List of ships captured in the 18th century

Foudroyant and Pégase entering Portsmouth Harbour, 1782, painted by Dominic Serres. The Royal Navy ship of the line HMS Foudroyant is seen here leading the captured French ship of the line Pégase into Portsmouth harbour after capturing her during the Third Battle of Ushant.
During times of war where naval engagements were frequent, many battles were fought that often resulted in the capture of the enemy's ships. The ships were often renamed and used in the service of the capturing country's navy. Merchant ships were also captured and taken into service by their captors.
1701–10[]
1702[]
- (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Bourbon (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy. - Espérance d'Angleterre (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Navy): The 10-gun ketch was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 10-gun ketch was captured by the French Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Prompt (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 76-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 76-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Vigo Bay, 23 October: The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy and Royal Netherlands Navy.
1703[]
- (
 French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 40-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 40-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - HMS Salisbury (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 10 April by the French Navy's and three privateers.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 10 April by the French Navy's and three privateers.
1704[]
- HMS Coventry (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Auguste and Jason.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Auguste and Jason. - HMS Elizabeth (
 Royal Navy): The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy. - HMS Falmouth (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
1705[]
- (
 French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Auguste (
 French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured on 19 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham, HMS Medway and .
French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured on 19 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham, HMS Medway and . - HMS Blackwall (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's .
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's . - L'Entreprise (
 French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate frigate was captured in May by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate frigate was captured in May by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Cabrita Point, 21 March: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Netherlands Navy. - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Pendennis (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured in October by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured in October by the French Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1706[]
- (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
1707[]
- (
 French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured in March by Dutch privateers.
French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured in March by Dutch privateers. - HMS Chester (
 Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy. - HMS Cumberland (
 Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 80-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's and .
Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 80-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's and . - HMS Grafton (
 Royal Navy): Action of 2 May 1707: The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Blekoualle, and Mars.
Royal Navy): Action of 2 May 1707: The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Blekoualle, and Mars. - HMS Hampton Court (
 Royal Navy): Action of 2 May 1707: The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Blekoualle, and .
Royal Navy): Action of 2 May 1707: The 70-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Blekoualle, and . - (
 Royal Navy): The 4-gun hoy was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 4-gun hoy was captured by the French Navy. - HMS Ruby (
 Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 40-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Mars.
Royal Navy): Battle at The Lizard, 21 October: The 40-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Mars. - (
 French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1708[]
- Blekoualle (
 French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 15 March by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 15 March by the Royal Navy. - Salisbury (
 French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 15 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Leopard.
French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 15 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Leopard. - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
1709[]
- HMS Adventure (
 Royal Navy): The 44-gun fourth rate was captured on 1 March by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 44-gun fourth rate was captured on 1 March by the French Navy. - HMS Blackwall (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy. - Coventry (
 French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 17 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Portland (1693).
French Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 17 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Portland (1693). - (
 French Navy): The 46-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 46-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 ): The 32-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's .
): The 32-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's . - (
 French Navy): The 38-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 38-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Gloucester (
 Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured on 26 October by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured on 26 October by the French Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 4-gun hoy was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 4-gun hoy was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Pembroke (
 Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
1710[]
- (
 French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by a French privateer.
Royal Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by a French privateer. - (
 French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Superbe (
 French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1711–20[]
1711[]
- Pembroke (
 French Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 62-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 62-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1712[]
- (
 French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1713[]
- (
 French Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
French Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
1714[]
- (
 Imperial Russian Navy): The 52-gun ship was captured by the Royal Swedish Navy.
Imperial Russian Navy): The 52-gun ship was captured by the Royal Swedish Navy.
1717[]
- Great Allen (
 Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured, looted, burnt and sunk off Cape St. Vincent by Queen Anne's Revenge (
Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured, looted, burnt and sunk off Cape St. Vincent by Queen Anne's Revenge ( Blackbeard).
Blackbeard). - La Concorde (
 France): The slave ship was captured on 28 November off Saint Vincent by Revenge and another ship (both
France): The slave ship was captured on 28 November off Saint Vincent by Revenge and another ship (both  Blackbeard).
Blackbeard). - Margaret (
 Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured on 5 December off Anguilla by Queen Anne's Revenge (
Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured on 5 December off Anguilla by Queen Anne's Revenge ( Blackbeard). She was looted and then released.
Blackbeard). She was looted and then released. - Whydah Gally (
 Great Britain): The slave ship was captured in late February in the Windward Passage by Sultana (
Great Britain): The slave ship was captured in late February in the Windward Passage by Sultana ( "Black Sam" Bellamy). She wrecked in a storm off Cape Cod two months later, taking Bellamy, 143 men, and 4.5 tons of treasure with her – and was the first pirate ship ever discovered in North America, in 1984.
"Black Sam" Bellamy). She wrecked in a storm off Cape Cod two months later, taking Bellamy, 143 men, and 4.5 tons of treasure with her – and was the first pirate ship ever discovered in North America, in 1984.
1718[]
- Principe de Asturias (
 Spain): Battle of Cape Passaro, 11 August. The 70-gun ship was captured by HMS Breda and HMS Captain.
Spain): Battle of Cape Passaro, 11 August. The 70-gun ship was captured by HMS Breda and HMS Captain. - Protestant Caesar (
 Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured on 9 April by Adventure, Revenge, Queen Anne's Revenge, and other ships (all
Great Britain): The merchant ship was captured on 9 April by Adventure, Revenge, Queen Anne's Revenge, and other ships (all  Blackbeard). She was looted, burnt and sunk.
Blackbeard). She was looted, burnt and sunk.
1719[]
- (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 10-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 10-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 30-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 30-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 52-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Ösel Island, 24 May: The 52-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Unknown date[]
- (
 French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured in 1713 or 1714 by the Royal Swedish Navy.
French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured in 1713 or 1714 by the Royal Swedish Navy.
1721–30[]
1722[]
- Ranger (
 Bartholomew Roberts): The pirate ship was captured on 5 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Swallow.
Bartholomew Roberts): The pirate ship was captured on 5 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Swallow. - Royal Fortune (
 Bartholomew Roberts): The pirate ship was captured on 10 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Swallow.
Bartholomew Roberts): The pirate ship was captured on 10 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Swallow.
1725[]
- Prince Frederick([[discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1349550/1/473433.pdf)" class="wikEdFilePreview" id="wikEdFilePreview7" style="width: 75px; height: 75px; display: none;">File:Captain Wittington Williams [1]]]: The British merchant ship was captured by the Spanish at Vera Cruz.
1731–40[]
1731[]
- (
 Royal Navy): The brig Rebecca, commanded by Robert Jenkins, was captured in April 1731 by the Spanish Navy, on suspicion of smuggling, being casus belli of the War of Jenkins' Ear.
Royal Navy): The brig Rebecca, commanded by Robert Jenkins, was captured in April 1731 by the Spanish Navy, on suspicion of smuggling, being casus belli of the War of Jenkins' Ear.
1739[]
- (
 Spanish Navy): The ship was captured on 3 March by the Royal Navy.[2]
Spanish Navy): The ship was captured on 3 March by the Royal Navy.[2]
1741–50[]
1744[]
- (
 Spain): The merchant ship was captured in February by the French Navy.
Spain): The merchant ship was captured in February by the French Navy.
1745[]
- (
 Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1746[]
- HMS Albany (
 Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy. - Auguste (
 French Navy): The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Navy): The 10-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 10-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy. - Mars (
 French Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in October by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in October by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the French Navy.
1747[]
- (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 50-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Invincible (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Monarque (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Renommée (
 French Navy): The 30-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): The 30-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy's . - (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Sérieux (
 French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): First Battle of Cape Finisterre, 3 May: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Severn (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 50-gun fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Terrible (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Second Battle of Cape Finisterre, 14 June: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Spanish Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured on 19 October by the Royal Navy, after the 4 battles of the Voyage of the Glorioso.
Spanish Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured on 19 October by the Royal Navy, after the 4 battles of the Voyage of the Glorioso.
1748[]
- (
 France): The Compagnie des Indes ship was captured by the French Navy.
France): The Compagnie des Indes ship was captured by the French Navy. - Magnanime (
 French Navy): The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
1751–60[]
1755[]
- Alcide (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 8 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dunkirk and HMS Torbay.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 8 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dunkirk and HMS Torbay. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
1756[]
- (
 French Navy): The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 58-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Warwick (
 Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured in March by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured in March by the French Navy.
1757[]
- Duc D'Aquitaine (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Greenwich (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 17 March by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 17 March by the French Navy.
1758[]
- Auguste (
 France): The privateer was captured by the British.
France): The privateer was captured by the British. - Belliqueux (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 2 November in the Irish Sea by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 2 November in the Irish Sea by the Royal Navy's . - Bienfaisant (
 French Navy): Siege of Louisbourg: The 64-gun ship was captured on 25 July by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): Siege of Louisbourg: The 64-gun ship was captured on 25 July by the Royal Navy's . - Echo (
 French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 24-gun sixth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Foudroyant (
 French Navy): Battle of Cartagena, 28 February: The 80-gun ship was captured on 28 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Hampton Court, HMS Monmouth and HMS Swiftsure.
French Navy): Battle of Cartagena, 28 February: The 80-gun ship was captured on 28 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Hampton Court, HMS Monmouth and HMS Swiftsure. - Mohawk (
 French Navy): Battle of Fort Niagara, 6–26 July: The snow was captured uncompleted at Fort Niagara, New France and completed as HMS Mohawk.
French Navy): Battle of Fort Niagara, 6–26 July: The snow was captured uncompleted at Fort Niagara, New France and completed as HMS Mohawk. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in February by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in February by the Royal Navy. - Raisonnable (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 29 May by the Royal Navy's HMS Achilles and HMS Dorsetshire.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 29 May by the Royal Navy's HMS Achilles and HMS Dorsetshire.
1759[]
- Aréthuse (
 French Navy): The 32-gun frigate was captured on 18 May by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham, HMS Thames and HMS Venus.
French Navy): The 32-gun frigate was captured on 18 May by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham, HMS Thames and HMS Venus. - Centaure (
 French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 74-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 74-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy. - Formidable (
 French Navy): Battle of Quiberon Bay, 20 November: The 80-gun ship was captured on 20 November by the Royal Navy's HMS Resolution.
French Navy): Battle of Quiberon Bay, 20 November: The 80-gun ship was captured on 20 November by the Royal Navy's HMS Resolution. - Modeste (
 French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 64-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 64-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy. - St Florentine (
 French Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Téméraire (
 French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 74-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Warspite.
French Navy): Battle of Lagos, 19 August: The 74-gun ship was captured on 18 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Warspite.
1761–70[]
1761[]
- (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in July by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in July by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 3 April by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 3 April by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured on 30 January by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured on 30 January by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Oriflamme (
 French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured on 1 April by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): The 56-gun ship was captured on 1 April by the Royal Navy's . - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Vestale (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured on 8 January by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The frigate was captured on 8 January by the Royal Navy. - Warwick (
 French Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured on 24 January by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 60-gun fourth rate was captured on 24 January by the Royal Navy.
1762[]
- Conquestador (
 Spanish Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): The 60-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy. - Hussar (
 Royal Navy): The Coventry-class frigate was captured on 23 May by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The Coventry-class frigate was captured on 23 May by the French Navy. - Hermione (
 Spanish Navy): The 28-gun frigate was captured in the action of 31 May 1762 by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): The 28-gun frigate was captured in the action of 31 May 1762 by the Royal Navy. - Reyna (
 Spanish Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy. - San Antonio (
 Spanish Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 13 August by the Royal Navy.
1770[]
- (
 Ottoman Navy): Battle of Chesma, 5–7 July: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Ottoman Navy): Battle of Chesma, 5–7 July: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
1771–80[]
1775[]
- (
 Royal Navy): The 10-gun sloop was captured by an American privateer.
Royal Navy): The 10-gun sloop was captured by an American privateer.
1776[]
- (
 Continental Navy): The sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's .
Continental Navy): The sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's . - (
 Continental Navy): Commanded by G. W. Babcock, captured 1776 by British cruisers at New York.[3]
Continental Navy): Commanded by G. W. Babcock, captured 1776 by British cruisers at New York.[3] - USS Warren (
 Continental Navy): The 14-gun schooner was captured on 26 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Liverpool.
Continental Navy): The 14-gun schooner was captured on 26 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Liverpool.
1777[]
- Delaware (
 United States Navy): The 24-gun frigate commanded by Captain Charles Alexander, was captured after running aground near Philadelphia on September 26, 1777. She was taken into the Royal Navy as the Delaware.
United States Navy): The 24-gun frigate commanded by Captain Charles Alexander, was captured after running aground near Philadelphia on September 26, 1777. She was taken into the Royal Navy as the Delaware. - USS Hancock (
 United States Navy): The 32-gun frigate was captured on 8 July by the Royal Navy's (44).
United States Navy): The 32-gun frigate was captured on 8 July by the Royal Navy's (44). - Industrious Bee (
 Great Britain): The brigantine was captured on 29 August by the Continental Navy's USS Lee.
Great Britain): The brigantine was captured on 29 August by the Continental Navy's USS Lee. - USS Lexington (1776) (
 United States Navy): The 14-gun brigantine was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Alert.
United States Navy): The 14-gun brigantine was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Alert. - (
 United States Navy): The 14-gun brig was captured by the Royal Navy.
United States Navy): The 14-gun brig was captured by the Royal Navy.
1778[]
- HMS Ceres (
 Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured in April by the French Navy's Iphigénie.
Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured in April by the French Navy's Iphigénie. - (
 Royal Navy): The 12-gun sloop was captured by the United States Navy.
Royal Navy): The 12-gun sloop was captured by the United States Navy. - Raleigh (
 United States Navy): The 32-gun frigate ran aground at Matinicus Isle, Maine and was abandoned. She was captured by the Royal Navy three days later and refloated.[4]
United States Navy): The 32-gun frigate ran aground at Matinicus Isle, Maine and was abandoned. She was captured by the Royal Navy three days later and refloated.[4]
1779[]
- Albemarle (
 France): The convict ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Albion.
France): The convict ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Albion. - HMS Ardent (
 Royal Navy): The 64-gun third rate was captured on 17 August by the French Navy's Junon.
Royal Navy): The 64-gun third rate was captured on 17 August by the French Navy's Junon. - HMS Ariel (
 Royal Navy): The Sphinx-class post ship was captured on 10 September by the French Navy's Amazone.
Royal Navy): The Sphinx-class post ship was captured on 10 September by the French Navy's Amazone. - Astrée (
 France): The privateer was captured on 13 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby.
France): The privateer was captured on 13 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby. - (
 United States Navy): The 14-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy.
United States Navy): The 14-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Montreal (
 Royal Navy): The Niger-class frigate was captured on 1 May by the French Navy's Bourgogne.
Royal Navy): The Niger-class frigate was captured on 1 May by the French Navy's Bourgogne.
1780[]
- Belle Poule (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured on 14 July by the Royal Navy's HMS Nonsuch.
French Navy): The frigate was captured on 14 July by the Royal Navy's HMS Nonsuch. - Boston (
 United States Navy): The 24-gun frigate was captured at the end of the siege of Charleston, South Carolina. She was taken into the Royal Navy as HMS Charleston.
United States Navy): The 24-gun frigate was captured at the end of the siege of Charleston, South Carolina. She was taken into the Royal Navy as HMS Charleston. - Diligente (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Fénix (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Fortune (
 Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 14-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy. - Guipuzcoano (
 Spain): Action of 8 January 1780: The armed merchantman was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spain): Action of 8 January 1780: The armed merchantman was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Monarca (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Princessa (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Protée (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 24 February by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 24 February by the Royal Navy. - Providence (
 United States Navy): The 28-gun frigate was captured at the end of the siege of Charleston, South Carolina. The Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Providence.
United States Navy): The 28-gun frigate was captured at the end of the siege of Charleston, South Carolina. The Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Providence. - San Fermín (
 Spain): Action of 8 January 1780: The 16-gun private corvette was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spain): Action of 8 January 1780: The 16-gun private corvette was captured by the Royal Navy. - San Miguel (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St. Vincent, 16 January: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 ): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships.
): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships. - (
 ): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships.
): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships. - Hillsborough (1774 ship) (
 ): The 30-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with 54 other British ships.
): The 30-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with 54 other British ships. - (
 ): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships.
): The 28-gun East India Company's Indiaman was captured in the Action of 9 August by the Spanish Navy, along with other 54 British ships. - Royal George (1777 ship) (
 ): The Spanish Navy captured the 28-gun East India Company's East Indiaman in the Action of 9 August, along with other 54 British ships.
): The Spanish Navy captured the 28-gun East India Company's East Indiaman in the Action of 9 August, along with other 54 British ships.
1781–90[]
1781[]
- Abondance (
 Kingdom of France): The Royal Navy captured the Baleine-class cargo ship on 12 December; the Navy took her into service as HMS Abondance.
Kingdom of France): The Royal Navy captured the Baleine-class cargo ship on 12 December; the Navy took her into service as HMS Abondance. - (
 USA): The 20-gun brig under the command of Captain James Magee was captured by British frigate, HMS Amphytrite off Cape Ann, Massachusetts. She was taken into the Royal Navy.[5]
USA): The 20-gun brig under the command of Captain James Magee was captured by British frigate, HMS Amphytrite off Cape Ann, Massachusetts. She was taken into the Royal Navy.[5] - Confederacy (
 United States Navy): HMS Roebuck (44) and Orpheus (32) captured the 36-gun frigate in March; the Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Confederate.
United States Navy): HMS Roebuck (44) and Orpheus (32) captured the 36-gun frigate in March; the Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Confederate. - Magicienne (
 French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 2 July by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham.
French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 2 July by the Royal Navy's HMS Chatham. - Mars (
 Dutch Republic): The 18-gun privateer brig-sloop was captured on 3 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Artois.
Dutch Republic): The 18-gun privateer brig-sloop was captured on 3 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Artois. - HMS Richmond (
 Royal Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 11 September by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 11 September by the French Navy. - HNLMS Rotterdam (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The fourth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Port Royal (
 Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 3 April by the Spanish Navy during the Siege of Pensacola.
Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 3 April by the Spanish Navy during the Siege of Pensacola. - HMS St Fermin (
 Royal Navy): The 16-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 4 April by the Spanish Navy's and .
Royal Navy): The 16-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 4 April by the Spanish Navy's and .
1782[]
- Actionnaire (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in April by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured in April by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured. - Ardent (
 French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The 64-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The 64-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Caton (
 French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - César (
 French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Glorieux (
 French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy
French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy - Hector (
 French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The Hector-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Saintes, 9–12 April: The Hector-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Hannibal (
 Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 21 January by the French Navy's Héros.
Royal Navy): The 50-gun fourth rate was captured on 21 January by the French Navy's Héros. - HMS Hector (
 Royal Navy): The Hector-class ship of the line was captured by the French Navy
Royal Navy): The Hector-class ship of the line was captured by the French Navy - HMS Iris (
 Royal Navy): The frigate was captured on 9 September by the French Navy's .
Royal Navy): The frigate was captured on 9 September by the French Navy's . - Jason (
 French Navy): Battle of the Mona Passage, 19 April: The 64-gun ship was captured on 19 April by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Mona Passage, 19 April: The 64-gun ship was captured on 19 April by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Pégase (
 French Navy): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured on 21 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Foudroyant.
French Navy): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured on 21 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Foudroyant. - San Miguel (
 Spanish Navy): Great Siege of Gibraltar, 24 June 1779 – 7 February 1783: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Spanish Navy): Great Siege of Gibraltar, 24 June 1779 – 7 February 1783: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Solitaire (
 French Navy): Action of 6 December 1782: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby.
French Navy): Action of 6 December 1782: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby. - South Carolina: The 40-gun frigate of the South Carolina navy was captured by HMs Diomede (44), HMS Quebec (32), and HMS Astraea (32) on December 22, 1782.
- Ville de Paris (
 French Navy): The 90-gun first rate was captured in April by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 90-gun first rate was captured in April by the Royal Navy.
1783[]
- Concorde (
 French Navy): The Concorde-class frigate was captured on 15 February by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): The Concorde-class frigate was captured on 15 February by the Royal Navy's . - HMS Coventry (
 Royal Navy): The 28-gun sixth rate was captured on 12 January by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 28-gun sixth rate was captured on 12 January by the French Navy.
1788[]
- (
 Swedish Navy): The 62-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): The 62-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Hogland, 17 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Hogland, 17 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Imperial Russian Navy): Battle of Hogland, 17 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Swedish Navy.
Imperial Russian Navy): Battle of Hogland, 17 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Swedish Navy. - A 64-gun ship (
 Ottoman Navy) was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy and commissioned as .
Ottoman Navy) was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy and commissioned as .
1789[]
- Princess Royal (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured in March by the Spanish Navy.
Great Britain): The sloop was captured in March by the Spanish Navy.
1790[]
- (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 60-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Ottoman Navy): Battle of Tendra, 8–9 September: The 78-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Ottoman Navy): Battle of Tendra, 8–9 September: The 78-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Reval, 13 May: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Reval, 13 May: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 66-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 74-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy. - (
 Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
Swedish Navy): Battle of Vyborg Bay, 4 July: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Imperial Russian Navy.
1791–1800[]
1793[]
- Adamant (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Saint Vincent by a French ship and sent to Martinique.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Saint Vincent by a French ship and sent to Martinique.[6] - Adventure (
 Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston, South Carolina, United States.[7]
Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston, South Carolina, United States.[7] - Albemarle (
 ): The East India Company's merchant ship was captured in May by a French privateer.
): The East India Company's merchant ship was captured in May by a French privateer. - Alceste (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon 18 September – 18 December: The Magicienne-class frigate was seized by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon 18 September – 18 December: The Magicienne-class frigate was seized by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Alcide (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Alcide (
 Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Alert (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille, Var.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille, Var.[8] - Alerte (
 French Navy): The brig was captured on 28 August by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The brig was captured on 28 August by the Royal Navy. - HMS Alert (
 Royal Navy): The brig was burnt and scuttled on 18 December. She was salvaged by the French Navy on 28 December.
Royal Navy): The brig was burnt and scuttled on 18 December. She was salvaged by the French Navy on 28 December. - Alodia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by Little Democrat and sent to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.[9]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by Little Democrat and sent to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.[9] - Amelia (
 Great Britain) The ship was captured while on a voyage from Barbados to St. John's, Newfoundland, British North America.[10]
Great Britain) The ship was captured while on a voyage from Barbados to St. John's, Newfoundland, British North America.[10] - Amity (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Club.[11]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Club.[11] - Ant (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Club.[11]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Club.[11] - Beau (
 France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12]
France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12] - Britannia: (
 Great Britain): A French privateer captured Britannia in July as Britannia was returning from her first whaling voyage.[13]
Great Britain): A French privateer captured Britannia in July as Britannia was returning from her first whaling voyage.[13] - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken into New York, United States.[14]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken into New York, United States.[14] - Brutus (
 France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - Camilla (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer but was later recaptured by Harriot and Speightown (both
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer but was later recaptured by Harriot and Speightown (both  Great Britain), which were operating under letters of marque.[8]
Great Britain), which were operating under letters of marque.[8] - Centaure (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Centaure (
 Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Censeur (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Pégase-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Pégase-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Censeur (
 Great Britain): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Chandenque (
 France): The schooner was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The schooner was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - Chilcomb (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by the French vessel Carmagnole and sent to New York.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by the French vessel Carmagnole and sent to New York.[6] - Cléopâtre (
 French Navy): Action of 18 June 1793: The Venus-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe.
French Navy): Action of 18 June 1793: The Venus-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe. - Commerce (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Galathée and taken to Brest, Finistère[15]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Galathée and taken to Brest, Finistère[15] - Commerce de Marseille (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Océan-class ship of the line was seized on 29 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Océan-class ship of the line was seized on 29 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Coningham (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Baltimore, Maryland, United States.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Baltimore, Maryland, United States.[7] - Conquérant (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Citoyen-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Citoyen-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Conquérant (
 Great Britain): The Citoyen-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Citoyen-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Culloden (
 Great Britain): The ship was seized as a prize at Dunkerque, Nord, France.[16]
Great Britain): The ship was seized as a prize at Dunkerque, Nord, France.[16] - Custine (
 France): The privateer was captured in the English Channel by and sent to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[17]
France): The privateer was captured in the English Channel by and sent to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[17] - Delight (
 France): The ship was captured by Mary and sent to Liverpool, Lancashire, Kingdom of Great Britain.[11]
France): The ship was captured by Mary and sent to Liverpool, Lancashire, Kingdom of Great Britain.[11] - Delight (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer off Grenada.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer off Grenada.[6] - Destin (
 French Navy): The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Diligent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8] - Doi (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the and sent to New York, United States.[7]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the and sent to New York, United States.[7] - (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Druid (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship on 5 November and sent to Dunkerque, Nord.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship on 5 November and sent to Dunkerque, Nord.[7] - Entreprenant (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Entreprenant (
 Great Britain): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - (
 French Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe.
French Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe. - Esther and Kitty (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to Bergen, Norway.[14]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to Bergen, Norway.[14] - Fancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Republican in November and sent to Martinique.[18]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Republican in November and sent to Martinique.[18] - Favourite (
 Great Britain): The ship was seized as a prize at Ostend, West Flanders, France.[16]
Great Britain): The ship was seized as a prize at Ostend, West Flanders, France.[16] - Flora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship while on a voyage from Wilmington, Delaware, United States to Jamaica. She was ordered to Cape François but was subsequently recaptured by HMS Spitfire.[19]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship while on a voyage from Wilmington, Delaware, United States to Jamaica. She was ordered to Cape François but was subsequently recaptured by HMS Spitfire.[19] - Généreux (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Généreux (
 Great Britain): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - George (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8] - George and Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by and sent into New York, United States.[11]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by and sent into New York, United States.[11] - Golden Age (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent to Philadelphia.[6][10]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent to Philadelphia.[6][10] - Good Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to a Norwegian port.[20]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to a Norwegian port.[20] - Good Intent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to New York.[14]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to New York.[14] - Greenaway (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent into Cadiz, Spain.[21]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent into Cadiz, Spain.[21] - Greyhound (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica by a French privateer.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica by a French privateer.[6] - Guerrier (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Guerrier (
 Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Hardi (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 64-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 64-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Hardi (
 Great Britain): The 64-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The 64-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Harriot (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent into Charleston.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent into Charleston.[7] - Héros (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Heureux (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Heureux (
 Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French vessel Citizen Genet and sent to Philadelphia.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French vessel Citizen Genet and sent to Philadelphia.[6] - Impérieuse (
 French Navy): The Minerve-class frigate was captured on 11 October by the Spanish Navy's and the Royal Navy's HMS Captain (1787).
French Navy): The Minerve-class frigate was captured on 11 October by the Spanish Navy's and the Royal Navy's HMS Captain (1787). - Jupiter (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Reunion and sent to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime but foundered before she reached port.[9]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Reunion and sent to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime but foundered before she reached port.[9] - Kitty (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.[7] - La Constance (
 France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - Languedoc (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 80-gun ship was seized on 29 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 80-gun ship was seized on 29 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Languedoc (
 Great Britain): The 80-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The 80-gun ship was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - La St. Dominique (
 France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - L'Egalité (
 France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12]
France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12] - Le Maria (
 France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12]
France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic ocean off the coast of Africa by the British ship Hope.[12] - Les Deux Amis (
 France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - Le Triomphant (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 80-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 80-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - (
 Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was burnt in December at Toulon. She was later salvaged and repaired by the French Navy.
Great Britain): The 74-gun ship was burnt in December at Toulon. She was later salvaged and repaired by the French Navy. - Lillies (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate La Blonde and sent into Brest, Finistère.[9]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate La Blonde and sent into Brest, Finistère.[9] - L'Oiseul (
 France): The armed lugger was captured in the Bay of Biscay off Belle Île, Morbihan by Lottery (
France): The armed lugger was captured in the Bay of Biscay off Belle Île, Morbihan by Lottery ( Great Britain).[11]
Great Britain).[11] - Lutine (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Magicienne-class frigate was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Magicienne-class frigate was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Maria (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7] - Mercure (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Centaure-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Mercure (
 Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Centaure-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Millica (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Baltimore.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Sans Culotte and sent to Baltimore.[7] - Modeste (
 French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate on 17 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Bedford.
French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate on 17 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Bedford. - Morning Star (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by and sent to Charleston.[11]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by and sent to Charleston.[11] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the mouth of the and sent to New York.[6]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the mouth of the and sent to New York.[6] - Nautilus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8] - Pompée (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized on 20 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized on 20 August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Nestor (
 France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14]
France): The snow was captured in the Bengal River.[14] - Prince William Henry (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship in the West Indies.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship in the West Indies.[7] - Puissant (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Pégase-class ship of the line was surrendered on 29 August to the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Pégase-class ship of the line was surrendered on 29 August to the Royal Navy. - Queen (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship in the West Indies.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship in the West Indies.[7] - Reddington (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in November by the French privateer Industry and sent to a Virginian port.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in November by the French privateer Industry and sent to a Virginian port.[7] - Robert (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to New York.[14]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to New York.[14] - Rooksby (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent into Cadiz, Spain.[21]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the and sent into Cadiz, Spain.[21] - Saint Jacques (
 France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by HMS Squirrel.[20]
France): The full-rigged ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by HMS Squirrel.[20] - Sans Culotte (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Océan-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The Océan-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Sans Culotte (
 Great Britain): The Océan-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Océan-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Scipion (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Souverain (
 French Navy): The Souverain-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): The Souverain-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Souverain (
 Great Britain): The Souverain-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Souverain-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Sovereign (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7] - Suffisant (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: The 74-gun ship was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Swift (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French warships in the Grand Banks of Newfoundland and was sent into Brest.[19]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French warships in the Grand Banks of Newfoundland and was sent into Brest.[19] - HMS Thames (
 Royal Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 25 October by the French Navy's .
Royal Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 25 October by the French Navy's . - Themistocle (
 French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Toulon: Téméraire-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Three Brothers (
 France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by .[8]
France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by .[8] - Tonnant (
 French Navy): The Tonnant-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
French Navy): The Tonnant-class ship of the line was seized in August by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Tonnant (
 Great Britain): The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon.
Great Britain): The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured in December by the French with the breaking of the Siege of Toulon. - Traveller (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8] - Two Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to Charleston.[7] - Venus (
 France): The privateer schooner was captured by the Royal Navy, in the West Indies.
France): The privateer schooner was captured by the Royal Navy, in the West Indies. - Vrouw Angina (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to a Norwegian port.[20]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured by a French privateer and sent to a Norwegian port.[20] - Vrouw Elizabeth Judity (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to Amsterdam and taken to , Seine-Maritime, France.[14]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to Amsterdam and taken to , Seine-Maritime, France.[14] - Vulture (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to Stavanger, Norway.[14]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and taken to Stavanger, Norway.[14] - York (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean sea by a French ship and sent into Marseille.[8]
1794[]
- Achille (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Annibal-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Annibal-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Alceste (
 Sardinian Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 10 June by the French Navy's Boudeuse.
Sardinian Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 10 June by the French Navy's Boudeuse. - HMS Alexander (
 Royal Navy): Action of 6 November 1794: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Jean Bart.
Royal Navy): Action of 6 November 1794: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the French Navy's Jean Bart. - Alliance (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Jamaica.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Jamaica.[22] - América (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Leviathan.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Leviathan. - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Fraternité while on a voyage from Loverpool to Africa. She was taken to L'Orient, Morbihan, France.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Fraternité while on a voyage from Loverpool to Africa. She was taken to L'Orient, Morbihan, France.[22] - Apollo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to Lancaster, Lancashire. She was taken to a French port.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to Lancaster, Lancashire. She was taken to a French port.[23] - Ariadne (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French while on a voyage from London to Livorno. She was sent to Toulon, Var, France.[24]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French while on a voyage from London to Livorno. She was sent to Toulon, Var, France.[24] - Atalanta (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Jamaica.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Jamaica.[22] - Babet (
 French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The corvette was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Arethusa and HMS Melampus (1785).
French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The corvette was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Arethusa and HMS Melampus (1785). - Beaufoy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by the French and taken to a French port.[25]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by the French and taken to a French port.[25] - Bergen (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured by a French privateer off Cayenne, French Guiana while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Suriname.[23]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured by a French privateer off Cayenne, French Guiana while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Suriname.[23] - Betsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by a French privateer and ordered to Genoa.[18]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by a French privateer and ordered to Genoa.[18] - Betsey and Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands to Newfoundland, British North America.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands to Newfoundland, British North America.[26] - Biens Aimée (
 France): The ship was captured at Bengal, India.[27]
France): The ship was captured at Bengal, India.[27] - Bonetto (
 Archduchy of Austria): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent into Brest, Finistère, France.[28]
Archduchy of Austria): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent into Brest, Finistère, France.[28] - Buop-Succes (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Goa to Lisbon.[25]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Goa to Lisbon.[25] - Cæsar (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship of the line and was ordered into a French port but was wrecked on the French coast.[29]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French ship of the line and was ordered into a French port but was wrecked on the French coast.[29] - Caroline (
 United States): The ship was captured by HMS Brilliant and HMS Thetis and sent to The Downs.[29]
United States): The ship was captured by HMS Brilliant and HMS Thetis and sent to The Downs.[29] - Charming Kitty (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by a French frigate while on a voyage from Milford Haven, Pembrokeshire to Gibraltar.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by a French frigate while on a voyage from Milford Haven, Pembrokeshire to Gibraltar.[22] - Citoyen (
 France): The ship was captured off Pondicherry, India.[27]
France): The ship was captured off Pondicherry, India.[27] - Colonel (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by three French frigates while on a voyage from the Bahamas to Liverpool. She was taken to L'Orient.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by three French frigates while on a voyage from the Bahamas to Liverpool. She was taken to L'Orient.[23] - Commerce (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French vessel while on a voyage from Maryland to Amsterdam, Dutch Republic. She was sent in to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[27]
United States): The ship was captured by a French vessel while on a voyage from Maryland to Amsterdam, Dutch Republic. She was sent in to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[27] - Copenhagen (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Sans Culotte and sent to Martinique.[27]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Sans Culotte and sent to Martinique.[27] - Deux Frères (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Invincible.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Invincible. - De Vrouw Margaretha (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured and sunk by a French privateer while on a voyage from Groningen to London, Great Britain.[26]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured and sunk by a French privateer while on a voyage from Groningen to London, Great Britain.[26] - Diana (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the North Channel and was sunk.[25]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the North Channel and was sunk.[25] - Diligence (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Málaga, Spain to Cork.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Málaga, Spain to Cork.[22] - Dispatch (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey to Oporto, Portugal.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey to Oporto, Portugal.[26] - Dryades (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bridport, Dorset to Quebec, British North America. She was taken to Brest, France.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bridport, Dorset to Quebec, British North America. She was taken to Brest, France.[22] - (
 French Navy): Action of 5 May 1794: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Orpheus.
French Navy): Action of 5 May 1794: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Orpheus. - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire by a French brig cutter.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire by a French brig cutter.[23] - Engageante (
 French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Concorde.
French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Concorde. - (
 French Navy): The 15-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Iphigenia.
French Navy): The 15-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Iphigenia. - Favourite (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel while on a voyage from Limerick, Ireland to London. She was sent to Brest, Finistère, France.[30]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel while on a voyage from Limerick, Ireland to London. She was sent to Brest, Finistère, France.[30] - Fly (
 Great Britain) The ship was captured by a French warship and taken to Virginia, United States.[18]
Great Britain) The ship was captured by a French warship and taken to Virginia, United States.[18] - Fly (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to San Sebastián, Spain.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to San Sebastián, Spain.[26] - Freedom (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to San Sebastián, Spain.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to San Sebastián, Spain.[26] - Friends (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Mevagissey, Cornwall to Guernsey.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Mevagissey, Cornwall to Guernsey.[26] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea while on a voyage from Sunderland, County Durham to Ostend, West Flanders, France. She was sent to Dunquerque, Nord.[27]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea while on a voyage from Sunderland, County Durham to Ostend, West Flanders, France. She was sent to Dunquerque, Nord.[27] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dartmouth, Devon to Newfoundland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dartmouth, Devon to Newfoundland.[26] - George (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 1 January by a French frigate and sent to L'Orient, Morbihan.[27]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 1 January by a French frigate and sent to L'Orient, Morbihan.[27] - Good Intent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barcelona, Spain to London. She was taken to L'Orient.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barcelona, Spain to London. She was taken to L'Orient.[22] - Hannibal (
 Great Britain): The collier was captured on 14 December by the Minerve off "Ivica" while on a voyage from Liverpool to Naples. She was recaptured on 25 December by HMS Tartar and sent to Corsica.[31]
Great Britain): The collier was captured on 14 December by the Minerve off "Ivica" while on a voyage from Liverpool to Naples. She was recaptured on 25 December by HMS Tartar and sent to Corsica.[31] - Hero (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime.[18]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime.[18] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and later recaptured and sent to Bermuda.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and later recaptured and sent to Bermuda.[26] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Barbados on 9 November by the French privateer brig Le Peuple François while on a voyage from London to Grenada.[25]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Barbados on 9 November by the French privateer brig Le Peuple François while on a voyage from London to Grenada.[25] - Horwood (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Dublin, Ireland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Dublin, Ireland.[26] - Impétueux (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Russell.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Russell. - James (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and sunk while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Limerick, Ireland.[25]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and sunk while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Limerick, Ireland.[25] - James and Rebecca (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Saint Vincent to London.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Saint Vincent to London.[22] - Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Swansea, Glamorgan to Oporto.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Swansea, Glamorgan to Oporto.[26] - John and Margaret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 July off the Isle of Lewis while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Cork, Ireland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 July off the Isle of Lewis while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Cork, Ireland.[26] - Juffrouw Alida (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured on 19 December in the North Sea off Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain by a French ship. She was recaptured on 26 December by British fishermen.[24]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured on 19 December in the North Sea off Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain by a French ship. She was recaptured on 26 December by British fishermen.[24] - Krageror (
 Denmark): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to Rotterdam, Dutch Republic. She was sent to Brest, Finistère, France.[27]
Denmark): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to Rotterdam, Dutch Republic. She was sent to Brest, Finistère, France.[27] - Lady Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the North Sea off the Dogger Bank. She was subsequently recaptured by (
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the North Sea off the Dogger Bank. She was subsequently recaptured by ( Royal Navy).[25]
Royal Navy).[25] - Law-Sacramento (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon.[25]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon.[25] - Lewis (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cadiz to Newfoundland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cadiz to Newfoundland.[26] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Guernsey, Channel Islands to Limerick, Ireland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Guernsey, Channel Islands to Limerick, Ireland.[26] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dartmouth to Bilbao, Spain.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dartmouth to Bilbao, Spain.[26] - Mary Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 August in the Atlantic Ocean (49°30′N 12°40′W / 49.500°N 12.667°W) by the while on a voyage from tobago to London.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 August in the Atlantic Ocean (49°30′N 12°40′W / 49.500°N 12.667°W) by the while on a voyage from tobago to London.[23] - Mermaid (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent into Brest.[28]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French vessel and sent into Brest.[28] - Mignonne (
 French Navy: The 32-gun frigate was captured on 10 August by the Royal Navy.
French Navy: The 32-gun frigate was captured on 10 August by the Royal Navy. - Mentor (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea 20 leagues (60 nautical miles (110 km) off the British coast by the and sent to Mandahl, Norway.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea 20 leagues (60 nautical miles (110 km) off the British coast by the and sent to Mandahl, Norway.[26] - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Gibraltar to London.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Gibraltar to London.[22] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on 10 June while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to an African port. She was taken into Brest.[25]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on 10 June while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to an African port. She was taken into Brest.[25] - Minerve (
 French Navy: The 38-gun frigate was scuttled by the French at Saint-Florent, Corsica on 18 February. She was salvaged by the Royal Navy the next day and taken into service as HMS St Fiorenzo.
French Navy: The 38-gun frigate was scuttled by the French at Saint-Florent, Corsica on 18 February. She was salvaged by the Royal Navy the next day and taken into service as HMS St Fiorenzo. - Nelly (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Memel, East Prussia to the River Clyde. She was set afire and sunk.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Memel, East Prussia to the River Clyde. She was set afire and sunk.[23] - Northumberland (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Annibal-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Annibal-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Pomone (
 French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The 40-gun frigate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Action of 23 April 1794: The 40-gun frigate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, , Ireland.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, , Ireland.[26] - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Grenada.[26]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Grenada.[26] - Perseverance (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Turks Islands to New Brunswick, British North America. She was taken to Providence, Rhode Island, United States.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Turks Islands to New Brunswick, British North America. She was taken to Providence, Rhode Island, United States.[22] - Princess Royal (
 Great Britain): A French squadron captured the off the Bonny River between 23 and 29 December 1794.[32]
Great Britain): A French squadron captured the off the Bonny River between 23 and 29 December 1794.[32] - Ranger (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to London.[22]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to London.[22] - Rose (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 31 December by the French while on a voyage from Livorno to Leith, Lothian.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 31 December by the French while on a voyage from Livorno to Leith, Lothian.[33] - Sandown (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Gulf of Mexico (23°40′N 83°58′W / 23.667°N 83.967°Won 18 July by the French privateer Guillotine. She was subsequently recaptured by , which also captured the French privateer.[34]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Gulf of Mexico (23°40′N 83°58′W / 23.667°N 83.967°Won 18 July by the French privateer Guillotine. She was subsequently recaptured by , which also captured the French privateer.[34] - Sans Pareil (
 French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Majestic.
French Navy): Glorious First of June: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Majestic. - Severn (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to New York, United States. She was taken to Brest, France.[34]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to New York, United States. She was taken to Brest, France.[34] - Sybille (
 French Navy): The Hébé-class frigate was captured on 17 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Romney.
French Navy): The Hébé-class frigate was captured on 17 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Romney. - Révolutionnaire (
 French Navy): The Seine-class frigate was captured on 21 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Artois.
French Navy): The Seine-class frigate was captured on 21 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Artois. - Roman Emperor (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and taken to Guadeloupe.[27]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and taken to Guadeloupe.[27] - Sally (
 Great Britain): The ship was reported to have been captured then recaptured.[27]
Great Britain): The ship was reported to have been captured then recaptured.[27] - HMS Speedy (
 Royal Navy): The Speedy-class brig was captured on 9 June by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The Speedy-class brig was captured on 9 June by the French Navy. - Sans Culotte (
 France): The privateer was captured by and sent to Saint Kitts.[27]
France): The privateer was captured by and sent to Saint Kitts.[27] - St. Antonia (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon.[25]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon.[25] - (
 French Navy): The brig was captured on 12 January by the Royal Navy's [35]
French Navy): The brig was captured on 12 January by the Royal Navy's [35] - Susannah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in October and sunk while on a voyage from London to a Portuguese port.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in October and sunk while on a voyage from London to a Portuguese port.[36] - Le Venguer (
 France): The sloop was captured by the British Army at Saint-Pierre on 17 February 1794, during the Battle of Martinique.
France): The sloop was captured by the British Army at Saint-Pierre on 17 February 1794, during the Battle of Martinique. - Vrude (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Bilbao, Spain. She was taken into Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime.[28]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Bilbao, Spain. She was taken into Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime.[28] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire by a French brig cutter while on a voyage from Riga, Latvia to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[23]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire by a French brig cutter while on a voyage from Riga, Latvia to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[23]
1795[]
- Achilles (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France while on a voyage from St. Andero, Spain to London.[37]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France while on a voyage from St. Andero, Spain to London.[37] - Alexandre (
 French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy's and HMS Sans Pareil.
French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The 74-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy's and HMS Sans Pareil. - Alfred (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brutus Français while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was taken to Charleston, South Carolina, United States.[38]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brutus Français while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was taken to Charleston, South Carolina, United States.[38] - Alice (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to Liverpool, Lancashire. She subsequently foundered.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barbados to Liverpool, Lancashire. She subsequently foundered.[33] - Alliantie (
 Batavian Republic Navy): 22 August: The 36-gun frigate was captured by the Royal Navy off Eigerøya, Norway.
Batavian Republic Navy): 22 August: The 36-gun frigate was captured by the Royal Navy off Eigerøya, Norway. - Britainca (
 Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Waterford. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo.[39]
Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Waterford. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo.[39] - Britannia: (
 Great Britain): A French privateer captured Britannia as she was on her way to the Caribbean with a cargo of slaves from West Africa.[40]
Great Britain): A French privateer captured Britannia as she was on her way to the Caribbean with a cargo of slaves from West Africa.[40] - Ann(
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Cadiz, Spain.[41]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Cadiz, Spain.[41] - Anna (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Jamaica. She was recaptured by HMS Success (
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Jamaica. She was recaptured by HMS Success ( Royal Navy) and arrived safely at Jamaica.[42]
Royal Navy) and arrived safely at Jamaica.[42] - Anna (
 Denmark): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Hull, Yorkshire, Great Britain to Salerno, Kingdom of Naples.[43]
Denmark): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Hull, Yorkshire, Great Britain to Salerno, Kingdom of Naples.[43] - Argo (
 Sweden): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland, United States to a Portuguese port. She was taken to Toulon, Var, France.[36]
Sweden): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland, United States to a Portuguese port. She was taken to Toulon, Var, France.[36] - Ashley (
 United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent, Portugal on 23 September by the French and was sunk.[44]
United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent, Portugal on 23 September by the French and was sunk.[44] - Bacchus (
 France): The ship was captured by HMS Cleopatra). She was taken to Bermuda.[31]
France): The ship was captured by HMS Cleopatra). She was taken to Bermuda.[31] - HMS Berwick (
 Royal Navy): The third rate was captured on 7 March by the French Navy's , and Vestale.
Royal Navy): The third rate was captured on 7 March by the French Navy's , and Vestale. - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Charlestown, South Carolina, United States.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Charlestown, South Carolina, United States.[33] - Brutus (
 French Navy): The 10-gun brig was captured on 10 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Mermaid.
French Navy): The 10-gun brig was captured on 10 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Mermaid. - Ça Ira (
 French Navy): Naval Battle of Genoa, 14 August: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Agamemnon.
French Navy): Naval Battle of Genoa, 14 August: The 80-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Agamemnon. - HMS Censeur (
 Royal Navy): Action of 7 October 1795: The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): Action of 7 October 1795: The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured by the French Navy. - Censeur (
 French Navy): Naval Battle of Genoa, 14 August: The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Naval Battle of Genoa, 14 August: The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - HMS Censeur (
 Royal Navy): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured in October by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The Pégase-class ship of the line was captured in October by the French Navy. - Columbus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on 14 January while on a voyage from Cadiz, Spain to London. She was taken to a French port.[42]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on 14 January while on a voyage from Cadiz, Spain to London. She was taken to a French port.[42] - Concordia (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun brig-sloop was seized by the Royal Navy as a prize of war.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun brig-sloop was seized by the Royal Navy as a prize of war. - Dom Successo (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Oporto.[37]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Oporto.[37] - Dove (
 United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 29 September by the French and was sunk. She was on a voyage from Poole, Dorset to Faro, Portugal.[44]
United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 29 September by the French and was sunk. She was on a voyage from Poole, Dorset to Faro, Portugal.[44] - Dragon (
 France): The ship was captured by the British at La Plata, Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.[38]
France): The ship was captured by the British at La Plata, Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata.[38] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne while on a voyage from Trieste to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic.[37]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne while on a voyage from Trieste to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic.[37] - Drumiate (
 Kingdom of Sicily): The ship was captured by the French frigate Minerve while on a voyage from Sicily to London. She was taken to Toulon, Var.[42]
Kingdom of Sicily): The ship was captured by the French frigate Minerve while on a voyage from Sicily to London. She was taken to Toulon, Var.[42] - Eliza (
 France): The ship was captured by a British frigate while on a voyage from France to the United States. She was taken to the Bahamas.[42]
France): The ship was captured by a British frigate while on a voyage from France to the United States. She was taken to the Bahamas.[42] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured by a French privateer in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from Jamaica to St. Domingo.[42]
Great Britain): The sloop was captured by a French privateer in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from Jamaica to St. Domingo.[42] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and sunk while on a voyage from New York to London.[45]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and sunk while on a voyage from New York to London.[45] - Formidable (
 French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Frederick (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Gibraltar.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Gibraltar.[36] - George (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Domingo.[42]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Domingo.[42] - Helena (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in February by the French while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken to L'Orient.[38]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in February by the French while on a voyage from Saint Petersburg, Russia to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken to L'Orient.[38] - Hendrick (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Vigo, Spain by a French privateer and was taken to Bayonne, Loire-Atlantique, France.[46]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Vigo, Spain by a French privateer and was taken to Bayonne, Loire-Atlantique, France.[46] - Industry(
 France): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by HMS Southampton and taken to Livorno.[41]
France): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by HMS Southampton and taken to Livorno.[41] - Iphigénie (
 French Navy): The Iphigénie-class frigate was captured on 14 February by the Spanish Navy.
French Navy): The Iphigénie-class frigate was captured on 14 February by the Spanish Navy. - James (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia to Saint Thomas, Virgin Islands.[47]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia to Saint Thomas, Virgin Islands.[47] - Jean (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Glasgow, Renfrewshire. She was subsequently recaptured by her crew and arrived at Glasgow.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Glasgow, Renfrewshire. She was subsequently recaptured by her crew and arrived at Glasgow.[36] - John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barcelona, Spain to Liverpool. She was taken to Brest.[42]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Barcelona, Spain to Liverpool. She was taken to Brest.[42] - Joseph (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 March by the while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to London. She was recaptured by HMS Lively.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 March by the while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to London. She was recaptured by HMS Lively.[33] - Latitia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by a French privateer while on a voyage from "Zant" to London. She was taken to Livorno.[38]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by a French privateer while on a voyage from "Zant" to London. She was taken to Livorno.[38] - (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured by HMS Lively (
French Navy): The frigate was captured by HMS Lively ( Royal Navy) and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[37]
Royal Navy) and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[37] - (
 French Navy): The corvette was captured by a British squadron led by Admiral Warren.[44]
French Navy): The corvette was captured by a British squadron led by Admiral Warren.[44] - Little Ben (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to an African port.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to an African port.[36] - Liveley (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by the .[37]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by the .[37] - Lucy (
 Great Britain): The schooner was captured by the French in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from Jamaica to St. Domingo.[42]
Great Britain): The schooner was captured by the French in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from Jamaica to St. Domingo.[42] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Venice.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Venice.[36] - Minerve (
 French Navy): The 40-gun frigate was captured on 23 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dido and HMS Lowestoffe.
French Navy): The 40-gun frigate was captured on 23 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dido and HMS Lowestoffe. - Pomona (
 United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 26 September by the French.[44]
United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 26 September by the French.[44] - Mermaid (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Charleston.[48]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Charleston.[48] - Momus (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured by the French and sent to a French port.[42]
Great Britain): The sloop was captured by the French and sent to a French port.[42] - Monmouth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on or before 5 February.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French on or before 5 February.[36] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Liverpool, Lancashire. She subsequently foundered.[31]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Liverpool, Lancashire. She subsequently foundered.[31] - Nelly (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from San Domingo to Jamaica.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from San Domingo to Jamaica.[33] - Nostra Senora da Arrabida (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Bengal.[37]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Bengal.[37] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 22 October by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 22 October by the Royal Navy. - Phyn : The ship was captured off Cuba on 23 January by the French privateer General Laveaux. She was sent to Charleston, South Carolina, United States, arriving on 19 February.[48]

Pique and HMS Blanche.
- Pique (
 French Navy): The 38-gun fifth rate frigate was captured on 4 January by the Royal Navy's HMS Blanche.
French Navy): The 38-gun fifth rate frigate was captured on 4 January by the Royal Navy's HMS Blanche. - Pickmans (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36] - Pomona (
 United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 29 September by the French and was sunk.[44]
United Kingdom): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape St. Vincent on 29 September by the French and was sunk.[44] - Providence (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, France while on a voyage from.[37]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, France while on a voyage from.[37] - Queen (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 March by the French frigate Embuscade (1789) while on a voyage from Tenerife, Canary Islands to London.[48]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 March by the French frigate Embuscade (1789) while on a voyage from Tenerife, Canary Islands to London.[48] - Richard (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to L'Orient, Morbihan.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to L'Orient, Morbihan.[33] - Richard (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by six privateers while on a voyage from New Providence, New Jersey, United States to Liverpool. She was taken to a South Carolina port.[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by six privateers while on a voyage from New Providence, New Jersey, United States to Liverpool. She was taken to a South Carolina port.[33] - Rosamund (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Domingo.[42]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Domingo.[42] - Russia Merchant (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to the West Indies. She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to the West Indies. She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[36] - San Bernando (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Santander, Spain to Falmouth, Cornwall Kingdom of Great Britain. She was subsequently recaptured and arrived at Falmouth.[36]
Spain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Santander, Spain to Falmouth, Cornwall Kingdom of Great Britain. She was subsequently recaptured and arrived at Falmouth.[36] - Speedy (
 French Navy): The Speedy-class brig was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Inconstant.
French Navy): The Speedy-class brig was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Inconstant. - Sprightly (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured and sunk by the .[37]
Great Britain): The brig was captured and sunk by the .[37] - St. Antonion (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Bengal.[37]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Bengal.[37] - Susannah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Vigo, Spain.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Vigo, Spain.[36] - Talbot (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to the Barbary Coast.[37]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken into Bayonne while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to the Barbary Coast.[37] - Thames (
 United Kingdom): The ship was recaptured from the French by HMS Orion.[44]
United Kingdom): The ship was recaptured from the French by HMS Orion.[44] - Thomas (
 Great Britain): The schooner was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Grenada. She was taken to Brest.[48]
Great Britain): The schooner was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Grenada. She was taken to Brest.[48] - Tigre (
 French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Barfleur.
French Navy): Battle of Groix, 23 June: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Barfleur. - Unity (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Liverpool. She subsequently foundered.[31]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Liverpool. She subsequently foundered.[31] - Unity (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Southampton, Hampshire. She was taken to Brest.[31]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto to Southampton, Hampshire. She was taken to Brest.[31] - (
 French Navy): The corvette was captured in October in the Irish Sea by a British privateer. She subsequently foundered in a storm with the loss of all hands.[49]
French Navy): The corvette was captured in October in the Irish Sea by a British privateer. She subsequently foundered in a storm with the loss of all hands.[49] - Vrouw Magdalena (
 Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36]
Dutch Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French and taken to Ostend or Bruges.[36] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to the West Indies. She was later recaptured by .[33]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to the West Indies. She was later recaptured by .[33] - William and Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Barbados. She was taken to St. Croix.[36]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Barbados. She was taken to St. Croix.[36]
1796[]
- Adolph (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy while on a voyage from Amsterdam, Batavian Republic to Cadiz, Spain. She was taken to Sheerness, Kent.[50]
United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy while on a voyage from Amsterdam, Batavian Republic to Cadiz, Spain. She was taken to Sheerness, Kent.[50] - Amazon (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 29 December by a French squadron and sunk.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 29 December by a French squadron and sunk.[51] - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to Carthagena, Spain.
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to Carthagena, Spain. - Betsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken into Aux Cayes, Hispaniola.[52]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken into Aux Cayes, Hispaniola.[52] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Britainca (
 Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Waterford. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo.[39]
Great Britain): The snow was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Waterford. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo.[39] - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Faial, Portugal. She was taken into L'Orient, Seine-Maritime.[53]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Faial, Portugal. She was taken into L'Orient, Seine-Maritime.[53] - Diana (
 Portugal): The brig was captured in the English Channel off Falmouth, Cornwall by a French frigate. She was subsequently recaptured by HMS Hornet.[54]
Portugal): The brig was captured in the English Channel off Falmouth, Cornwall by a French frigate. She was subsequently recaptured by HMS Hornet.[54] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796,: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796,: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea while on a voyage from London to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to "Ferrajo".[55]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea while on a voyage from London to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to "Ferrajo".[55] - Eliza of Cornwall (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Dutch privateer. She was later recaptured by HMS Fox, which also captured the Dutch privateer.[54]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Dutch privateer. She was later recaptured by HMS Fox, which also captured the Dutch privateer.[54] - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by a French privateer and was taken into Gorée.[52]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by a French privateer and was taken into Gorée.[52] - Ferret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 31 January by the French privateer Carmagnole while on a voyage from Jamaica to Liverpool, Lancashire. She was taken to Havana, Cuba.[56]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 31 January by the French privateer Carmagnole while on a voyage from Jamaica to Liverpool, Lancashire. She was taken to Havana, Cuba.[56] - Fortitude (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Galatea and sent to Falmouth, Cornwall.[57]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Galatea and sent to Falmouth, Cornwall.[57] - Fortune (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dartmouth, Devon by a French privateer. She was set afire and sunk.[56]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dartmouth, Devon by a French privateer. She was set afire and sunk.[56] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon to an English port. She was taken to L'Orient, Charente-Maritime.[56]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon to an English port. She was taken to L'Orient, Charente-Maritime.[56] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer on 2 October while on a voyage from Weymouth, Dorset to London. She was later recaptured and taken to Portsmouth. The privateer was also captured.[58]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer on 2 October while on a voyage from Weymouth, Dorset to London. She was later recaptured and taken to Portsmouth. The privateer was also captured.[58] - Good Samaritan (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[59]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[59] - Governor Parr (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Nova Scotia, British North America.[53]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Nova Scotia, British North America.[53] - Harrison (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured off the Isle of Wight by a French privateer, but was subsequently recaptured and taken to Cowes.[58]
Great Britain): The brig was captured off the Isle of Wight by a French privateer, but was subsequently recaptured and taken to Cowes.[58] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was recaptured but was the captured again by the French.[60]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Windward Passage while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was recaptured but was the captured again by the French.[60] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Jamaica.[61]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Jamaica.[61] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Hirondelle.[59]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Hirondelle.[59] - James and Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bangor to London. She was taken to Fécamp, Seine-Maritime, France.[58]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bangor to London. She was taken to Fécamp, Seine-Maritime, France.[58] - James and William (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo and HMS Polyphemus.[39]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by a French schooner while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Apollo and HMS Polyphemus.[39] - Jengularre (
 France): The ship was captured by a Guernsey-based privateer and was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[52]
France): The ship was captured by a Guernsey-based privateer and was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[52] - John and Thomas (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Land's End, Cornwall by a French privateer on 30 September.[58]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Land's End, Cornwall by a French privateer on 30 September.[58] - Lavinia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Cork, Ireland. She was taken to L'Orient.[56]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Cork, Ireland. She was taken to L'Orient.[56] - Live Oak (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Hirondelle while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool.[59]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Hirondelle while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool.[59] - L'Unité (
 French Navy): The corvette was captured on 20 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Inconstant.
French Navy): The corvette was captured on 20 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Inconstant. - Margaret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Sémillante while on a voyage from Leith, Lothian to Lisbon, Portugal. She was set afire and sank.[56]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French frigate Sémillante while on a voyage from Leith, Lothian to Lisbon, Portugal. She was set afire and sank.[56] - Maria (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies. She was taken to Saint Martin.[50]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies. She was taken to Saint Martin.[50] - Martinico (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French while on a voyage from "Sassee" to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken to Salice, Corsica.[50]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French while on a voyage from "Sassee" to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken to Salice, Corsica.[50] - Mary Ann (
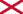 Ireland): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Dublin to Jamaica and was taken to Aux Cayes.[55]
Ireland): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Dublin to Jamaica and was taken to Aux Cayes.[55] - Mary Gracie (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[53]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[53] - Mentor (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by a French privateer and was taken into Gorée.[52]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa by a French privateer and was taken into Gorée.[52] - Nile (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from the to London. She was taken into Tunis, Beylik of Tunis.[50]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from the to London. She was taken into Tunis, Beylik of Tunis.[50] - Nostra Senora de Arabida (
 Portugal): The ship was captured in the Indian Ocean by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon. She was taken to Mauritius.[59]
Portugal): The ship was captured in the Indian Ocean by the French while on a voyage from Bengal to Lisbon. She was taken to Mauritius.[59] - Nostra Senora de Pedude de St. Antonio (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Rio de Janeiro to Oporto. She was taken to Vigo, Spain.[59]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Rio de Janeiro to Oporto. She was taken to Vigo, Spain.[59] - Pacific (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Galatea and sentto Falmouth, Cornwall.[62]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Galatea and sentto Falmouth, Cornwall.[62] - Proserpine (
 French Navy): The Hébé-class frigate was captured on 13 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dryad.
French Navy): The Hébé-class frigate was captured on 13 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Dryad. - Ranger (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Barbados by a French privateer.[54]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Barbados by a French privateer.[54] - Sireene (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The sloop was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The sloop was captured by the Royal Navy. - Tamise (
 French Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 8 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Santa Margarita.
French Navy): The Richmond-class frigate was captured on 8 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Santa Margarita. - Thomas and Ellen (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured on 18 March by a French privateer. She was recaptured the next day off Barfleur, Manche, France by the Royal Navy's HMS Druid and HMS Syren and taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[57]
Great Britain): The sloop was captured on 18 March by a French privateer. She was recaptured the next day off Barfleur, Manche, France by the Royal Navy's HMS Druid and HMS Syren and taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[57] - Thomas and Sarah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 22 April by the French privateer Adventure while on a voyage from Ancona, Kingdom of Sicily to an English port.[62]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 22 April by the French privateer Adventure while on a voyage from Ancona, Kingdom of Sicily to an English port.[62] - Three Sisters (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by a Dutch squadron.[53]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean by a Dutch squadron.[53] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): Capitulation of Saldanha Bay on 17 August 1796: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Unité (
 French Navy): The Charmante-class frigate was captured on 11 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Révolutionnaire.
French Navy): The Charmante-class frigate was captured on 11 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Révolutionnaire. - Unitey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer off the coast of Norway while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to the Firth of Forth. She was taken to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[59]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer off the coast of Norway while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to the Firth of Forth. She was taken to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[59] - Vine (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[61]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[61] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by a French privateer. and taken to Bergen, Norway.[52]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by a French privateer. and taken to Bergen, Norway.[52] - (
 Royal Netherlands Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 19 January by the Royal Navy.
Royal Netherlands Navy): The 64-gun ship was captured on 19 January by the Royal Navy.
1797[]
- (
 France): The chasse-marée was captured on 25 July by (
France): The chasse-marée was captured on 25 July by ( Great Britain).[63]
Great Britain).[63] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown 11 October: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown 11 October: The 68-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Ahoy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the West Indies She was later recaptured and taken to Tortola.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the West Indies She was later recaptured and taken to Tortola.[64] - Alegria (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Alert (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa.[39]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa.[39] - Alfred (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Irish Sea by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Limerick, Ireland.[39]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Irish Sea by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to Limerick, Ireland.[39] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Antigua (
 Great Britain): The sailing barge was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Vincent to London. She was taken in toe L'Orient, Seine-Maritime, France.[66]
Great Britain): The sailing barge was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Vincent to London. She was taken in toe L'Orient, Seine-Maritime, France.[66] - Atalante (
 French Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured on 10 January by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoebe.
French Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured on 10 January by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoebe. - Bea Fi (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Bernardo (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to Algeciras, Spain.[39]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken to Algeciras, Spain.[39] - Calypso (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate, set afire and sunk. She was on a voyage from Lisbon to London.[67]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French frigate, set afire and sunk. She was on a voyage from Lisbon to London.[67] - Carolina (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Draper (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by the French. She was on a voyage from Oporto to Dublin, Ireland.[67]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by the French. She was on a voyage from Oporto to Dublin, Ireland.[67] - Duke of Cumberland (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 6 November by Spanish Frigates. She was taken to the River Plata.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 6 November by Spanish Frigates. She was taken to the River Plata.[68] - Eliza (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off the coast of Lincolnshire by the French privateer Enterprize. She was subsequently released.[69]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off the coast of Lincolnshire by the French privateer Enterprize. She was subsequently released.[69] - Elizabeth and Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Irish Sea by the French while on a voyage from Limerick to London.[39]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Irish Sea by the French while on a voyage from Limerick to London.[39] - Enigheten (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Naples. She was taken to Genoa.[69]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Cornish port to Naples. She was taken to Genoa.[69] - (
 Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - Eider Stroman (
 France): The ship was captured in the English Channel by the British privateer Lottery while on a voyage from Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine. She was taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[66]
France): The ship was captured in the English Channel by the British privateer Lottery while on a voyage from Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine. She was taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[66] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia, United States to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Jago de Cuba.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia, United States to Jamaica. She was taken to St. Jago de Cuba.[64] - (
 Venetian Navy): The 66-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The 66-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - Fame (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to Oporto.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to Oporto.[64] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - George (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Martinique to London. She was taken to Curaçao.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Martinique to London. She was taken to Curaçao.[51] - (
 Venetian Navy): The ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The ship was captured by the French Navy. - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Hampshire (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 2 January by the French privateer Patriot while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 2 January by the French privateer Patriot while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[51] - Hercule (
 French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Mars.
French Navy): The 74-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Mars. - (
 Royal Navy): The 32-gun fifth rate was taken over by mutineers on 22 September and handed to the Spanish Navy five days later.
Royal Navy): The 32-gun fifth rate was taken over by mutineers on 22 September and handed to the Spanish Navy five days later. - Hero (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Liverpool. She was taken to Saint Croix.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Liverpool. She was taken to Saint Croix.[51] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[64] - Hopewell (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from London to Antigua. She was later retaken by her crew and arrived at Portsmouth, Hampshire. The privateer was captured and taken to Appledore, Devon.[66]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from London to Antigua. She was later retaken by her crew and arrived at Portsmouth, Hampshire. The privateer was captured and taken to Appledore, Devon.[66] - James (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Jamaica. She was taken to Saint Martin.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Jamaica. She was taken to Saint Martin.[51] - John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to a Cuban port.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to a Cuban port.[64] - Jonge Batavia (
 United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured by the Hired armed cutter Swan (
United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured by the Hired armed cutter Swan ( Royal Navy. She was taken to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[51]
Royal Navy. She was taken to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[51] - La Justine Adelaide (
 France): The privateer was captured in the English Channel off Fécamp, Seine-Maritime by the Royal Navy's . She was taken to Deal, Kent, Great Britain.[70]
France): The privateer was captured in the English Channel off Fécamp, Seine-Maritime by the Royal Navy's . She was taken to Deal, Kent, Great Britain.[70] - Kitty (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from an Indian port to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from an Indian port to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[64] - London Packet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Aberdeenshire on 11 September by the French privateer Jason. She was on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to Portsmouth.[66]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Aberdeenshire on 11 September by the French privateer Jason. She was on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to Portsmouth.[66] - Mansel (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Weymouth, Dorset to King's Lynn, Norfolk.[39]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Weymouth, Dorset to King's Lynn, Norfolk.[39] - Margaret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Liverpool. She was taken to St. Jago de Cuba.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Liverpool. She was taken to St. Jago de Cuba.[64] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the Atlantic Ocean off Charleston, South Carolina, United States while on a voyage from London to Savannah, Georgia. She was taken to Port-de-Paix, Hispaniola.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the Atlantic Ocean off Charleston, South Carolina, United States while on a voyage from London to Savannah, Georgia. She was taken to Port-de-Paix, Hispaniola.[64] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the West Indies while on a voyage from Demerara to Liverpool. She was later recaptured.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the West Indies while on a voyage from Demerara to Liverpool. She was later recaptured.[64] - (
 Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51] - Modena Delz (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Neptune (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by Forbes (
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by Forbes ( Great Britain while on a voyage from Surinam to Amsterdam. She was sent to Martinico.[39]
Great Britain while on a voyage from Surinam to Amsterdam. She was sent to Martinico.[39] - Néréide
 French Navy A Sybille class 36-gun, copper-hulled, frigate of the French Navy. Captured 22 December 1797 by HMS Phoebe.[71][72] [Note 1]
French Navy A Sybille class 36-gun, copper-hulled, frigate of the French Navy. Captured 22 December 1797 by HMS Phoebe.[71][72] [Note 1] - Oak (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to London. She was taken to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[69]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to London. She was taken to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[69] - Pallas (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Charleston while on a voyage from the Clyde to Charleston. She was taken to Port-aux-Paix.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Charleston while on a voyage from the Clyde to Charleston. She was taken to Port-aux-Paix.[64] - Patrouina (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to an American port. She was taken to Havana, Cuba.[64]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to an American port. She was taken to Havana, Cuba.[64] - Piodade (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Pomona (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Maryland to Saint Domingo She was taken into Léogâne, Hispaniola.[51]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Maryland to Saint Domingo She was taken into Léogâne, Hispaniola.[51] - Roa Nova (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Sally (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Guadeloupe.[69]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Guadeloupe.[69] - (
 Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - San Joaquim (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - San José (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February: The 114-gun first rate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February: The 114-gun first rate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain. - San Nicolás (
 Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February: The 80-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain.
Spanish Navy): Battle of Cape St Vincent, 14 February: The 80-gun third rate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain. - Santa Cruz (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - St. Nicholas (
 Spain): The ship was captured by a Royal Navy squadron under the command of Lord Hugh Seymour. She was taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[70]
Spain): The ship was captured by a Royal Navy squadron under the command of Lord Hugh Seymour. She was taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[70] - St. Teràza (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - Swallow (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by a French privateer. She was on a voyage from Barbados to Newfoundland, British North America.[67]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and sunk by a French privateer. She was on a voyage from Barbados to Newfoundland, British North America.[67] - Tartu (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured on 5 January by the Royal Navy's .
French Navy): The frigate was captured on 5 January by the Royal Navy's . - Tattler (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51] - Trinidade (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - (
 France): The 6-gun privateer schooner was captured on 2 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire.
France): The 6-gun privateer schooner was captured on 2 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. - Truenzo (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from a Brazilian port to Oporto.[65] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy.
Venetian Navy): The 70-gun ship was captured by the French Navy. - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Battle of Camperdown, 11 October: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Weston (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French.[51] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Martinique. She was taken to Cayenne, French Guiana.[51]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Martinique. She was taken to Cayenne, French Guiana.[51]
1798[]
- Alexander (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lancaster to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[73]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lancaster to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[73] - Alfred (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Liverpool, Lancashire She was taken to a French port.[74]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Liverpool, Lancashire She was taken to a French port.[74] - HMS Ambuscade (
 Royal Navy): Action of 14 December 1798: The 32-gun fifth-rate was captured by the French Navy's Bayonnaise.
Royal Navy): Action of 14 December 1798: The 32-gun fifth-rate was captured by the French Navy's Bayonnaise. - American Eagle (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London. She was taken to Saint-Martin, Île de Ré, Finistère, France.[68]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London. She was taken to Saint-Martin, Île de Ré, Finistère, France.[68] - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Filey, Yorkshire on 10 November by a French privateer.[74]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Filey, Yorkshire on 10 November by a French privateer.[74] - Apollo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was taken to a French port.[74]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was taken to a French port.[74] - Aquilon (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Brave (
 France): The privateer was captured on 24 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix.
France): The privateer was captured on 24 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix. - Aurora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Pillau, East Prussia. She was taken to Arendal, Norway.[75]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Pillau, East Prussia. She was taken to Arendal, Norway.[75] - Barbara (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[68] - Betsey (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to New York. She was later recaptured and taken to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[76]
Great Britain): The brig was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to New York. She was later recaptured and taken to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[76] - Betsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured of the coast of Africa on 3 June by the while on a voyage from Liverpool to an African port.[77]
Great Britain): The ship was captured of the coast of Africa on 3 June by the while on a voyage from Liverpool to an African port.[77] - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto. She was on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Oporto.[78]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto. She was on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Oporto.[78] - HMS Charlotte (
 Royal Navy): The 8-gun schooner was captured on 16 October by the French privateer Enfant Prodigue.
Royal Navy): The 8-gun schooner was captured on 16 October by the French privateer Enfant Prodigue. - Clermont (
 Great Britain): Captured by a French privateer. She was recaptured by Brooks, a British slave ship.
Great Britain): Captured by a French privateer. She was recaptured by Brooks, a British slave ship. - Columbus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Antoinette while on a voyage from New York, United States to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic. She was taken to La Rochelle, Charente-Maritime, France.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Antoinette while on a voyage from New York, United States to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic. She was taken to La Rochelle, Charente-Maritime, France.[68] - Conquérant (
 French Navy):Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Citoyen-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Audacious.
French Navy):Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Citoyen-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Audacious. - HMS Crash (
 Royal Navy): The gun-brig ran aground at Vlieland, Netherlands and was seized by the Dutch as a prize of war.
Royal Navy): The gun-brig ran aground at Vlieland, Netherlands and was seized by the Dutch as a prize of war. - Croyable (
 French Navy): A French privateer captured by Stephen Decatur commander of Delaware, off , New Jersey, 7 July 1798.
French Navy): A French privateer captured by Stephen Decatur commander of Delaware, off , New Jersey, 7 July 1798. - Dart (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto, Portugal.[78]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto, Portugal.[78] - Dione (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French privateer Racoon. She was later recaptured by HMS Pigmy and taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[79]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French privateer Racoon. She was later recaptured by HMS Pigmy and taken to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[79] - Décade (
 French Navy): The 36-gun fifth rate was captured on 24 August by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 36-gun fifth rate was captured on 24 August by the Royal Navy. - Dorothea Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Severn while on a voyage from Saint-Thomas, Virgin Islands to Havana, Cuba. She was taken to Môle-Saint-Nicolas, Hispaniola.
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French ship Severn while on a voyage from Saint-Thomas, Virgin Islands to Havana, Cuba. She was taken to Môle-Saint-Nicolas, Hispaniola. - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, Hampshire to "Tentris". She was taken to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine.[73]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, Hampshire to "Tentris". She was taken to Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine.[73] - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland to a British port. She was later recaptured and taken to Dartmouth, Devon.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland to a British port. She was later recaptured and taken to Dartmouth, Devon.[79] - Entreprenante (
 French Navy): The 10-gun cutter was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 10-gun cutter was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the Royal Navy. - Flora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico to Dublin, Ireland. She was later recaptured and taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[76]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico to Dublin, Ireland. She was later recaptured and taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[76] - Franklin (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Freedom (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Dragon while on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to London. She was taken to Bergen, Norway.[74]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Dragon while on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to London. She was taken to Bergen, Norway.[74] - Fulminante (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Espoir.
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Espoir.

Capture of Furie and Waakzaamheid
- Furie (
 United Netherlands Navy): Action of 24 October 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius (1797).
United Netherlands Navy): Action of 24 October 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius (1797). - Gantil (
 France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68]
France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68] - General Gray (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the South Seas to London. She was taken to a French port.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the South Seas to London. She was taken to a French port.[68] - Good Intent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from London to Galway, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the American privateer Atlantic.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from London to Galway, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the American privateer Atlantic.[79] - Guerrier (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Magnifique-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy and was burnt as she was too severely damaged to be of use.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Magnifique-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy and was burnt as she was too severely damaged to be of use. - Hercule (
 French Navy): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured on 21 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Mars.
French Navy): The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured on 21 April by the Royal Navy's HMS Mars. - Hoche (
 French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Immortalité (
 French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Romaine-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Fisgard.
French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Romaine-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Fisgard. - Jamaica (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer. She was later retaken by her crew and taken to St. Domingo.[80]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer. She was later retaken by her crew and taken to St. Domingo.[80] - Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was taken to a French port.[74]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was taken to a French port.[74] - Jean (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Virginia, United States. She was taken to Puerto Rico.[75]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to Virginia, United States. She was taken to Puerto Rico.[75] - Kelper (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was taken to Vlissingen, Zeeland, Batavian Republic.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was taken to Vlissingen, Zeeland, Batavian Republic.[68] - Lark (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Racoon. She was later recaptured by HMS Pigmy and taken to Portsmouth.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Racoon. She was later recaptured by HMS Pigmy and taken to Portsmouth.[79] - HMS Leander(
 Royal Navy): Action of 18 August 1798: The fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Le Genereux.
Royal Navy): Action of 18 August 1798: The fourth rate was captured by the French Navy's Le Genereux. - Le Brave (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix. She was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[81]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix. She was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[81] - L'Invincible General Bonaparte (
 France): The 20-gun privateer was captured on 9 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Boadicea.
France): The 20-gun privateer was captured on 9 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Boadicea. - Loire (
 French Navy): The 44-gun frigate was captured on 18 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Anson and HMS Kangaroo.
French Navy): The 44-gun frigate was captured on 18 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Anson and HMS Kangaroo. - Lydia (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to "Hambro'". She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[68]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to "Hambro'". She was taken to Brest, Finistère, France.[68] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to the West Indies. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[79] - Mercure (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile: The Séduisant-class ship of the line ran aground and was captured on 1 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Alexander. She was set afire and burnt.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile: The Séduisant-class ship of the line ran aground and was captured on 1 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Alexander. She was set afire and burnt. - HMS Musquito (
 Royal Navy): The ship-sloop was captured in September at Puerto Padre, Cuba, by three Spanish frigates.
Royal Navy): The ship-sloop was captured in September at Puerto Padre, Cuba, by three Spanish frigates. - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to the West Indies. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Alarm.[77]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to the West Indies. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Alarm.[77] - Nanine (
 France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68]
France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68] - Neutrality (
 Great Britain): the ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland, United States to Bremen. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Dispatch and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[81]
Great Britain): the ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland, United States to Bremen. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Dispatch and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[81] - Ocean (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Bengal to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[76]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Bengal to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[76] - Peep of Day (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto.[78]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto.[78] - Peuple Souverain (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Souverain-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Souverain-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Phillippa (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto.[78]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer off Oporto.[78] - Pigou (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States to China. She was taken to Nantes, Loire-Atlantique, France.[79]
United States): The ship was captured by a French frigate while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States to China. She was taken to Nantes, Loire-Atlantique, France.[79] - Poplar (
 Great Britain): the ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Martinico. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[81]
Great Britain): the ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Martinico. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[81] - Prince of Wales (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (47°40′N 18°00′W / 47.667°N 18.000°W) on 11 October by the French privateer La Confiance while on a voyage from Bristol to the West Indies. She was recaptured later that day by the British privateer King Pepple and taken to King's Road.[82]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (47°40′N 18°00′W / 47.667°N 18.000°W) on 11 October by the French privateer La Confiance while on a voyage from Bristol to the West Indies. She was recaptured later that day by the British privateer King Pepple and taken to King's Road.[82] - Quaker (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to Jamaica. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to Jamaica. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[68] - Racoon (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Pigmy. She was taken to Portsmouth.[79]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Pigmy. She was taken to Portsmouth.[79] - (
 French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Iphigénie-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Melampus.
French Navy): Battle of Tory Island, 12 October: The Iphigénie-class frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Melampus. - Resource (
 France): The brig, a privateer, was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Phaeton and HMS Stag (1794).[83]
France): The brig, a privateer, was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Phaeton and HMS Stag (1794).[83] - Sally (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Puerto Rico. She was later burnt.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken to Puerto Rico. She was later burnt.[68] - Maltese ship San Giovanni (
 Maltese Navy): The 64-gun third rate was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy.
Maltese Navy): The 64-gun third rate was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy. - Santa Dorotea (
 Spanish Navy): Action of 15 July 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Lion.
Spanish Navy): Action of 15 July 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Lion. - San Zaccharia (
 Maltese Navy): Mediterranean campaign of 1798: The 64-gun ship was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy.
Maltese Navy): Mediterranean campaign of 1798: The 64-gun ship was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy.

HMS Jason capturing the Seine.
- Sante Elisabeth (
 Maltese Navy): The 32-gun frigate was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy.
Maltese Navy): The 32-gun frigate was surrendered on 11 June to the French Navy. - Seine (
 French Navy): The Seine-class frigate was captured on 30 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Jason and HMS Pique.
French Navy): The Seine-class frigate was captured on 30 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Jason and HMS Pique. - Sophie (
 France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68]
France): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution.[68] - Spartiate (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - St. Johannes (
 United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Boston, Massachusetts to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily.[77]
United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Boston, Massachusetts to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily.[77] - Superb (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to London. She was taken to Bayonne, Ille-et-Vilaine.[68]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to London. She was taken to Bayonne, Ille-et-Vilaine.[68] - Surprize (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 December by a French privateer.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 December by a French privateer.[79] - Swallow (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon to Newfoundland.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon to Newfoundland.[79] - Three Friends (flag unknown): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Havana, Cuba to Hambro'. She was taken to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[76]
- Tonnant (
 French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Nile, 1–3 August: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Torride (
 French Navy): The aviso was captured at Abukir on 25 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Goliath.
French Navy): The aviso was captured at Abukir on 25 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Goliath. - Ultima Sperranza (
 Grand Duchy of Tuscany): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from India to Livorno. She was taken to Algeciras, Spain.[76]
Grand Duchy of Tuscany): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from India to Livorno. She was taken to Algeciras, Spain.[76] - Vaillante (
 French Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 7 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Indefatigable.
French Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 7 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Indefatigable. - Vine (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was later recaptured by the British privateer Marquis of Townsend and taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[77]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Virginia, United States to London. She was later recaptured by the British privateer Marquis of Townsend and taken to Jersey, Channel Islands.[77] - Venus (
 Great Britain): the ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to Saint Thomas, Virgin Isles. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[81]
Great Britain): the ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to Saint Thomas, Virgin Isles. She was taken to a Puerto Rican port.[81] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Action of 24 October 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius.[84]
United Netherlands Navy): Action of 24 October 1798: The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius.[84] - William and John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to a Hispaniolan port.[76]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Jamaica. She was taken to a Hispaniolan port.[76] - William and Thomas (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Clyde to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[73]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Clyde to Savannah, Georgia, United States. She was taken to Guadeloupe.[73]
1799[]
- Abigail (
 United States): The ship was captured on 15 October by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from a Virginian port to Bremen. She was recaptured on 20 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton and sent in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[85]
United States): The ship was captured on 15 October by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from a Virginian port to Bremen. She was recaptured on 20 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton and sent in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[85] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London.[87] - Admiraal de Ruyter (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel, North Holland by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel, North Holland by the Royal Navy.[88] - (
 Spanish Navy): The 14-gun xebec was captured on 22 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Espoir.[88]
Spanish Navy): The 14-gun xebec was captured on 22 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Espoir.[88] - Alarm (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Alceste (
 French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 18 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Bellona.
French Navy): The Magicienne-class frigate was captured on 18 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Bellona. - Alerte (
 French Navy): The brig was captured on 17 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain.
French Navy): The brig was captured on 17 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Captain. - Ambuscade (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 32-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 32-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - Amphitrite (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - Anacréon (
 France): The privateer brig was captured on 26 June by the Royal Navy's .
France): The privateer brig was captured on 26 June by the Royal Navy's . - Anna Maria (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Altona to Saint-Thomas, Virgin Islands. She was taken to Tenerife, Spain.[89]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Altona to Saint-Thomas, Virgin Islands. She was taken to Tenerife, Spain.[89] - Aréthuse (
 French Navy): The corvette was captured on 10 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Excellent.
French Navy): The corvette was captured on 10 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Excellent. - Astrea (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 November by the French privateer Scipio. She was recaptured on 10 November by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe.[90]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 November by the French privateer Scipio. She was recaptured on 10 November by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe.[90] - Atlas (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Genoa to Liverpool. Lancashire. She was taken in to , Spain.[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Genoa to Liverpool. Lancashire. She was taken in to , Spain.[91] - Aurora (
 United States): The ship was captured in the by a French privateer.[92]
United States): The ship was captured in the by a French privateer.[92] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Belle Antoinette (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Bonafide (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the English Channel. She was taken into Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French in the English Channel. She was taken into Saint-Malo, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[93] - Brabant (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques.[85]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques.[85] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 54-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Calcutta (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 6 December by the French Navy's and . She was recaptured later that day by the Royal Navy's .[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 6 December by the French Navy's and . She was recaptured later that day by the Royal Navy's .[87] - Catherina (
 Hamburg): The brig was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured on 24 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
Hamburg): The brig was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured on 24 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - HNLMS Cerberus (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident 30 August: The 64-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Charles (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France.[95] - Chateau Margo (
 Portugal): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Oporto to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured and taken in to Lisbon.[93]
Portugal): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Oporto to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured and taken in to Lisbon.[93] - Cleopatra (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[85]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[85] - Concord (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92] - Constitution (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Crash (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's and .
United Netherlands Navy): The 16-gun brig-sloop was captured by the Royal Navy's and . - Columbus (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95] - Commerce (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured on 27 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured on 27 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - Courier (
 France): The ship was captured in March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Zealous.[88]
France): The ship was captured in March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Zealous.[88] - Creeping Kate (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Jamaica to Cork. She was taken in to a Cuban port.[90]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Jamaica to Cork. She was taken in to a Cuban port.[90] - De Draak (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 24-gun ship was captured on 12 September in the North Sea off Texel, North Holland by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 24-gun ship was captured on 12 September in the North Sea off Texel, North Holland by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88] - Delaware (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to . She was taken in to .[93]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to . She was taken in to .[93] - Delight (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from London to Peterhead, Aberdeenshire. She was taken in to Arendal, Norway.[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from London to Peterhead, Aberdeenshire. She was taken in to Arendal, Norway.[91] - Diussee (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Dolphin (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 15 September in the North Sea off Vlieland, Friesland by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 15 September in the North Sea off Vlieland, Friesland by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88] - Dragon (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Dreighorlahn (
 Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Duchess of Gordon (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto by the French privateer Le Deuble a Quatee while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Oporto. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[96][97][98] She was recaptured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto by the French privateer Le Deuble a Quatee while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Oporto. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[96][97][98] She was recaptured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - Duncombe (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was taken in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[87][99]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was taken in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[87][99] - Eagle (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was taken in to St. Ubes.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was taken in to St. Ubes.[87] - Echo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 April by a French privateer while on a voyage from Poole to Newfoundland, British North America. She was subsequently recaptured by Mate (
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 8 April by a French privateer while on a voyage from Poole to Newfoundland, British North America. She was subsequently recaptured by Mate ( Great Britain and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[100]
Great Britain and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[100] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was later recaptured and sent in to Plymouth.[85]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was later recaptured and sent in to Plymouth.[85] - El Vincejo (
 Spanish Navy): captured this 18-gun ship on 19 March;[88] the Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Vincejo.
Spanish Navy): captured this 18-gun ship on 19 March;[88] the Royal Navy took her into service as HMS Vincejo. - Eenroon (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured, by the Royal Navy's HMS Brilliant and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured, by the Royal Navy's HMS Brilliant and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Expedition (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Favourite (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from St. Michael's Mount, Cornwall to London. She was recaptured by a Jersey privateer and sent in to St. Ives, Cornwall.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from St. Michael's Mount, Cornwall to London. She was recaptured by a Jersey privateer and sent in to St. Ives, Cornwall.[87] - Felicidad (
 Spain): The privateer was captured on 24 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
Spain): The privateer was captured on 24 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - Ferret (
 France): The privateer was captured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Viper. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[101]
France): The privateer was captured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Viper. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[101] - Flora (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Belfast, Ireland. She was taken into Calais, France.[93]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Belfast, Ireland. She was taken into Calais, France.[93] - Flora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Dublin, Ireland to Oporto, Portugal.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Dublin, Ireland to Oporto, Portugal.[87] - Follock (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]

HMS Sybille and the French frigate Forte.
- Forte (
 French Navy): The Forte-class frigate was captured on 1 March off the coast of Bengal by the Royal Navy's HMS Sybille.
French Navy): The Forte-class frigate was captured on 1 March off the coast of Bengal by the Royal Navy's HMS Sybille. - (
 Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy.
Royal Navy): The 18-gun sloop was captured by the French Navy. - Fortune (
 France): The ship was captured by the British Revenue Cutter (
France): The ship was captured by the British Revenue Cutter ( Great Britain).[95]
Great Britain).[95] - Foudroyant (
 France): The privateer was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (48°30′N 15°00′W / 48.500°N 15.000°W) by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix. She was taken to Cork, Ireland.[102]
France): The privateer was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (48°30′N 15°00′W / 48.500°N 15.000°W) by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix. She was taken to Cork, Ireland.[102] - Fox (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 April by the French privateer Courageux while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to Bilbao, Spain.[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 April by the French privateer Courageux while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to Bilbao, Spain.[91] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Saint-Malo.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Saint-Malo.[93] - Galathea (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 16-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 16-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - Geir (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 12 September in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 12 September in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrow and HMS Wolverine.[88] - Gelderland (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - General Prescot (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus but four Spanish Navy frigates recaptured her again. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[103]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus but four Spanish Navy frigates recaptured her again. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[103] - Golondrina (
 Spain): The 14-gun packet ship was captured on 24 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Mermaid and HMS Sylph.[88]
Spain): The 14-gun packet ship was captured on 24 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Mermaid and HMS Sylph.[88] - Good Union (
 Great Britain): The privateer was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French. She was taken in to Toulon, Var, France.[93]
Great Britain): The privateer was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by the French. She was taken in to Toulon, Var, France.[93] - Harlequin (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 28 October while on a voyage from Liverpool to Martinico.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 28 October while on a voyage from Liverpool to Martinico.[92] - Harriet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to Africa. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst and sent in to Cork, Ireland.[88]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to Africa. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst and sent in to Cork, Ireland.[88] - Hanover (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Venice to and English port. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[103]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Venice to and English port. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[103] - Harmony (
 United States): The ship was captured on 22 December by the French while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[104]
United States): The ship was captured on 22 December by the French while on a voyage from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[104] - Hazard (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Paimpol, Finistère, France.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Paimpol, Finistère, France.[93] - Hazard (
 United States): The ship was captured, bit was later recaptured by the British ship Mona.[92]
United States): The ship was captured, bit was later recaptured by the British ship Mona.[92] - Hector (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Helder (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 32-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 32-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Herel (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[93] - Hero (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Mercury and HMS Venerable.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Mercury and HMS Venerable.[87] - Heron (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Hevle Reill (
 Denmark): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was taken in to Kinsale, County Cork, Ireland.[92]
Denmark): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was taken in to Kinsale, County Cork, Ireland.[92] - Hirondelle (
 France): The privateer was captured in March in the English Channel 9 leagues (27 nautical miles (50 km) north west of the Île de Batz, Finistère by the Royal Navy's HM hired brig Telegraph.[88]
France): The privateer was captured in March in the English Channel 9 leagues (27 nautical miles (50 km) north west of the Île de Batz, Finistère by the Royal Navy's HM hired brig Telegraph.[88] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London.[87] - Howda (
 Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Hunter (
 France): The privateer schooner was captured by the Royal Navy, in the West Indies.
France): The privateer schooner was captured by the Royal Navy, in the West Indies. - Hussard (
 France): The corvette was captured on 20 August in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy.
France): The corvette was captured on 20 August in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy. - Infanta Amelia (
 Spanish Navy): The 12-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 6 August in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo.
Spanish Navy): The 12-gun sloop-of-war was captured on 6 August in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo. - Johanna (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95] - John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Great Yarmouth, Norfolk to Poole, Dorset. She was taken in to Boulogne.[100]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Great Yarmouth, Norfolk to Poole, Dorset. She was taken in to Boulogne.[100] - John (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto, Portsmouth to Newfoundland, British North America. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques.[105]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Oporto, Portsmouth to Newfoundland, British North America. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Pyrénées-Atlantiques.[105] - John and Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dungarvan, County Waterford, Ireland to Poole, Dorset.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Dungarvan, County Waterford, Ireland to Poole, Dorset.[93] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): The cutter was captured on 20 August in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): The cutter was captured on 20 August in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy. - Alerte (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88] - Courageuse (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88] - La Dame de Grace (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - La Dangereuse (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - La Fondre (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88] - (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 18 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy.[88] - La Maria Rose (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - La Négresse (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - Résolue (
 France): The privateer was captured on 31 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[93]
France): The privateer was captured on 31 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[93] - (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 20 August in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde.[88]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 20 August in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde.[88] - Layr (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Boulogne, Pas-de-Calais, France.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was sent in to Boulogne, Pas-de-Calais, France.[93] - Leander (
 French Navy): The fourth rate was captured on 3 March by Turko-Russian forces at Corfu and returned to the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The fourth rate was captured on 3 March by Turko-Russian forces at Corfu and returned to the Royal Navy. - Le Bordeloes (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Révolutionnaire. She was taken in to Plymouth.[85]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Révolutionnaire. She was taken in to Plymouth.[85] - Le Grand Feraillard (
 France): The privateer was captured on 11 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoebe.[106]
France): The privateer was captured on 11 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoebe.[106] - L'Épervier (
 France): The ship was captured in March by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus.[88]
France): The ship was captured in March by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus.[88] - Les Deux Frères (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - L'Espérance (
 France): The privateer was captured on 22 December in the Atlantic Ocean off Viana do Castelo, Portugal by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
France): The privateer was captured on 22 December in the Atlantic Ocean off Viana do Castelo, Portugal by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - Le St. Jacques (
 France): The ship was captured on 13 September in the English Channel off L'Orient, Ille-et-Vilaine by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton.[88]
France): The ship was captured on 13 September in the English Channel off L'Orient, Ille-et-Vilaine by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton.[88] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 64-gun floating battery was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 64-gun floating battery was captured by the Royal Navy. - Liguria (
 Genoa): The ship was captured on 7 August in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's .[88]
Genoa): The ship was captured on 7 August in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's .[88] - L'Insurgente
 French Navy Captured by USS Constellation 9 February 1799.[107]
French Navy Captured by USS Constellation 9 February 1799.[107] - Lion (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French She was sent into Boulogne.[93]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French She was sent into Boulogne.[93] - Liveley (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 9 November by a Spanish privateer off the coast of Berbice while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 9 November by a Spanish privateer off the coast of Berbice while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies.[92] - Lydia (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was subsequently wrecked on The Olives rocks.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was subsequently wrecked on The Olives rocks.[95] - Lynx (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured on 9 October in the Ems by the Royal Navy's HMS Circe and HMS Hawke.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured on 9 October in the Ems by the Royal Navy's HMS Circe and HMS Hawke.[88] - Margaret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to a Portuguese port.[95]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to a Portuguese port.[95] - Marianne (
 France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88]
France): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's ).[88] - Mars (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 44-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from the Clyde to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was taken in to the Passage Islands.[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from the Clyde to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was taken in to the Passage Islands.[91] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Texel, North Holland, Batavian Republic. She was taken in to Calais.
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Texel, North Holland, Batavian Republic. She was taken in to Calais. - Mary Campbell (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from the Clyde to New Providence, New Jersey, United States. She was taken in to the Passage Islands.[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from the Clyde to New Providence, New Jersey, United States. She was taken in to the Passage Islands.[91] - Matilda (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92] - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Tortola. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Pomone and taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Tortola. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Pomone and taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[93] - Minerva (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to New Providence, New Jersey, United States. She was taken in to a Puerto Rican port.[103]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to New Providence, New Jersey, United States. She was taken in to a Puerto Rican port.[103] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Dingle, County Cork, Ireland to Lisbon, Portugal. She was later recaptured and arrived at Dingle.[87]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Dingle, County Cork, Ireland to Lisbon, Portugal. She was later recaptured and arrived at Dingle.[87] - Nostra Señora de la Soledade (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon.
Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon. - Pallas (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95] - Patrick (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the French on 12 January while on a voyage from Dublin to Oporto She was set afire and sunk.[100]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the French on 12 January while on a voyage from Dublin to Oporto She was set afire and sunk.[100] - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Dublin, Ireland. She was taken in to "Camarines".[91]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Dublin, Ireland. She was taken in to "Camarines".[91] - Pelican (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French on 30 January in the English Channel off Start Point, Devon. She was recaptured on 3 February by the Royal Navy's hired armed cutter King George and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[108]
Great Britain): The brig was captured by the French on 30 January in the English Channel off Start Point, Devon. She was recaptured on 3 February by the Royal Navy's hired armed cutter King George and taken to Plymouth, Devon.[108] - HMS Penelope (
 Royal Navy): The 18-gun ship was captured on 7 July by the Spanish Navy's .[88]
Royal Navy): The 18-gun ship was captured on 7 July by the Spanish Navy's .[88] - Perseus (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured on 9 October in the Ems by the Royal Navy's HMS Circe and HMS Hawke.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured on 9 October in the Ems by the Royal Navy's HMS Circe and HMS Hawke.[88] - Phoenix (
 Spanish Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured in July in the West Indies by the Royal Navy's .[88]
Spanish Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured in July in the West Indies by the Royal Navy's .[88] - Plumper (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92] - Polly (
 Ireland): The sloop was captured by the French. She was sent into Port-Blanc, Côtes-du-Nord, France.[93]
Ireland): The sloop was captured by the French. She was sent into Port-Blanc, Côtes-du-Nord, France.[93] - Polly (
 United States): The brig was captured on 16 October off A Coruña, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton while on a voyage from Marblehead, Massachusetts to Bilbao, Spain. She was taken in to Plymouth.[85]
United States): The brig was captured on 16 October off A Coruña, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Triton while on a voyage from Marblehead, Massachusetts to Bilbao, Spain. She was taken in to Plymouth.[85] - Princess Amelia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 20 January by the French privateer Spartiate. She was set afire and sunk.[95]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 20 January by the French privateer Spartiate. She was set afire and sunk.[95] - Princess Royal (
 Great Britain): The French privateer Malartic captured Princess Royal in October or November 1799 off the coast of Sumatra.
Great Britain): The French privateer Malartic captured Princess Royal in October or November 1799 off the coast of Sumatra. - Prudente (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured on 9 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Daedalus.
French Navy): The frigate was captured on 9 February by the Royal Navy's HMS Daedalus. - Rebecca (
 France): The privateer was captured on 27 April in the Atlantic Ocean 20 leagues (60 nautical miles (110 km) west of Ouessant, Finistère by the Royal Navy's Hired armed cutter Black Joke.[88]
France): The privateer was captured on 27 April in the Atlantic Ocean 20 leagues (60 nautical miles (110 km) west of Ouessant, Finistère by the Royal Navy's Hired armed cutter Black Joke.[88] - (
 French Navy): The felucca was captured on 26 June in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy.[88]
French Navy): The felucca was captured on 26 June in the Atlantic Ocean off Surinam by the Royal Navy.[88] - (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Cayenne, French Guiana to Surinam.[109]
French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Cayenne, French Guiana to Surinam.[109] - Rosa (
 Hamburg): The ship was captured by a privateer in the North Sea off the coast of the Batavian Republic.[100]
Hamburg): The ship was captured by a privateer in the North Sea off the coast of the Batavian Republic.[100] - Sally (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto, Portugal.[89]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto, Portugal.[89] - Sans Quartier (
 France): The privateer was captured on 9 April in the English Channel off Chausey, Manche by the Royal Navy's HMS Danae.[88]
France): The privateer was captured on 9 April in the English Channel off Chausey, Manche by the Royal Navy's HMS Danae.[88] - Santa Antonio (
 Spanish Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 23 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Terpsichore.[88]
Spanish Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured on 23 June in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Terpsichore.[88] - (
 Spanish Navy): The frigate was captured off Ferrol by the Royal Navy's HMS Alcmene, HMS Naiad and HMS Triton. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[106]
Spanish Navy): The frigate was captured off Ferrol by the Royal Navy's HMS Alcmene, HMS Naiad and HMS Triton. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[106] - Santa Cecilia (
 Spanish Navy): The 32-gun fifth rate was captured on 25 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Surprise.
Spanish Navy): The 32-gun fifth rate was captured on 25 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Surprise. - (
 Spanish Navy): The 42-gun frigate was captured on 6 February in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo.[88]
Spanish Navy): The 42-gun frigate was captured on 6 February in the Mediterranean Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo.[88] - Seaforth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York, United States to Barbados. She was subsequently wrecked on 6 August on Tortuga.[105]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York, United States to Barbados. She was subsequently wrecked on 6 August on Tortuga.[105] - Snarke (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to London. She was taken in to Boulogne.[105]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Bristol, Gloucestershire to London. She was taken in to Boulogne.[105] - Somerset (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 17 November in the English Channel off Weymouth, Dorset by a French privateer while on a voyage from Poole, Dorset to Liverpool. She was late recaptured by a cutter from Weymouth.[90]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 17 November in the English Channel off Weymouth, Dorset by a French privateer while on a voyage from Poole, Dorset to Liverpool. She was late recaptured by a cutter from Weymouth.[90] - St. Antonio y Animas (
 Spain): The privateer, a schooner, was captured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94]
Spain): The privateer, a schooner, was captured on 25 December by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[94] - Stockport (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French.[95] - Sultana (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to Lisbon. she was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[93]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from London to Lisbon. she was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[93] - Susannah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dartmouth, Devon by a French privateer while on a voyage from Dartmouth to Torbay, Devon. She was recaptured and brought into Brixham, Devon.[79]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dartmouth, Devon by a French privateer while on a voyage from Dartmouth to Torbay, Devon. She was recaptured and brought into Brixham, Devon.[79] - Swan (
 France): The cutter was captured in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Anson. She was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[86]
France): The cutter was captured in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Anson. She was taken to Plymouth, Devon.[86] - Swift (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Leviathan and HMS Vanguard).[85]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Leviathan and HMS Vanguard).[85] - (
 Spanish Navy): The 40-gun frigate was captured on 16 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Ethalion.[88]
Spanish Navy): The 40-gun frigate was captured on 16 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Ethalion.[88] - Three Friends (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86]
Great Britain): The ship was captured, then recaptured and was taken to Lisbon.[86] - Tuley (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 29 November by the French privateed Vengeance. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 29 November by the French privateed Vengeance. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[110] - Ucca Cardagora (
 Spanish Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured in March in the West Indies by the Royal Navy's . She was set afire and burnt.[88]
Spanish Navy): The 12-gun ship was captured in March in the West Indies by the Royal Navy's . She was set afire and burnt.[88] - Undaunted (
 United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured on 13 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy's .[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured on 13 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy's .[88] - Unie (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 44-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Union (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95]
United States): The ship was captured by the French. She was taken to Bordeaux.[95] - Urwachten (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 66-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 66-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy.[88] - Utrecht (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 68-gun ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Texel by the Royal Navy.[88] - Vengeur (
 France): The privateer was captured on 24 November by the Royal Navy's .
France): The privateer was captured on 24 November by the Royal Navy's . - Valk (
 United Netherlands Navy): The 20-gun ship was captured in November in the Zuyder Zee by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The 20-gun ship was captured in November in the Zuyder Zee by the Royal Navy.[88] - Vengeance (
 United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured on 14 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy's . She was set afire and sunk.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured on 14 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by boats from the Royal Navy's . She was set afire and sunk.[88] - Venus (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident: The 24-gun ship was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Vreedelust (
 Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88]
Batavian Republic): Vlieter Incident: The East Indiaman was captured on 28 August in the North Sea off the Dutch coast by the Royal Navy.[88] - Vriendschap (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[103]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[103] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy.
United Netherlands Navy): Vlieter Incident, 30 August: The 70-gun ship was captured by the Royal Navy. - Willcock (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Liverpool to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[100]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Liverpool to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[100] - (
 Royal Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by two Spanish gunboats.[88]
Royal Navy): The 14-gun ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea by two Spanish gunboats.[88] - Young Jonah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[92]
1800[]
- A.B.C. (
 United States): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire and taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111]
United States): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire and taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111] - Abigail (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to London.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to London.[112] - Acteon (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[114]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[114] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Ferrailleur while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Boston, Massachusetts, United States. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Dublin Volunteer.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Ferrailleur while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Boston, Massachusetts, United States. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Dublin Volunteer.[115] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Bermuda to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus and sent to Cork, Ireland.[116]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Bermuda to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cerberus and sent to Cork, Ireland.[116] - Active (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Whitby, Yorkshire to London. She was taken in to a Dutch port.[117]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Whitby, Yorkshire to London. She was taken in to a Dutch port.[117] - Adelphi (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Leeward Islands to Falmouth, Cornwall. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from the Leeward Islands to Falmouth, Cornwall. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[118] - Adjutor Dahl (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm and Marquis of Townsend while on a voyage from St. Andero to Lisbon. She was taken in to Guernsey.[119]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm and Marquis of Townsend while on a voyage from St. Andero to Lisbon. She was taken in to Guernsey.[119] - Adrihoa (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off the coast of Africa.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off the coast of Africa.[96] - Adventure (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96] - Albanaise (
 French Navy): The 12-gun brig was captured on 4 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix and .
French Navy): The 12-gun brig was captured on 4 June by the Royal Navy's HMS Phoenix and . - Africa (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a number of Spanish gunboats while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a number of Spanish gunboats while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[120] - Africa (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French privateers while on a voyage from Demerara to London. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French privateers while on a voyage from Demerara to London. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[121] - Ajax (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was sent in to St. Andero, Spain.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was sent in to St. Andero, Spain.[104] - HMS Albanaise (
 Royal Navy): The 14-gun brig was captured on 22 November by her crew in a mutiny and surrendered the next day to the Spanish Navy.
Royal Navy): The 14-gun brig was captured on 22 November by her crew in a mutiny and surrendered the next day to the Spanish Navy. - Albion (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer on 16 March in the English Channel off the Isle of Wight. She was on a voyage from London to Plymouth, Devon.[122]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer on 16 March in the English Channel off the Isle of Wight. She was on a voyage from London to Plymouth, Devon.[122] - Alert (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by Spanish gun boats off Gibraltar while on a voyage from Naples, Kingdom of Sicily to Bristol, Gloucestershire.[123][124]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by Spanish gun boats off Gibraltar while on a voyage from Naples, Kingdom of Sicily to Bristol, Gloucestershire.[123][124] - Alkmonack (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[125] - Amelia (flag unknown): The ship was captured and taken in to Jamaica while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to Hamburg.[122]
- Amiable Elenore (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Venice.[117]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Venice.[117] - Amicitia (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[126]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Livorno. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[126] - Amity (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 March by a French privateer while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London. She was ordered in to La Rochelle, Ille-et-Vilaine, France,[104] but was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst and HMS Nymphe.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 March by a French privateer while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to London. She was ordered in to La Rochelle, Ille-et-Vilaine, France,[104] but was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst and HMS Nymphe.[125] - Amphitrite (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off the coast of Africa.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off the coast of Africa.[96] - Andorida (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French galiot L'Abeille.[127]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French galiot L'Abeille.[127] - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Croix, Virgin Islands to Aux Cayes, Hispaniola. She was taken in to St. Domingo.[128]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Croix, Virgin Islands to Aux Cayes, Hispaniola. She was taken in to St. Domingo.[128] - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[129]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[129] - Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Croix to Aux Cayes and return. She was taken in to Santo Domingo, Hispaniola.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from St. Croix to Aux Cayes and return. She was taken in to Santo Domingo, Hispaniola.[120] - Apollo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113] - Ariadne (
 United States): The ship was captured by thwe Spanish while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to Liverpool, Great Britain. She was taken in to St. Andero, Spain.[112]
United States): The ship was captured by thwe Spanish while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to Liverpool, Great Britain. She was taken in to St. Andero, Spain.[112] - Arrogant (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from to Limerick. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[113]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from to Limerick. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[113] - Athénien (
 French Navy): Siege of Malta (1798–1800): The Royal Navy seized the 64-gun third rate as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Malta (1798–1800): The Royal Navy seized the 64-gun third rate as a prize of war. - Augusta (flag unknown): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Archangelsk, Russia to London. She was taken in to Cuxhaven.[121]
- Augustus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French privateer Le Marengo.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French privateer Le Marengo.[130] - Aurora (
 United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Virginia to Cartagena, Spain. She was taken in to Jamaica.[131]
United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Virginia to Cartagena, Spain. She was taken in to Jamaica.[131] - Aurora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from "Zant" to Hull, Yorkshire. She was later recaptured and taken in to Gibraltar.[132]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from "Zant" to Hull, Yorkshire. She was later recaptured and taken in to Gibraltar.[132] - Austrias (
 United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from , Cuba to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She was taken in to Port Royal, Jamaica.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from , Cuba to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. She was taken in to Port Royal, Jamaica.[127] - Bacchus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from Newhaven, East Sussex to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was taken in to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime, France.[127][128]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from Newhaven, East Sussex to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was taken in to Cherbourg, Seine-Maritime, France.[127][128] - Balladore (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to London.[133]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to London.[133] - Bardon (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 9 November in the North Sea by a French privateer.[134]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 9 November in the North Sea by a French privateer.[134] - Beaver (
 Great Britain): The schooner was captured on 27 March by a French privateer and was sunk by her.[104]
Great Britain): The schooner was captured on 27 March by a French privateer and was sunk by her.[104] - Bee (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a number of Spanish gunboats off Gibraltar while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Gibraltar.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a number of Spanish gunboats off Gibraltar while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Gibraltar.[120] - Betsey (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the British privateer Mayflower while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Lisbon, Portugal and was taken in to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[135]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the British privateer Mayflower while on a voyage from Amsterdam to Lisbon, Portugal and was taken in to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[135] - Betsey (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127] - Betsey (
 British North America): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste.[120]
British North America): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste.[120] - Bee (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica by the Spanish and was sent in to a Cuban port.[131]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica by the Spanish and was sent in to a Cuban port.[131]

USS Boston capturing Berceau
- Bellona (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French privateers while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was later recaptured and arrived at Jamaica.[129]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French privateers while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was later recaptured and arrived at Jamaica.[129] - Berceau (
 French Navy): The ship was captured on 12 October by the United States Navy's USS Boston. She was subsequently repaired and returned to the French.[115]
French Navy): The ship was captured on 12 October by the United States Navy's USS Boston. She was subsequently repaired and returned to the French.[115] - Berwick (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Perseverant while on a voyage from Leith, Lothian to London.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Perseverant while on a voyage from Leith, Lothian to London.[118] - Bilboa (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto while on a voyage from London to Oporto.[96][98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto while on a voyage from London to Oporto.[96][98] - Bom Success e Expedicao (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to China. She was taken in to Mauritius.[125]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon to China. She was taken in to Mauritius.[125] - Boreas (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Bouganville (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's . She subsequently collided with her and foundered.[118]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's . She subsequently collided with her and foundered.[118] - Britannia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Hamburg. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Bury and taken in to Gibraltar.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste while on a voyage from New Brunswick, British North America to Hamburg. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Bury and taken in to Gibraltar.[120] - Briton (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November by a French privateer, She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November by a French privateer, She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[121] - Brothers (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Liverpool to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[96][98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Liverpool to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[96][98] - Brothers (
 United States): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellona while bound to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[137]
United States): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellona while bound to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[137] - Brownlow (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French [privateer while on a voyage from London to Belfast, County Down, Ireland. She was taken in to Paimpol, Côtes-du-Nord, France.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French [privateer while on a voyage from London to Belfast, County Down, Ireland. She was taken in to Paimpol, Côtes-du-Nord, France.[121] - Buffalo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Hamburgh. She was taken in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Hamburgh. She was taken in to Ostend, West Flanders, France.[118] - Caldwell (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Rage while on a voyage from Quebec to London.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Rage while on a voyage from Quebec to London.[96] - Cam's Delight (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to Bristol, Gloucestershire.[97]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to Bristol, Gloucestershire.[97] - Carolina (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured on 12 November by the Royal Navy's and was sent in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain.[130]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured on 12 November by the Royal Navy's and was sent in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain.[130] - Caroline (
 Jersey): The ship was captured on 14 April by the French privateer Le Diable Quatre while on a voyage from Jersey to Quebec. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[115]
Jersey): The ship was captured on 14 April by the French privateer Le Diable Quatre while on a voyage from Jersey to Quebec. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[115] - Caroline (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two Spanish privatters while on a voyage from Jamaica to Vera Cruz.[138]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two Spanish privatters while on a voyage from Jamaica to Vera Cruz.[138] - Caroline (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Oporto, Portugal. She was later recaptured by the Portuguese and taken in to Viana, Portugal.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Oporto, Portugal. She was later recaptured by the Portuguese and taken in to Viana, Portugal.[113] - Carteret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Falmouth, Cornwall. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jamaica to Falmouth, Cornwall. She was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[104] - Cazadol (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the British privateer 'Mayflower while on a voyage from Bordeaux, France to Ferrol, Spain. She was sent in to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[135]
Spain): The ship was captured by the British privateer 'Mayflower while on a voyage from Bordeaux, France to Ferrol, Spain. She was sent in to Guernsey, Channel Islands.[135] - Ceres (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 May by the French privateer L'Heureux. She was recaptured on 8 June and was taken in to the Isles of Scilly.[129]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 May by the French privateer L'Heureux. She was recaptured on 8 June and was taken in to the Isles of Scilly.[129] - Ceres (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch privateer Braave while on a voyage from Glasgow, Renfrewshire to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[139]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch privateer Braave while on a voyage from Glasgow, Renfrewshire to Charleston, South Carolina, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Nymphe and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[139] - Charlotta (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cleopatra while bound for New York, United States. She was taken in to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[135]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cleopatra while bound for New York, United States. She was taken in to Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America.[135] - Charlotte (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Palma, Mallorca, Spain.[140]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Palma, Mallorca, Spain.[140] - Charlotte (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Halifax, British North America to London. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[140]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Halifax, British North America to London. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[140] - Charlotte (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[131]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Cork to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[131] - Christian (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Dutch privateer while on a voyage from London to Montrose, Forfarshire.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Dutch privateer while on a voyage from London to Montrose, Forfarshire.[121] - Columbia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Orleans, French Louisiana to Hambro'. She was sent in to Jamaica.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New Orleans, French Louisiana to Hambro'. She was sent in to Jamaica.[96] - Columbia (
 Great Britain): The ship on 6 January in the Atlantic Ocean (49°30′N 11°00′W / 49.500°N 11.000°W) by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia to Great Britain1.[92]
Great Britain): The ship on 6 January in the Atlantic Ocean (49°30′N 11°00′W / 49.500°N 11.000°W) by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia to Great Britain1.[92] - Columbia (
 Guernsey): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[141]
Guernsey): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[141] - Commercial (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Coquet Island, Northumberland on 26 October by the French privateer La Mouche. She was taken in to Bremen.[142]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Coquet Island, Northumberland on 26 October by the French privateer La Mouche. She was taken in to Bremen.[142] - Commerce (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto, Portugal. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto, Portugal. She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley.[96] - Concord (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from China to America. She was taken in t Isle de France.[96]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from China to America. She was taken in t Isle de France.[96] - Concord (
 Jersey): The French privateer La Grand Decide captured Concord while Concord was on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands to Newfoundland, British North America. La Grand Decide took Concord in to a French port.[135]
Jersey): The French privateer La Grand Decide captured Concord while Concord was on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands to Newfoundland, British North America. La Grand Decide took Concord in to a French port.[135] - Concorde (
 French Navy): Action of 4 August 1800: The Nymphe-class frigate was captured off the coast of Brazil by the Royal Navy's HMS Belliqueux.
French Navy): Action of 4 August 1800: The Nymphe-class frigate was captured off the coast of Brazil by the Royal Navy's HMS Belliqueux. - George (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[143]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[143] - Convenienta (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm and Marquis of Townsend while on a voyage from St. Andero to Lisbon. She was taken in to Guernsey.[119]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm and Marquis of Townsend while on a voyage from St. Andero to Lisbon. She was taken in to Guernsey.[119] - Cortis (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's and was sent in to Lisbon, Portugal.[127]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's and was sent in to Lisbon, Portugal.[127] - Countess of Bute (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Brave while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was later recaptured by HMS Doris and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[134]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Brave while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily. She was later recaptured by HMS Doris and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[134] - Countess of Lauderdale (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (48°44′N 18°40′W / 48.733°N 18.667°W) by the French privateer Gersonge while on a voyage from the West Indies to London.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (48°44′N 18°40′W / 48.733°N 18.667°W) by the French privateer Gersonge while on a voyage from the West Indies to London.[135] - Cultivator (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Minerve while on a voyage from Demerara to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Minerve while on a voyage from Demerara to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius.[135] - Dædalus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Portsmouth, Hampshire to the West Indies. She was later recaptured and taken in to Antigua.[141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Portsmouth, Hampshire to the West Indies. She was later recaptured and taken in to Antigua.[141] - Dart (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[144]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[144] - Deb (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Faro, Portugal to Gibraltar. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Faro, Portugal to Gibraltar. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[120] - Defiance (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured in the English Channel on by the French privateer Hero. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[134]
Great Britain): The brig was captured in the English Channel on by the French privateer Hero. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[134] - Dégo (
 French Navy): Siege of Malta (1798–1800): The 64-gun ship was seized by the Royal Navy on 4 September as a prize of war.
French Navy): Siege of Malta (1798–1800): The 64-gun ship was seized by the Royal Navy on 4 September as a prize of war. - HMS Danae (
 Royal Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 14 March in a mutiny by her crew and was handed over to the French Navy the next day.
Royal Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 14 March in a mutiny by her crew and was handed over to the French Navy the next day. - Der Gute Wind (
 Hamburg): The ship was captured by a British privateer while on a voyage from Spain to Hamburg. She was taken in to Gibraltar.[128]
Hamburg): The ship was captured by a British privateer while on a voyage from Spain to Hamburg. She was taken in to Gibraltar.[128] - Diana (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from the Cape of Good Hope to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Antigua.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from the Cape of Good Hope to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Antigua.[121] - Diamond (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 October by the French privateer Le Grand Decide while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Portsmouth, Hampshire. She was taken in to a French port.[137]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 October by the French privateer Le Grand Decide while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia, British North America to Portsmouth, Hampshire. She was taken in to a French port.[137] - Dick (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 15 October by the French privateer La Grand Decide while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa. recaptured Dick on 16 October.[145]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 15 October by the French privateer La Grand Decide while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa. recaptured Dick on 16 October.[145] - Diligence (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea.[146]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea.[146] - Dispatch (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147] - Dolphin (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by Dutch while on a voyage from Great Yarmouth, Norfolk to Cuxhaven. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by Dutch while on a voyage from Great Yarmouth, Norfolk to Cuxhaven. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[135] - Dorset (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer, Norfolk by the French privateer Chasseur, She was taken in to Boulogne, or Dunquerque. France.[121][148]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer, Norfolk by the French privateer Chasseur, She was taken in to Boulogne, or Dunquerque. France.[121][148] - Dublin Packet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York, United States to Livorno. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[133]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York, United States to Livorno. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[133] - Duke of Athol (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Scarborough, Yorkshire.[146]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Scarborough, Yorkshire.[146] - (
 United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrogant and HMS Orpheus.[149]
United Netherlands Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Arrogant and HMS Orpheus.[149] - Duke of Kent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 February by the French privateer L'Anuge while on a voyage from Halifax to Liverpool.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 February by the French privateer L'Anuge while on a voyage from Halifax to Liverpool.[104] - Duke of Kent (
 Great Britain): The French privateer Le Grande Decide captured Duke of Kent on 27 October. Her captors plundered and then released her.[137]
Great Britain): The French privateer Le Grande Decide captured Duke of Kent on 27 October. Her captors plundered and then released her.[137] - Duke of York (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147] - Eagle (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Victor Hugues while on a voyage from the Clyde to Jamaica.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Victor Hugues while on a voyage from the Clyde to Jamaica.[115] - Eagle (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while bound for Quebec.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while bound for Quebec.[150] - Echo (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York to Montserrat. She was taken in to Saint Barthélemy.[125]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York to Montserrat. She was taken in to Saint Barthélemy.[125] - Edward (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea on 12 November by the French privateer Le Marengo and was sunk by her.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea on 12 November by the French privateer Le Marengo and was sunk by her.[130] - Eight Brothers (
 France): The privateer was captured in the North Sea off Vlissingen, Batavian Republic by the British privateer Lady Ann. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[151]
France): The privateer was captured in the North Sea off Vlissingen, Batavian Republic by the British privateer Lady Ann. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[151] - El Belos (
 Spain): The ship was captured on 11 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde while on a voyage from Havana, Cuba to A Coruña. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[120]
Spain): The ship was captured on 11 August by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde while on a voyage from Havana, Cuba to A Coruña. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[120] - El Feliz (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Portuguese while on a voyage from A Coruña to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[113]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Portuguese while on a voyage from A Coruña to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[113] - Elisabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bougainville while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Liverpool. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bougainville while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Liverpool. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion.[118] - Eliza (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS York while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to Santo Domingo. She was taken in to Jamaica.[97]
United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS York while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina to Santo Domingo. She was taken in to Jamaica.[97] - Eliza (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 24 March by a French privateer while bound for Lisbon. She was sent in to La Rochelle.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 24 March by a French privateer while bound for Lisbon. She was sent in to La Rochelle.[104] - Eliza (
 Ireland): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Dublin to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to St. Andero, Spain.[137]
Ireland): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Dublin to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to St. Andero, Spain.[137] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's Hired armed cutter Nile and taken in to Dover, Kent.[97]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's Hired armed cutter Nile and taken in to Dover, Kent.[97] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to A Coruña.[97]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to A Coruña.[97] - Elizabeth (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 A[sentence fragment] while on a voyage from London to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[132]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 A[sentence fragment] while on a voyage from London to Amsterdam, Batavian Republic. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[132] - Ellison (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea on 12 November by the French privateer Le Marengo and was sunk by her.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea on 12 November by the French privateer Le Marengo and was sunk by her.[130] - El Marte (
 Spain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Vera Cruz, United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves to Cadiz, Spain. She was sent in to Lisbon.[152]
Spain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Vera Cruz, United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves to Cadiz, Spain. She was sent in to Lisbon.[152] - El Roi Carlos (
 Spain): The ship was captured on 17 September by the Royal Navy's HMS Doris while on a voyage from Havana, Cuba to Spain. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[153]
Spain): The ship was captured on 17 September by the Royal Navy's HMS Doris while on a voyage from Havana, Cuba to Spain. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[153] - (
 Spanish Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's .[154]
Spanish Navy): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's .[154] - Emilie (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Cybille. She was later taken by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst.[114]
United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Cybille. She was later taken by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst.[114] - Emilie (
 France): The schooner was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cambrian and while on a voyage from Bordeaux to Guadeloupe. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[112]
France): The schooner was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cambrian and while on a voyage from Bordeaux to Guadeloupe. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[112] - Emma (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while outbound from Swanage, Dorset. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Eurydice and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while outbound from Swanage, Dorset. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Eurydice and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[112] - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Figueiras, Portugal.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Figueiras, Portugal.[118] - Endeavour (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Enterprize (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147] - Experiment (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Grenada to London. She was taken in to St. Martins.[120]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Grenada to London. She was taken in to St. Martins.[120] - Fairy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Renominee while on a voyage from Lancaster to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Renominee while on a voyage from Lancaster to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[110] - Fame (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by four Spanish privateers while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by four Spanish privateers while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[110] - Fame (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, Hampshire to Jersey.[155]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Southampton, Hampshire to Jersey.[155] - Fame (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from San Sebastián, Puerto Rico to Charlestown. She was later retaken by her crew and went ib to Jamaica.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from San Sebastián, Puerto Rico to Charlestown. She was later retaken by her crew and went ib to Jamaica.[121] - Fancy (
 United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from New York to Martinique. She was taken in to St. Martins.[120]
United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from New York to Martinique. She was taken in to St. Martins.[120] - Fancy de Jersey (
 Jersey): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Guernsey, Channel Islands to Leith, Lothian. She was later recaptured off Gorey, Jersey by the Royal Navy's HMS Speedwell and taken in to Yarmouth, Isle of Wight.[125]
Jersey): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Guernsey, Channel Islands to Leith, Lothian. She was later recaptured off Gorey, Jersey by the Royal Navy's HMS Speedwell and taken in to Yarmouth, Isle of Wight.[125] - Fanny (
 United States): The brig was captured by the British while on a Voyage from Saint-Domingue, Hispaniola to Baltimore, Maryland. She was taken in to Jamaica.[147]
United States): The brig was captured by the British while on a Voyage from Saint-Domingue, Hispaniola to Baltimore, Maryland. She was taken in to Jamaica.[147] - Farn (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115]
France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115] - Favourite (
 France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Ortegal, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius while on a voyage from Cayenne, French Guiana to Bordeaux, Loire Atlantique.[135]
France): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Ortegal, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Sirius while on a voyage from Cayenne, French Guiana to Bordeaux, Loire Atlantique.[135] - Fedre Lunder (
 Denmark-Norway): The ship was captured by a British privateer and was taken in to The Downs.[115]
Denmark-Norway): The ship was captured by a British privateer and was taken in to The Downs.[115] - Felicidade da Silva (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Port Passage to Lisbon. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[133]
Portugal): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Port Passage to Lisbon. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[133] - Ferrailleur (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115]
France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115] - Field (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Ems while on a voyage from Emden, Holy Roman Empire to Hull, Yorkshire. She was taken in to Delfzijl, Batavian Republic.[153]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Ems while on a voyage from Emden, Holy Roman Empire to Hull, Yorkshire. She was taken in to Delfzijl, Batavian Republic.[153] - Flora (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to Jamaica. She was later recaptured and arrived at Jamaica.[129] Flora was captured a third time and sent in to Málaga, Spain.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool to Jamaica. She was later recaptured and arrived at Jamaica.[129] Flora was captured a third time and sent in to Málaga, Spain.[150] - Fortune (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[117]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[117] - Fox (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Cork to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[126]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Cork to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[126] - Fraternity (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[114]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[114] - Free Briton (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer, Norfolk by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[148]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer, Norfolk by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[148] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured and was sent in to Terschelling, Friesland, Batavian Republic.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured and was sent in to Terschelling, Friesland, Batavian Republic.[104] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Guernsey.[155]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland to Guernsey.[155] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[133]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[133] - Friendship (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 30 November in the Atlantic Ocean (41°30′N 11°30′W / 41.500°N 11.500°W) by the Spanish privater Nostra Señora del Carmen. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 30 November in the Atlantic Ocean (41°30′N 11°30′W / 41.500°N 11.500°W) by the Spanish privater Nostra Señora del Carmen. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[136] - HMS Fulminante (
 Royal Navy): The cutter was captured on 2 June by the French privateer Deux Frères.
Royal Navy): The cutter was captured on 2 June by the French privateer Deux Frères. - Fulminante (
 French Navy): The cutter was captured in September by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The cutter was captured in September by the Royal Navy. - Gannet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 December in the North Sea by a French privateer.[146]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 12 December in the North Sea by a French privateer.[146] - Generalinde (
 France): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Saint Croix, Virgin Islands to Havana, Cuba and returne. She was taken in to Bermuda.[133]
France): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Saint Croix, Virgin Islands to Havana, Cuba and returne. She was taken in to Bermuda.[133] - General Massina (
 France): The corvetto was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Barbados.[116]
France): The corvetto was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Barbados.[116] - Généreux (
 French Navy): Battle of the Malta Convoy, 18 February: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Battle of the Malta Convoy, 18 February: The Téméraire-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Generous Planter (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Eole while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was taken in to Brest, Finistère, France.[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Eole while on a voyage from London to Jamaica. She was taken in to Brest, Finistère, France.[110] - George (
 United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia to St. Thomas, Virgin Islands. She was later recaptured and sent in to Charleston, South Carolina.[156]
United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia to St. Thomas, Virgin Islands. She was later recaptured and sent in to Charleston, South Carolina.[156] - George (
 Kingdom of Ireland): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157]
Kingdom of Ireland): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157] - George and Mary (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured by a French privateer on 28 May off the Isle of Wight.[155]
Great Britain): The sloop was captured by a French privateer on 28 May off the Isle of Wight.[155] - Gram (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and was sent in to Brest.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and was sent in to Brest.[104] - Goodhope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Gibraltar to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[112] - Good Intent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 26 January by the Dutch in the North Sea off Sunderland, County Durham and was scuttled.[158]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 26 January by the Dutch in the North Sea off Sunderland, County Durham and was scuttled.[158] - Good Intent (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from London to Lisbon, Portugal.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from London to Lisbon, Portugal.[115] - Guèpe (
 France): The privateer brig was captured on 29 August by the Royal Navy.
France): The privateer brig was captured on 29 August by the Royal Navy. - Guillaume Tell (
 French Navy): Action of 31 March 1800: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): Action of 31 March 1800: The Tonnant-class ship of the line was captured by the Royal Navy. - Gute Erwarting (
 Prussia): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Danzig to London, Great Britain. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain.[147]
Prussia): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Danzig to London, Great Britain. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk, Great Britain.[147] - Gypsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico, West Indies to Liverpool, Lancashire. She was later recaptured and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico, West Indies to Liverpool, Lancashire. She was later recaptured and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[150] - Haabet (
 Denmark): The ship was captured by the British. She was taken in to Jamaica.[147]
Denmark): The ship was captured by the British. She was taken in to Jamaica.[147] - Hardy (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[147]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[147] - Hebe (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer on 11 November while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Teignmouth, Devon. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS St Fiorenzo and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[159]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer on 11 November while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Teignmouth, Devon. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS St Fiorenzo and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[159] - Hero (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Bermuda by a privateer.[160] She was later recaptured by the United States Navy and taken in to St. Kitts.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Bermuda by a privateer.[160] She was later recaptured by the United States Navy and taken in to St. Kitts.[121] - Hiram (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 13 September in the Atlantic Ocean by the French privateer Courier. She was sent in to Cayenne, French Guiana.[160]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 13 September in the Atlantic Ocean by the French privateer Courier. She was sent in to Cayenne, French Guiana.[160] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Portugal. She was taken in to "Vivera".[97]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Portugal. She was taken in to "Vivera".[97] - Hope (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[125]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[125] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Emsworth, Hampshire to London.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Emsworth, Hampshire to London.[112] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish off Havana, Cuba while on a voyage from British Honduras to London.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish off Havana, Cuba while on a voyage from British Honduras to London.[147] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dover, Kent while on a voyage from Liverpool to London. She was taken in to Calais, France.[121]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel off Dover, Kent while on a voyage from Liverpool to London. She was taken in to Calais, France.[121] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Dunquerque, France.[148]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Dunquerque, France.[148] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The Portsmouth-registered ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The Portsmouth-registered ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The Poole-registered ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna.[136]
Great Britain): The Poole-registered ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna.[136] - Hoyden (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 January by the French privateer Le Rage while on a voyage from Newofoundland to Dartmouth, Devon.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 January by the French privateer Le Rage while on a voyage from Newofoundland to Dartmouth, Devon.[96] - Hope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Montrose, Forfarshire.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Montrose, Forfarshire.[125] - Hunter (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Lisbon, Portugal. She was later recaptured and arrived at Lisbon.[159]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Newfoundland, British North America to Lisbon, Portugal. She was later recaptured and arrived at Lisbon.[159] - Impregnable (
 France): The privateer was captured off the Dutch coast.[147]
France): The privateer was captured off the Dutch coast.[147] - Industry (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire. She was later recaptured by the British lugger Phœnix and taken in to Bridlington, Yorkshire.[146]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire. She was later recaptured by the British lugger Phœnix and taken in to Bridlington, Yorkshire.[146] - Inverness (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Irvine, Ayrshire to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the British sloop Spey and sent in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Irvine, Ayrshire to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the British sloop Spey and sent in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150] - Jamaica (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off St. Lucia while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Martinico, West Indies. She was ordered in to Guadeloupe but was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment and taken in to Bermuda.[104][115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off St. Lucia while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to Martinico, West Indies. She was ordered in to Guadeloupe but was recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment and taken in to Bermuda.[104][115] - Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Atlantic Ocean (42°46′N 16°00′W / 42.767°N 16.000°W) by the French privateer Vengeance. She was recaptured on 25 March off Cape Finisterre, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 18 March in the Atlantic Ocean (42°46′N 16°00′W / 42.767°N 16.000°W) by the French privateer Vengeance. She was recaptured on 25 March off Cape Finisterre, Spain by the Royal Navy's HMS Argo.[125] - Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[135] - Jane (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa. She was subsequently recaptured by the British ships Herriot and Trident and taken in to Liverpool.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Africa. She was subsequently recaptured by the British ships Herriot and Trident and taken in to Liverpool.[136] - Jane and Sarah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French navy frigate and sunk while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Lisbon.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French navy frigate and sunk while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Lisbon.[127] - Jenny (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Cork, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's .[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Cork, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's .[110] - Jersey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Ireland.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Ireland.[118] - Johannes (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Hannibal. She was sent in to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[161]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Hannibal. She was sent in to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[161] - John and Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea.[146]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea.[146] - Jonge Wilhelm (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Dordrecht. She was sent in to Vlissingen.[131]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Dordrecht. She was sent in to Vlissingen.[131] - Josephus (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Livorno. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[120]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Livorno. She was taken in to Cadiz, Spain.[120] - Juno (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127] - Juno (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London. She was sent in to a French port.[162]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London. She was sent in to a French port.[162] - Jupiter (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico to London. She was taken in to St. Martin's.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Martinico to London. She was taken in to St. Martin's.[127] - Juliana (
 Denmark): The brig was captured by the British privateer Alert while on a voyage from Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France to Senegal. She was taken in to Weymouth, Dorset, Great Britain.[161]
Denmark): The brig was captured by the British privateer Alert while on a voyage from Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France to Senegal. She was taken in to Weymouth, Dorset, Great Britain.[161] - Keeling (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to London. She was taken in to a French port.[131]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Liverpool to London. She was taken in to a French port.[131] - L'Actiff (
 France): The privateer was captured in the Bay of Biscay off Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique by the Royal Navy's HMS Thames. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[113]
France): The privateer was captured in the Bay of Biscay off Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique by the Royal Navy's HMS Thames. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[113] - La Constance (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Cynthia and taken in to Guernsey.[139]
France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Cynthia and taken in to Guernsey.[139] - La Dorine (
 France): The brig was captured by the Jersey privateer Phoenix.[163]
France): The brig was captured by the Jersey privateer Phoenix.[163] - Lady Harewood (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 1 January in the Atlantic Ocean (38°11′N 15°10′W / 38.183°N 15.167°W) by the French privateer Volunteer. She was sent in to Nantes, Loire-Atlantique, France.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 1 January in the Atlantic Ocean (38°11′N 15°10′W / 38.183°N 15.167°W) by the French privateer Volunteer. She was sent in to Nantes, Loire-Atlantique, France.[96] - La Fortune (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby (1776) and was sent in to The Downs.[127]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Ruby (1776) and was sent in to The Downs.[127] - La Jean (
 France): The brig was captured by the Jersey privateer Phoenix.[163]
France): The brig was captured by the Jersey privateer Phoenix.[163] - La Mouche (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Minerva.[154]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Minerva.[154] - Lancaster (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 17 June in the Atlantic Ocean (50°46′N 25°00′W / 50.767°N 25.000°W) by the French privateer Brave while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia, United States to Lancaster, Lancashire. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Magicienne and sent in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 17 June in the Atlantic Ocean (50°46′N 25°00′W / 50.767°N 25.000°W) by the French privateer Brave while on a voyage from Savannah, Georgia, United States to Lancaster, Lancashire. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Magicienne and sent in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150] - La Paix (
 France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion. She was taken in to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[126]
France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion. She was taken in to Portsmouth, Hampshire, Great Britain.[126] - La Rancine (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's .[154]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's .[154] - Lark (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[98] - Latona (
 Portugal): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Memel, East Prussia to Lisbon. She was later recaptured by the British privateer Earl Spencer and taken in to Oporto.[132]
Portugal): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Memel, East Prussia to Lisbon. She was later recaptured by the British privateer Earl Spencer and taken in to Oporto.[132] - L'Augusta (
 France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment while on a voyage from Guadeloupe to France. She was sent in to Bermuda.[115]
France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment while on a voyage from Guadeloupe to France. She was sent in to Bermuda.[115] - (
 French Navy): The corvette was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Melpomene. She was sent in to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[150]
French Navy): The corvette was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Melpomene. She was sent in to Portsmouth, Hampshire.[150] - La Vengeance (
 France): The privateer was captured on 2 March in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Nereide. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain.[164]
France): The privateer was captured on 2 March in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Nereide. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain.[164] - Le Guadeloupean (
 France): The privateer was captured by the United States Navy's USS Enterprise. She was taken into St. Kitts.[121]
France): The privateer was captured by the United States Navy's USS Enterprise. She was taken into St. Kitts.[121] - Leith (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157] - Le Scipio (
 France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion. She was taken in to Portsmouth.[126]
France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion. She was taken in to Portsmouth.[126] - Lewes (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Figueira, Portugal.[128]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Figueira, Portugal.[128] - L'Heureux Courier (
 France): The privateer, a brig, was captured on 18 April off Ouessant, Finistère by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was brought in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111][115][133]
France): The privateer, a brig, was captured on 18 April off Ouessant, Finistère by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire. She was brought in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111][115][133] - Liberty (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96] - Lion (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the French galiot L'Abeille.[127]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the French galiot L'Abeille.[127] - Lively (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to a Galician port.[96][98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Liverpool, Lancashire to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to a Galician port.[96][98] - Lord Duncan (
 Great Britain): The French privateer Le Brave captured Lord Duncan while she was on a voyage from Antigua to Glasgow, Renfrewshire. The Royal Navy's HMS Viper later recaptured Lord Duncan and took her in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150]
Great Britain): The French privateer Le Brave captured Lord Duncan while she was on a voyage from Antigua to Glasgow, Renfrewshire. The Royal Navy's HMS Viper later recaptured Lord Duncan and took her in to Falmouth, Cornwall.[150] - Lord Petre (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Mogadore to London. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Mogadore to London. She was taken in to a Spanish port.[141] - Louis (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer in the Bay of Bengal. She was on a voyage from the East Indies to America.[163][165]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer in the Bay of Bengal. She was on a voyage from the East Indies to America.[163][165] - Louisa (
 Sweden): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Barcelona, Spain. She was taken in to Tripoli, Ottoman Tripolitania. Eighteen other Swedish vessels were taken in the same action.[136]
Sweden): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Barcelona, Spain. She was taken in to Tripoli, Ottoman Tripolitania. Eighteen other Swedish vessels were taken in the same action.[136] - L'Union (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Lord Nelson. She was taken in to Guernsey.[113]
France): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Lord Nelson. She was taken in to Guernsey.[113] - Magicienne (
 France): The schooner was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde.[154]
France): The schooner was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Clyde.[154] - Marcus (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[133]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[133] - Margaret and Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Grand Decide while on a voyage from New Providence, New Jersey, United States to London. She was taken in to L'Orient, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[129]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Grand Decide while on a voyage from New Providence, New Jersey, United States to London. She was taken in to L'Orient, Ille-et-Vilaine, France.[129] - Maria (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Barcelona, Spain. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Lisbon, Portugal to Barcelona, Spain. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[112] - Maria (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Martinico, West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Martinico, West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[141] - Maria (
 Kingdom of Sicily): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Naples to Hamburgh. She was taken in to Port Mahon, Spain.[134]
Kingdom of Sicily): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Naples to Hamburgh. She was taken in to Port Mahon, Spain.[134] - Mars (
 France): The privateer was captured on 28 March in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst. She was sent in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[114][125]
France): The privateer was captured on 28 March in the Bay of Biscay by the Royal Navy's HMS Amethyst. She was sent in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[114][125] - Martha and Mary (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste.[120]
United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Auguste.[120] - Martin (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia to Spain. She was taken in to Saint Sebastian's.[166]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Virginia to Spain. She was taken in to Saint Sebastian's.[166] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands] to Madeira, Portugal. She was sent in to Brest.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Jersey, Channel Islands] to Madeira, Portugal. She was sent in to Brest.[104] - Mary (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while bound for Baltimore, Maryland, United States. She was taken in to Curaçao.[115]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the French while bound for Baltimore, Maryland, United States. She was taken in to Curaçao.[115] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar.[147] - Mary (
 Guernsey): The ship was captured by the French privateer Aurora while on a voyage from Guernsey to Trinidad. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Rusce and was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[126]
Guernsey): The ship was captured by the French privateer Aurora while on a voyage from Guernsey to Trinidad. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Rusce and was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[126] - Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 March while on a voyage from , United States to London.[163]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 7 March while on a voyage from , United States to London.[163] - Mary (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127] - Mary (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bayonis while on a voyage from New York to Jamaica. She was returned after being plundered, taking on board the crew of the American merchantmen Brothers and Sophia, which had alson been captured by Bellona.[137]
United States): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bayonis while on a voyage from New York to Jamaica. She was returned after being plundered, taking on board the crew of the American merchantmen Brothers and Sophia, which had alson been captured by Bellona.[137] - Mary and Margaret (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Mary Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto, Portugal. She was subsequently recaptured.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto, Portugal. She was subsequently recaptured.[113] - Mayflower (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Land's End, Cornwall on 9 December by a privateer.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean off Land's End, Cornwall on 9 December by a privateer.[113] - Mediterranean (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96] - Mercury (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment. She was taken in to Bermuda.[115]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Experiment. She was taken in to Bermuda.[115] - Merlin (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies.[115] - Metis (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[136] - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 25 February by the French privateer La Laure while on a voyage from St. Thomas to London. She was taken in to Brest.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 25 February by the French privateer La Laure while on a voyage from St. Thomas to London. She was taken in to Brest.[104] - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Minerva while on a voyage from London to Boston, Massachusetts, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Minerva while on a voyage from London to Boston, Massachusetts, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[125] - Minerva (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from Demerara, British Guiana to London. She was taken in to the .[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from Demerara, British Guiana to London. She was taken in to the .[147] - Minerva (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to Dublin. She was taken in to Morlaix, Finistère, France[165]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Danzig, Prussia to Dublin. She was taken in to Morlaix, Finistère, France[165] - Minerva (
 United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Norfolk, Virginia to Martinique. She was later recaptured and was sent in to Dominica.[144]
United States): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Norfolk, Virginia to Martinique. She was later recaptured and was sent in to Dominica.[144] - Molly (flag unknown): The ship was captured in the Atlantic Ocean (49°40′N 11°00′W / 49.667°N 11.000°W) by the French privateer Cole while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland, United States to Hull, Yorkshire, Great Britain. She was sent in to a Spanish port.[156]
- Monarch (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Quebec to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[153]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Quebec to London. She was later recaptured and taken in to Plymouth, Devon.[153] - Moses Meyer (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to New York, United States. She was later recaptured and taken in to St. Kitts.[138]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to New York, United States. She was later recaptured and taken in to St. Kitts.[138] - Naard Ligt (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was sent in to Dartmouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was sent in to Dartmouth, Devon, Great Britain.[111] - Nancy (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyuage from Jamaica to New Providence, New Jersey She was taken in to Cuba.[96]
United States): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyuage from Jamaica to New Providence, New Jersey She was taken in to Cuba.[96] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and taken into Vigo, Spain.[98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish and taken into Vigo, Spain.[98] - Nancy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Lisbon. She was taken in to Palma, Mallorca, Spain.[140]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Lisbon. She was taken in to Palma, Mallorca, Spain.[140] - Neptune (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea on 10 January by a French privateer while on a voyage from Livorno to London. She was taken in to Bastia, Corsica, France.[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the Mediterranean Sea on 10 January by a French privateer while on a voyage from Livorno to London. She was taken in to Bastia, Corsica, France.[104] - Neptune (
 Great Britain): The ship was recaptured by the British revenue cutter HMRC Dolphin. She was taken in to Mount's Bay.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was recaptured by the British revenue cutter HMRC Dolphin. She was taken in to Mount's Bay.[113] - Nettly (
 Great Britain): The sloop was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The sloop was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Neutrality (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken in to Guadeloupe.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken in to Guadeloupe.[127] - Newark (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Aberdeenshire by the French privateer Le Marengo while on a voyage from Hamburg to Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Aberdeenshire by the French privateer Le Marengo while on a voyage from Hamburg to Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Northumberland.[130] - Newhaven (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken in to Guadeloupe.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French and taken in to Guadeloupe.[127] - New Success (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Lively and taken in to Guernsey.[167]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from London to Limerick, Ireland. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Lively and taken in to Guernsey.[167] - Nile (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[121][148]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[121][148] - Nimrod (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 March by a French privateer and was sunk by her.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 27 March by a French privateer and was sunk by her.[115] - Neptune (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Romney while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Tenerife, Spain. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[129]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the Royal Navy's HMS Romney while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Tenerife, Spain. She was taken in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[129] - Nostra Señora de Camo (
 Portugal): The schooner was captured by the French privateer Heureux Courier at St Michael Island She was later recaptured by the Jersey privateer Tartar and taken in to Jersey.[163]
Portugal): The schooner was captured by the French privateer Heureux Courier at St Michael Island She was later recaptured by the Jersey privateer Tartar and taken in to Jersey.[163] - Nostra Señora de los Dolores (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution while on a voyage from Barcelona to Vera Crus and was taken in to Guernsey.[151]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Guernsey privateer Resolution while on a voyage from Barcelona to Vera Crus and was taken in to Guernsey.[151] - Nostra Señora de Rosario e Santa Margaretta (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Pernambuco to Lisbon. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[126]
Portugal): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Pernambuco to Lisbon. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[126] - Nymph (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from Mouth Bay to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley and taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Vengeance while on a voyage from Mouth Bay to Naples, Kingdom of Sicily She was subsequently recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley and taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[115] - Nymph (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar by three privateers while on a voyage from Gallipoli, Ottoman Empire to London.[119]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar by three privateers while on a voyage from Gallipoli, Ottoman Empire to London.[119] - Oak (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French while on a voyage from Gainsborough, Lincolnshire to London.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French while on a voyage from Gainsborough, Lincolnshire to London.[115] - Ocean (
 France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Favourite and was taken in to Leith, Lothian[166]
France): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Favourite and was taken in to Leith, Lothian[166] - Palladium (
 Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Cork to Jamaica. She was taken in to A Coruña, Spain.[122]
Ireland): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Cork to Jamaica. She was taken in to A Coruña, Spain.[122] - (
 French Navy): The 36-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy.
French Navy): The 36-gun fifth rate was captured by the Royal Navy. - Paquet de Fayal (
 Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Madeira. She was taken in to Tenerife, Spain.[160]
Portugal): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Lisbon to Madeira. She was taken in to Tenerife, Spain.[160] - Patriot (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Jersey privateer Revenge while on a voyage from Saint-Domingue, Hispaniola to Spain. She was taken in to Jersey.[168]
United States): The ship was captured by the Jersey privateer Revenge while on a voyage from Saint-Domingue, Hispaniola to Spain. She was taken in to Jersey.[168] - Pearson (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's and sent to the Isles of Scilly.[116]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was recaptured by the Royal Navy's and sent to the Isles of Scilly.[116] - Peggy (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Retaliation while on a voyage from Cartagena, Spain to New York. She was sent in to Kingston, Jamaica.[156]
United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Retaliation while on a voyage from Cartagena, Spain to New York. She was sent in to Kingston, Jamaica.[156] - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Arrange while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Guernsey. She was taken in to L'Orient.[129][163]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Arrange while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Guernsey. She was taken in to L'Orient.[129][163] - Peggy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Oporto. She was later recaptured by the Portuguese and was taken in to Viana, Portugal.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Oporto. She was later recaptured by the Portuguese and was taken in to Viana, Portugal.[113] - Penelope (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Oporto.[96] - Phœnix (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Afrique while on a voyage from the West Indies to livorno. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[153]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Afrique while on a voyage from the West Indies to livorno. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[153] - Piersou (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 11 July by the French privateer L'Ecole while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's .[169]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 11 July by the French privateer L'Ecole while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's .[169] - Polly (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaice while bound for London. She was later recaptured and put into St. Lucca, Jamaica.[134]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaice while bound for London. She was later recaptured and put into St. Lucca, Jamaica.[134] - Pomona (
 Hamburg): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to Hamburg. She was taken in to Jamaica.[141]
Hamburg): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to Hamburg. She was taken in to Jamaica.[141] - Portland (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York, United States to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[112]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from New York, United States to Liverpool. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[112] - Portland (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia to Jamaica. She was taken in to a Cuban port.[133]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Halifax, Nova Scotia to Jamaica. She was taken in to a Cuban port.[133] - Portland (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by two French privateers. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Racoon and taken to The Downs.[167]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by two French privateers. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Racoon and taken to The Downs.[167] - President (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Spanish while of a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain to Palermo, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[136]
United States): The ship was captured by the Spanish while of a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain to Palermo, Kingdom of Sicily. She was taken in to Algeciras, Spain.[136] - Princess Amelia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 11 May by the French privateer La Decide while on a voyage from the Leeward Islands to Falmouth, Cornwall.[126][141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 11 May by the French privateer La Decide while on a voyage from the Leeward Islands to Falmouth, Cornwall.[126][141] - Princess Charlotte (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to New York, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Hussar and taken in to Cork, Ireland.[141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Falmouth, Cornwall to New York, United States. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Hussar and taken in to Cork, Ireland.[141] - Princess Royal (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was recaptured on 9 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Repulse.[170]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was recaptured on 9 March by the Royal Navy's HMS Repulse.[170] - Princess Royal (
 Jersey): The ship was captured on 1 May while on a voyage from Jersey to Labrador, British North America. She was recaptured on 5 May by the British privateer Venus.[141]
Jersey): The ship was captured on 1 May while on a voyage from Jersey to Labrador, British North America. She was recaptured on 5 May by the British privateer Venus.[141] - Providence (
 Jersey): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Decide.[141]
Jersey): The ship was captured by the French privateer La Decide.[141] - Raccoon (
 France): The privateer brig was captured on 27 September off A Coruña, Spain by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[143]
France): The privateer brig was captured on 27 September off A Coruña, Spain by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[143] - Ranger (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Plymouth, Devon to Aberdeen. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[125]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch while on a voyage from Plymouth, Devon to Aberdeen. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[125] - Rapid (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar while on a voyage from London to Gibraltar.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Gibraltar while on a voyage from London to Gibraltar.[127] - Rebecca (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off the coast of Africa.[147] - Recovery (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer and abandoned. She was found by the Royal Navy's HMS Speedwell and was towed to Falmouth, Cornwall.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer and abandoned. She was found by the Royal Navy's HMS Speedwell and was towed to Falmouth, Cornwall.[113] - Resolution (
 United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by a French privateer.[127] - Richmond (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from a Batavia to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was later recaptured and sent in to Martinique.[156]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from a Batavia to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. She was later recaptured and sent in to Martinique.[156] - Robert (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire (1782) while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland to Rotterdam, Batavian Republic.[171]
United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Spitfire (1782) while on a voyage from Baltimore, Maryland to Rotterdam, Batavian Republic.[171] - Rose-Bud (
 Guernsey): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[125]
Guernsey): The ship was captured by the French privateer Mars.[125] - Ross (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Port Mahon to Gibraltar. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[160]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish while on a voyage from Port Mahon to Gibraltar. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[160] - Salvadora (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Swiftsure while on a voyage from Cadiz to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Gibraltar.[141]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Swiftsure while on a voyage from Cadiz to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Gibraltar.[141] - Santa da Grocez (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to Cadiz. She was sent in to Lisbon.[152]
Spain): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to Cadiz. She was sent in to Lisbon.[152] - Santa Isable (
 Spain): The brig was captured by the British privateer Earl St. Vincent. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain.[126]
Spain): The brig was captured by the British privateer Earl St. Vincent. She was taken in to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain.[126] - Sarah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Virginia, United States. She was taken in to Curacoa.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Grenada to Virginia, United States. She was taken in to Curacoa.[96] - Sarah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was later recaptured and taken in to Newhaven, East Sussex.[172]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French. She was later recaptured and taken in to Newhaven, East Sussex.[172] - Sarah Ann (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 21 January by the French Navy's Berceau while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to New Providence, The Bahamas. On 5 February the Antiguan privateer Peggy recaptured her.[141]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 21 January by the French Navy's Berceau while on a voyage from Cork, Ireland to New Providence, The Bahamas. On 5 February the Antiguan privateer Peggy recaptured her.[141] - Seaflower (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French and was taken in to Guadeloupe.[127]
United States): The ship was captured by the French and was taken in to Guadeloupe.[127] - Sea Nymph (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to a Portuguese port.[171]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Lisbon to Oporto, Portugal. She was taken in to a Portuguese port.[171] - S. Fr. de Asis (
 Spain): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115]
Spain): The privateer was captured by the Guernsey privateer Mayflower and was taken in to Guernsey.[115] - Shandy Hall (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French Navy frigates while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Portugal, She was set afire and sunk.[110]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two French Navy frigates while on a voyage from Newfoundland to Portugal, She was set afire and sunk.[110] - Sirene (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer and was taken in to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[135] - Six Sisters (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while on a voyage from the West Indies to Lancaster, Lancashire.[144][150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while on a voyage from the West Indies to Lancaster, Lancashire.[144][150] - Snake (
 Jersey): The privateer was captured by the French privateer Vangeur.[133]
Jersey): The privateer was captured by the French privateer Vangeur.[133] - Sophia (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Penzance, Cornwall to Livorno. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[131]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a Spanish privateer while on a voyage from Penzance, Cornwall to Livorno. She was taken in to Vigo, Spain.[131] - Sophia (
 United States): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from St. Thomas, Virgin Islands to Halifax.[137]
United States): The ship was captured on 12 August off Bermuda by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from St. Thomas, Virgin Islands to Halifax.[137] - Southo (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Smyrna to London. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[117]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from Smyrna to London. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[117] - Sovereign (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[115] - Speculation (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Martinique to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[128]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Martinique to Jamaica. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[128] - Speedy (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from St. Michael's Mount, Cornwall to London. She was later retaken by her crew and arrived at Youghal, County Cork, Ireland[104]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer while on a voyage from St. Michael's Mount, Cornwall to London. She was later retaken by her crew and arrived at Youghal, County Cork, Ireland[104] - Stafford (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Land's End, Cornwall She was recaptured by the British sloop Sushsante and taken in to Dartmouth, Devon.[98]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Land's End, Cornwall She was recaptured by the British sloop Sushsante and taken in to Dartmouth, Devon.[98] - Stephen (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from British Honduras to London.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from British Honduras to London.[150] - St. James Planter (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm, Dispatch and Marquis of Townsend and taken in to Guernsey.[139]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bellone while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was later recaptured by the Guernsey privateers Alarm, Dispatch and Marquis of Townsend and taken in to Guernsey.[139] - Sukey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Impregnable while on a voyage from Emden, Holy Roman Empire to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was taken in to Delfzijl, Batavian Republic.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Impregnable while on a voyage from Emden, Holy Roman Empire to Guernsey, Channel Islands. She was taken in to Delfzijl, Batavian Republic.[147] - (
 French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Bombay.[173]
French Navy): The frigate was captured by the Royal Navy's . She was taken in to Bombay.[173] - Susannah (flag unknown): The ship was captured and taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[171]
- Susannah (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[159]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Dutch. She was taken in to Texel, Batavian Republic.[159] - Swan (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured then abandoned.[144]
Great Britain): The ship was captured then abandoned.[144] - Swan (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 June by the French privateer Gersonge while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Galloway, Ayrshire.[135]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 June by the French privateer Gersonge while on a voyage from Oporto, Portugal to Galloway, Ayrshire.[135] - Swift (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Bergen while on a voyage from Sierra Leone to London. She was taken in to Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain.[172]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Bergen while on a voyage from Sierra Leone to London. She was taken in to Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain.[172] - Sybil (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured but was recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Ruse. She was taken in to Dartmouth, Devon.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured but was recaptured by the Guernsey privateer Ruse. She was taken in to Dartmouth, Devon.[113] - Tanner (
 United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to New York. She was taken in to Jamaica.[120]
United States): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Vera Cruz to New York. She was taken in to Jamaica.[120] - Tartar (
 Spain): The privateer was captured by Venus, of Liverpool. She was taken in to Kinsale, County Cork, Ireland.[104]
Spain): The privateer was captured by Venus, of Liverpool. She was taken in to Kinsale, County Cork, Ireland.[104] - Tartar (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French off Benin and sunk.[147] - Tartar (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by two Spanish Navy ships while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Martinico, West Indies.[126]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by two Spanish Navy ships while on a voyage from Madeira, Portugal to Martinico, West Indies.[126] - Tigre (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French.[115]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea by the French.[115] - Tom (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Eole.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer L'Eole.[118] - Trelawney (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bougainville while on a voyage from Liverpool to Livorno. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion.[118]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Bougainville while on a voyage from Liverpool to Livorno. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Endymion.[118] - Triton (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish. She was taken in to Oporto, Portugal.[113] - Two Angels (flag unknown): The ship was captured by the United States Navy's USS Boston while on a voyage from Cape Francois to Bordeaux, Loire-Atlantique, France.[115]
- Union (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to a British port.[155]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Charleston, South Carolina, United States to a British port.[155] - Union (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[155]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Africa to the West Indies. She was taken in to Guadeloupe.[155] - Union (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Northumberland by a French privateer while on a voyage from King's Lynn to Bo'ness, Lothian.[174]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the North Sea off , Northumberland by a French privateer while on a voyage from King's Lynn to Bo'ness, Lothian.[174] - Valiant (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[172]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a French privateer. She was taken in to Málaga, Spain.[172] - Vangeur (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Bordeaux to Cape Francois. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[112]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's while on a voyage from Bordeaux to Cape Francois. She was taken in to Plymouth, Devon, Great Britain.[112] - Veloz Bascongada (
 Spain): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Santona to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Jamaica.[132]
Spain): The ship was captured by the British while on a voyage from Santona to Vera Cruz. She was taken in to Jamaica.[132]

HMS Seine and Vengeance.
- Vengeance (
 French Navy): The Résistance-class frigate was captured on 21 August in the Mona Passage by the Royal Navy's HMS Seine.
French Navy): The Résistance-class frigate was captured on 21 August in the Mona Passage by the Royal Navy's HMS Seine. - Vénus (
 French Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 22 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Indefatigable.
French Navy): The 20-gun corvette was captured on 22 October by the Royal Navy's HMS Indefatigable. - Venus (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley and sent in to Oporto.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured. She was later recaptured by the Royal Navy's HMS Netley and sent in to Oporto.[96] - Victory (flag unknown): The ship was captured and taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[171]
- Vine (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire.[113]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the North Sea off Flamborough Head, Yorkshire.[113] - Violet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Littlehampton, West Sussex to Whitby, Yorkshire. She was taken to Boulogne, Pas-de-Calais, France.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Littlehampton, West Sussex to Whitby, Yorkshire. She was taken to Boulogne, Pas-de-Calais, France.[130] - Volunteer (
 France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's and was taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[96]
France): The privateer was captured by the Royal Navy's and was taken in to Lisbon, Portugal.[96] - Vrouw Taatje (
 Batavian Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[171]
Batavian Republic): The ship was captured while on a voyage from Rotterdam to Lisbon, Portugal. She was taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[171] - Wareham (
 United States): The ship was captured on 12 March by a French privateer. She was subsequently released.[104]
United States): The ship was captured on 12 March by a French privateer. She was subsequently released.[104] - Warren (
 United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cleopatra. She was taken in to Halifax.[135]
United States): The ship was captured by the Royal Navy's HMS Cleopatra. She was taken in to Halifax.[135] - Welsarden (
 Sweden): The ship was captured while on a voyage from St. Ubes, Spain to Gothenburg. She was taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[159]
Sweden): The ship was captured while on a voyage from St. Ubes, Spain to Gothenburg. She was taken in to Jersey, Channel Islands.[159] - Whitby Packet (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Littlehampton to Hull. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[130]
Great Britain): The ship was captured in the English Channel by a French privateer while on a voyage from Littlehampton to Hull. She was taken in to Boulogne, France.[130] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while on a voyage from the West Indies to Liverpool.[150]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French privateer Le Brave while on a voyage from the West Indies to Liverpool.[150] - William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by a privateer in the West Indies.[157] - William (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured in the North Sea by a Dutch privateer. She was later recaptured and sent in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[130]
Great Britain): The brig was captured in the North Sea by a Dutch privateer. She was later recaptured and sent in to Great Yarmouth, Norfolk.[130] - William and Betsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London. She was taken in to L'Orient, Morbihan, France.[96]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from Newfoundland to London. She was taken in to L'Orient, Morbihan, France.[96] - William and Betsey (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne.[148]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 16 November in the North Sea off Cromer by the French privateer Chasseur. She was taken in to Boulogne.[148] - William and Mary (
 Great Britain): The brig was captured on 10 December in the English Channel off Start Point, Devon by the French privateer Hero she was recaptured on 12 December by the Royal Navy's .[134]
Great Britain): The brig was captured on 10 December in the English Channel off Start Point, Devon by the French privateer Hero she was recaptured on 12 December by the Royal Navy's .[134] - William and Mary (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136]
Great Britain): The ship was captured by the Spanish between 28 October and 30 November. She was taken in to Bologna, Spain.[136] - Williamson (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured on 19 April by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[131]
Great Britain): The ship was captured on 19 April by the French privateer Bellona while on a voyage from Jamaica to London. She was taken in to Bordeaux.[131] - Winyau (
 United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain. She was taken in to Brest.[97]
United States): The ship was captured by the French while on a voyage from New York to Falmouth, Cornwall, Great Britain. She was taken in to Brest.[97] - Young William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured while bound from the South Seas to London. She was later recaptured and sent in to Cork, Ireland.[127]
Great Britain): The ship was captured while bound from the South Seas to London. She was later recaptured and sent in to Cork, Ireland.[127] - Young William (
 Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica while bound for London.[134]
Great Britain): The ship was captured off Jamaica while bound for London.[134]
Unknown date[]
- Truelove (
 United States): American War of Independence, 1775-83: The privateer was captured by the British.
United States): American War of Independence, 1775-83: The privateer was captured by the British.
See also[]
- List of ships captured in the 19th century
- Bibliography of early American naval history
References[]
- ^ discovery.ucl.ac.uk/1349550/1/473433.pdf
- ^ "Daily Event for January 17". Maritime Quest. Retrieved 31 October 2011.
- ^ Griffis, 1972 p.4
- ^ Preble, 1892, p.12
- ^ Maclay, Edgar Stanton. A History of American Privateers. New York: D. Appleton and Company, 1899.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Ship News". The Times. No. 2802. London. 10 October 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Ship News". The Times. No. 2837. London. 20 November 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ship News". The Times. No. 2556. London. 23 March 1793. col A, p. 4.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 2816. London. 26 October 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 2828. London. 9 November 1793. col A, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f "Ship News". The Times. No. 2707. London. 12 June 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c "(untitled)". The Times. No. 2775. London. 10 September 1793. col C, p. 3.
- ^ Lloyd's List №5228. Accessed 20 December 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Ship News". The Times. No. 2868. London. 25 December 1793. col C, p. 4.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 2850. London. 4 December 1793. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 2537. London. 19 February 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 2543. London. 25 February 1793. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "(untitled)". The Times. No. 2967. London. 19 April 1794. col C, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 2862. London. 18 December 1793. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 2768. London. 2 September 1793. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 2810. London. 19 October 1793. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Ship News". The Times. No. 941009 (sic). London. 9 October 1794. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Ship News". The Times. No. 941015 (sic). London. 15 October 1794. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 950103 (sic). London. 3 January 1795. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Ship News". The Times. No. 95010 (sic). London. 1 January 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Ship News". The Times. No. 940809 (sic). London. 9 August 1794. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ship News". The Times. No. 2910. London. 12 February 1794. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 2922. London. 26 February 1794. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 2937. London. 15 March 1794. col D, p. 3.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 2889. London. 18 January 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 952304 (sic). London. 4 March 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ Lloyd's List, №2715.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ship News". The Times. No. 950314 (sic). London. 14 March 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 941016 (sic). London. 16 October 1794. col B, p. 3.
- ^ Norie, J. W. (1842). The naval gazetteer, biographer and chronologist; containing a history of the late wars from ... 1793 to ... 1801; and from ... 1803 to 1815, and continued, as to the biographical part to the present time. London: C. Wilson. p. 406.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Ship News". The Times. No. 952011 (sic). London. 11 February 1795. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ship News". The Times. No. 950318 (sic). London. 18 March 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 950613 (sic). London. 13 June 1795. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Ship News". The Times. No. 3790. London. 11 January 1797. col B, p. 3.
- ^ Lloyd's List №2870.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3427. London. 31 October 1795. col B-C, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ship News". The Times. No. 950321 (sic). London. 21 March 1795. col D, p. 2.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 3460. London. 9 December 1795. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f "Ship News". The Times. No. 3420. London. 23 October 1795. col D, p. 2.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 960102 (sic). London. 2 January 1796. col D, p. 2.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 3493. London. 16 January 1796. col D, p. 3.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 3478. London. 30 December 1795. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 950420 (sic). London. 20 April 1795. col B, p. 3.
- ^ "(untitled)". The Times. No. 3413. London. 15 October 1795. p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 3670. London. 24 August 1796. col C, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Ship News". The Times. No. 3841. London. 13 March 1797. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 35058. London. 3 February 1796. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 3607. London. 9 June 1796. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 3514. London. 10 February 1796. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3523. London. 20 February 1796. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 3546. London. 30 March 1796. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3549. London. 2 April 1796. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 3709. London. 8 October 1796. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f "(untitled)". The Times. No. 3784. London. 4 January 1797. col C, p. 3.
- ^ "(untitled)". The Times. No. 3513. London. 9 March 1796. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3636. London. 13 July 1796. col C, p. 2.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3592. London. 23 May 1796. col D, p. 4.
- ^ "No. 14033". The London Gazette. 1 August 1797. p. 732.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Ship News". The Times. No. 4071. London. 20 December 1797. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Ship News". The Times. No. 4005. London. 22 September 1797. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4015. London. 4 October 1797. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 3792. London. 13 January 1797. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Ship News". The Times. No. 4173. London. 18 April 1798. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 3867. London. 12 April 1797. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 3906. London. 29 May 1797. col C, p. 3.
- ^ James, Chamier, 1859 pp.151-157
- ^ Yonge, 1863 pp.238-242
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 4121. London. 16 February 1798. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 4332. London. 14 November 1798. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 4164. London. 7 April 1798. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f "Ship News". The Times. No. 4230. London. 14 July 1798. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4287. London. 20 September 1798. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4357. London. 14 December 1798. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ship News". The Times. No. 4384. London. 16 January 1799. col A, p. 4.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4295. London. 29 September 1798. col A, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4191. London. 9 May 1798. col D, p. 3.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4313. London. 20 October 1798. col B, p. 3.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4365. London. 25 December 1798. col A-B, p. 4.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4325. London. 6 November 1798. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Ship News". The Times. No. 4623. London. 26 October 1799. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ship News". The Times. No. 4407. London. 12 February 1799. col C, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lloyd's Marine List – January 14". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12221. 14 January 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi "Naval Journal". Portsmouth Telegraph or Mottley's Naval and Military Journal. No. 13. 6 January 1800.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 4424. London. 4 March 1799. col A, p. 3.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 4645. London. 21 November 1799. col B, p. 4.
- ^ a b c d e f "Ship News". The Times. No. 4492. London. 25 May 1799. col D, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Lloyd's Marine List – January 21". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12224. 22 January 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Ship News". The Times. No. 4455. London. 10 April 1799. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f "From the London Gazette". The Hull Packet. No. 668. 25 February 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Ship News". The Times. No. 4450. London. 4 April 1799. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u "Ship News". The Times. No. 4711. London. 5 February 1800. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Lloyd's Marine List – February 7". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12231. 10 February 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Intelligence from Lloyd's List, February 4". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2719. 17 February 1800.
- ^ "Ship News". The Hull Packet. No. 662. 14 January 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 4470. London. 27 April 1799. col C, p. 3.
- ^ "Exeter, Wednesday, January 1". Trewman's Exeter Flying Post. No. 1891. 2 January 1800. p. 2.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4410. London. 15 February 1799. col B, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4567. London. 21 August 1799. col C, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Lloyd's Marine List – April 1". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12253. 5 April 1800.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". The Times. No. 4615. London. 17 October 1799. col D, p. 3.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 4622. London. 25 October 1799. col A-B, p. 3.
- ^ Harrison, 1858 p.156
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4406. London. 11 February 1799. col A, p. 3.
- ^ "(untitled)". The Times. No. 4614. London. 16 October 1799. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d e f "Lloyd's Marine List – January 18". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12227. 1 February 1800.
- ^ a b c "Plymouth". Trewnan's Exeter Flying Post. No. 1907. 24 April 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lloyd's Marine List – May 6". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12268. 10 May 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Lloyd's Marine News – Dec. 16. 1800". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12367. 20 December 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Plymouth, April 6". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12256. 12 April 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u "Lloyd's Marine List – April 22". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12262. 26 April 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – July 25". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12302. 28 July 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine List – Nov. 11". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12352. 15 November 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lloyd's Marine List – February 25". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12239. 1 March 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – Oct. 17". Calendonian Mercury. No. 12341. 20 October 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Lloyd's Marine List – August 26". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12316. 30 August 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Lloyd's Marine List – Nov. 28". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12359. 1 December 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – March 21". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12248. 24 March 1800.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4938. London. 29 October 1800. col B, p. 3.
- ^ "Lloyd's Marine List – Oct. 28". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12346. 1 November 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Lloyd's Marine List – April 8". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12256. 12 April 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lloyd's Marine List – May 20". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12274. 24 May 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "Lloyd's Marine List – August 5". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12307. 9 August 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Times. No. 4884. London. 27 August 1800. col C, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Lloyd's Marine List – June 13". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12284. 16 June 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Ship News". Hull Packet. No. 696. 18 November 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Lloyd's List= April 29". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12265. 3 May 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine List – August 22". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12314. 25 August 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "Lloyd's Marine List – June 24". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12289. 28 June 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Lloyd's Marine News – Dec. 9. 1800". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12364. 13 December 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Intelligence from Lloyd's List - JULY 15". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2742. 28 July 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Lloyd's Marine News – Dec. 26. 1800". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12371. 29 December 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f "Lloyd's Marine List – Nov. 4". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12349. 8 November 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – Sept. 9". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12322. 13 September 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – Oct. 7". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12337. 11 October 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – April 18". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12260. 21 April 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Lloyd's Marine List – May 27". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12277. 31 May 1800.
- ^ "(untitled)". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12357. 27 November 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – Oct. 10". Calendonian Mercury. No. 12338. 13 October 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine List – June 27". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12290. 30 June 1800.
- ^ "Ship News". The Hull Packet. No. 693. 28 October 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Lloyd's Marine News – Dec. 19. 1800". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12368. 22 December 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Lloyd's Marine List – May 13". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12271. 17 May 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Ship News". The Hull Packet. No. 698. 2 December 1800.
- ^ "Lloyd's Marine List – Oct. 31". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12347. 3 November 1800.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Lloyd's Marine List – July 8". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12295. 12 July 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – May 9". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12269. 12 May 1800.
- ^ a b "Ship News". The Times. No. 4915. London. 2 October 1800. col C, p. 3.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine List – Sept. 26". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12332. 29 September 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2755. 27 October 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Lloyd's Marine List – June 3". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12280. 7 June 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Ship News". The Times. No. 4775. London. 22 April 1800. col D, p. 4.
- ^ a b c "Ship News". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2753. 13 October 1800.
- ^ "Edinburgh, February 10". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2719. 17 February 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine List – Nov. 25". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12358. 29 November 1800.
- ^ a b c d "Lloyd's Marine News – Nov 14". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12354. 20 November 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – Sept. 2". Caledonian Mercury. No. 123196. 6 September 1800.
- ^ "Ship News". The Times. No. 4974. London. 11 December 1800. col B, p. 2.
- ^ a b c d e f "Intelligence from Lloyd's List - June 17". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2738. 30 June 1800.
- ^ "Ship News". The Hull Packet. No. 670. 11 March 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – June 20". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12287. 23 June 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine List – June 10". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12283. 14 June 1800.
- ^ a b "Lloyd's Marine News – Dec. 2". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12361. 26 December 1800.
- ^ "Lloyd's Marine List – June 6". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12281. 9 June 1800.
- ^ "Intelligence from Lloyd's List, July 29". Aberdeen Journal. No. 2744. 11 August 1800.
- ^ "LOSS of the REPULSE MAN OF WAR". The Hull Packet. No. 672. 25 March 1800.
- ^ a b c d e "Lloyd's Marine List – Sept. 23". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12331. 27 September 1800.
- ^ a b c "Lloyd's Marine List – Sept. 19". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12329. 22 September 1800.
- ^ "(untitled)". Casledonian Mercury. No. 12256. 12 April 1800.
- ^ "(untitled)". Caledonian Mercury. No. 12346. 1 November 1800.
Bibliography[]
- Allen, By Gardner Weld (1909). Our naval war with France.
Houghton Mifflin, Boston, New York. p. 323. OCLC 197401914. Url - Cooper, James Fenimore (1826). History of the navy of the United States of America.
Stringer & Townsend, New York. p. 508. OCLC 197401914. Url - Griffis, William Elliot (1887). Matthew Calbraith Perry: a typical American naval officer.
Cupples and Hurd, Boston. p. 459. Url - Harrison, Henry William (1858). Battlefields and naval exploits of the United States: ...
H. C. Peck & Theo. Bliss, Philadelphia. p. 448. Url - Hill, Frederic Stanhope (1905). Twenty-six historic ships.
G.P. Putnam's Sons, New York and London. p. 515. OCLC 1667284. Url - James, William; Chamier, Frederick (1837). The naval history of Great Britain: from the declaration of war by France in 1793 to the accession of George IV, Volume 6.
Richard Bentley, London. p. 568. Url - Preble, George Henry (1892). History of the United States Navy-yard, Portsmouth, N. H.
U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington. p. 219. Url - Yonge, Charles Duke. The history of the British Navy: from the earliest period to the present time : in two volumes, Volume 2. Bentley, 1863. p. 809. Url
Notes[]
- ^ Néréide was captured three different times: 1st capture by British on 20 December 1797; 2nd capture by French on 23 August 1810; 3rd capture by British 3 December 1810.
Categories:
- 18th-century maritime incidents
- Lists of captured ships