Hoabinhian
| Part of a series on |
| Prehistoric and ancient cultures of Vietnam |
|---|
| Paleolithic |
| Sơn Vi culture (20,000–12,000 BC) |
| Mesolithic |
| Hoabinhian (12,000–10,000 BC) |
| Neolithic |
|
| Bronze Age |
|
| Iron Age |
|
The term Hòa Bình culture (Vietnamese: Văn hóa Hòa Bình, in French culture de Hoà Bình) was first used by French archaeologists working in Northern Vietnam to describe Holocene period archaeological assemblages excavated from rock shelters. The related English adjective Hoabinhian (French hoabianien) became a common term in the English-based literature to describe stone artifact assemblages in Southeast Asia that contain flaked, cobble artifacts, dated to c. 10,000–2000 BCE.[1] The term was originally used to refer to a specific ethnic group, restricted to a limited period with a distinctive subsistence economy and technology. More recent work (e.g., Shoocongdej 2000) uses the term to refer to artifacts and assemblages with certain formal characteristics.[2] However, in 2016 a rockshelter was identified in Yunnan (China), where artifacts belonging to the Hoabinhian technocomplex were recognized, suggesting they lived in parts of Northern Vietnam and Southern China. These artifacts date from 41,500 BCE.[3]
Bacsonian is often regarded as a variation of the Hoabinhian industry characterized by a higher frequency of edge-grounded cobble artifacts compared to earlier Hoabinhian artifacts, dated to c. 8000–4000 BCE.[4][5]
Pre-Hoabinian technology[]
Hà Văn Tấn outlined in his paper his definition of a lithic technology that occurred before the Hoabinian. He found primitive flakes in stratigraphy below Hoabinian pebble tools across several sites in Southeast Asia which led him to name the flake technology, Nguomian — named after a large assembly of flakes found at the Nguom rockshelter in the Bac Thai province in Vietnam.[6] Hoabininhian technology is also claimed to be a continuation of the Sonvian technology.[6]
History of definitions[]
In 1927 Madeleine Colani published some details of her nine excavations in the northern Vietnamese province of Hòa Bình. As a result of her work the First Congress of Prehistorians of the Far East in 1932 agreed to define the Hoabinhian as
a culture composed of implements that are in general flaked with somewhat varied types of primitive workmanship. It is characterised by tools often worked only on one face, by hammerstones, by implements of sub-triangular section, by discs, short axes and almond shaped artefacts, with an appreciable number of bone tools (Matthews 1966).
Despite the general terms of the definition, Colani's Hoabinhian is an elaborate typology as indicated by the 82 artefacts from Sao Dong that Colani classified into 28 types (Matthews 1966). The original typology is so complicated that most Hoabinhian sites are identified simply by the presence of sumatraliths (White & Gorman 1979). The chronology of Hoabinhian artifacts was assumed to be Holocene because of the extant fauna found in the assemblages and the absence of extinct fauna by Colani and others working before the availability of radiocarbon dating methods in the 1950s.
Problems with Colani's typology were exposed by Matthews (1964) who analysed metric and technological attributes of unifacially flaked cobble artifacts from Hoabinhian levels at Rockshelter, Kanchanaburi Province, west-central Thailand. His aim was to determine if Hoabinhian artefact types described by Colani could be defined as clusters of constantly recurring attributes such as length, width, thickness, mass, length-width ratio and cortex amount and distribution. Matthews found that Hoabinhian types did not exist and instead Hoabinhian artifacts reflect a continuous range of shapes and sizes.
Following his archaeological excavation and surveys in Mae Hong Son Province, northwest Thailand, Chester Gorman (1970) proposed a more detailed definition as follows
- A generally unifacial flaked tool tradition made primarily on water rounded pebbles and large flakes detached from these pebbles
- Core tools ("Sumatraliths") made by complete flaking on one side of a pebble and grinding stones also made on rounded pebbles, usually in association with iron oxide
- A high incidence of used flakes (identified from edge-damage characteristics)
- Fairly similar assemblages of food remains including remains of extant shellfish, fish and small-to-medium-size mammals
- A cultural and ecological orientation to the use of rockshelters generally occurring near freshwater streams in an upland karstic topography (though Hoabinhian shell middens do indicate at least one other ecological orientation)
- Edge-grinding and cord-marked ceramics occurring, individually or together, in the upper layers of Hoabinhian deposits

Gorman's work included a number of radiocarbon dates that confirmed the Holocene age of the Hoabinhian. Gorman's carbon-14 dates place Hoabinhian levels at spirit cave between 12,000 and 8000 BP, these levels have also produced cord-marked ceramics.[7]The term was redefined in 1994 by archaeologists attending a conference held in Hanoi. At this conference Vietnamese archaeologists presented evidence of Hoabinhian artifacts dating to 17,000 years before the present. A vote was held where it was agreed that[8]
- The concept of the Hoabinhian should be kept
- The best concept for "Hoabinhian" was an industry rather than a culture or techno-complex
- The chronology of the Hoabinhian industry dates is from "late-to-terminal Pleistocene to early-to-mid Holocene"
- The term "Sumatralith" should be retained
- The Hoabinhian Industry should be referred to as a "cobble" rather that a "pebble" tool industry
- The Hoabinhian should not be referred to as a "Mesolithic" phenomenon
Geographical distribution[]
Since the term was first used to describe assemblages from sites in Vietnam, many sites throughout mainland and island Southeast Asia have been described as having Hoabinhian components. The apparent concentration of more than 120 Hoabinhian sites in Vietnam reflects intensive research activities in this area rather the location of a centre of the prehistoric Hoabinhian activity.
The oldest Hoabinhian complex was discovered at Xiaodong, a large rockshelter in Yunnan, China, 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Burmese border. It is the only Hoabinhian site discovered in China.[9]
Archaeological sites in Terengganu, Sumatra, Thailand, Laos, Myanmar and Cambodia have been identified as Hoabinhian, although the quality and quantity of descriptions vary and the relative significance of the Hoabinhian component at these sites can be difficult to determine.
Recent archaeological research indicates that variation in Hoabinhian artifacts across regions are largely influenced by local, region-specific proximity to resources and changes in environmental conditions.[10]
Beyond this core area, some archaeologists argue that there are isolated inventories of stone artifacts displaying Hoabinhian elements in Nepal, South China, Taiwan and Australia (Moser 2001).
The Hoabinhian and plant domestication[]
Gorman (1971) claimed that Spirit Cave included remains of Prunus (almond), Terminalia, Areca (betel), Vicia (broadbean) or Phaseolus, Pisum (pea) or Raphia Lagenaria (bottle gourd), Trapa (water caltrop), Piper (pepper), Madhuca (butternut), Canarium, Aleurites (candle nut), and Cucumis (a cucumber type) in layers dating to c. 9800-8500 BP. None of the recovered specimens differed from their wild phenotypes. He suggested that these may have been used as foods, condiments, stimulants, for lighting and that the leguminous plants in particular 'point to a very early use of domesticated plants' (Gorman 1969:672). He later wrote (1971:311) that 'Whether they are definitely early cultigens (see Yen n.d.:12) remains to be established... What is important, and what we can say definitely, is that the remains indicate the early, quite sophisticated use of particular species which are still culturally important in Southeast Asia.'
In 1972 W. G. Solheim, as the director of the project of which Spirit Cave was part, published an article in Scientific American discussing the finds from Spirit Cave. While Solheim noted that the specimens may 'merely be wild species gathered from the surrounding countryside', he claimed that the inhabitants at Spirit Cave had 'an advanced knowledge of horticulture'. Solheim's chronological chart suggests that 'incipient agriculture' began at about 20,000 BC in southeast Asia. He also suggests that ceramic technology was invented at 13,000 BC although Spirit Cave does not have ceramics until after 6800 BC.
Although Solheim concludes that his reconstruction is 'largely hypothetical', his overstatement of the results of Gorman's excavation has led to inflated claims of Hoabinhian agriculture. These claims have detracted from the significance of Spirit Cave as a site with well-preserved evidence of human subsistence and palaeoenvironmental conditions during the Hoabinhian.
Viet (2004), however, focuses on mainly Hoabinhians in Viet Nam. Within his wide range of study of this area, Da But is a site he works on that is dated to about fifth to sixth millennium BC to the end of the third millennium BC. Within this site, Viet sees that the food Hoabinhians mostly focus on are mountainous shellfish, nuts, and fruit. Interesting enough, the site even shows a new shellfish species that they consumed: an as-yet-unnamed species of freshwater clam of Corbicula spp; species are known to live in swampy areas and lakes.
The general food sources of Hoabinhians were gathered from the follow environmental conditions:
- Limestone rock mountains (delivering land snails and some small mammals)
- Mountain water sources like streams, small rivers, swamps and lakes (providing snails and fish)
- Valley earthen surfaces (nuts, fruits, fungi, vegetables, wild cereals, and wild mammals)[11]
Hoabinhian stone artefact technology[]
An experimental Hoabinhian assemblage was created and analyzed by Marwick (2008), which identified variables and methods that are the most useful in analyzing Hoabinhian assemblages. In particular he advocated for the use of a new method involving the dorsal cortex location of a flake. This method in particular was found to be especially useful in determining reduction intensity and may prove instrumental in answering broader archaeological questions involving subsistence, geographic range, and domestication.[12] Based on Marwick's own research[12] and Shoocongdej's (2000, 2006), behavioral ecological models were applied to examine human behavior through lithic assemblages which found in Tham Lod and Ban Rai rockshelters. In theory, high frequencies of pre-processing should reflect logistical mobility strategy. However, at Tham Lod, a high frequencies of pre-processing (CPM) but a residential mobility strategy (ODM) and a low intensity of occupation (PCM) was observed: We can see an internal conflict between models. An multiple optima model is proposed to explain this contradictory result. Multiple optima model allows more than one optimal scenario and is valid to explain high time-devoting lithic technology (i.e., pre-processing of lithic) and more residential mobility strategy in the same time.[13]
Ethnolinguistic affilation[]
The Hoabinhians are regarded as the native population of parts of Mainland Southeast Asia. Previously, the exact origin and relation of Hoabinhians and modern populations was disputed, but recent evidence link them to Austroasiatic populations and a wider East Asian-related cluster (not to be confused with modern day East Asians).
Genetics[]

A recent study by Tagore et al. 2021 found that the Hoabinhians can be demonstrably linked to Austroasiatic-speaking populations of Southeast Asia, specifically of the Malay Peninsula. The Hoabinhians, samplified by the 8,000 year old hunter gatherer sample from Laos and Malaysia, were closest to modern Semai people, Temuan people, and Jah Hut people on the Malay Peninsula as well as the isolated Nicobarese people, followed by modern Khmer people. In contrast to a previous study by McColl 2018, that suggested a close relation between Hoabinhians and the Andamanese peoples (Onge), Tagore et. al. did not find any evidence for such a close relation; on the contrary, provided evidence for geneflow of East Asian-related ancestry towards the Onge/Andamanese (similarly as previous studies, that estimated about 32% East Asian-related ancestry in Andamanese Onge[15]). Additionally, they concluded that Austroasiatic likely spread prior to the development of rice-agriculture, which later spread with a more "northern East Asian component", and that linguistic affiliation does not necessarily correspond with genetic ancestry, noting the internal diversity of modern Austroasiatic groups, especially the Munda branch.[16]
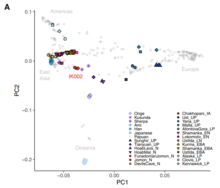
Another study, Liu et al. 2020, modeled the Andamanese/Onge as 45% East Asian-related and 55% Papuan-related. The Hoabhinians were found to be largely East Asian genetically speaking, but more basal than modern East Asians.[18]
A 2021 study by Carlhoff et al. analyzed the remains of an ancient preboreal holocene hunter-gatherer from South Sulawesi, as well as the genomes of two Hoabinhian hunter-gatherer samples from Laos and Malaysia. The two Hoabinhian samples were found to have largely "Basal-East Asian" ancestry and represent an early diverged East Asian-related population. The Holocene hunter-gatherer sample from South Sulawesi in contrast had ancestry from two distinct populations. The hunter-gatherer individual had approximately ~50% "Basal-East Asian" ancestry and ~50% "Papuan-related" ancestry, and was positioned in between modern East Asians and Papuans of Oceania. The authors concluded that East Asian-related ancestry expanded much earlier into Maritime Southeast Asia than previously suggested, long before the expansion of Austroasiatic and Austronesian groups.[19]
Similarly another study (Larena et al. 2021) found that distinctive Basal-East Asian (East-Eurasian) ancestry originated in Mainland Southeast Asia at ~50,000BC, and was widespreaded in Southeast Asia prior to the expansion of Austronesians. East Asian-related ancestry dominated Insular Southeast Asia already since 15,000BC and East Asian-related groups reached the Philippines before 12,000BC.[20]
References[]
- ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). "Hoabinhian". Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology. Springer. p. 238. ISBN 978-0-306-46158-3.
- ^ Marwick, Ben (2018). "The Hoabinhian of Southeast Asia and its Relationship to Regional Pleistocene Lithic Technologies". In Robinson, Erick; Sellet, Frederic (eds.). Lithic Technological Organization and Paleoenvironmental Change. Studies in Human Ecology and Adaptation. Vol. 9. Springer. pp. 63–78. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-64407-3. ISBN 978-3-319-64407-3.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Bellwood, Peter (2007). Prehistory of the Indo-Malaysian Archipelago. ANU E Press. pp. 161–167. ISBN 978-1-921313-12-7.
- ^ Kipfer, Barbara Ann (2000). "Bacsonian". Encyclopedic Dictionary of Archaeology. Springer. p. 50. ISBN 978-0-306-46158-3.
- ^ a b Van Tan H. (1997) The Hoabinhian and before. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association (Chiang Mai Papers, Volume 3) 16: 35-41
- ^ Who Needs the Past?: Indigenous Values and Archaeology by Robert Layton, page 154
- ^ "WebCite query result". Archived from the original on 2009-10-26.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ Xueping Ji; Kathleen Kuman; R.J. Clarke; Hubert Forestier; Yinghua Li; Juan Ma; Kaiwei Qiu; Hao Li; Yun Wu (December 2015). "The oldest Hoabinhian technocomplex in Asia (43.5 ka) at Xiaodong rockshelter, Yunnan Province, southwest China". Quaternary International. 400: 166–174. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2015.09.080.
- ^ Marwick, B. (2013). "Multiple Optima in Hoabinhian flaked stone artifact palaeoeconomics and palaeoecology at two archaeological sites in Northwest Thailand". Journal of Anthropological Archaeology. 32 (4): 553–564. doi:10.1016/j.jaa.2013.08.004.
- ^ Viet, Nguyen. Hoabinhian Food Strategy in Viet Nam. pp. 14–15.
- ^ a b Marwick, Ben (2008). "What attributes are important for the measurement of assemblage reduction intensity? Results from an experimental stone artefact assemblage with relevance to the Hoabinhian of mainland Southeast Asia". Journal of Archaeological Science. Vol. 35. pp. 1189–1200. doi:10.1016/j.jas.2007.08.007.
- ^ Marwick, Ben (2013). "Multiple Optima in Hoabinhian flaked stone artefact palaeoeconomics and palaeoecology at two archaeological sites in Northwest Thailand". Journal of Anthropological Archaeology. Vol. 32. pp. 553–564. doi:10.1016/j.jaa.2013.08.004.
- ^ Carlhoff, Selina; Duli, Akin; Nägele, Kathrin; Nur, Muhammad; Skov, Laurits; Sumantri, Iwan; Oktaviana, Adhi Agus; Hakim, Budianto; Burhan, Basran; Syahdar, Fardi Ali; McGahan, David P.; Bulbeck, David; Perston, Yinika L.; Newman, Kim; Saiful, Andi Muhammad; Ririmasse, Marlon; Chia, Stephen; Pulubuhu, Dwia Aries Tina; Jeong, Choongwon; Peter, Benjamin M.; Prüfer, Kay; Powell, Adam; Krause, Johannes; Posth, Cosimo; Brumm, Adam (August 2021). "Genome of a middle Holocene hunter-gatherer from Wallacea". Nature. 596 (7873): 543–547. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03823-6. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 8387238. PMID 34433944.
- ^ Chaubey G (2015). "East Asian Ancestry in India" (PDF). Indian Journal of Physical Anthropology and Human Genetics. 34 (2): 193–199.
- ^ Tagore, Debashree; Aghakhanian, Farhang; Naidu, Rakesh; Phipps, Maude E.; Basu, Analabha (2021-03-29). "Insights into the demographic history of Asia from common ancestry and admixture in the genomic landscape of present-day Austroasiatic speakers". BMC Biology. 19 (1): 61. doi:10.1186/s12915-021-00981-x. ISSN 1741-7007. PMC 8008685. PMID 33781248.
McColl et al. suggested that ancient SEA hunter-gatherers (Hòabìnhian) share some ancestry with the Onge, Jehai, Papuan, and Indian populations. We therefore ran the ADMIXTURE analysis including the Jarawa, Onge, and the Papuans as possible founder populations in addition to the previous set of AAI, AAM, TB, and EA. Contrary to their claim, we found no evidence of Onge, Jarawa, and Papuan ancestries in the ANC samples (results of ADMIXTURE run hence not shown). We regressed the AAI ancestry (and the EA-like ancestry) of the ancient genomes jointly on the age of the sample and the latitude where these samples were found (Supplementary Table 7).
- ^ Gakuhari, Takashi; Nakagome, Shigeki; Rasmussen, Simon; Allentoft, Morten E.; Sato, Takehiro; Korneliussen, Thorfinn; Chuinneagáin, Blánaid Ní; Matsumae, Hiromi; Koganebuchi, Kae; Schmidt, Ryan; Mizushima, Souichiro (2020-08-25). "Ancient Jomon genome sequence analysis sheds light on migration patterns of early East Asian populations". Communications Biology. 3 (1): 437. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01162-2. ISSN 2399-3642. PMC 7447786. PMID 32843717.
- ^ Liu, Dang; Duong, Nguyen Thuy; Ton, Nguyen Dang; Van Phong, Nguyen; Pakendorf, Brigitte; Van Hai, Nong; Stoneking, Mark (2020-04-28). "Extensive Ethnolinguistic Diversity in Vietnam Reflects Multiple Sources of Genetic Diversity". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 37 (9): 2503–2519. doi:10.1093/molbev/msaa099. ISSN 0737-4038. PMC 7475039. PMID 32344428.
- ^ Carlhoff, Selina; Duli, Akin; Nägele, Kathrin; Nur, Muhammad; Skov, Laurits; Sumantri, Iwan; Oktaviana, Adhi Agus; Hakim, Budianto; Burhan, Basran; Syahdar, Fardi Ali; McGahan, David P. (August 2021). "Genome of a middle Holocene hunter-gatherer from Wallacea". Nature. 596 (7873): 543–547. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03823-6. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 8387238. PMID 34433944.
The qpGraph analysis confirmed this branching pattern, with the Leang Panninge individual branching off from the Near Oceanian clade after the Denisovan gene flow, although with the most supported topology indicating around 50% of a basal East Asian component contributing to the Leang Panninge genome (Fig. 3c, Supplementary Figs. 7–11).
- ^ Larena, Maximilian; Sanchez-Quinto, Federico; Sjödin, Per; McKenna, James; Ebeo, Carlo; Reyes, Rebecca; Casel, Ophelia; Huang, Jin-Yuan; Hagada, Kim Pullupul; Guilay, Dennis; Reyes, Jennelyn (2021-03-30). "Multiple migrations to the Philippines during the last 50,000 years". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 118 (13): e2026132118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2026132118. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 8020671. PMID 33753512.
Literature[]
- Colani M. (1927) L'âge de la pierre dans la province de Hoa Binh. Mémoires du Service Géologique de l'Indochine 13
- Flannery, KV. (1973) The origins of agriculture. Annual Review of Anthropology 2: 271-310
- Forestier H, Zeitoun V, Winayalai C and Métais C (2013). The open-air site of Huai Hin (Northwestern Thailand): Chronological perspectives for the Hoabinhian. Comptes Rendus Palevol 12(1)
- Gorman C. (1969) Hoabinhian: A pebble tool complex with early plant associations in Southeast Asia. Science 163: 671-3
- Gorman C. (1970) Excavations at Spirit Cave, North Thailand: Some interim interpretations. Asian Perspectives 13: 79-107
- Gorman C. (1971) The Hoabinhian and After: Subsistence Patterns in Southeast Asia during the Late Pleistocene and Early Recent Periods. World Archaeology 2: 300-20
- Matthews JM. (1964) The Hoabinhian in Southeast Asia and elsewhere. PhD thesis. Australian National University, Canberra
- Matthews JM. (1966) A Review of the 'Hoabinhian' in Indo-China. Asian Perspectives 9: 86-95
- Marwick, B. (2008) What attributes are important for the measurement of assemblage reduction intensity? Results from an experimental stone artefact assemblage with relevance to the Hoabinhian of mainland Southeast Asia. Journal of Archaeological Science 35(5): 1189-1200
- Marwick, B. and M. K. Gagan (2011) Late Pleistocene monsoon variability in northwest Thailand: an oxygen isotope sequence from the bivalve Margaritanopsis laosensis excavated in Mae Hong Son province. Quaternary Science Reviews 30(21-22): 3088-3098
- Moser, J. (2001) Hoabinhian: Geographie und Chronologie eines steinzeitlichen Technocomplexes in Südostasien Köln, Lindensoft.
- Pookajorn S. (1988) Archaeological research of the Hoabinhian culture or technocomplex and its comparison with ethnoarchaeology of the Phi Tong Luang, a hunter-gatherer group of Thailand. Tübingen: Verlag Archaeologica Venatoria: Institut fur Urgeschichte der Universitat Tübingen.
- Shoocongdej R. (2000) Forager Mobility Organization in Seasonal Tropical Environments of Western Thailand. World Archaeology 32: 14-40.
- Solheim, W.G. (1972) An earlier agricultural revolution. Scientific American 226: 34-41
- Van Tan H. (1994) The Hoabinhian in Southeast Asia: Culture, cultures or technocomplex? Vietnam Social Sciences 5: 3-8
- Van Tan H. (1997) The Hoabinhian and before. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association (Chiang Mai Papers, Volume 3) 16: 35-41
- White JC, Gorman C. (2004) Patterns in "amorphous" industries: The Hoabinhian viewed through a lithic reduction sequence. IN Paz, V. (ed) Southeast Asian archaeology: Wilhelm G. Solheim II Festschrift University of the Philippines Press, Quezon City. pp. 411–441.
- White JC, Penny D, Kealhofer L and Maloney B 2004. Vegetation changes from the late Pleistocene through the Holocene from three areas of archaeological significance in Thailand. Quaternary International 113(1)
- Zeitoun, V., Forestier, H., Pierret, A., Chiemsisouraj, C., Lorvankham, M., Latthagnot, A., ... & Norkhamsomphou, S. (2012). Multi-millennial occupation in northwestern Laos: Preliminary results of excavations at the Ngeubhinh Mouxeu rock-shelter. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 11(4), 305-313.
See also[]
- Ancient Vietnam
- Prehistoric Thailand
- Archaeological cultures of Southeast Asia
- Archaeological cultures in Vietnam
- Mesolithic cultures of Asia
- Archaeological cultures in Cambodia