic system. During the Cold War, Cuba also supported Soviet policy in Afghanistan, Poland, Angola, Ethiopia, Nicaragua, and El Salvador.[9] The Soviet-Cuban intervention in Angola contributed to the downfall of the apartheid regime in South Africa.[10][11]
The extraordinarily weak Cuban economy was solely supported by Soviet subsidies. With the dissolution of the USSR in 1991 the subsidies disappeared and Cuba was plunged into a severe economic crisis known as the Special Period that ended in 2000 when Venezuela began providing Cuba with subsidized oil. In 2019, Miguel Diaz-Canel was elected President of Cuba by the national assembly.[12] The country has been politically and economically isolated by the United States since the Revolution, but has gradually gained access to foreign commerce and travel as efforts to normalise diplomatic relations have progressed.[13][14][15][16][17] Domestic economic reforms are also beginning to modernize Cuba's socialist economy.[18]
Pre-Columbian History (Prehistory - 1500)[]

Cuba's earliest known human inhabitants colonized the island in the 4th millennium BC.[19] The oldest known Cuban archeological site, Levisa, dates from approximately 3100 BC.[20] A wider distribution of sites date from after 2000 BC, most notably represented by the Cayo Redondo and Guayabo Blanco cultures of western Cuba. These neolithic cultures used ground stone and shell tools and ornaments, including the dagger-like gladiolitos, which are believed to have had a ceremonial role.[21] The Cayo Redondo and Guayabo Blanco cultures lived a subsistence lifestyle based on fishing, hunting and collecting wild plants.[21]
Prior to Columbus' arrival, the indigenous Guanajatabey, who had inhabited Cuba for centuries, were driven to the far west of the island by the arrival of subsequent waves of migrants, including the Taíno and Ciboney. These people had migrated north along the Caribbean island chain.
The Taíno and Siboney were part of a cultural group commonly called the Arawak, who inhabited parts of northeastern South America prior to the arrival of Europeans. Initially, they settled at the eastern end of Cuba, before expanding westward across the island. The Spanish Dominican clergyman and writer Bartolomé de las Casas estimated that the Taíno population of Cuba had reached 350,000 by the end of the 15th century. The Taíno cultivated the yuca root, harvested it and baked it to produce cassava bread. They also grew cotton and tobacco, and ate maize and sweet potatoes. According to History of the Indians, they had "everything they needed for living; they had many crops, well arranged".[22]
Spanish Conquest and Early Colonization (1492 - 1800)[]

Christopher Columbus, on his first Spanish-sponsored voyage to the Americas in 1492, sailed south from what is now the Bahamas to explore the northeast coast of Cuba and the northern coast of Hispaniola. Columbus, who was searching for a route to India, believed the island to be a peninsula of the Asian mainland.[23][24] The first sighting of a Spanish ship approaching the island was on 27 October 1492, probably at Bariay, Holguín Province, on the eastern point of the island.[25]
During a second voyage in 1494, Columbus passed along the south coast of the island, landing at various inlets including what was to become Guantánamo Bay. With the Papal Bull of 1493, Pope Alexander VI commanded Spain to conquer, colonize and convert the pagans of the New World to Catholicism.[26] On arrival, Columbus observed the Taíno dwellings, describing them as "looking like tents in a camp. All were of palm branches, beautifully constructed".[27]
The Spanish began to create permanent settlements on the island of Hispaniola, east of Cuba, soon after Columbus' arrival in the Caribbean, but the coast of Cuba was not fully mapped by Europeans until 1508, when Sebastián de Ocampo completed this task.[28] In 1511, Diego Velázquez de Cuéllar set out from Hispaniola to form the first Spanish settlement in Cuba, with orders from Spain to conquer the island. The settlement was at Baracoa, but the new settlers were greeted with stiff resistance from the local Taíno population. The Taínos were initially organized by cacique (chieftain) Hatuey, who had himself relocated from Hispaniola to escape the brutalities of Spanish rule on that island. After a prolonged guerrilla campaign, Hatuey and successive chieftains were captured and burnt alive, and within three years the Spanish had gained control of the island. In 1514, a settlement was founded in what was to become Havana.
Clergyman Bartolomé de las Casas observed a number of massacres initiated by the invaders as the Spanish swept over the island, notably the massacre near Camagüey of the inhabitants of Caonao. According to his account, some three thousand villagers had traveled to Manzanillo to greet the Spanish with loaves, fishes and other foodstuffs, and were "without provocation, butchered".[29] The surviving indigenous groups fled to the mountains or the small surrounding islands before being captured and forced into reservations. One such reservation was Guanabacoa, which is today a suburb of Havana.[30]

In 1513, Ferdinand II of Aragon issued a decree establishing the encomienda land settlement system that was to be incorporated throughout the Spanish Americas. Velázquez, who had become Governor of Cuba relocating from Baracoa to Santiago de Cuba, was given the task of apportioning both the land and the indigenous peoples to groups throughout the new colony. The scheme was not a success, however, as the natives either succumbed to diseases brought from Spain such as measles and smallpox, or simply refused to work, preferring to slip away into the mountains.[25] Desperate for labor to toil the new agricultural settlements, the Conquistadors sought slaves from surrounding islands and the continental mainland. However, these new arrivals followed the indigenous peoples by also dispersing into the wilderness or dying of disease.[25]
Despite the difficult relations between the natives and the new Europeans, some cooperation was in evidence. The Spanish were shown by the natives how to nurture tobacco and consume it in the form of cigars. There were also many unions between the largely male Spanish colonists and indigenous women. Modern-day studies have revealed traces of DNA that renders physical traits similar to Amazonian tribes in individuals throughout Cuba,[31] although the native population was largely destroyed as a culture and civilization after 1550. Under the Spanish New Laws of 1552, indigenous Cuban were freed from encomienda, and seven towns for indigenous peoples were set up. There are indigenous descendant Cuban (Taíno) families in several places, mostly in eastern Cuba. The indigenous community at Caridad de los Indios, Guantánamo, is one such nucleus. An association of indigenous families in Jiguani, near Santiago, is also active. The local indigenous population also left their mark on the language, with some 400 Taíno terms and place-names surviving to the present day. The name of Cuba itself, Havana, Camagüey, and many others were derived from Classic Taíno, and indigenous words such as tobacco, hurricane and canoe were transferred to English and are used today.[30]
Arrival of African Slaves (1500 - 1820)[]

The Spanish established sugar and tobacco as Cuba's primary products, and the island soon supplanted Hispaniola as the prime Spanish base in the Caribbean.[32] Further field labor was required. African slaves were then imported to work the plantations as field labor. However, restrictive Spanish trade laws made it difficult for Cubans to keep up with the 17th and 18th century advances in processing sugar cane pioneered in Barbados, Jamaica and Saint-Domingue. Spain also restricted Cuba's access to the slave trade, instead issuing foreign merchants asientos to conduct it on Spain's behalf. The advances in the system of sugar cane refinement did not reach Cuba until the Haitian Revolution in the nearby French colony of Saint-Domingue led to thousands of refugee French planters to flee to Cuba and other islands in the West Indies, bringing their slaves and expertise in sugar refining and coffee growing into eastern Cuba in the 1790s and early 19th century.[33]
In the 19th century, Cuban sugar plantations became the most important world producer of sugar, thanks to the expansion of slavery and a relentless focus on improving the island's sugar technology. Use of modern refining techniques was especially important because the British Slave Trade Act 1807 abolished the slave trade in the British Empire (with slavery itself being abolished in the Slavery Abolition Act 1833). The British government set about trying to eliminate the transatlantic slave trade. Under British diplomatic pressure, in 1817 Spain agreed to abolish the slave trade from 1820 in exchange for a payment from London. Cubans rapidly rushed to import further slaves in the time legally left to them. Over a 100,000 new slaves were imported from Africa between 1816 and 1820.[33] In other words, 100,000 African people were kidnapped and forced into slavery. In spite of the new restrictions a large-scale illegal slave trade continued to flourish in the following years.[34]
Many Cubans were torn between desire for the profits generated by sugar and a repugnance for slavery, which they saw as morally, politically, and racially dangerous to their society. By the end of the 19th century, slavery was abolished. However, prior to the abolition of slavery, Cuba gained great prosperity from its sugar trade. Originally, the Spanish had ordered regulations on trade with Cuba, which kept the island from becoming a dominant sugar producer. The Spanish were interested in keeping their trade routes and slave trade routes protected. Nevertheless, Cuba's vast size and abundance of natural resources made it an ideal place for becoming a booming sugar producer. When Spain opened the Cuban trade ports, it quickly became a popular place. New technology allowed a much more effective and efficient means of producing sugar. They began to use water mills, enclosed furnaces, and steam engines to produce higher-quality sugar at a much more efficient pace than elsewhere in the Caribbean.
The boom in Cuba's sugar industry in the 19th century made it necessary for the country to improve its transportation infrastructure. Planters needed safe and efficient ways to transport the sugar from the plantations to the ports, in order to maximize their returns. Many new roads were built, and old roads were quickly repaired. Railroads were built relatively early, easing the collection and transportation of perishable sugar cane. It was now possible for plantations all over this large island to have their sugar shipped quickly and easily.
Sugar plantations[]
Cuba failed to prosper before the 1760s, due to Spanish trade regulations. Spain had set up a trade monopoly in the Caribbean, and their primary objective was to protect this, which they did by barring the islands from trading with any foreign ships. The resultant stagnation of economic growth was particularly pronounced in Cuba because of its great strategic importance in the Caribbean, and the stranglehold that Spain kept on it as a result.

As soon as Spain opened Cuba's ports up to foreign ships, a great sugar boom began that lasted until the 1880s. The island was perfect for growing sugar, being dominated by rolling plains, with rich soil and adequate rainfall. By 1860, Cuba was devoted to growing sugar, having to import all other necessary goods. Cuba was particularly dependent on the United States, which bought 82 percent of its sugar. In 1820, Spain abolished the slave trade, hurting the Cuban economy even more and forcing planters to buy more expensive, illegal, and "troublesome" slaves (as demonstrated by the slave rebellion on the Spanish ship Amistad in 1839).[35]
Cuba Under Attack (1500 - 1800)[]


Colonial Cuba was a frequent target of buccaneers, pirates and French corsairs seeking Spain's New World riches. In response to repeated raids, defenses were bolstered throughout the island during the 16th century. In Havana, the fortress of Castillo de los Tres Reyes Magos del Morro was built to deter potential invaders, which included the English privateer Francis Drake, who sailed within sight of Havana harbor but did not disembark on the island.[36] Havana's inability to resist invaders was dramatically exposed in 1628, when a Dutch fleet led by Piet Heyn plundered the Spanish ships in the city's harbor.[37] In 1662, English pirate Christopher Myngs captured and briefly occupied Santiago de Cuba on the eastern part of the island, in an effort to open up Cuba's protected trade with neighboring Jamaica.[37]
Nearly a century later, the British Royal Navy launched another invasion, capturing Guantánamo Bay in 1741 during the War of Jenkins' Ear with Spain. Edward Vernon, the British admiral who devised the scheme, saw his 4,000 occupying troops capitulate to raids by Spanish troops, and more critically, an epidemic, forcing him to withdraw his fleet to British Jamaica.[38] In the War of the Austrian Succession, the British carried out unsuccessful attacks against Santiago de Cuba in 1741 and again in 1748. Additionally, a skirmish between British and Spanish naval squadrons occurred near Havana in 1748.[38]
The Seven Years' War, which erupted in 1754 across three continents, eventually arrived in the Spanish Caribbean. Spain's alliance with the French pitched them into direct conflict with the British, and in 1762 a British expedition of five warships and 4,000 troops set out from Portsmouth to capture Cuba. The British arrived on 6 June, and by August had Havana under siege.[39] When Havana surrendered, the admiral of the British fleet, George Keppel, the 3rd Earl of Albemarle, entered the city as a new colonial governor and took control of the whole western part of the island. The arrival of the British immediately opened up trade with their North American and Caribbean colonies, causing a rapid transformation of Cuban society.[39]
Though Havana, which had become the third-largest city in the Americas, was to enter an era of sustained development and closening ties with North America during this period, the British occupation of the city proved short-lived. Pressure from London sugar merchants fearing a decline in sugar prices forced a series of negotiations with the Spanish over colonial territories. Less than a year after Havana was seized, the Peace of Paris was signed by the three warring powers, ending the Seven Years' War. The treaty gave Britain Florida in exchange for Cuba on France's recommendation to Spain, The French advised that declining the offer could result in Spain losing Mexico and much of the South American mainland to the British.[39] In 1781, General Bernardo de Gálvez, the Spanish governor of Louisiana, reconquered Florida for Spain with Mexican, Puerto Rican, Dominican, and Cuban troops.[40]
Reformism, Annexation, and Independence (1800 - 1898)[]
In the early 19th century, three major political currents took shape in Cuba: reformism, annexation and independence. In addition, spontaneous and isolated actions carried out from time to time added a current of abolitionism. The 1776 Declaration of Independence by the thirteen of the British colonies of North America and the successes of the French Revolution of 1789 influenced early Cuban liberation movements, as did the successful revolt of black slaves in Haiti in 1791. One of the first of such movements in Cuba, headed by the free black Nicolás Morales, aimed at gaining equality between "mulatto and whites" and at the abolition of sales taxes and other fiscal burdens. Morales' plot was discovered in 1795 in Bayamo, and the conspirators were jailed.
Reform, autonomy and separatist movements[]
As a result of the political upheavals caused by the Iberian Peninsular War of 1807-1814 and of the removal of Ferdinand VII from the Spanish throne in 1808, a western separatist rebellion emerged among the Cuban Creole aristocracy in 1809 and 1810. One of its leaders, , drafted Cuba's first constitution, declaring the island a sovereign state, presuming the rule of the country's wealthy, maintaining slavery as long as it was necessary for agriculture, establishing a social classification based on skin color and declaring Catholicism the official religion. This conspiracy also failed, and the main leaders were sentenced to prison and deported to Spain.[41] In 1812 a mixed-race abolitionist conspiracy arose, organized by José Antonio Aponte, a free-black carpenter in Havana. He and others were executed.
The Spanish Constitution of 1812, and the legislation passed by the Cortes of Cádiz after it was set up in 1808, instituted a number of liberal political and commercial policies, which were welcomed in Cuba but also curtailed a number of older liberties. Between 1810 and 1814 the island elected six representatives to the Cortes, in addition to forming a locally-elected Provincial Deputation.[42] Nevertheless, the liberal regime and the Constitution proved ephemeral: Ferdinand VII suppressed them when he returned to the throne in 1814. Therefore, by the end of the 1810s, some Cubans were inspired by the successes of Simón Bolívar in South America, despite the fact that the Spanish Constitution was restored in 1820. Numerous secret-societies emerged, most notably the so-called "Soles y Rayos de Bolívar", founded in 1821 and led by . It aimed to establish the free (a Taíno name for the center of the island[43]), and it had branches in five districts of the island.
In 1823 the society's leaders were arrested and condemned to exile. In the same year, King Ferdinand VII, with French help and with the approval of the Quintuple Alliance, managed to abolish constitutional rule in Spain yet again and to re-establish absolutism. As a result, the national militia of Cuba, established by the Constitution and a potential instrument for liberal agitation, was dissolved, a permanent executive military commission under the orders of the governor was created, newspapers were closed, elected provincial representatives were removed and other liberties suppressed.
This suppression, and the success of independence movements in the former Spanish colonies on the North American mainland, led to a notable rise of Cuban nationalism. A number of independence conspiracies developed during the 1820s and 1830s, but all failed. Among these were the "Expedición de los Trece" (Expedition of the 13) in 1826, the "Gran Legión del Aguila Negra" (Great Legion of the Black Eagle) in 1829, the "Cadena Triangular" (Triangular Chain) and the "Soles de la Libertad" (Suns of Liberty) in 1837. Leading national figures in these years included Félix Varela (1788-1853) and Cuba's first revolutionary poet, José María Heredia (1803-1839).[44]
Between 1810 and 1826, 20,000 royalist refugees from the Latin American Revolutions arrived in Cuba. They were joined by others who left Florida when Spain ceded it to the United States in 1819. These influxes strengthened loyalist pro-Spanish sentiments on the island.[45]
Antislavery and independence movements[]
In 1826 the first armed uprising for independence took place in Puerto Príncipe (Camagüey Province), led by Francisco de Agüero and Andrés Manuel Sánchez. Agüero, a white man, and Sánchez, a mulatto, were both executed, becoming the first popular martyrs of the Cuban independence movement.[46]
The 1830s saw a surge of activity from the reformist movement, whose main leader, José Antonio Saco, stood out for his criticism of Spanish despotism and of the slave trade. Nevertheless, this surge bore no fruit; Cubans remained deprived of the right to send representatives to the Spanish parliament, and Madrid stepped up repression.
Nonetheless, Spain had long been under pressure to end the slave trade. In 1817 Ferdinand VII signed a decree,[47] to which the Spanish Empire did not adhere. Under British diplomatic pressure, the Spanish government signed a treaty in 1835 which pledged to eventually abolish slavery and the slave trade.[citation needed] In this context, black revolts in Cuba increased, and were put down with mass executions. One of the most significant was the (Ladder Conspiracy), which started in March 1843 and continued until 1844. The conspiracy took its name from a torture method, in which blacks were tied to a ladder and whipped until they confessed or died. The Ladder Conspiracy involved free blacks and slaves, as well as white intellectuals and professionals. It is estimated[by whom?] that 300 blacks and mulattos died from torture, 78 were executed, over 600 were imprisoned and over 400 expelled from the island.[48][49] (See comments in new translation of Villaverde's "Cecilia Valdés".) The executed included the leading poet (1809-1844), now commonly known as "Plácido".[50] José Antonio Saco, one of Cuba's most prominent thinkers, was expelled from Cuba.[51]

Following the 1868–1878 rebellion of the Ten Years' War, all slavery was abolished by 1886, making Cuba the second-to-last country in the Western Hemisphere to abolish slavery, with Brazil being the last. Instead of blacks, slave traders looked for others sources of cheap labour, such as Chinese colonists and Indians from Yucatán. Another feature of the population was the number of Spanish-born colonists, known as peninsulares, who were mostly adult males; they constituted between ten and twenty per cent of the population between the middle of the 19th century and the great depression of the 1930s.
The possibility of annexation by the United States[]
Black unrest and attempts by the Spanish metropolis to abolish slavery motivated many Creoles to advocate Cuba's annexation by the United States, where slavery was still legal. Other Cubans supported the idea due to their desire for American-style economic development and democratic freedom. The annexation of Cuba was repeatedly proposed by government officials in the United States. In 1805, President Thomas Jefferson considered annexing Cuba for strategic reasons, sending secret agents to the island to negotiate with Captain General Someruelos.
In April 1823, U.S. Secretary of State John Quincy Adams discussed the rules of political gravitation, in a theory often referred to as the "ripe fruit theory". Adams wrote, "There are laws of political as well as physical gravitation; and if an apple severed by its native tree cannot choose but fall to the ground, Cuba, forcibly disjoined from its own unnatural connection with Spain, and incapable of self-support, can gravitate only towards the North American Union which by the same law of nature, cannot cast her off its bosom".[52] He furthermore warned that "the transfer of Cuba to Great Britain would be an event unpropitious to the interest of this Union".[53] Adams voiced concern that a country outside of North America would attempt to occupy Cuba upon its separation from Spain. He wrote, "The question both of our right and our power to prevent it, if necessary, by force, already obtrudes itself upon our councils, and the administration is called upon, in the performance of its duties to the nation, at least to use all the means with the competency to guard against and forfend it".[54]
On 2 December 1823, U.S. President James Monroe specifically addressed Cuba and other European colonies in his proclamation of the Monroe Doctrine. Cuba, located just 94 miles (151 km) from Key West, Florida, was of interest to the doctrine's founders, as they warned European forces to leave "America for the Americans".[55]
The most outstanding attempts in support of annexation were made by the Venezuelan filibuster General Narciso López, who prepared four expeditions to Cuba in the US. The first two, in 1848 and 1849, failed before departure due to U.S. opposition. The third, made up of some 600 men, managed to land in Cuba and take the central city of Cárdenas, but failed eventually due to a lack of popular support. López's fourth expedition landed in Pinar del Río province with around 400 men in August 1851; the invaders were defeated by Spanish troops and López was executed.
The Struggle for Independence[]

In the 1860s, Cuba had two more liberal-minded governors, Serrano and Dulce, who encouraged the creation of a Reformist Party, despite the fact that political parties were forbidden. But they were followed by a reactionary governor, Francisco Lersundi, who suppressed all liberties granted by the previous governors and maintained a pro-slavery regime.[56] On 10 October 1868, the landowner Carlos Manuel de Céspedes declared Cuban independence and freedom for his slaves. This began the Ten Years' War, which lasted from 1868 to 1878. The Dominican Restoration War (1863–65) brought to Cuba an unemployed mass of former Dominican white and light-skinned mulattos who had served with the Spanish Army in the Dominican Republic before being evacuated to Cuba and discharged from the army.[57] Some of these former soldiers joined the new Revolutionary Army and provided its initial training and leadership.[57][58]

With reinforcements and guidance from the Dominicans, the Cuban rebels defeated Spanish detachments, cut railway lines, and gained dominance over vast sections of the eastern portion of the island.[59] The Spanish government used the Voluntary Corps to commit harsh and bloody acts against the Cuban rebels, and the Spanish atrocities fuelled the growth of insurgent forces in eastern Cuba; however, they failed to export the revolution to the west. On 11 May 1873, Ignacio Agramonte was killed by a stray bullet; Céspedes was surprised and killed on 27 February 1874. In 1875, Máximo Gómez began an invasion of Las Villas west of a fortified military line, or trocha, bisecting the island.[60] The trocha was built between 1869 and 1872; the Spanish erected it to prevent Gómez to move westward from Oriente province.[61] It was the largest fortification built by the Spanish in the Americas.[62]
Gómez was controversial in his calls to burn sugar plantations to harass the Spanish occupiers. After the American admiral Henry Reeve was killed in 1876, Gómez ended his campaign. By that year, the Spanish government had deployed more than 250,000 troops to Cuba, as the end of the Third Carlist War had freed up Spanish soldiers for the suppression of the revolt. On 10 February 1878, General Arsenio Martínez Campos negotiated the Pact of Zanjón with the Cuban rebels, and the rebel general Antonio Maceo's surrender on 28 May ended the war. Spain sustained 200,000 casualties, mostly from disease; the rebels sustained 100,000–150,000 dead and the island sustained over $300 million in property damage.[57] The Pact of Zanjón promised the manumission of all slaves who had fought for Spain during the war, and slavery was legally abolished in 1880. However, dissatisfaction with the peace treaty led to the Little War of 1879–80.
Conflicts in the Late 19th Century (1886 - 1900)[]
Background[]
Social, Political, and Economic Change[]
During the time of the so-called "Rewarding Truce", which encompassed the 17 years from the end of the Ten Years' War in 1878, fundamental changes took place in Cuban society. With the abolition of slavery in October 1886, former slaves joined the ranks of farmers and urban working class. Most wealthy Cubans lost their rural properties, and many of them joined the urban middle class. The number of sugar mills dropped and efficiency increased, with only companies and the most powerful plantation owners owning them. The numbers of campesinos and tenant farmers rose considerably. Furthermore, American capital began flowing into Cuba, mostly into the sugar and tobacco businesses and mining. By 1895, these investments totalled $50 million. Although Cuba remained Spanish politically, economically it became increasingly dependent on the United States.[63]
These changes also entailed the rise of labour movements. The first Cuban labour organization, the Cigar Makers Guild, was created in 1878, followed by the Central Board of Artisans in 1879, and many more across the island.[64] Abroad, a new trend of aggressive American influence emerged, evident in Secretary of State James G. Blaine's expressed belief that all of Central and South America would some day fall to the US. Blaine placed particular importance on the control of Cuba. "That rich island", he wrote on 1 December 1881, "the key to the Gulf of Mexico, is, though in the hands of Spain, a part of the American commercial system…If ever ceasing to be Spanish, Cuba must necessarily become American and not fall under any other European domination".[65] Blaine's vision did not allow the existence of an independent Cuba.[66]
Martí's Insurrection and the Start of the War[]
After his second deportation to Spain in 1878, the pro-independence Cuban activist José Martí moved to the United States in 1881, where he began mobilizing the support of the Cuban exile community in Florida, especially in Ybor City in Tampa and Key West.[67] He sought a revolution and Cuban independence from Spain, but also lobbied to oppose U.S. annexation of Cuba, which some American and Cuban politicians desired. Propaganda efforts continued for years and intensified starting in 1895.[68][69]
After deliberations with patriotic clubs across the United States, the Antilles and Latin America, the Partido Revolucionario Cubano (Cuban Revolutionary Party) was officially proclaimed on 10 April 1892, with the purpose of gaining independence for both Cuba and Puerto Rico. Martí was elected delegate, the highest party position. By the end of 1894, the basic conditions for launching the revolution were set.[70] In Foner's words, "Martí's impatience to start the revolution for independence was affected by his growing fear that the United States would succeed in annexing Cuba before the revolution could liberate the island from Spain".[66]
On 25 December 1894, three ships, the Lagonda, the Almadis and the Baracoa, set sail for Cuba from Fernandina Beach, Florida, loaded with armed men and supplies. Two of the ships were seized by U.S. authorities in early January, who also alerted the Spanish government, but the proceedings went ahead. The insurrection began on 24 February 1895, with uprisings all across the island. In Oriente the most important ones took place in Santiago, Guantánamo, Jiguaní, San Luis, El Cobre, El Caney, Alto Songo, Bayate and Baire. The uprisings in the central part of the island, such as Ibarra, Jagüey Grande and Aguada, suffered from poor co-ordination and failed; the leaders were captured, some of them deported and some executed. In the province of Havana the insurrection was discovered before it got off and the leaders detained. Thus, the insurgents further west in Pinar del Río were ordered to wait.
Martí, on his way to Cuba, gave the Proclamation of Montecristi in Santo Domingo, outlining the policy for Cuba's war of independence: the war was to be waged by blacks and whites alike; participation of all blacks was crucial for victory; Spaniards who did not object to the war effort should be spared, private rural properties should not be damaged; and the revolution should bring new economic life to Cuba.[65][71]
On 1 and 11 April 1895, the main rebel leaders landed on two expeditions in Oriente: Major Antonio Maceo and 22 members near Baracoa and Martí, Máximo Gómez and four other members in Playitas. Around that time, Spanish forces in Cuba numbered about 80,000, of which 20,000 were regular troops, and 60,000 were Spanish and Cuban volunteers. The latter were a locally enlisted force that took care of most of the guard and police duties on the island. Wealthy landowners would volunteer a number of their slaves to serve in this force, which was under local control and not under official military command. By December, 98,412 regular troops had been sent to the island and the number of volunteers had increased to 63,000 men. By the end of 1897, there were 240,000 regulars and 60,000 irregulars on the island. The revolutionaries were far outnumbered.[65]
The rebels came to be nicknamed "Mambis" after a black Spanish officer, Juan Ethninius Mamby, who joined the Dominicans in the fight for independence in 1846.[72] The Spanish soldiers referred to the Dominican insurgents as "the men of Mamby" and "Mambis".[73] When the Ten Years' War broke out in 1868, some of the same soldiers were assigned to Cuba, importing what had by then become a derogatory Spanish slur. The Cubans adopted the name with pride.[74]
After the Ten Years' War, possession of weapons by private individuals was prohibited in Cuba. Thus, one of the most serious and persistent problems for the rebels was a shortage of suitable weapons. This lack of arms forced them to utilise guerrilla tactics, using the environment, the element of surprise, fast horses and simple weapons such as machetes. Most of their firearms were acquired in raids on the Spaniards. Between 11 June 1895 and 30 November 1897, 60 attempts were made to bring weapons and supplies to the rebels from outside Cuba, but only one succeeded, largely due to British naval protection. 28 of these resupply attempts were halted within U.S. territory, five were intercepted by the U.S. Navy, four by the Spanish Navy, two were wrecked, one was driven back to port by a storm, and the fate of another is unknown.[65]
Escalation of the War[]

Martí was killed on 19 May 1895, during a reckless charge against entrenched Spanish forces, but Máximo Gómez (a Dominican) and Antonio Maceo (a mulatto)[75] fought on, taking the war to all parts of Oriente. Gómez used scorched-earth tactics, which entailed dynamiting passenger trains and burning the Spanish loyalists' property and sugar plantations—including many owned by Americans.[76] By the end of June all of Camagüey was at war. Continuing west, Gómez and Maceo joined up with veterans of the 1868 war, Polish internationalists, General Carlos Roloff and Serafín Sánchez in Las Villas, swelling their ranks and boosting their arsenal. In mid-September, representatives of the five Liberation Army Corps assembled in Jimaguayú, Camagüey, to approve the Jimaguayú Constitution. This constitution established a central government, which grouped the executive and legislative powers into one entity, the Government Council, which was headed by and Bartolomé Masó.
After a period of consolidation in the three eastern provinces, the liberation armies headed for Camagüey and then for Matanzas, outmanoeuvring and deceiving the Spanish Army several times. The revolutionaries defeated the Spanish general Arsenio Martínez Campos, himself the victor of the Ten Years' War, and killed his most trusted general at . Campos tried the same strategy he had employed in the Ten Years' War, constructing a broad defensive belt across the island, about 80 kilometres (50 mi) long and 200 metres (660 ft) wide. This line, called the trocha, was intended to limit rebel activities to the eastern provinces, and consisted of a railroad, from Jucaro in the south to Moron in the north, on which armored railcars could travel. At various points along this railroad there were fortifications, at intervals of 12 metres (39 ft) there were posts and at intervals of 400 metres (1,300 ft) there was barbed wire. In addition, booby traps were placed at the locations most likely to be attacked.
For the rebels, it was essential to bring the war to the western provinces of Matanzas, Havana and Pinar del Río, where the island's government and wealth was located. The Ten Years' War failed because it had not managed to proceed beyond the eastern provinces.[65] In a successful cavalry campaign, overcoming the trochas, the rebels invaded every province. Surrounding all the larger cities and well-fortified towns, they arrived at the westernmost tip of the island on 22 January 1896, exactly three months after the invasion near Baraguá.[77][78]
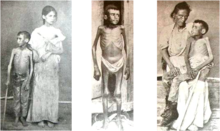
Unable to defeat the rebels with conventional military tactics,[79] the Spanish government sent Gen. Valeriano Weyler y Nicolau (nicknamed The Butcher), who reacted to these rebel successes by introducing terror methods: periodic executions, mass exiles, and the destruction of farms and crops. These methods reached their height on 21 October 1896, when he ordered all countryside residents and their livestock to gather in various fortified areas and towns occupied by his troops within eight days. Hundreds of thousands of people had to leave their homes, creating appalling conditions of overcrowding in the towns and cities. This was the first recorded and recognized use of concentration camps where non-combatants were removed from their land to deprive the enemy of succor and then the internees were subjected to appalling conditions. The Spanish also employed the use of concentration camps in the Philippines shortly after, again resulting in massive non-combatant fatalities.[80] It is estimated that this measure caused the death of at least one-third of Cuba's rural population.[81] The forced relocation policy was maintained until March 1898.[65]
Since the early 1880s, Spain had also been suppressing an independence movement in the Philippines, which was intensifying; Spain was thus now fighting two wars, which placed a heavy burden on its economy. In secret negotiations in 1896, Spain turned down the United States' offers to buy Cuba.
Maceo was killed on 7 December 1896, in Havana province, while returning from the west.[82] As the war continued, the major obstacle to Cuban success was weapons supply. Although weapons and funding came from within the United States, the supply operation violated American laws, which were enforced by the U.S. Coast Guard; of 71 resupply missions, only 27 got through, with 5 being stopped by the Spanish and 33 by the U.S. Coast Guard.[83]
In 1897, the liberation army maintained a privileged position in Camagüey and Oriente, where the Spanish only controlled a few cities. Spanish liberal leader Praxedes Sagasta admitted in May 1897: "After having sent 200,000 men and shed so much blood, we don't own more land on the island than what our soldiers are stepping on".[84] The rebel force of 3,000 defeated the Spanish in various encounters, such as the battle of La Reforma and the surrender of Las Tunas on 30 August, and the Spaniards were kept on the defensive. Las Tunas had been guarded by over 1,000 well-armed and well-supplied men.
As stipulated at the Jimaguayú Assembly two years earlier, a second Constituent Assembly met in La Yaya, Camagüey, on 10 October 1897. The newly adopted constitution decreed that a military command be subordinated to civilian rule. The government was confirmed, naming Bartolomé Masó as president and Domingo Méndez Capote as vice president. Thereafter, Madrid decided to change its policy toward Cuba, replacing Weyler, drawing up a colonial constitution for Cuba and Puerto Rico, and installing a new government in Havana. But with half the country out of its control, and the other half in arms, the new government was powerless and rejected by the rebels.
The USS Maine Incident[]

The Cuban struggle for independence had captured the North American imagination for years and newspapers had been agitating for intervention with sensational stories of Spanish atrocities against the native Cuban population. Americans came to believe that Cuba's battle with Spain resembled United States's Revolutionary War. This continued even after Spain replaced Weyler and said it changed its policies, and the North American public opinion was very much in favor of intervening in favor of the Cubans.[85]
In January 1898, a riot by Cuban-Spanish loyalists against the new autonomous government broke out in Havana, leading to the destruction of the printing presses of four local newspapers which published articles critical of the Spanish Army. The U.S. Consul-General cabled Washington, fearing for the lives of Americans living in Havana. In response, the battleship USS Maine was sent to Havana in the last week of January. On 15 February 1898, the Maine was destroyed by an explosion, killing 268 crewmembers. The cause of the explosion has not been clearly established to this day, but the incident focused American attention on Cuba, and President William McKinley and his supporters could not stop Congress from declaring war to "liberate" Cuba.
In an attempt to appease the United States, the colonial government took two steps that had been demanded by President McKinley: it ended the forced relocation policy and offered negotiations with the independence fighters. However, the truce was rejected by the rebels and the concessions proved too late and too ineffective. Madrid asked other European powers for help; they refused and said Spain should back down.
On 11 April 1898, McKinley asked Congress for authority to send U.S. troops to Cuba for the purpose of ending the civil war there. On 19 April, Congress passed joint resolutions (by a vote of 311 to 6 in the House and 42 to 35 in the Senate) supporting Cuban independence and disclaiming any intention to annex Cuba, demanding Spanish withdrawal, and authorizing the president to use as much military force as he thought necessary to help Cuban patriots gain independence from Spain. This was adopted by resolution of Congress and included from Senator Henry Teller the Teller Amendment, which passed unanimously, stipulating that "the island of Cuba is, and by right should be, free and independent".[86] The amendment disclaimed any intention on the part of the United States to exercise jurisdiction or control over Cuba for other than pacification reasons, and confirmed that the armed forces would be removed once the war is over. Senate and Congress passed the amendment on 19 April, McKinley signed the joint resolution on 20 April and the ultimatum was forwarded to Spain. War was declared on 20/21 April 1898.
"It's been suggested that a major reason for the U.S. war against Spain was the fierce competition emerging between Joseph Pulitzer's New York World and William Randolph Hearst's New York Journal", Joseph E. Wisan wrote in an essay titled "The Cuban Crisis As Reflected in the New York Press" (1934).[87] He stated that "In the opinion of the writer, the Spanish–American War would not have occurred had not the appearance of Hearst in New York journalism precipitated a bitter battle for newspaper circulation." It has also been argued that the main reason the United States entered the war was the failed secret attempt, in 1896, to purchase Cuba from a weaker, war-depleted Spain.[65]
The Cuban Theatre of the Spanish–American War[]

Hostilities started hours after the declaration of war when a U.S. contingent under Admiral William T. Sampson blockaded several Cuban ports. The Americans decided to invade Cuba and to start in Oriente where the Cubans had almost absolute control and were able to co-operate, for example, by establishing a beachhead and protecting the U.S. landing in Daiquiri. The first U.S. objective was to capture the city of Santiago de Cuba in order to destroy Linares' army and Cervera's fleet. To reach Santiago they had to pass through concentrated Spanish defences in the San Juan Hills and a small town in El Caney. Between 22 and 24 June 1898 the Americans landed under General William R. Shafter at Daiquirí and Siboney, east of Santiago, and established a base. The port of Santiago became the main target of U.S. naval operations, and the American fleet attacking Santiago needed shelter from the summer hurricane season. Nearby Guantánamo Bay, with its excellent harbour, was chosen for this purpose and attacked on 6 June. The Battle of Santiago de Cuba, on 3 July 1898, was the largest naval engagement during the Spanish–American War, and resulted in the destruction of the Spanish Caribbean Squadron.
Resistance in Santiago consolidated around Fort Canosa,[88] while major battles between Spaniards and Americans took place at Las Guasimas on 24 June, and at El Caney and San Juan Hill on 1 July,[89] after which the American advance ground to a halt. American losses at Las Guasimas were 16 killed and 52 wounded; the Spanish lost 12 dead and 24 wounded.[90] The Americans lost 81 killed in action and 360 wounded in action in taking El Caney, where the Spanish defenders lost 38 killed, 138 wounded and 160 captured.[90] At San Juan, the Americans lost 144 dead, 1,024 wounded, and 72 missing; Spanish losses were 58 killed, 170 wounded, and 39 captured.[90] Spanish troops successfully defended Fort Canosa, allowing them to stabilize their line and bar the entry to Santiago. The Americans and Cubans began a siege of the city,[91] which surrendered on 16 July after the defeat of the Spanish Caribbean Squadron. Thus, Oriente fell under the control of Americans and the Cubans, but U.S. General Nelson A. Miles would not allow Cuban troops to enter Santiago, claiming that he wanted to prevent clashes between Cubans and Spaniards. Thus, Cuban General Calixto García, head of the mambi forces in the Eastern department, ordered his troops to hold their respective areas and resigned, writing a letter of protest to General Shafter.[86]
After losing the Philippines and Puerto Rico, which had also been invaded by the United States, and with no hope of holding on to Cuba, Spain sued for peace on 17 July 1898.[92] On 12 August, the U.S. and Spain signed a protocol of peace, in which Spain agreed to relinquish all claim of sovereignty over and title of Cuba.[93] On 10 December 1898, the U.S. and Spain signed the formal Treaty of Paris, recognizing continuing U. S. military occupation.[94] Although the Cubans had participated in the liberation efforts, the United States prevented Cuba from sending representatives to the Paris peace talks or signing the treaty, which set no time limit for U.S. occupation and excluded the Isle of Pines from Cuba.[95] Although the U.S. president had no objection to Cuba's eventual independence, U.S. General William R. Shafter refused to allow Cuban General Calixto García and his rebel forces to participate in the surrender ceremonies in Santiago de Cuba.
U.S. Occupation (1898 - 1902)[]
After the last Spanish troops left the island in December 1898, the government of Cuba was temporarily handed over to the United States on 1 January 1899. The first governor was General John R. Brooke. Unlike Guam, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines, the United States did not annex Cuba because of the restrictions imposed in the Teller Amendment.[96]
Political changes[]
The U.S. administration was undecided on Cuba's future status. Once it had been pried away from the Spaniards it was to be assured that it moved and remained in the U.S. sphere. How this was to be achieved was a matter of intense discussion and annexation was an option, not only on the mainland but also in Cuba. McKinley spoke about the links that should exist between the two nations.[97]
Brooke set up a civilian government, placed U.S. governors in seven newly created departments, and named civilian governors for the provinces as well as mayors and representatives for the municipalities. Many Spanish colonial government officials were kept in their posts. The population were ordered to disarm and, ignoring the Mambi Army, Brooke created the Rural Guard and municipal police corps at the service of the occupation forces. Cuba's judicial powers and courts remained legally based on the codes of the Spanish government. Tomás Estrada Palma, Martí's successor as delegate of the Cuban Revolutionary Party, dissolved the party a few days after the signing of the Paris Treaty in December 1898, claiming that the objectives of the party had been met. The revolutionary Assembly of Representatives was also dissolved. Thus, the three representative institutions of the national liberation movement disappeared.[98]
Economic changes[]
Before the United States officially took over the government, it had already begun cutting tariffs on American goods entering Cuba, without granting the same rights to Cuban goods going to the United States.[99] Government payments had to be made in U.S. dollars.[95] In spite of the Foraker Amendment, which prohibited the U.S. occupation government from granting privileges and concessions to American investors, the Cuban economy was soon dominated by American capital.[99] The growth of American sugar estates was so quick that in 1905 nearly 10% of Cuba's total land area belonged to American citizens. By 1902, American companies controlled 80% of Cuba's ore exports and owned most of the sugar and cigarette factories.[100]
Immediately after the war, there were several serious barriers for foreign businesses attempting to operate in Cuba. Three separate pieces of legislation—the Joint Resolution of 1898, the Teller Amendment, and the Foraker Amendment—threatened foreign investment. The Joint Resolution of 1898 stated that the Cuban people are by right free and independent, while the Teller Amendment further declared that the United States could not annex Cuba. These two pieces of legislation were crucial in appeasing anti-imperialists as the United States intervened in the war in Cuba. Similarly, the Foraker Amendment, which prohibited the U.S. military government from granting concessions to American companies, was passed to appease anti-imperialists during the occupational period. Although these three statutes enabled the United States to gain a foothold in Cuba, they presented obstacles for American businesses to acquire land and permits. Eventually, Cornelius Van Horne of the Cuba Company, an early railroad company in Cuba, found a loophole in "revocable permits" justified by preexisting Spanish legislation that effectively allowed railroads to be built in Cuba. General Leonard Wood, the governor of Cuba and a noted annexationist, used this loophole to grant hundreds of franchises, permits, and other concessions to American businesses.[101]
Once the legal barriers were overcome, American investments transformed the Cuban economy. Within two years of entering Cuba, the Cuba Company built a 350-mile railroad connecting the eastern port of Santiago to the existing railways in central Cuba. The company was the largest single foreign investment in Cuba for the first two decades of the twentieth century. By the 1910s it was the largest company in the country.[102] The improved infrastructure allowed the sugar cane industry to spread to the previously underdeveloped eastern part of the country. As many small Cuban sugar cane producers were crippled with debt and damages from the war, American companies were able to quickly and cheaply take over the sugar cane industry. At the same time, new productive units called centrales could grind up to 2,000 tons of cane a day making large-scale operations most profitable.[103] The large fixed cost of these centrales made them almost exclusively accessible to American companies with large capital stocks. Furthermore, the centrales required a large, steady flow of cane to remain profitable, which led to further consolidation in the industry. Cuban cane farmers who had formerly been landowners became tenants on company land, funneling raw cane to the centrales. By 1902, 40% of the country's sugar production was controlled by North Americans.[104]
With American corporate interests firmly rooted in Cuba, the U.S. tariff system was adjusted accordingly to strengthen trade between the nations. The Reciprocity Treaty of 1903 lowered the U.S. tariff on Cuban sugar by 20%. This gave Cuban sugar a competitive edge in the American marketplace. At the same time, it granted equal or greater concessions on most items imported from the United States. Cuban imports of American goods went from $17 million in the five years before the war, to $38 million in 1905, and eventually to over $200 million in 1918. Likewise, Cuban exports to the United States reached $86 million in 1905 and rose to nearly $300 million in 1918.[105]
Elections and independence[]
Popular demands for a Constituent Assembly soon emerged.[95] In December 1899, the U.S. War Secretary assured the Cuban populace that the occupation was temporary, that municipal and general elections would be held, that a Constituent Assembly would be set up, and that sovereignty would be handed to Cubans. Brooke was replaced by General Leonard Wood to oversee the transition. Parties were created, including the Cuban National Party, the Federal Republican Party of Las Villas, the Republican Party of Havana and the Democratic Union Party.
The first elections for mayors, treasurers and attorneys of the country's 110 municipalities for a one-year-term took place on 16 June 1900, but balloting was limited to literate Cubans older than 21 and with properties worth more than $250. Only members of the dissolved Liberation Army were exempt from these conditions. Thus, the number of about 418,000 male citizens over 21 was reduced to about 151,000. 360,000 women were totally excluded. The same elections were held one year later, again for a one-year-term.
Elections for 31 delegates to a Constituent Assembly were held on 15 September 1900 with the same balloting restrictions. In all three elections, pro-independence candidates, including a large number of mambi delegates, won overwhelming majorities.[106] The Constitution was drawn up from November 1900 to February 1901 and then passed by the Assembly. It established a republican form of government, proclaimed internationally recognized individual rights and liberties, freedom of religion, separation between church and state, and described the composition, structure and functions of state powers.
On 2 March 1901, the U.S. Congress passed the Army Appropriations Act, stipulating the conditions for the withdrawal of United States troops remaining in Cuba following the Spanish–American War. As a rider, this act included the Platt Amendment, which defined the terms of Cuban-U.S. relations until 1934. It replaced the earlier Teller Amendment. The amendment provided for a number of rules heavily infringing on Cuba's sovereignty:
- That the government of Cuba shall never enter into any treaty with any foreign power which will impair the independence of Cuba, nor in any manner permit any foreign power to obtain control over any portion of the island.
- That Cuba would contract no foreign debt without guarantees that the interest could be served from ordinary revenues.
- That Cuba consent that the United States may intervene for the preservation of Cuban independence, to protect life, property, and individual liberty, and to discharging the obligations imposed by the treaty of Paris.
- That the Cuban claim to the Isle of Pines (now called Isla de la Juventud) was not acknowledged and to be determined by treaty.
- That Cuba commit to providing the United States "lands necessary for coaling or naval stations at certain specified points to be agreed upon".
As a precondition to Cuba's independence, the United States demanded that this amendment be approved fully and without changes by the Constituent Assembly as an appendix to the new constitution. Faced with this alternative, the appendix was approved, after heated debate, by a margin of four votes. Governor Wood admitted: "Little or no independence had been left to Cuba with the Platt Amendment and the only thing appropriate was to seek annexation".[106]
In the presidential elections of 31 December 1901, Tomás Estrada Palma, a U.S. citizen still living in the United States, was the only candidate. His adversary, General Bartolomé Masó, withdrew his candidacy in protest against U.S. favoritism and the manipulation of the political machine by Palma's followers. Palma was elected to be the Republic's first President, although he only returned to Cuba four months after the election. The U.S. occupation officially ended when Palma took office on 20 May 1902.[107]
Early 20th Century Developments (1902 - 1959)[]
In 1902, the United States handed over control to a Cuban government. As a condition of the transfer, the Cuban state had included in its constitution provisions implementing the requirements of the Platt Amendment, which among other things gave the United States the right to intervene militarily in Cuba. Havana and Varadero soon became popular tourist resorts. Though some efforts were made to ease Cuba's ethnic tensions through government policies, racism and informal discrimination towards blacks and mestizos remained widespread during this era.[108]
President Tomás Estrada Palma was elected in 1902, and Cuba was declared independent, though Guantanamo Bay was leased to the United States as part of the Platt Amendment. The status of the Isle of Pines as Cuban territory was left undefined until 1925, when the United States finally recognized Cuban sovereignty over the island. Estrada Palma, a frugal man, governed successfully for his four-year term; yet when he tried to extend his time in office, a revolt ensued.
The Second Occupation of Cuba, also known as the Cuban Pacification, was a major US military operation that began in September 1906. After the collapse of President Palma's regime, US President Roosevelt ordered an invasion and established an occupation that would continue for nearly two-and-a-half years. The stated goal of the operation was to prevent fighting between the Cubans, to protect North American economic interests, and to hold free elections. In 1906, the United States representative William Howard Taft, notably with the personal diplomacy of Frederick Funston, negotiated an end of the successful revolt led by the young general ,[109] who had served under Antonio Maceo in the final war of independence. Estrada Palma resigned, and the United States Governor Charles Magoon assumed temporary control until 1909.[110] In this period, Agustín Martín Veloz and Francisco (Paquito) Rosales founded the embryonic Cuban Communist Party in the area of Manzanillo.[111] Following the election of José Miguel Gómez in November 1908, Cuba was deemed stable enough to allow a withdrawal of American troops, which was completed in February 1909.
For three decades, the country was led by former War of Independence leaders, who after being elected did not serve more than two constitutional terms. The Cuban presidential succession was as follows: José Miguel Gómez (1908–1912); Mario García Menocal (1913–1920); Alfredo Zayas (1921–25) and Gerardo Machado (1925–1933).[112]
Under the Liberal Gómez the participation of Afro-Cubans in the political process was curtailed when the Partido Independiente de Color was outlawed and bloodily suppressed in 1912, as American troops reentered the country to protect the sugar plantations.[113] Gómez's successor, Mario Menocal of the Conservative Party, was a former manager for the Cuban American Sugar Corporation. During his presidency income from sugar rose steeply.[114] Menocal's reelection in 1916 was met with armed revolt by Gómez and other Liberals (the so-called "Chambelona War"), prompting the United States to send in Marines, again to safeguard American interests. Gómez was defeated and captured and the rebellion was snuffed out.[115]
In World War I, Cuba declared war on Imperial Germany on 7 April 1917, one day after the United States entered the war. Despite being unable to send troops to fight in Europe, Cuba played a significant role as a base to protect the West Indies from German U-boat attacks. A draft law was instituted, and 25,000 Cuban troops raised, but the war ended before they could be sent into action.
Alfredo Zayas, who had taken part in the Liberal rebellion of 1916–17, was elected president in 1920 and took office in 1921. When the Cuban financial system collapsed after a drop in sugar prices, Zayas secured a loan from the United States in 1922. Despite the country's nominal independence, one historian has concluded that the continued U.S. military intervention and economic dominance had once again made Cuba "a colony in all but name."[116]
Post-World War I[]
President Gerardo Machado was elected by popular vote in 1925, but he was constitutionally barred from reelection. Machado, determined to modernize Cuba, set in motion several massive civil works projects such as the Central Highway, but at the end of his constitutional term he held on to power. The United States, despite the Platt Amendment, decided not to interfere militarily. In the late 1920s and early 1930s a number of Cuban action groups, including some Mambí, staged a series of uprisings that either failed or did not affect the capital.
The Sergeants' Revolt undermined the institutions and coercive structures of the oligarchic state. The young and relatively inexperienced revolutionaries found themselves pushed into the halls of state power by worker and peasant mobilisations. Between September 1933 and January 1934 a loose coalition of radical activists, students, middle-class intellectuals, and disgruntled lower-rank soldiers formed a Provisional Revolutionary Government. This coalition was directed by a popular university professor, Dr Ramón Grau San Martín. The Grau government promised a 'new Cuba' which would belong to all classes, and the abrogation of the Platt Amendment. While the revolutionary leaders certainly wanted diplomatic recognition by Washington, they believed their legitimacy stemmed from the popular support which brought them to power, and not from the approval of the United States' Department of State.
To this end, throughout the autumn of 1933, the government decreed a dramatic series of reforms. The Platt Amendment was unilaterally abrogated, and all the political parties of the Machadato were dissolved. The Provisional Government granted autonomy to the University of Havana, women obtained the right to vote, the eight-hour day was decreed, a minimum wage was established for cane-cutters, and compulsory arbitration was promoted. The government created a Ministry of Labour, and a law was passed establishing that 50 per cent of all workers in agriculture, commerce and industry had to be Cuban citizens. The Grau regime set agrarian reform as a priority, promising peasants legal title to their lands. For the first time in Cuban history the country was governed by people who did not negotiate the terms of political power with Spain (before 1898), or with the United States (after 1898). The Provisional Government survived until January 1934, when it was overthrown by an equally loose anti-government coalition of right-wing civilian and military elements. Led by a young mestizo sergeant, Fulgencio Batista, this movement was supported by the United States.[117]
The 1940 Constitution and the Batista Era[]

Rise of Batista[]
In 1940, Cuba conducted free and fair national elections.[118][119] Fulgencio Batista, was originally endorsed by Communist leaders in exchange for the legalization of the Communist party and Communist domination of the labor movement. The reorganization of the labor movement during this time was capped with the establishment of the Confederacion de Trajabadores de Cuba (Confederation of Cuban Workers, or CTC), in 1938. However, in 1947, the Communists lost control of the CTC, and their influence in the trade union movement gradually declined into the 1950s. The assumption of the Presidency by Batista in 1952 and the intervening years to 1958 placed tremendous strain on the labor movement, with some independent union leaders resigning from the CTC in opposition to Batista's rule.[120] The relatively progressivist 1940 Constitution was adopted by the Batista administration.[118][119] The constitution denied Batista the possibility of running consecutively in the 1944 election.
Rather than endorsing Batista's hand-picked successor Carlos Zayas, the Cuban people elected Ramón Grau San Martín in 1944. A populist physician, who had briefly held the presidency in the 1933 revolutionary process, Grau made a deal with labor unions to continue Batista's pro-labor policies.[121] Grau's administration coincided with the end of World War II, and he presided over an economic boom as sugar production expanded and prices rose. He instituted programs of public works and school construction, increasing social security benefits and encouraging economic development and agricultural production. However, increased prosperity brought increased corruption, with nepotism and favoritism flourishing in the political establishment, and urban violence, a legacy of the early 1930s, reappearing on a large scale.[121][122] The country was also steadily gaining a reputation as a base for organized crime, with the Havana Conference of 1946 seeing leading Mafia mobsters descend upon the city.[123]
Grau's presidency was followed by that of Carlos Prío Socarrás, also elected democratically, but whose government was tainted by increasing corruption and violent incidents among political factions. Around the same time, Fidel Castro became a public figure at the University of Havana. Eduardo Chibás – the leader of the Partido Ortodoxo (Orthodox Party), a liberal democratic group – was widely expected to win in 1952 on an anticorruption platform. However, Chibás committed suicide before he could run for the presidency, and the opposition was left without a unifying leader.[124]
Taking advantage of the opportunity, Batista, who was expected to win only a small minority of the 1952 presidential vote, seized power in an almost bloodless coup three months before the election was to take place. President Prío did nothing to stop the coup, and was forced to leave the island. Due to the corruption of the previous two administrations, the general public reaction to the coup was somewhat accepting at first. However, Batista soon encountered stiff opposition when he temporarily suspended the balloting and the 1940 constitution, and attempted to rule by decree. Nonetheless, elections were held in 1954 and Batista was re-elected under disputed circumstances. Opposition parties mounted a blistering campaign, and continued to do so, using the Cuban free press throughout Batista's tenure in office.[125]
Economic Expansion[]
Although corruption was rife under Batista, Cuba did flourish economically during his regime. Wages rose significantly;[126] according to the International Labour Organization, the average industrial salary in Cuba was the world's eighth-highest in 1958, and the average agricultural wage was higher than in developed nations such as Denmark, West Germany, Belgium, and France.[126][127] Although a third of the population still lived in poverty (according to Batista's government), Cuba was one of the five most developed countries in Latin America by the end of the Batista era,[128] with 56% of the population living in cities.[129]
In the 1950s, Cuba's gross domestic product (GDP) per capita was roughly equal to that of contemporary Italy, and significantly higher than that of countries such as Japan, although Cuba's GDP per capita was still only a sixth as large as that of the United States.[126] Labour rights were also favourable – an eight-hour day had been established in 1933, long before most other countries, and Cuban workers were entitled to a months's paid holiday, nine days' sick leave with pay, and six weeks' holiday before and after childbirth.[130]
Cuba also had Latin America's highest per capita consumption rates of meat, vegetables, cereals, automobiles, telephones and radios during this period.[127][130][131]: 186 Cuba had the fifth-highest number of televisions per capita in the world, and the world's eighth-highest number of radio stations (160). According to the United Nations, 58 different daily newspapers operated in Cuba during the late 1950s, more than any Latin American country save Brazil, Argentina and Mexico.[132] Havana was the world's fourth-most-expensive city at the time,[118] and had more cinemas than New York.[128] Cuba furthermore had the highest level of telephone penetration in Latin America, although many telephone users were still unconnected to switchboards.[129]
Moreover, Cuba's health service was remarkably developed. By the late 1950s, it had one of the highest numbers of doctors per capita – more than in the United Kingdom at that time – and the third-lowest adult mortality rate in the world. According to the World Health Organization, the island had the lowest infant mortality rate in Latin America, and the 13th-lowest in the world – better than in contemporary France, Belgium, West Germany, Israel, Japan, Austria, Italy, Spain, and Portugal.[127][133][134] Additionally, Cuba's education spending in the 1950s was the highest in Latin America, relative to GDP.[127] Cuba had the fourth-highest literacy rate in the region, at almost 80% according to the United Nations – higher than that of Spain at the time.[132][133][134]
This article's factual accuracy is disputed. (August 2019) |
Stagnation and Dissatisfaction[]
However, the United States, rather than Latin America, was the frame of reference for educated Cubans.[118][129] Cubans travelled to the United States, read American newspapers, listened to American radio, watched American television, and were attracted to American culture.[129] Middle-class Cubans grew frustrated at the economic gap between Cuba and the US.[118] The middle class became increasingly dissatisfied with the administration, while labour unions supported Batista until the very end.[118][121]
Large income disparities arose due to the extensive privileges enjoyed by Cuba's unionized workers.[135] Cuban labour unions had established limitations on mechanization and even banned dismissals in some factories.[130] The labour unions' privileges were obtained in large measure "at the cost of the unemployed and the peasants".[135]
Cuba's labour regulations ultimately caused economic stagnation. Hugh Thomas asserts that "militant unions succeeded in maintaining the position of unionized workers and, consequently, made it difficult for capital to improve efficiency."[136] Between 1933 and 1958, Cuba increased economic regulation enormously.[121] The regulation led to declining investment.[121] The World Bank also complained that the Batista administration raised the tax burden without assessing its impact. Unemployment was high; many university graduates could not find jobs.[121] After its earlier meteoric rise, the Cuban gross domestic product grew at only 1% annually on average between 1950 and 1958.[129]
Political Repression and Human Rights Abuses[]
In 1940, while receiving military, financial, and logistical support from the United States,[137][138] Batista suspended the 1940 Constitution and revoked most political liberties, including the right to strike. He then aligned with the wealthiest landowners who owned the largest sugar plantations, and presided over a stagnating economy that widened the gap between rich and poor Cubans.[139] Eventually it reached the point where most of the sugar industry was in U.S. hands, and foreigners owned 70% of the arable land.[140] As such, Batista's repressive government then began to systematically profit from the exploitation of Cuba's commercial interests, by negotiating lucrative relationships with both the American Mafia, who controlled the drug, gambling, and prostitution businesses in Havana, and with large U.S.-based multinational companies who were awarded lucrative contracts.[139][141] To quell the growing discontent amongst the populace—which was subsequently displayed through frequent student riots and demonstrations—Batista established tighter censorship of the media, while also utilizing his Bureau for the Repression of Communist Activities secret police to carry out wide-scale violence, torture and public executions. These murders mounted in 1957, as Fidel Castro gained more publicity and influence. Many people were killed, with estimates ranging from hundreds to about 20,000 people killed.[142][143][144][145]
The Rise of Communism (1947 - 1959)[]

In 1952, Fidel Castro, a young lawyer running for a seat in the Chamber of Representatives for the Partido Ortodoxo, founded in 1947 to oppose government corruption and reform, circulated a petition to depose Batista's government on the grounds that it had illegitimately suspended the electoral process. However, the courts did not act on the petition and ignored Castro's legal challenges. Castro thus resolved to use armed force to overthrow Batista; he and his brother Raúl gathered supporters, and on 26 July 1953 led an attack on the Moncada Barracks near Santiago de Cuba. The attack ended in failure – the authorities killed several of the insurgents, captured Castro himself, tried him and sentenced him to 15 years in prison. However, the Batista government released him in 1955, when amnesty was given to many political prisoners, including the ones that assaulted the Moncada barracks. Castro and his brother subsequently went into exile in Mexico, where they met the Argentine revolutionary Ernesto "Che" Guevara. While in Mexico, Guevara and the Castros organized the 26 July Movement with the goal of overthrowing Batista. In December 1956, Fidel Castro led a group of 82 fighters to Cuba aboard the yacht Granma, landing in the eastern part of the island. Despite a pre-landing rising in Santiago by Frank País Pesqueira and his followers among the urban pro-Castro movement, Batista's forces promptly killed, dispersed or captured most of Castro's men.[146]
Castro managed to escape into the Sierra Maestra mountains with as few as 12 fighters, aided by the urban and rural opposition, including Celia Sanchez and the bandits of Cresencio Perez's family. Castro and Guevara then began a guerrilla campaign against the Batista régime, with their main forces supported by numerous poorly armed escopeteros and the well-armed fighters of Frank País' urban organization. Growing anti-Batista resistance, including a bloodily crushed rising by Cuban Navy personnel in Cienfuegos, soon led to chaos in the country. At the same time, rival guerrilla groups in the Escambray Mountains also grew more effective. Castro attempted to arrange a general strike in 1958, but could not win support among Communists or labor unions.[131] Multiple attempts by Batista's forces to crush the rebels ended in failure.[147][148] Castro's forces were able to acquire captured weapons, including 12 mortars, 2 bazookas, 12 machine guns mounted on tripods, 21 light machine guns, 142 M-1 rifles, and 200 Dominican Cristobal submachine guns.[5] The biggest prize for the rebels was a government M4 Sherman tank, which would be used in the Battle of Santa Clara.
The United States imposed trade restrictions on the Batista administration and sent an envoy who attempted to persuade Batista to leave the country voluntarily.[118] With the military situation becoming untenable, Batista fled on 1 January 1959, and Castro took over. Within months of taking control, Castro moved to consolidate his power by marginalizing other resistance groups and figures and imprisoning and executing opponents and dissident former supporters.[149] As the revolution became more radical and continued its marginalization of the wealthy, of landowners, and of some of those who opposed its direction, thousands of Cubans fled the island, eventually, over decades, forming a large exile community in the United States.[150] Cuban Americans today constitute a large percentage of the population of the U.S. state of Florida, and constitute a significant voting bloc.
Castro's Cuba (1959 - 2006)[]

Politics[]
On 1 January 1959, Che Guevara marched his troops from Santa Clara to Havana, without encountering resistance.[151] Meanwhile, Fidel Castro marched his soldiers to the Moncada Army Barracks, where all 5,000 soldiers in the barracks defected to the Revolutionary movement.[151] On 4 February 1959, Fidel Castro announced a massive reform plan which included a public works project, land reform granting nearly 200,000 families farmland, and also nationalization plans of various industries.[152]
The new government of Cuba soon encountered opposition from militant groups and from the United States, which had supported Batista politically and economically.[153] Fidel Castro quickly purged political opponents from the administration. Loyalty to Castro and the revolution became the primary criterion for all appointments.[154] Mass organisation such as labor unions that opposed the revolutionary government were made[by whom?] illegal.[131][page needed] By the end of 1960, all opposition newspapers had been closed down and all radio and television stations had come under state control.[131]: 189 Teachers and professors found to have involvement with counter-revolution were purged.[131]: 189 Fidel's brother Raúl Castro became the commander of the Revolutionary Armed Forces.[131] : 189 In September 1960, a system of neighborhood watch networks, known as Committees for the Defense of the Revolution (CDR), was created.[131]: 189
In July 1961, two years after the 1959 Revolution, the Integrated Revolutionary Organizations (IRO) was formed, merging Fidel Castro's 26th of July Movement with Blas Roca's Popular Socialist Party and Faure Chomón's Revolutionary Directory 13 March. On 26 March 1962, the IRO became the United Party of the Cuban Socialist Revolution (PURSC), which, in turn, became the Communist Party on 3 October 1965, with Castro as First Secretary. In 1976 a national referendum ratified a new constitution, with 97.7% in favour.[155] The constitution secured the Communist Party's central role in governing Cuba, but kept party affiliation out of the election process.[156] Other smaller parties exist but have little influence and are not permitted to campaign against the program of the Communist Party.
Break with the United States[]
Castro's resentment of American influence[]
The United States recognized the Castro government on 7 January 1959, six days after Batista fled Cuba. President Eisenhower sent a new ambassador, Philip Bonsal, to replace Earl E. T. Smith, who had been close to Batista.[157] The Eisenhower administration, in agreement with the American media[158] and Congress, did this with the assumption that "Cuba [would] remain in the U.S. sphere of influence". Foreign-policy professor Piero Gleijeses argued that if Castro had accepted these parameters, he would be allowed to stay in power. Otherwise he would be overthrown.[159][need quotation to verify]
Among the opponents of Batista, many wanted to accommodate the United States. However, Castro belonged to a faction which opposed U.S. influence. Castro did not forgive the U.S. supply of arms to Batista during the revolution. On 5 June 1958, at the height of the revolution, he had written: "The Americans are going to pay dearly for what they are doing. When the war is over, I'll start a much longer and bigger war of my own: the war I'm going to fight against them. That will be my true destiny".[160] (The United States had stopped supplies to Batista in March 1958, but left its Military Advisory Group in Cuba).[161] Thus, Castro had no intention to bow to the United States. "Even though he did not have a clear blueprint of the Cuba he wanted to create, Castro dreamed of a sweeping revolution that would uproot his country's oppressive socioeconomic structure and of a Cuba that would be free of the United States".[162]
Breakdown of relations[]
Only six months after Castro seized power, the Eisenhower administration began to plot his ouster. The United Kingdom was persuaded[by whom?] to cancel a sale of Hawker Hunter fighter aircraft to Cuba. The US National Security Council (NSC) met in March 1959 to consider means to institute a régime-change and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) began arming guerillas inside Cuba in May.[153]
In January 1960 Roy R. Rubottom, Jr., Assistant Secretary of State for Inter-American Affairs, summarized the evolution of Cuba–United States relations since January 1959:
"The period from January to March might be characterized as the honeymoon period of the Castro government. In April a downward trend in US–Cuban relations had been evident… In June we had reached the decision that it was not possible to achieve our objectives with Castro in power and had agreed to undertake the program referred to by Undersecretary of State Livingston T. Merchant. On 31 October in agreement with the Central Intelligence Agency, the Department had recommended to the President approval of a program along the lines referred to by Mr. Merchant. The approved program authorized us to support elements in Cuba opposed to the Castro government while making Castro's downfall seem to be the result of his own mistakes."[163][164][165]
In March 1960 the French ship La Coubre blew up in Havana Harbor as it unloaded munitions, killing dozens. The CIA blamed the explosion on the Cuban government.
Relations between the United States and Cuba deteriorated rapidly as the Cuban government, in reaction to the refusal of Royal Dutch Shell, Standard Oil and Texaco to refine petroleum from the Soviet Union in Cuban refineries under their control, took control of those refineries in July 1960. The Eisenhower administration promoted a boycott of Cuba by oil companies, to which Cuba responded by nationalizing the refineries in August 1960. Both sides continued to escalate the dispute. Cuba expropriated more US-owned properties, notably those belonging to the International Telephone and Telegraph Company (ITT) and to the United Fruit Company. In the Castro government's first agrarian reform law, on 17 May 1959, the state sought to limit the size of land holdings, and to distribute that land to small farmers in "Vital Minimum" tracts. This law served as a pretext for seizing lands held by foreigners and for redistributing them to Cuban citizens.
Formal disconnection[]
The United States severed diplomatic relations with Cuba on 3 January 1961, and further restricted trade in February 1962.[166] The Organization of American States, under pressure from the United States, suspended Cuba's membership in the body on 22 January 1962, and the U.S. government banned all U.S.–Cuban trade on 7 February. The Kennedy administration extended this ban on 8 February 1963, forbidding U.S. citizens to travel to Cuba or to conduct financial or commercial transactions with the country.[167] At first the embargo did not extend to other countries, and Cuba traded with most European, Asian and Latin American countries and especially with Canada. However, the United States later pressured other nations and American companies with foreign subsidiaries to restrict trade with Cuba. The Helms–Burton Act of 1996 makes it very difficult for foreign companies doing business with Cuba to also do business in the United States, forcing them to choose between the two marketplaces.
Bay of Pigs invasion[]

In April 1961, less than four months into the Kennedy administration, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) executed a plan that had been developed under the Eisenhower administration. This military campaign to topple Cuba's revolutionary government is now known as the Bay of Pigs Invasion (or La Batalla de Girón in Cuba).[153][168] The aim of the invasion was to empower existing opposition militant groups to "overthrow the Communist regime" and establish "a new government with which the United States can live in peace."[168] The invasion was carried out by a CIA-sponsored paramilitary group of over 1,400 Cuban exiles called Brigade 2506. Arriving in Cuba by boat from Guatemala on 15 April, the brigade landed on the beach Playa Girón and initially overwhelmed Cuba's counter-offensive. But by 20 April, the brigade surrendered and was publicly interrogated before being sent back to the US. Recently inaugurated president John F. Kennedy assumed full responsibility for the operation, even though he had vetoed the reinforcements requested during the battle. The invasion helped further build popular support for the new Cuban government.[169] The Kennedy administration thereafter began Operation Mongoose, a covert CIA campaign of sabotage against Cuba, including the arming of militant groups, sabotage of Cuban infrastructure, and plots to assassinate Castro.[170][171] All this reinforced Castro's distrust of the US, and set the stage for the Cuban Missile Crisis.
The Cuban Missile Crisis[]
Tensions between the two governments peaked again during the October 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis. The United States had a much larger arsenal of long-range nuclear weapons than the Soviet Union, as well as medium-range ballistic missiles (MRBMs) in Turkey, whereas the Soviet Union had a large stockpile of medium-range nuclear weapons which were primarily located in Europe. Cuba agreed to let the Soviets secretly place SS-4 Sandal and SS-5 Skean MRBMs on their territory. Reports from inside Cuba to exile sources questioned the need for large amounts of ice going to rural areas, which led to the discovery of the missiles, confirmed by Lockheed U-2 reconnaissance photos. The United States responded by establishing a cordon in international waters to stop Soviet ships from bringing in more missiles (designated a quarantine rather than a blockade to avoid issues with international law). At the same time, Castro was getting a little too extreme for the liking of Moscow, so at the last moment the Soviets called back their ships. In addition, they agreed to remove the missiles already there in exchange for an agreement that the United States would not invade Cuba. Only after the fall of the Soviet Union was it revealed that another part of the agreement was the removal of U.S. missiles from Turkey. It also turned out that some submarines that the U.S. Navy blocked were carrying nuclear missiles and that communication with Moscow was tenuous, effectively leaving the decision of firing the missiles at the discretion of the captains of those submarines. In addition, following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the Russian government revealed that nuclear-armed FROGs (Free Rocket Over Ground) and Ilyushin Il-28 Beagle bombers had also been deployed in Cuba.
Military build-up[]

In the 1961 New Year's Day parade, the Communist administration exhibited Soviet tanks and other weapons.[154] Cuban officers received extended military training in the Soviet Union, becoming proficient in the use of advanced Soviet weapons systems, including MIG jet fighters, submarines, sophisticated artillery, and other ground and air defense equipment. For most of the approximately 30 years of the Cuban-Soviet military collaboration, Moscow provided the Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces—virtually free of charge—with nearly all of its equipment, training, and supplies, worth approximately $1 billion annually.[172] By 1982, Cuba possessed the best equipped and largest per capita armed forces in Latin America.[173]
Suppression of dissent[]
Military Units to Aid Production or UMAPs (Unidades Militares para la Ayuda de Producción) – in effect, forced labor concentration camps – were established in 1965 as a way to eliminate alleged "bourgeois" and "counter-revolutionary" values in the Cuban population. In July 1968, the name "UMAP" was erased and paperwork associated with the UMAP was destroyed. The camps continued as "Military Units".[174]
By the 1970s, the standard of living in Cuba was "extremely spartan" and discontent was rife.[175] Castro changed economic policies in the first half of the 1970s.[175] In the 1970s unemployment reappeared as problem. The solution was to criminalize unemployment with 1971 Anti-Loafing Law; the unemployed would be put into jail.[131]: 194 One alternative was to go fight Soviet-supported wars in Africa.[131]: 194
In any given year, there were about 20,000 dissidents held and tortured under inhuman prison conditions.[131]: 194 Homosexuals were imprisoned in internment camps in the 1960s, where they were subject to medical-political "reeducation".[176] The Black Book of Communism estimates that 15,000–17,000 people were executed.[177] The anti-Castro Archivo Cuba estimates that 4,000 people were executed.[178]
Emigration[]
The establishment of a socialist system in Cuba led to the fleeing of many hundreds of thousands of upper- and middle-class Cubans to the United States and other countries since Castro's rise to power. By 1961, thousands of Cubans had fled Cuba for the United States. On 22 March of that year, an exile council was formed.[118] The council planned to defeat the Communist regime and form a provisional government with José Miró Cardona, a noted leader in the civil opposition against Batista, to serve as temporary president until elections could be held.
Between 1959 and 1993, some 1.2 million Cubans left the island for the United States,[179] often by sea in small boats and fragile rafts. Between 30,000 and 80,000 Cubans are estimated to have died trying flee Cuba during this period.[180] In the early years a number of those who could claim dual Spanish-Cuban citizenship left for Spain. Over the course of several decades, a number of Cuban Jews were allowed to emigrate to Israel after quiet negotiations; the majority of the 10,000 or so Jews who were in Cuba in 1959 eventually left the country. By the time of the collapse of the Soviet Union, Cubans were living in many different countries, some in member countries of the European Union. Spain, Italy, Mexico, and Canada have particularly large Cuban communities.
On 6 November 1965, Cuba and the United States agreed to an airlift for Cubans who wanted to emigrate to the United States. The first of these so-called Freedom Flights left Cuba on 1 December 1965, and by 1971 over 250,000 Cubans had flown to the United States. In 1980 another 125,000 came to United States during a six-month period in the Mariel boatlift, including some criminals and people with psychiatric diagnoses. It was discovered that the Cuban government was using the event to rid Cuba of the unwanted segments of its society. In 2012, Cuba abolished its requirement for exit permits, allowing Cuban citizens to travel to other countries more easily.[14]
Involvement in Third World conflicts[]

From its inception, the Cuban Revolution defined itself as internationalist, seeking to spread its revolutionary ideals abroad and gain a variety of foreign allies. Although still a developing country itself, Cuba supported African, Central and South American and Asian countries in the fields of military development, health and education.[181] These "overseas adventures" not only irritated the United States but were also quite often a source of dispute with Cuba's ostensible allies in the Kremlin.[182]
The Sandinista insurgency in Nicaragua, which led to the demise of the Somoza dictatorship in 1979, was openly supported by Cuba. However, it was on the African continent where Cuba was most active, supporting a total of 17 liberation movements or leftist governments, in countries including Angola, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Guinea-Bissau, and Mozambique. Cuba offered to send troops to Vietnam, but the initiative was turned down by the Vietnamese.[183]
Cuba had some 39,000–40,000 military personnel abroad by the late 1970s, with the bulk of the forces in Sub-Saharan Africa but with some 1,365 stationed among Algeria, Iraq, Libya, and South Yemen.[184] Its Angolan involvement was particularly intense and noteworthy with heavy assistance given to the Marxist–Leninist MPLA in the Angolan Civil War.
Cuban soldiers in Angola were instrumental in the defeat of South African and Zairian troops.[185] Cuban soldiers also defeated the FNLA and UNITA armies and established MPLA control over most of Angola.[186] Cuba's presence in Mozambique was more subdued, involving by the mid-1980s 700 Cuban military and 70 civilian personnel.[187] In 1978, in Ethiopia, 16,000 Cuban combatants, along with the Soviet-supported Ethiopian army, defeated an invasion force of Somalians.[185] South African soldiers were again drawn into the Angolan Civil War in 1987–88, and several inconclusive battles were fought between Cuban and South African forces.[188] Cuban-piloted MiG-23s performed airstrikes against South African forces in South West Africa during the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale.[189]
Moscow used Cuban surrogate troops in Africa and the Middle East because they had a high level of training for combat in Third World environments, familiarity with Soviet weapons, physical toughness and a tradition of successful guerrilla warfare dating back to the uprisings against Spain in the 19th century.[190] Cuban forces in Africa were mainly black and mulatto.[191]
An estimated 7,000–11,000 Cubans died in conflicts in Africa. Many Cuban soldiers died not as a result of hostile action but by accidents, friendly fire, or diseases such as malaria and yellow fever; many others died by suicide.
Cuba was unable to pay on its own for the costs of its overseas military activities. After it lost its subsidies from the USSR, Cuba withdrew its troops from Ethiopia (1989), Nicaragua (1990), Angola (1991), and elsewhere.
Angola[]


Cuba's involvement in the Angolan Civil War began in the 1960s, when relations were established with the leftist Movement for the Popular Liberation of Angola (MPLA). The MPLA was one of three organisations struggling to gain Angola's independence from Portugal, the other two being UNITA and the National Liberation Front of Angola (FNLA). In August and October 1975, the South African Defence Force (SADF) intervened in Angola in support of the UNITA and FNLA (Operation Savannah). Cuban troops began to arrive in Angola in early October 1975. On 6 October, Cubans and the MPLA clashed with the FNLA and South African troops at Norton de Matos and were badly defeated. The Cubans blocked an advancing South African mechanized column on 4 November with 122mm rocket fire, causing the South Africans to request heavy artillery which could out-distance the rockets. Castro reacted to the presence of the South African armored column by announcing Operation Carlota, a massive resupply of Angola, on 5 November.[192][193]
An anti-Communist force made up of 1,500 FNLA fighters, 100 Portuguese mercenaries, and two battalions of the Zairian army passed near the city of Quifangondo, only 30 km north of Luanda, at dawn on 10 November. The force, supported by South African aircraft and three 140 mm artillery pieces, marched in a single line along the Bengo River to face an 800-strong Cuban force across the river. Cuban and MPLA troops bombarded the FNLA with mortar and 122 mm rockets, destroying most of the FNLA's armored cars and 6 Jeeps carrying antitank rockets in the first hour of fighting. The Cuban-led force shot 2,000 rockets at the FNLA.[194] Cubans then drove forward, launching RPG-7 rocket grenades, shooting with anti-aircraft guns, killing hundreds. The South Africans, with their aged World War II-era guns were powerless to intervene, and subsequently retreated via Ambrizete to SAS President Steyn, a South African navy frigate. The Cuba-MPLA victory at the Battle of Quifangondo largely ended the FNLA's importance in the conflict. On 25 November, as SADF armored cars and UNITA infantry tried to cross a bridge, Cubans hidden along the banks of the river attacked; as many as 90 South African and UNITA troops were killed or wounded, and 7 or 8 SADF armored cars were destroyed. The Cubans suffered no casualties.[195] Between 9 and 12 December, Cuban and South African troops fought between Santa Comba and Quibala, in what became known as the "Battle of Bridge 14". The Cubans were severely defeated, losing 200 killed. The SADF suffered only 4 casualties.[196] At the same time, UNITA troops and another South African mechanized unit captured Luso. Following these defeats, the number of Cuban troops airlifted to Angola more than doubled, from about 400 per week to perhaps 1,000. The Cuban forces mounted a counter-offensive beginning in January 1976 that impelled South African withdrawal by the end of March. South Africa spent the following decade launching bombing and strafing raids from its bases in South West Africa into southern Angola.
In February 1976, Cuban forces launched Operation Pañuelo Blanco (White Handkerchief) against 700 FLEC irregulars operating in the Necuto area. The irregulars laid minefields which caused the Cubans some casualties as they pursued them into the jungle. Further skirmishing continued throughout the month. In early April, the irregulars were encircled and cut off from supplies. Nearly 100 FLEC irregulars were killed over two nights as they tried to break their encirclement; a further 100 irregulars died and 300 were taken prisoner when the Cubans moved in for the kill the next day.[197]
In 1987–88, South Africa again sent military forces to Angola to stop an advance of FAPLA forces (MPLA) against UNITA, leading to the Battle of Cuito Cuanavale, where the SADF was unable to defeat the FAPLA and Cuban forces. The Cuban press described the campaign as follows:
The Cubans were obliged to accept the challenge and fight on terrain selected by the South Africans while taking measures to strike at the enemy in another direction. On 13 January of this year there was a South African offensive on Cuito Cuanavale and another big attack on 14 February where 150 armored vehicles were used. The second attack was thwarted by a small group of tanks. On 25 February, 1 March and 23 March came the last three attacks that were repulsed with heavy losses for the enemy. Thousands of mines were planted which destroyed many South African tanks. The enemy offensive was shattered by the Angolan and Cuban forces.[198]
At the height of its operation, Cuba had as many as 50,000 soldiers stationed in Angola.[192] On 22 December 1988, Angola, Cuba, and South Africa signed the Tripartite Accord in New York, arranging for the retreat of South African and Cuban troops within 30 months, and the implementation of the 10-year-old UN Security Council Resolution 435 for the independence of Namibia. The Cuban intervention, for a short time, turned Cuba into a "global player" in the midst of the Cold War. Their presence helped the MPLA retain control over large parts of Angola, and their military actions are also credited with helping secure Namibia's independence. The withdrawal of the Cubans ended 13 years of foreign military presence in Angola. At the same time, Cuba removed its troops from the Republic of the Congo and Ethiopia.[193][199]
Guinea-Bissau[]
Some 40–50 Cubans fought against Portugal in Guinea-Bissau each year from 1966 until independence in 1974 (see Guinea-Bissau War of Independence). They helped in military planning and they were in charge of the artillery.
Algeria[]
As early as 1961, Cuba supported the National Liberation Front in Algeria against France.[192] In October 1963, shortly after Algeria gained its independence, Morocco started a border dispute in which Cuba sent a battalion of 40 tanks and several hundred troops to help Algeria. However, a truce between the two North African countries was signed within the week.
A memorandum issued on 20 October 1963 by Raúl Castro mandated a high standard of behavior for the troops, with strict instructions being given on their proper conduct during foreign interventions.[200]
Congo[]
In 1964, Cuba supported the Simba Rebellion of adherents of Patrice Lumumba in Congo-Leopoldville (present-day Democratic Republic of the Congo).[192] Among the insurgents was Laurent-Désiré Kabila, who would overthrow long-time dictator Mobutu 30 years later. However, the 1964 rebellion ended in failure.[201] In the Mozambican Civil War and in Congo-Brazzaville (today the Republic of the Congo), Cubans acted as military advisors. Congo-Brazzaville furthermore acted as a supply base for the Angola mission.[192]
Syria[]
In late 1973, there were 4,000 Cuban tank troops in Syria as part of an armored brigade which took part in the Yom Kippur War until May 1974.[202] Cuba did not confirm any casualties.[203]
Ethiopia[]

Fidel Castro was a supporter of the Marxist–Leninist dictator Mengistu Haile Mariam, whose regime killed hundreds of thousands during the Ethiopian Red Terror of the late 1970s, and who was later convicted of genocide and crimes against humanity. Cuba provided substantial military support to Mariam during the latter's conflict with the Somali dictator Siad Barre in the Ogaden War (July 1977–March 1978), stationing around 24,000 troops in Ethiopia.[192][204][205] Castro explained this to Erich Honecker, communist dictator of East Germany, by saying that Siad Barre was "above all a chauvinist".[204]
From October 1977 until January 1978, the Somali forces attempted to capture Harar during the Battle of Harar, where 40,000 Ethiopians had regrouped and re-armed with Soviet-supplied artillery and armor; backed by 1,500 Soviet advisors (34 of whom died in Ethiopia, 1977–90) and 16,000 Cuban troops,[206] they engaged the attackers in vicious fighting. Though the Somali forces reached the city outskirts by November, they were too exhausted to take the city and eventually had to withdraw to await the Ethiopian counterattack.
The expected Ethiopian-Cuban attack occurred in early February; however, it was accompanied by a second attack that the Somalis did not expect. A column of Ethiopian and Cuban troops crossed northeast into the highlands between Jijiga and the border with Somalia, bypassing the Somali force defending the Marda Pass. Mil Mi-6 helicopters heli-lifted Cuban BMD-1 and ASU-57 armored vehicles behind enemy lines. The attackers were thus able to assault from two directions in a "pincer" action, allowing the re-capture of Jijiga in only two days while killing 3,000 defenders.[207] The Somali defense collapsed and every major Ethiopian town was recaptured in the following weeks. Recognizing that his position was untenable, Siad Barre ordered the Somali armed forces to retreat back into Somalia on 9 March 1978.
The executing of civilians and refugees, and rape of women by the Ethiopian and Cuban troops was prevalent throughout the war.[208][209][d] Assisted by Soviet advisors, the Cubans launched a second offensive in December 1979 directed at the population's means of survival, including the poisoning and destruction of wells and the killing of cattle herds.[208]
Intelligence cooperation between Cuba and the Soviets[]
As early as September 1959, Valdim Kotchergin, a KGB agent, was seen in Cuba.[211][212] Jorge Luis Vasquez, a Cuban who was imprisoned in East Germany, states that the East German Stasi trained the personnel of the Cuban Interior Ministry (MINIT).[213] The relationship between the KGB and the Cuban Intelligence Directorate (DI) was complex and marked by both times of close cooperation and times of extreme competition. The Soviet Union saw the new revolutionary government in Cuba as an excellent proxy agent in areas of the world where Soviet involvement was not popular on a local level. Nikolai Leonov, the KGB chief in Mexico City, was one of the first Soviet officials to recognize Fidel Castro's potential as a revolutionary, and urged the Soviet Union to strengthen ties with the new Cuban leader. The USSR saw Cuba as having far more appeal with new revolutionary movements, western intellectuals, and members of the New Left, given Cuba's perceived David and Goliath struggle against U.S. "imperialism". In 1963, shortly after the Cuban Missile Crisis, 1,500 DI agents, including Che Guevara, were invited to the USSR for intensive training in intelligence operations.
Contemporary Cuba (1991 - Present)[]

Starting from the mid-1980s,[214] Cuba experienced a crisis referred to as the "Special Period". When the Soviet Union, the country's primary source of trade, was dissolved in late 1991, a major supporter of Cuba's economy was lost, leaving it essentially paralyzed because of the economy's narrow basis, focused on just a few products with just a few buyers. National oil supplies, which were mostly imported, were severely reduced. Over 80% of Cuba's trade was lost and living conditions declined. A "Special Period in Peacetime" was declared, which included cutbacks on transport and electricity and even food rationing. In response, the United States tightened up its trade embargo, hoping it would lead to Castro's downfall. But the government tapped into a pre-revolutionary source of income and opened the country to tourism, entering into several joint ventures with foreign companies for hotel, agricultural and industrial projects. As a result, the use of U.S. dollars was legalized in 1994, with special stores being opened which only sold in dollars. There were two separate economies, dollar-economy and the peso-economy, creating a social split in the island because those in the dollar-economy made much more money (as in the tourist-industry). However, in October 2004, the Cuban government announced an end to this policy: from November U.S. dollars would no longer be legal tender in Cuba, but would instead be exchanged for convertible pesos (since April 2005 at the exchange rate of $1.08) with a 10% tax payable to the state on the exchange of U.S. dollars cash – though not on other forms of exchange.
A Canadian Medical Association Journal paper states that "The famine in Cuba during the Special Period was caused by political and economic factors similar to the ones that caused a famine in North Korea in the mid-1990s. Both countries were run by authoritarian regimes that denied ordinary people the food to which they were entitled when the public food distribution collapsed; priority was given to the elite classes and the military."[215] The government did not accept American donations of food, medicines and money until 1993,[215] forcing many Cubans to eat anything they could find. In the Havana zoo, the peacocks, the buffalo and even the rhea were reported to have disappeared during this period.[216] Even domestic cats were reportedly eaten.[216]
Extreme food shortages and electrical blackouts led to a brief period of unrest, including numerous anti-government protests and widespread increases in urban crime. In response, the Cuban Communist Party formed hundreds of "rapid-action brigades" to confront protesters. The Communist Party's daily publication, Granma, stated that "delinquents and anti-social elements who try to create disorder and an atmosphere of mistrust and impunity in our society will receive a crushing reply from the people". In July 1994, 41 Cubans drowned attempting to flee the country aboard a tugboat; the Cuban government was later accused of sinking the vessel deliberately.[217]
Thousands of Cubans protested in Havana during the Maleconazo uprising on 5 August 1994. However, the regime's security forces swiftly dispersed them.[218] A paper published in the Journal of Democracy states this was the closest that the Cuban opposition could come to asserting itself decisively.[218]
Continued isolation and regional engagement[]
Although contacts between Cubans and foreign visitors were made legal in 1997,[219][220] extensive censorship had isolated it from the rest of the world. In 1997, a group led by Vladimiro Roca, a decorated veteran of the Angolan war and the son of the founder of the Cuban Communist Party, sent a petition, entitled La Patria es de Todos ("the homeland belongs to all") to the Cuban general assembly, requesting democratic and human rights reforms. As a result, Roca and his three associates were sentenced to imprisonment, from which they were eventually released.[221] In 2001, a group of Cuban activists collected thousands of signatures for the Varela Project, a petition requesting a referendum on the island's political process, which was openly supported by former U.S. President Jimmy Carter during his 2002 visit to Cuba. The petition gathered sufficient signatures to be considered by the Cuban government, but was rejected on an alleged technicality. Instead, a plebiscite was held in which it was formally proclaimed that Castro's brand of socialism would be perpetual.
In 2003, Castro cracked down on independent journalists and other dissidents in an episode which became known as the "Black Spring".[222][223][224][225] The government imprisoned 75 dissident thinkers, including 29 journalists,[222] librarians, human rights activists, and democracy activists, on the basis that they were acting as agents of the United States by accepting aid from the U.S. government.
Though it was largely diplomatically isolated from the West at this time, Cuba nonetheless cultivated regional allies. After the rise to power of Hugo Chávez in Venezuela in 1999, Cuba and Venezuela formed an increasingly close relationship based on their shared leftist ideologies, trade links and mutual opposition to U.S. influence in Latin America.[226] Additionally, Cuba continued its post-revolution practice of dispatching doctors to assist poorer countries in Africa and Latin America, with over 30,000 health workers deployed overseas by 2007.[227]
End of Fidel Castro's presidency[]
In 2006, Fidel Castro fell ill and withdrew from public life. The following year, Raúl Castro became Acting President, replacing his brother as the de facto leader of the country. In a letter dated 18 February 2008, Fidel Castro announced his formal resignation at the 2008 National Assembly meetings, saying "I will not aspire nor accept—I repeat I will not aspire or accept—the post of President of the Council of State and Commander in Chief."[228] In the autumn of 2008, Cuba was struck by three separate hurricanes, in the most destructive hurricane season in the country's history; over 200,000 were left homeless, and over US$5 billion of property damage was caused.[229][230] In March 2012, the retired Fidel Castro met Pope Benedict XVI during the latter's visit to Cuba; the two men discussed the role of the Catholic Church in Cuba, which has a large Catholic community.[231]
Improving foreign relations[]
In July 2012, Cuba received its first American goods shipment in over 50 years, following the partial relaxation of the U.S. embargo to permit humanitarian shipments.[13] In October 2012, Cuba announced the abolition of its much-disliked exit permit system, allowing its citizens more freedom to travel abroad.[14] In February 2013, after his reelection as president, Raúl Castro stated that he would retire from government in 2018 as part of a broader leadership transition.[232][233] In July 2013, Cuba became embroiled in a diplomatic scandal after Chong Chon Gang, a North Korean ship illegally carrying Cuban weapons, was impounded by Panama.[234]
Cuba and Venezuela maintained their alliance after Hugo Chávez's death in March 2013, but the severe economic strife suffered by Venezuela in the mid-2010s lessened its ability to support Cuba, and may ultimately have contributed to the thawing of Cuban-American relations.[235] In December 2014, after a highly publicized exchange of political prisoners between the United States and Cuba, U.S. President Barack Obama announced plans to re-establish diplomatic relations with Cuba after over five decades of severance.[15] He stated that the U.S. government intended to establish an embassy in Havana and improve economic ties with the country. Obama's proposal received both strong criticism and praise from different elements of the Cuban American community.[236] In April 2015, the U.S. government announced that Cuba would be removed from its list of state sponsors of terrorism, on which it had been included since 1982.[237] The U.S. embassy in Havana was formally reopened in August 2015.[17] The Trump administration has recently re-closed the US Embassy in Havana.
Economic reforms[]
As of 2015, Cuba remains one of the few officially socialist states in the world. Though it remains diplomatically isolated and afflicted by economic inefficiency, major currency reforms were begun in the 2010s, and efforts to free up domestic private enterprise are now underway.[18] Living standards in the country have improved significantly since the turmoil of the Special Period, with GDP per capita in terms of purchasing power parity rising from less than US$2,000 in 1999 to nearly $10,000 in 2010.[238] Tourism has furthermore become a significant source of prosperity for Cuba.[239]
Despite the reforms, Cuba remains afflicted by chronic shortages of food and medicines. The electrical and water services are still unreliable. In July 2021, the largest protests since the Maleconazo uprising of 1994 erupted over these problems and the government's response to the COVID-19 pandemic.[240]
See also[]
- History of the Caribbean
- History of Cuban nationality
- History of Latin America
- List of colonial governors of Cuba
- List of Cuba hurricanes
- List of Presidents of Cuba
- Politics of Cuba
- Spanish Empire
- Spanish colonization of the Americas
- Timeline of Cuban history
Notes[]
- ^ Cuba was officially atheist from 1962 until 1992.[4]
- ^ Massive quantities of advanced Soviet military hardware, including batteries of surface-to-air missiles, flowed to the island, and in October 1962 the Cuban Missile Crisis occurred.
- ^ After Dominican dictator Rafael Trujillo formed an anti-Castro foreign legion of 3,000 soldiers-of-fortune, including 200 Cuban exiles and 400 Spanish volunteers from the Blue Division (which had fought for Germany on the Eastern Front during WWII), Castro sponsored or organized several attempts to unseat him.[5] On 14 June 1959, approximately 200 Dominican exiles and Cuban revolutionaries launched an invasion of the Dominican Republic from Cuba with the hope of overthrowing the Trujillo regime. Trujillo's forces quickly routed the invaders.[5] A week later, another group of invaders in 2 yachts were intercepted and blasted by mortar fire and bazookas from the shore.[6] Trujillo's planes, directed by his son Ramfis, commander of the air force, zoomed low over the yachts and shot rockets, killing most of the invaders. A few survivors managed to swim to the shore and escape into the forest; the military used napalm to get them out.[6] The leaders of the invasion were taken aboard a Dominican Air Force plane and then pushed out in mid-air, falling to their deaths.[7] Trujillo responded by supporting an October 1960 uprising in the Escambray Mountains by 1,000 Cuban counter-revolutionaries.[5] The rebels were defeated and their leader, William Morgan, was captured and executed.[5]
- ^ Cuba lost 400 killed in the conventional war,[206] but its heaviest casualties came in the irregular war that followed. From March 1978 to November 1979, irregular hostilities claimed, according to the WSLF, 60,000 lives,[206] including 25,000 civilians and 6,000 Cuban soldiers supporting the Ethiopians.[210]
- ^ "CIA World Factbook: Cuba: Introduction: Background". Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2016.
- ^ "A guide to the United States' history of recognition, diplomatic, and consular relations, by country, since 1776: Cuba". US State Department – Office of the Historian. Archived from the original on 21 February 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- ^ Rumbaut, Luis E.; Rumbaut, Rubén G. (2009). "Cuba: The Cuban Revolution at 50". Latin American Perspectives. 36 (1): 84–98. doi:10.1177/0094582x08329137. JSTOR 27648162. S2CID 154491534.
- ^ "Cuba (09/01)".
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Clodfelter 2017, p. 637.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Tunzelmann, Alex von (2012). Red Heat: Conspiracy, Murder and the Cold War in the Caribbean.
- ^ "The Assassination of Rafael Trujillo"
- ^ George, Edward (2004). The Cuban Intervention in Angola, 1965-1991: From Che Guevara to Cuito Cuanavale. Routledge. p. 42.
- ^ Cuban Communism. Transaction Publishers. 1995. p. 167.
- ^ Cuban Identity and the Angolan Experience. Palgrave Macmillan. 2012. p. 179.
- ^ "Why the Cuban military machine should intervene in Syria". 21 October 2015.
- ^ "Live: Miguel Diaz-Canel Bermudez elected as President of the Republic". en.granma.cu. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cuba receives first US shipment in 50 years". Al Jazeera. 14 July 2012. Archived from the original on 16 July 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "US welcomes Cuba decision to end foreign travel permits". BBC. 16 October 2012. Archived from the original on 18 October 2012. Retrieved 21 October 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Obama hails 'new chapter' in US-Cuba ties". BBC News. 17 December 2014. Archived from the original on 17 December 2014. Retrieved 18 December 2014.
- ^ "Cuba's love for Obama swells: Bay of Pigs veterans reflect on the 'inconceivable'". The Guardian. 17 April 2015. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "US flag raised over reopened Cuba embassy in Havana". BBC News. 15 August 2015. Archived from the original on 18 August 2015. Retrieved 27 August 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cuba's economy: Money starts to talk". The Economist. 20 July 2013. Archived from the original on 24 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Allaire, p. 678
- ^ Allaire, p. 686
- ^ Jump up to: a b Allaire, p. 688
- ^ Historia de las Indias (vol. 3). Biblioteca Ayacucho: Caracas (1986). pp. 81–101.
- ^ Carla Rahn Phillips (1993). The Worlds of Christopher Columbus (reprint, illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 205. ISBN 978-0-521-44652-5.
- ^ Thomas Suarez (1999). Early Mapping of Southeast Asia. Tuttle Publishing. p. 109. ISBN 978-962-593-470-9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A new history. Yale University Press. Chapter 5.
- ^ Bakewell, Peter. A History of Latin America. Blackwell Publishers. pp. 129–130.
- ^ Willis Fletcher Johnson (1920). The History of Cuba (Volume 1). New York. p. 228.
- ^ Las Casas, A Short Account, p. 29
- ^ Jump up to: a b Thomas, Hugh. Cuba: The Pursuit of Freedom (2nd edition). p. 14.
- ^ "Cuban Site Casts Light on an Extinct People" Archived 5 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine. Anthony DePalma. The New York Times. 5 July 1998. Retrieved 8 December 2012.
- ^ Peter Bakewell. A History of Latin America. Bakewell Books. p. 74.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Thomas, Hugh. Cuba: A History. Penguin, 2013 p. 89
- ^ Thomas, Hugh. Cuba: A History. Penguin, 2013 p. 91
- ^ "The Cuban Slave Market". MysticSeaport.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2009. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
- ^ Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A new history. Yale University Press. p. 32.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A new history. Yale University Press. pp. 34–35.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Gott, Richard (2004). Cuba: A new history. Yale University Press. pp. 39–41.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Thomas, Hugh. Cuba: The Pursuit of Freedom (2nd edition). Chapter One.
- ^ Larrie D. Ferreiro (2016). Brothers at Arms: American Independence and the Men of France and Spain Who Saved It. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-101-87524-7.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José and Juan Jacobin (1998). History of Cuba: The Challenge of the Yoke and the Star: Biography of a People. Havana: Editoral SI-MAR. ISBN 959-7054-19-1. p. 35.
- ^ Rieu-Millan, Marie Laure (1990). Los diputados americanos en las Cortes de Cádiz: Igualdad o independencia. Madrid: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas. p. 41. ISBN 978-84-00-07091-5.
- ^ Estrada, Alfredo José. Havana: Autobiography of a City. St. Martin's Publishing Group, 2016, p. 102
- ^ Navarro, José Cantón (1998). History of Cuba. La Habana. pp. 36–38. ISBN 959-7054-19-1.
- ^ Thomas pp. 84-85
- ^ Simons, Geoff: Cuba. From Conquistador to Castro, London 1996, p. 138.
- ^
Martínez Almira, Magdalena. "APUNTES sobre la ABOLICIÓN ESCLAVITUD EN ESPAÑA" (PDF) (in Spanish). Universidad de Alicante. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
[...] en 1817 Fernando VII firmo una real cédula que prohíbe la introducción de esclavos africanos en las posesiones españolas y que entraría en vigor en 1820.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José (1998). History of Cuba. La Habana. p. 40. ISBN 959-7054-19-1.
- ^ "Gabriel de la Concepción Valdés – Plácido". AfroCubaWeb.com. Archived from the original on 13 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Gabriel de la Concepción Valdés "Plácido" (1809–1844)" (in Spanish). damisela.com. Archived from the original on 15 October 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Algo más que un sabio maestro (in Spanish). Cubanet Independente. 18 June 2003. Archived from the original on 13 November 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Worthington, Chauncey Ford (2001). Writings of John Quincy Adams (vol. VII). Boston, Massachusetts. p. 372.
- ^ Worthington, Chauncey Ford (2001). Writings of John Quincy Adams (vol. VII). Boston, Massachusetts. p. 373.
- ^ Worthington, Chauncey Ford (2001). Writings of John Quincy Adams (vol. VII). Boston, Massachusetts. p. 379.
- ^ Díez de Medina, Raúl (1934). Autopsy of the Monroe doctrine: The strange story of inter-American relations. New York. p. 21.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba, p. 42.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Scheina, Robert L. (2003). Latin America's Wars: Volume 1. Potomac Books.
- ^ Villafana, Frank (2017). Expansionism: Its Effects on Cuba's Independence. Routledge.
- ^ Foner, Philip S. (1989). Antonio Maceo: The "Bronze Titan" of Cuba's Struggle for Independence. NYU Press.
- ^ "Cuba - First War for Independence / The Ten Years War - 1868-1878". GlobalSecurity.org.
- ^ Editions, Dupont Circle; Chao, Raúl Eduardo (2009). Baraguá: Insurgents and Exiles in Cuba and New York During the Ten Year War on Independence (1868–1878). p. 293.
- ^ Cecil, Leslie (2012). New Frontiers in Latin American Borderlands. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 37.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. pp. 53–55.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. pp. 55–57.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "Spanish-Cuban-American War - History of Cuba". Archived from the original on 16 April 2008. Retrieved 19 April 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Foner, Philip: The Spanish-Cuban-American War and the Birth of American Imperialism. Quoted in: "The War for Cuban Independence" Archived 16 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine. HistoryofCuba.com. Retrieved 27 January 2013.
- ^ Gerald E. Poyo, With All, and for the Good of All: The Emergence of Popular Nationalism in the Cuban Communities of the United States, 1848–1898 (Duke University Press, 1989).
- ^ George W. Auxier, "The propaganda activities of the Cuban Junta in precipitating the Spanish–American War, 1895–1898." Hispanic American Historical Review 19.3 (1939): 286-305. in JSTOR Archived 20 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Schellings, William J. "Florida and the Cuban Revolution, 1895–1898." Florida Historical Quarterly (1960): 175-186. in JSTOR Archived 25 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. pp. 59–60.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 61.
- ^ "Weekend Economists Split for Havana February 6-8, 2015 - Democratic Underground". www.democraticunderground.com. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Smith, Iain R.; Stucki, Andreas (1 September 2011). "The Colonial Development of Concentration Camps (1868–1902)" (PDF). The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History. 39 (3): 417–437. doi:10.1080/03086534.2011.598746. ISSN 0308-6534. S2CID 159576119.
- ^ "Spanish-Cuban-American War - History of Cuba". www.historyofcuba.com. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Clodfelter 2017, p. 308.
- ^ Jones, Howard (2009). Crucible of Power: A History of American Foreign Relations to 1913. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 270.
- ^ "Spanish American War Chronology". SpanAmWar.com. Archived from the original on 23 October 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. pp. 64–65.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer (2009). The encyclopedia offers two complete volumes of alphabetically organized entries ... Philippine- American Wars: A Political, Social, and Military History, Volume 1. ABC-CLIO. p. 246.
- ^ Smith, Iain R.; Stucki, Andreas (1 September 2011). "The Colonial Development of Concentration Camps (1868–1902)" (PDF). The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History. 39 (3): 417–437. doi:10.1080/03086534.2011.598746. ISSN 0308-6534. S2CID 159576119.
- ^ Canalejas, José in Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 66.
- ^ "The Death of Cuban General Antonio Maceo". SpanAmWar.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ French Ensor Chadwick. "The Role of US Coast Guard 1895–1898 before entry of US in the war". SpanAmWar.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 69.
- ^ "Crucible of Empire: The Spanish–American War". PBS. Archived from the original on 7 December 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2007.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba, p. 71.
- ^ Wisan, Joseph E. (1955). "The Cuban Crisis As Reflected in the New York Press". In Greene, Theodore P. (ed.). American imperialism in 1898. Heath. OCLC 1060537142.
- ^ Daley#, L. (2000). El Fortin Canosa en la Cuba del 1898. in Los Ultimos Dias del Comienzo. Ensayos sobre la Guerra Hispano-Cubana-Estadounidense. B. E. Aguirre and E. Espina (eds.). RiL Editores: Santiago de Chile. pp. 161–71.
- ^ The Battles at El Caney and San Juan Hill Archived 14 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine. HomeOfHeroes.com. Retrieved 28 June 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Clodfelter 2017, p. 255.
- ^ Daley 2000, pp. 161–71
- ^ "The Spanish American War Centennial Website!". spanamwar.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Protocol of Peace Embodying the Terms of a Basis for the Establishment of Peace Between the Two Countries". Washington, D.C., U.S.A. 12 August 1898. Archived from the original on 12 October 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ "Treaty of Peace Between the United States and Spain". The Avalon project at Yale law School. 10 December 1898. Archived from the original on 23 May 2015. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ The Teller Amendment. East Tennessee State University. 1898. Archived from the original on 13 November 2007. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 78.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 74.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba. p. 76
- ^ Juan C. Santamarina. "The Cuba Company and the Expansion of American Business in Cuba, 1898–1915". Business History Review 74.01 (Spring 2000): 41–83. pp. 52–53.
- ^ Santamarina 2000, p. 42.
- ^ Smith 1995, p. 33.
- ^ Smith 1995, p. 34.
- ^ Smith 1995, p. 35.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba, p. 79.
- ^ Cantón Navarro, José. History of Cuba, p. 81.
- ^ "Nation and Multiculturalism in Cuba: A Comparison with the United States and Brazil". GeorgeZarur.com.br. 2005. Archived from the original on 10 February 2015. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "A Biography of General Enrique Loynaz del Castillo". Spanamwar.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Charles Magoon (1861–1920)". Library.thinkquest.org. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Manzanillo". CNCTV.cu. Archived from the original on 14 November 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ "Alfredo Zayas". Latin American Studies. Archived from the original on 9 October 2007. Retrieved 2 November 2007.
- ^ Richard Gott, Cuba: A New History, pp. 123–24.
- ^ Louis A. Pérez, Jr., Intervention, Revolution, and Politics in Cuba, 1913–1921, p. 4.
- ^ Richard Gott, Cuba: A New History, pp. 127–28.
- ^ Richard Gott, Cuba: A New History, p. 129.
- ^ Whitney 2000:436-437.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Leslie Bethell (1993). Cuba. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-43682-3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Julia E. Sweig (2004). Inside the Cuban Revolution. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01612-5.
- ^ "Cuban Labor Practices". U.S. Department of State Archive. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Jorge I. Domínguez. Cuba.
- ^ "Ramon Grau San Martin" Archived 15 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Answers.com. Retrieved 27 November 2011.
- ^ "Havana Conference – 1946" Archived 12 December 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Crime Magazine. Retrieved 2 December 2012.
- ^ Gipson, Therlee (11 September 2018). Fidel Castro Negro Blood. Lulu.com. ISBN 978-0-359-08074-8.
- ^ "Foreign Relations of the United States, 1958–1960, Cuba, Volume VI - Office of the Historian". history.state.gov. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Servando Gonzalez. The Secret Fidel Castro.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Cuba Before Fidel Castro". Contacto. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Cuban revolution at 50: Heroic myth and prosaic failure". The Economist. 30 December 2008. Archived from the original on 20 September 2012. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Thomas G. Paterson. Contesting Castro.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Cuba: The Unnecessary Revolution". Neoliberalismo.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2015. Retrieved 17 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j Paul H. Lewis. Authoritarian regimes in Latin America.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cuba Facts: Issue 43". Cuba Transition Project. December 2008. Archived from the original on 9 July 2012. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kirby Smith; Hugo Llorens. "Renaissance and decay: A comparison of socioeconomic indicators in pre-Castro and current-day Cuba" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Still Stuck on Castro – How the press handled a tyrant's farewell". Reason. Archived from the original on 20 September 2012. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Eric N. Baklanoff. "Cuba on the eve of the socialist transition: A reassessment of the backwardness-stagnation thesis" (PDF). Cuba in Transition. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 July 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Hugh Thomas. Cuba, The Pursuit of Freedom. p. 1173.
- ^ Guerra, Lillian (2010). Grandin, Greg; Joseph, Gilbert M. (eds.). Beyond Paradox. A Century of Revolution. American Encounters/Global Interactions. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. pp. 199–238. ISBN 978-0-8223-4737-8.
- ^ Fidel: The Untold Story. (2001). Directed by Estela Bravo. First Run Features. (91 min). Viewable clip. "Batista's forces were trained by the United States, which also armed them with tanks, artillery, and aircraft."
- ^ Jump up to: a b Historical Dictionary of the 1950s, by James Stuart Olson, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2000, ISBN 0-313-30619-2, pp. 67–68.
- ^ Fidel: The Untold Story. (2001). Directed by Estela Bravo. First Run Features. (91 min). Viewable clip.
- ^ Havana Nocturne: How the Mob Owned Cuba and Then Lost It to the Revolution, by T. J. English, William Morrow, 2008, ISBN 0-06-114771-0.
- ^ CIA (1963). Political Murders in Cuba -- Batista Era Compared with Castro Regime
- ^ Wickham-Crowley, Timothy P. (1990). Exploring Revolution: Essays on Latin American Insurgency and Revolutionary Theory. Armonk and London: M.E. Sharpe. P. 63 "Estimates of hundreds or perhaps about a thousand deaths due to Batista's terror are also supported by comments made by Fidel Castro and other Batista critics during the war itself."
- ^ Guerra, Lillian (2012). Visions of Power in Cuba: Revolution, Redemption, and Resistance, 1959–1971. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press. p. 42 "The likely total was probably closer to three to four thousand."
- ^ Conflict, Order, and Peace in the Americas, by the Lyndon B. Johnson School of Public Affairs, 1978, p. 121. "The US-supported Batista regime killed 20,000 Cubans"
- ^ "History Cuban Revolution for Android - APK Download". APKPure.com. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ "Air war over Cuba 1956–1959". ACIG.org. 30 November 2011. Archived from the original on 18 March 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2013.
- ^ "1958: Battle of La Plata (El Jigüe)". Cuba 1952–1959. 15 December 2009. Archived from the original on 29 October 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ Juan Clark Cuba (1992). Mito y Realidad: Testimonio de un Pueblo. Saeta Ediciones (Miami). pp. 53–70.
- ^ "Cuban Exile Community". LatinAmericanStudies.org. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Cuban History: Bay of Pigs". www.marxists.org. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ "CASTRO OUTLINES SWEEPING PLANS; Talks of Transformed Cuba in Five Years, Based on Agrarian Reform". timesmachine.nytimes.com. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Chomsky, N. (2003). Hegemony or Survival. Metropolitan Books. Archived from the original on 13 December 2010. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Clifford L. Staten. The history of Cuba.
- ^ Nohlen, p. 197
- ^ "Cuba: Elections and Events 1991–2001" Archived 1 March 2007 at the Wayback Machine. UCSD Latin American Election Statistics Home. 2010. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ Gleijeses, Piero (1 March 2011). Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington, and Africa, 1959-1976. Univ of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-6162-2.
- ^ "The Eisenhower era (article) | 1950s America". Khan Academy. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- ^ Gleijeses, Piero (2002). Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington and Africa, 1959–1976. University of North Carolina Press. p. 14.
- ^ Castro to Celia Sanches, 5 June 1958 in Franqui: Diary, p. 338.
- ^ Paterson in: Contesting Castro, p. 242.
- ^ Quotations from "Unofficial Visit of Prime Minister Castro of Cuba to Washington – A Tentative Evaluation", enclosed in Herter to Eisenhower, 23 April 1959, jFRUS 1958–60, 6:483, and Special NIE in: "The Situation in the Caribbean through 1959", 30 June 1959, p. 3, NSA
- ^ NSC meeting, 14 January 1960, FRUS 1958-60, 6:742–43.
- ^ Braddock to SecState, Havana, 1 February 1960, FRUS 1958–60, 6:778.
- ^
Compare:
Gleijeses, Piero (2002). "Castro's Cuba, 1959-1964". Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington, and Africa, 1959–1976. Envisioning Cuba. Univ of North Carolina Press (published 2011). pp. 14–15. ISBN 9780807861622. Retrieved 25 February 2018.
At an NSC meeting on 14 January 1960, Under Secretary Livingstone Merchant noted that 'our present objective was to adjust all our actions in such a way as to accelerate the development of an opposition in Cuba which would bring about ... a new government favorable to U.S. interests.' He then asked the assistant secretary for inter-American affairs, Roy Rubottom, to summarize the evolution of U.S.-Cuban relations since January 1959: [...] 'The period from January to March might be characterized as the honeymoon period of the Castro government. In April a downward trend in US–Cuban relations had been evident… In June we had reached the decision that it was not possible to achieve our objectives with Castro in power and had agreed to undertake the program referred to by Mr. Merchant. [...] On 31 October, in agreement with the Central Intelligence Agency, the Department had recommended to the President approval of a program along the lines referred to by Mr. Merchant. The approved program authorized us to support elements in Cuba opposed to the Castro government while making Castro's downfall seem to be the result of his own mistakes.'
- ^ "Case Studies in Economic Sanctions and Terrorism: US v. Gta 5 (1960– : Castro)" (PDF). Peterson Institute for International Economics. October 2011. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
7 February 1962[:] By presidential proclamation, US bans virtually all imports from Cuba.
- ^ Priestland, Jane (editor, 2003). British Archives on Cuba: Cuba under Castro 1959–1962. Archival Publications International Limited: London. ISBN 1-903008-20-4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b US Department of State, Foreign Relations of the United States 1961–1963, Volume X Cuba, 1961–1962 Washington, D.C. [1] Archived 1 November 2013 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Angelo Trento. Castro and Cuba : From the revolution to the present. Arris books. 2005.
- ^ Domínguez, Jorge I. "The @#$%& Missile Crisis (Or, What was 'Cuban' about US Decisions during the Cuban Missile Crisis". Diplomatic History: The Journal of the Society for Historians of Foreign Relations, Vol. 24, No. 2, (Spring 2000): 305–15.)
- ^ Jack Anderson (18 January 1971). "6 Attempts to Kill Castro Laid to CIA". The Washington Post
- ^ "Cuban Military Culture" (PDF).
- ^ "CUBAN ARMED FORCES AND THE SOVIET MILITARY PRESENCE" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Agustín Blázquez; Jaums Sutton. "UMAP: Castro's genocide plan". Archived from the original on 21 July 2012. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Leslie Bethell. The Cambridge History of Latin America.
- ^ Katherine Hirschfeld. Health, politics, and revolution in Cuba since 1898.
- ^ Black Book of Communism. p. 664
- ^ "Fidel Castro: las muertes, desapariciones y detenciones que se le atribuyen al líder de la Revolución Cubana" (in Spanish). BBC Mundo. 3 December 2016. Archived from the original on 7 January 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- ^ "Press Releases" Archived 9 July 2009 at the Portuguese Web Archive. US Census Bureau. Retrieved 16 February 2013.
- ^ Power Kills Archived 15 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine. R.J. Rummel.
- ^ Parameters: Journal of the US Army War College. U.S. Army War College. 1977. p. 13.
- ^ Jim Lobe. "Subject: Cuba followed US into Angola" Archived 8 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine. StrategyPage.com. 2004. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- ^ The Origins of the Angolan Civil War: Foreign Intervention and Domestic Political Conflict, 1961-76. Springer. 2016. p. 141.
- ^ Suchlicki, Jaime (1989). The Cuban Military Under Castro. Transaction Publishers. p. 41.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Holloway, Thomas H. (2011). A Companion to Latin American History. John Wiley & Sons.
- ^ Africa, Problems & Prospects: A Bibliographic Survey. U.S. Department of the Army. 1977. p. 221.
- ^ "Cuban Intervention in Africa".
- ^ Clodfelter 2017, p. 566.
- ^ "The Cuban Army Abroad – Meet Castro's Foreign Cold Warriors".
- ^ "Role of Cuban Soldier in Angola". The New York Times. 3 March 1976.
- ^ Eckstein, Susan (1994). Back from the Future: Cuba Under Castro. Princeton University Press. p. 187.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Gleijeses, Piero: Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington, and Africa, (The University of North Carolina Press)
- ^ Jump up to: a b Jihan El Tahri. Une Odyssée Africaine (France, 2006, 59mn).
- ^ James, Martin W. (2004). Historical Dictionary of Angola. Scarecrow Press. p. 15.
- ^ Stapleton, Timothy J. (2010). A Military History of South Africa: From the Dutch-Khoi Wars to the End of Apartheid: From the Dutch-Khoi Wars to the End of Apartheid. ABC-CLIO. p. 171.
- ^ Guimaraes, Fernando Andresen (2016). The Origins of the Angolan Civil War: Foreign Intervention and Domestic Political Conflict, 1961-76. Springer. p. 223.
- ^ George, Edward (2004). The Cuban Intervention in Angola, 1965-1991: From Che Guevara to Cuito Cuanavale. Routledge. p. 118.
- ^ Statement in Granma 8 June 1988.
- ^ "Cuba Factsheet" . US Department of State. 30 August 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- ^ PDF copy of the memorandum Archived 9 April 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Centro de Informacion de la Defensa de las Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias (CIDFAR – Information Centre of the Revolutionary Armed Forces). 20 October 1963. Retrieved 3 February 2013.
- ^ Ernesto "Che" Guevara (2001). The African Dream: The Diaries of the Revolutionary War in the Congo – With an Introduction by Richard Gott. New York: Grove Press.
- ^ "Foreign Intervention by Cuba" (PDF).
- ^ "Cuban Tank Crews In the 1974 Syria/Israel War".
- ^ Jump up to: a b Odd Arne Westad. The global Cold War.
- ^ Samuel M. Makinda. Superpower diplomacy in the Horn of Africa.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Clodfelter 2017, p. 557.
- ^ "Ogaden War". GlobalSecurity.org.
- ^ Jump up to: a b De Waal, Alexander (1991). Evil days : thirty years of war and famine in Ethiopia. Human Rights Watch. New York: Human Rights Watch. pp. 78–86. ISBN 1-56432-038-3. OCLC 24504262.
- ^ Clapham, Christopher (1990). Transformation and Continuity in Revolutionary Ethiopia. CUP Archive. p. 235.
- ^ "Ogaden War Producing Little but Refugees". The New York Times. 18 November 1979.
- ^ British Foreign Office. Chancery American Department, Foreign Office, London, 2 September 1959 (2181/59) to British Embassy Havana. Classified as restricted. Released 2000 among British Foreign Office papers. FOREIGN OFFICES FILES FOR CUBA Part 1: Revolution in Cuba. "In our letter 1011/59 May 6 we mentioned that a Russian workers' delegation had been invited to participate in the May Day celebrations here, but had been delayed. The interpreter with the party, which arrived later and stayed in Cuba a few days, was called Vadim Kotchergin although he was at the time using what he subsequently claimed was his mother's name of Liston (?). He remained in the background, and did not attract any attention."
- ^ El campo de entrenamiento "Punto Cero" donde el Partido Comunista de Cuba (PCC) adiestra a terroristas nacionales e internacionales. Cuban American Foundation. 7 November 2005. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008. Retrieved 8 January 2008. (English title: The training camp "Point Zero" where the Communist Party of Cuba (PCC) trained national and international terrorists)
"… Los coroneles soviéticos de la KGB Vadim Kochergin y Victor Simonov (ascendido a general en 1970) fueron entrenadores en "Punto Cero" desde finales de los años 60 del siglo pasado. Uno de los" graduados" por Simonov en este campo de entrenamiento es Ilich Ramírez Sánchez, más conocido como "Carlos El Chacal". Otro "alumno" de esta instalación del terror es el mexicano Rafael Sebastián Guillén, alias "subcomandante Marcos", quien se "graduó" en "Punto Cero" a principio de los años 80." - ^ Levitin, Michael (4 November 2007). La Stasi entrenó a la Seguridad cubana. Nuevo Herald. Archived from the original (– Scholar search) on 28 September 2008.
- ^ Jorge F. Pérez-López. Cuba's second economy.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Health consequences of Cuba's Special Period". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association Journal. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 179 (3): 257. 2008. doi:10.1503/cmaj.1080068. PMC 2474886. PMID 18663207.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Venezuela and Cuba: Parrot diplomacy". The Economist. 24 July 2008. Archived from the original on 1 August 2009. Retrieved 27 February 2015.
- ^ Maria C. Werlau. "Cuba: The Tugboat Massacre of July 13, 1994" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 October 2007. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Carl Gershman; Orlando Gutierrez (January 2009). "Can Cuba Change?" (PDF). Journal of Democracy. 20 (1). Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 September 2009. Retrieved 26 August 2009.
- ^ Rennie, David. "Cuba 'apartheid' as Castro pulls in the tourists" Archived 3 September 2003 at the Wayback Machine. The Daily Telegraph. 8 June 2002. Retrieved 28 June 2013.
- ^ Corbett, Ben (2004). This Is Cuba: An Outlaw Culture Survives. Westview Press. p. 33. ISBN 0-8133-3826-3.
- ^ "Cuban Economist Vladimiro Roca Released from Prison" Archived 20 December 2014 at the Wayback Machine. The National Academies: Committee on Human Rights. Retrieved 2 August 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Carlos Lauria; Monica Campbell; María Salazar (18 March 2008). "Cuba's Long Black Spring". The Committee To Protect Journalists. Archived from the original on 30 August 2011. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- ^ "Black Spring of 2003: A former Cuban prisoner speaks". The Committee to Protect Journalists. 20 March 2009. Archived from the original on 30 August 2011. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- ^ "Three years after "black spring" the independent press refuses to remain in the dark". Reporters Without Borders. 2006. Archived from the original on 21 March 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2013.
- ^ "Cuba – No surrender by independent journalists, five years on from "black spring"" (PDF). The Reporters Without Borders. March 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 July 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ^ "Venezuela ends upbeat Cuba visit". BBC News. 24 August 2005. Archived from the original on 9 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Robert Huish and John M. Kirk (2007), "Cuban Medical Internationalism and the Development of the Latin American School of Medicine", Latin American Perspectives, 34; 77
- ^ "Cuba quiet after Castro announces resignation" Archived 19 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine. CNN. 19 February 2008. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Cuba Hurricanes 2008". Canadian Red Cross. Archived from the original on 17 September 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- ^ "Cuban storms damage 'worst ever'". BBC. 16 September 2008. Archived from the original on 31 August 2013. Retrieved 9 July 2013.
- ^ "Fidel Castro meets Pope Benedict" Archived 14 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine. The Guardian. 29 March 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ^ "Cuban leader Raul Castro says he will retire in 2018". Reuters. 25 February 2013. Archived from the original on 3 June 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ^ "Cuba in 'gradual power transfer'". BBC News. 26 July 2013. Archived from the original on 27 July 2013. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- ^ "Cuba claims ownership of missile parts found on North Korean ship in Panama". The Daily Telegraph. 17 July 2013. Archived from the original on 17 July 2013. Retrieved 18 July 2013.
- ^ "How Venezuela's Collapse Helped Thaw Cuban-American Relations". Time. 18 December 2014. Archived from the original on 24 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Did Obama Just Lose Florida?". New York. 17 December 2014. Archived from the original on 18 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Cuba off the U.S. terrorism list: Goodbye to a Cold War relic". Los Angeles Times. 17 April 2015. Archived from the original on 18 April 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ "Cuba - GDP - per capita (PPP)". Index Mundi. 2011. Archived from the original on 9 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Cuba Tourism Expected To Rise After Obama Change". Huffington Post. 22 December 2014. Archived from the original on 7 January 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Fletcher, Pascal (14 July 2021). "Cuba protests: Frustration at government runs deep". BBC Monitoring. Retrieved 14 July 2021.
References[]
- Louis, Allaire (2000). "Archaeology of the Caribbean Region". In Frank Salomon (ed.). South America. The Cambridge History of the Native Peoples of the Americas. III. Stuart B. Schwartz (third ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-63075-4.
Bibliography and further reading[]
- Castillo Ramos, Ruben (1956). "Muerto Edesio, El rey de la Sierra Maestra". Bohemia XLVIII No. 9 (12 August 1956). pp. 52–54, 87.
- Chomsky, Aviva; Carr, Barry; Smorkaloff, Pamela Maria, eds. (2004). The Cuba Reader: History, Culture, Politics. Durham, NC & London: Duke University Press.
- Clodfelter, M. (2017). Warfare and Armed Conflicts: A Statistical Encyclopedia of Casualty and Other Figures, 1492-2015 (4th ed.). Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland. ISBN 978-0786474707.
- De Paz Sánchez, Manuel Antonio; Fernández, José; López, Nelson (1993–1994). El bandolerismo en Cuba (1800–1933). Presencia canaria y protesta rural. Santa Cruz de Tenerife. Two volumes.
- Foner, Philip S. (1962). A History of Cuba and its Relations with the United States.
- Franklin, James (1997). Cuba and the United States: A Chronological History. Ocean Press.
- Gleijeses, Piero (2002). Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington, and Africa, 1959–1976. University of North Carolina Press. 552 pp.
- Gott, Richard. (2004). Cuba: A New History.
- Hernández, Rafael and Coatsworth, John H., eds. (2001). Culturas Encontradas: Cuba y los Estados Unidos. Harvard University Press. 278 pp.
- Hernández, José M. (1993). Cuba and the United States: Intervention and Militarism, 1868–1933. University of Texas Press. 288 pp.
- Johnson, Willis Fletcher (1920). The History of Cuba. New York: B.F. Buck & Company, Inc.
- Kapcia, Antoni. (2021) A Short History of Revolutionary Cuba: Revolution, Power, Authority and the State from 1959 to the Present Day
- Kirk, John M. and McKenna, Peter (1997). Canada-Cuba Relations: The Other Good Neighbor Policy. University Press of Florida. 207 pp.
- McPherson, Alan (2003). Yankee No! Anti-Americanism in U.S.-Latin American Relations. Harvard University Press. 257 pp.
- Morley, Morris H. and McGillian, Chris. Unfinished Business: America and Cuba after the Cold War, 1989–2001. Cambridge University Press. 253 pp.
- Offner, John L. (2002). An Unwanted War: The Diplomacy of the United States and Spain over Cuba, 1895–1898. University of North Carolina Press, 1992. 306 pp.
- Paterson, Thomas G. (1994). Contesting Castro: The United States and the Triumph of the Cuban Revolution. Oxford University Press. 352 pp.
- Pérez, Louis A., Jr. (1998). The War of 1898: The United States and Cuba in History and Historiography. University of North Carolina Press. 192 pp.
- Pérez, Louis A. (1990). Cuba and the United States: Ties of Singular Intimacy. University of Georgia Press. 314 pp.
- Perez, Louis A. (1989). Lords of the Mountain: Social Banditry and Peasant Protest in Cuba, 1878–1918. Pitt Latin American Series: University of Pittsburgh Press. ISBN 0-8229-3601-1.
- Schwab, Peter (1999). Cuba: Confronting the U.S. Embargo. New York: St. Martin's. 226 pp.
- Staten, Clifford L. (2005). The History of Cuba. Palgrave Essential Histories.
- Thomas, Hugh (1998). Cuba or the Pursuit of Freedom. ISBN 978-0-306-80827-2.
- Tone, John Lawrence (2006). War and Genocide in Cuba, 1895–1898.
- Walker, Daniel E. (2004). No More, No More: Slavery and Cultural Resistance in Havana and New Orleans. University of Minnesota Press. 188 pp.
- Whitney, Robert W. (2001). State and Revolution in Cuba: Mass Mobilization and Political Change, 1920–1940. Chapel Hill and London: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 0-8078-2611-1.
- Zeuske, Michael (2004). Insel der Extreme: Kuba im 20. Jahrhundert. Zürich: Rotpunktverlag. ISBN 3-85869-208-5.
- Zeuske, Michael (2004). Schwarze Karibik: Sklaven, Sklavereikulturen und Emanzipation. Zürich: Rotpunktverlag. ISBN 3-85869-272-7.
- Danielle Bleitrach, Viktor Dedaj, Jacques-François Bonaldi. Cuba est une île, Cuba es una isla, Le Temps des cerises, 2004. ISBN 978-2-8410-9499-8.
External links[]
- Post-USSR: Modern Cuban Struggles, 1991 video from the Dean Peter Krogh Foreign Affairs Digital Archives
- Reflecting on Cuba's Bloody History. Peter Coyote. San Francisco Chronicle. 4 March 2009.
- Deena Stryker Photographs of Cuba, 1963-1964 and undated – Duke University Libraries Digital Collections
- Cuban Historical and Literary Manuscript Collection – University of Miami Libraries Digital Collections
- American Settlers in Cuba – Historic photographs and information on American settlers in Cuba before the Revolution
- Latin American Network Information Center. "Cuba: History". Country Directory. USA: University of Texas at Austin.
- Digital Photographic Archive of Historic Havana- a digital archive of 1055 significant buildings in the Historic Center of Havana
- APKRader- Paid APK Download For Free.
- History of Cuba
- Spanish Empire
