List of crewed lunar landers
This list is incomplete; you can help by . (July 2020) |
This is a list of designs for crewed lunar landers, spacecraft intended to land on the Moon. A key aspect is achieving a soft landing, and for an ascent stage to successfully escape the Moon's gravity.[1] Another aspect is how many stages the design has to undergo to achieve its objective, and the number of passengers and amount of payload it can carry.[1]
| Name | Manufacturer | Operator (program and operational timeline) | Stages | Crew | Payload Mass | Status | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altair | Northrop Grumman | NASA (Constellation, 2005-2009) | Descent, Ascent | 4 | 14,500 kg (32,000 lb) | Canceled | 
|
| Apollo Lunar Module | Grumman | NASA (Apollo, 1969–1972) | Descent, Ascent | 2 | Retired | 
| |
| Boeing Lunar Lander | Boeing | Boeing, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Descent, Ascent | Rejected | [1] | ||
| Dynetics HLS | Dynetics | Dynetics, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Single-stage with drop tanks | 2-4 | Rejected | [2] | |
| Integrated Lander Vehicle | Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory | Blue Origin, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Draper Laboratory, NASA | Transfer, Descent, Ascent | 2 | Rejected | [3] | |
| LK | RSC Energia/Yuzhnoye Design Office | Soviet Union (N1-L3, 1969-1974) | Descent, Ascent | 1 | Canceled | 
| |
| Lockheed Martin Lunar Lander | Lockheed Martin | Lockheed Martin, NASA (Artemis, 2017–present) | Single-stage | 4 | 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) | Proposed | [4] |
| Starship | SpaceX | SpaceX | Single-stage | Planned |  [5] [5]
| ||
| Starship HLS | SpaceX | NASA (Artemis, 2017–present), SpaceX | Single-stage | 4 | 100–200 t (220,000–440,000 lb) | Planned | [6] |
| [2] | British Interplanetary Society | Single-stage | 3 | Studies (1939, 1947) | |||
| Von Braun Lunar Lander[3] | US (1977) | Single-stage with drop tanks | 20 | 259 metric tons (with a crew of 10) | Study (1952) | ||
| Horizon LERV[4] | US Army (Project Horizon, 1966) | Descent, Ascent | 10 - 16 | 2,700 - 22,000 kg | Study (1959) | 
| |
| Lunex Lunar Lander[5] | US Air Force (Lunex Project, 1967) | Descent, Ascent | 3 | 20,500 kg | Study (1958-1961) | 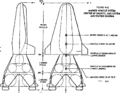
| |
| Gemini lunar lander | NASA Langley Research Center, (Project Gemini, 1963) | Single | 1 | Canceled | 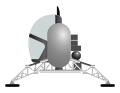
| ||
| LEK[6] | Soviet Union, (Zvezda Moon base, 1974) | Descent, Ascent, Reentry | 3 | Canceled | |||
| FLO Eagle lander | NASA (Space Exploration Initiative, 1992–93) | Descent, Ascent | 4 | 5,000 kg | Canceled | 
|
See also[]
- Human spaceflight
- Lunar module – Lunar lander designed for human spaceflight
References[]
- ^ a b "NASA studying three-stage approach to human-class lunar landers". SpaceNews.com. 2018-11-20. Retrieved 2019-11-08.
- ^ "BIS Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com.
- ^ "Von Braun Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com.
- ^ "Horizon LERV". www.astronautix.com.
- ^ "Lunex Lunar Lander". www.astronautix.com.
- ^ "Archived copy". www.astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 16 March 2006. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links[]
Categories:
- Crewed spacecraft
- Landers (spacecraft)