Meadville, Pennsylvania
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2020) |
Meadville, Pennsylvania | |
|---|---|
| City of Meadville | |
 Downtown Meadville | |
 Seal | |
| Etymology: David Mead, founder[1] | |
 Location of Meadville in Crawford County, Pennsylvania | |
 Location of Pennsylvania in the United States | |
 Meadville Location in Pennsylvania | |
| Coordinates: 41°39′N 80°9′W / 41.650°N 80.150°WCoordinates: 41°39′N 80°9′W / 41.650°N 80.150°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Pennsylvania |
| County | Crawford |
| Founded | 1788-05-12 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | H. Leroy Stearns (D) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4.38 sq mi (11.34 km2) |
| • Land | 4.37 sq mi (11.32 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.01 km2) |
| Elevation | 1,400 ft (400 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 13,388 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 12,655 |
| • Density | 2,894.56/sq mi (1,117.48/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP Codes | 16335, 16388 |
| Area code(s) | 814 |
| FIPS code | 42-48360 |
| Website | www |
| Designated | November 1, 1946[4] |

Meadville is a city in and the county seat of Crawford County, Pennsylvania, United States.[5] The city is within 40 miles (64 km) of Erie and within 90 miles (140 km) of Pittsburgh. It was the first permanent settlement in Northwestern Pennsylvania. The population was 13,388 at the 2010 census.[6] The city of Meadville is the principal city of the Meadville, PA Micropolitan Statistical Area. As well as one of two cities, the other being Erie, that make up the larger Erie-Meadville, PA Combined Statistical Area.
History[]
Meadville was settled on May 12, 1788, by a party of settlers led by David Mead. Its location was chosen well, for it lies at the confluence of Cussewago Creek and French Creek, and was only a day's travel by boat to the safety of Fort Franklin.
Their settlement was in a large meadow, first cleared by Native Americans led by Chief Custaloga, and well suited for growing maize. The village Custaloga built here was known as Cussewago. Custaloga's name first appeared in western Pennsylvania's history in George Washington's journal of 1754.[7] When Washington arrived in the village of Venango (Fort Machault), Custaloga was in charge of the wampum of his nation. This wampum was a message that was sent to the Six Nations if the French refused to leave the land. Custaloga was the chief of the Munsee or Wolf Clan of Delawares and he also ruled over the Delawares at the town of Cussewago, at the present site of Meadville.[8]
The neighboring Iroquois and Lenape befriended the isolated settlement, but their enemies, including the Wyandots, were not so amiable. The threat of their attacks caused the settlement to be evacuated for a time in 1791.
Around 1800, many of the settlers to the Meadville area came after receiving for service in the Revolutionary War. Meadville became an important transportation center after the construction of the in 1837 and of the Beaver and Erie Canal it connected to at Conneaut Lake and subsequent railroad development.
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Meadville played a small part in the Underground Railroad helping escaping slaves to freedom. An event in September 1880 led to the end of segregation by race in the state's public schools. At the South Ward schools, Elias Allen tried unsuccessfully to enroll his two children. He appealed to the Crawford County Court of Common Pleas, and Judge Pearson Church declared unconstitutional the 1854 state law mandating separate schools for Negro children. This law was amended, effective July 4, 1881, to prohibit such segregation.[9]
By the late 19th century, Meadville's economy was also driven by logging, agriculture, and iron production. The Talon Corporation, headquartered in Meadville, played a major role in the development of the zipper. Since the clothing industry was largely unaffected by the Great Depression, the community saw a population boom at that time. During World War II, the nearby Keystone Ordnance plant brought additional jobs to the area.
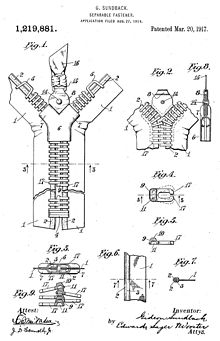
The high demand for zippers created favorable conditions for the Talon Company, and so became Meadville's most crucial industry. The company encountered significant difficulties after it was absorbed by Textron industries in 1968, eventually ending up bankrupt. Today, nothing remains of Talon in Meadville except for a few run-down buildings. However, as a result of the need for close tolerances and tool and die makers, a cottage industry of tool and die shops was established which resulted in Meadville, earning the city the nickname Tool City with more tool shops per capita than any place else in the United States.
In 1886, a blacksmith from Evansburg, Pennsylvania, George B. DeArment, began hand-forging farrier's tools and selling them from town to town out of the back of a wagon. The business eventually became known as the Champion Bolt and Clipper Company. In 1904, now named Channellock, the company moved to a 12,000-square-foot (1,100 m2) facility in Meadville and added nippers, pinchers, and open-end wrenches to its product line. George B. DeArment's two sons, Almon W. and J. Howard DeArment became partners in the company in 1911 and expanded the product line again to include hammers. In 1923, the company moved again to a 33,000-square-foot (3,100 m2) facility at its current location. Four years later, the name of the company was changed to the Champion–DeArment Tool Company.
Talon remained a major employer, along with the Erie Railroad, American Viscose Corporation (later known as Avtex Fibers), Channellock tools, and . The area actually saw an increase in population during the Great Depression and the economy continued to grow past World War ll.[10] In the 1980s, the Great Lakes region saw a decline in heavy industry. By the early 1990s, Channellock and Dad's were the only large companies operating in Meadville. This blow to the local economy was softened by a subsequent surge in light industry, mainly tool and die machine shops. The area has seen growth in the 1990s and the first decade of the 21st century. The song "Bittersweet Motel" by Vermont jam band, Phish, was inspired when keyboardist Page McConnell left a wedding in Meadville and drove to the Pittsburgh Airport.
In addition to the Meadville Downtown Historic District, several buildings are listed on the National Register of Historic Places: Baldwin-Reynolds House, Bentley Hall (Allegheny College), Independent Congregational Church, Dr. J. R. Mosier Office, Roueche House, Ruter Hall (Allegheny College), and Judge Henry Shippen House.[11]
Attractions[]
Baldwin-Reynolds house[]

Originally built in 1843 by United States Supreme Court Justice Henry Baldwin. Just a few months after the house was complete, Henry Baldwin died in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. After his death, the house became a girls’ school for three years until it was sold to a local businessman, William Reynolds. Thus, the house became The Baldwin-Reynolds House and now serves as a museum of history, the arts and cultural experiences in northwest Pennsylvania. The Baldwin-Reynold house offers free tours in the summer.[12]

David Mead's House[]
A replica of founder David Mead's log cabin, the first permanent settlement in northwestern Pennsylvania, is located at Bicentennial Park along the banks of French Creek. The replica was built as a part of Meadville's Bicentennial celebration in 1988. The cabin is used as an educational resource for school tours and the general public.[13]
Diamond Park[]

Diamond Park is Meadville's central park and has been used for a variety of different purposes for over two centuries. In the 19th century, the park was used as militia drill grounds leading up to and during the Civil War. After the Civil War was over, Diamond Park became more open to the public with grass, statues, monuments and a gazebo. It is now used as a recreational park for the community.[14]

The Meadville Market House[]

The Market House is a prominent historical building located in downtown Meadville. It is the oldest continuously-run market structure in the state of Pennsylvania, and still serves as a hub for local farmers. Farmers markets are still held on Saturdays.[14]
Education[]
Colleges[]
Meadville is the home of Allegheny College, a liberal arts college with approximately 1,700 students. Allegheny was founded in April 1815[15] by the Reverend Timothy Alden, a graduate of Harvard's School of Divinity. The college was historically affiliated with the United Methodist Church after 1833, although it is currently non-sectarian. The first class, consisting of four male students, began their studies on July 4, 1816, without any formal academic buildings. Within six years, Alden accumulated sufficient funds to begin building a campus. The first building erected, the library, was designed by Alden himself, and is a notable example of early American architecture. Bentley Hall is named in honor of Dr. William Bentley, who donated his private library to the College, a collection of considerable value and significance. In 1824, Thomas Jefferson wrote to Alden, expressing the hope that his University of Virginia could someday possess the richness of Allegheny's library.[16] Alden served as president of the college until 1831, when financial and enrollment difficulties forced his resignation. Ruter Hall was built in 1853.[17]
Meadville Theological School was established in 1844 by a wealthy businessman and Unitarian named Harm Jan Huidekoper. It moved to Chicago in 1926.[18]
Primary and secondary education[]
- Meadville Area Senior High School (grades 9-12)
- Meadville Middle School (grades 7-8)
- First District Elementary School (grades K-6)
- Neason Hill Elementary School (grades K-6)
- Second District Elementary School (grades K-6)
- West End Elementary School (grades K-6)
Private/charter schools:
- Calvary Baptist Christian Academy (grades K-12)
- Seton Catholic School (grades K-8)
- The Learning Center K-8 Independent School (grades K-8)
Geography[]
Meadville is located at 41°39′N 80°9′W / 41.650°N 80.150°W (41.642, −80.147).[19]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 4.4 square miles (11 km2), all of it land.
Demographics[]
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1810 | 457 | — | |
| 1820 | 649 | 42.0% | |
| 1830 | 1,076 | 65.8% | |
| 1840 | 1,319 | 22.6% | |
| 1850 | 2,578 | 95.5% | |
| 1860 | 3,702 | 43.6% | |
| 1870 | 7,103 | 91.9% | |
| 1880 | 8,860 | 24.7% | |
| 1890 | 9,520 | 7.4% | |
| 1900 | 10,291 | 8.1% | |
| 1910 | 12,780 | 24.2% | |
| 1920 | 14,568 | 14.0% | |
| 1930 | 16,698 | 14.6% | |
| 1940 | 18,919 | 13.3% | |
| 1950 | 18,972 | 0.3% | |
| 1960 | 16,671 | −12.1% | |
| 1970 | 16,573 | −0.6% | |
| 1980 | 15,544 | −6.2% | |
| 1990 | 14,318 | −7.9% | |
| 2000 | 13,685 | −4.4% | |
| 2010 | 13,388 | −2.2% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 12,655 | [3] | −5.5% |
| Sources:[5][20][21][22] | |||
As of the census of 2017, there were 12,973 people, 5,376 households, and 2,891 families residing in the city. The population density was 3.060.1 people per square mile (1,214.7/km2). There were 5,985 housing units at an average density of 1,375.5 per square mile (531.2/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 87.5% (11,487) White, 5.28% African American, 0.18% Native American, 2.4% (320) Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 0.34% from other races, and 3.2% (420) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.4% (5) of the population.
There were 5,376 households, out of which 17.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 36.5% were married couples living together, 13.4% had a female householder with no husband present, and 46.8% were non-families. 38.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 16.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.18 and the average family size was 2.86.
In the city the population was spread out, with 19.4% under the age of 18, 20.0% from 18 to 24, 22.0% from 25 to 44, 19.9% from 45 to 64, and 18.7% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36 years. There are currently 6,171 males (46.6%) while there are currently 7,067 females (53.4%).
The median income for a household in the city was $33,848, and the median income for a family was $54,069. Males had a median income of $32,813 versus $22,579 for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,290. About 13.7% of families and 22.7% of the population were below the poverty line, including 25.3% of those under age 18 and 13.3% of those age 65 or over.[23]
Notable people[]
- Meghan Allen, Playboy model
- Henry Baldwin, Supreme Court justice, lone dissenter in the Amistad case
- John Joseph Bittner, geneticist and cancer biologist, who studied the genetics of breast cancer
- Journey Brown, Penn State running back
- Cameron Carpenter, Grammy-nominated organist
- Ernestine Cobern Beyer, poet and children's author
- George Washington Cullum U.S. Army general from the civil war
- John Dick, U.S. Congressman from Pennsylvania
- Samuel Bernard Dick, U.S. Congressman from Pennsylvania
- Lavantia Densmore Douglass (1827–1899), social reformer
- Jack Dunn, Major League pitcher and Minor League Baseball team owner
- R. Budd Dwyer, former PA State Treasurer
- Todd Erdos, Major League Baseball player
- John Wilson Farrelly, U.S. Representative for Pennsylvania's 22nd congressional district from 1847 to 1849
- Patrick Farrelly, U.S. Representative for Pennsylvania's 18th congressional district from 1823 to 1826
- Randy Fichtner, former Offensive Coordinator of the Pittsburgh Steelers, graduate of Meadville Area Senior High
- Charles Homer Haskins, historian, advisor to President Woodrow Wilson
- Todd Holland, television and film director and producer
- Carl Hovde (1926–2009), professor and dean during the Columbia University protests of 1968[24]
- Henry Shippen Huidekoper, Lieutenant Colonel of the 150th PA Volunteer Infantry Regiment. Awarded the Medal of Honor for meritorious service on July 1, 1863 at the Battle of Gettysburg
- Alison Irwin, reality show competitor
- Lynn Jones, former Major League Baseball player
- Virginia Kirkus, creator of Kirkus Reviews
- Wade Manning, former National Football League player
- Alexander S. McDill, congressman from Wisconsin
- Ross A. McGinnis, US Army soldier who was killed in the Iraq War December 4, 2006, and was posthumously awarded the United States' highest decoration for bravery, the Medal of Honor.
- Tammy Pescatelli, comedian
- Branch Rickey, Baseball executive
- Raymond P. Shafer, former governor of Pennsylvania
- Michael S. Smith, jazz drummer and percussionist
- Sharon Stone (1958-), actress
- Gideon Sundback, member of the National Inventors Hall of Fame for his work on the development of the zipper
- Jay Tessmer, former Major League Baseball player
- Vicki Van Meter, record-setting child pilot
- John K. Williams, Wisconsin state legislator
- Andrew J. Yorty, Wisconsin state legislator
References[]
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 204.
- ^ "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 28, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- ^ "PHMC Historical Markers Search" (Searchable database). Pennsylvania Historical and Museum Commission. Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ Royster. "The Journal of Major George Washington (1754)".
- ^ "Washington's 2 Journals 1753-1754". frenchandindianwarfoundation.org. Retrieved April 8, 2019.
- ^ HistoricalMarkers.com [1] Retrieved on December 14, 2008.
- ^ "Complete History of Crawford County". www.crawfordcountypa.net. Retrieved April 9, 2019.
- ^ "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ^ Cheney, Jim (August 26, 2016). "Visiting the Baldwin-Reynolds House Museum in Meadville". UncoveringPA. Retrieved April 8, 2019.
- ^ "David Mead Log Cabin, Meadville - LocationsHub". rs.locationshub.com. Retrieved April 8, 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "History - Meadville". sites.google.com. Retrieved April 8, 2019.
- ^ Stewart, Anne W. (February 7, 2003). "Nothing New Under the Sun". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved August 26, 2009.
- ^ Haskins, Charles H.; Hull, William I. (1902). A History of Education in Pennsylvania. Washington Government Printing Office. p. 10.
- ^ "National Historic Landmarks & National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania" (Searchable database). CRGIS: Cultural Resources Geographic Information System. Note: This includes John P. Davis (December 1977). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Ruter Hall" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 5, 2014. Retrieved June 23, 2013.
- ^ Harm Jan Huidekoper, Dictionary of Unitarian & Universalist Biography.
- ^ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- ^ "Number of Inhabitants: Pennsylvania" (PDF). 18th Census of the United States. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- ^ "Pennsylvania: Population and Housing Unit Counts" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- ^ "Incorporated Places and Minor Civil Divisions Datasets: Subcounty Population Estimates: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2012". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 17, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ "U.S. Census Bureau QuickFacts: Meadville city, Pennsylvania; UNITED STATES". www.census.gov. Retrieved April 9, 2019.
- ^ Hevesi, Dennis. "Carl F. Hovde, Former Columbia Dean, Dies at 82", The New York Times, September 10, 2009 Accessed September 11, 2009.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Meadville, Pennsylvania. |
- Meadville, Pennsylvania
- County seats in Pennsylvania
- Populated places established in 1788
- Cities in Crawford County, Pennsylvania
- Cities in Pennsylvania
- 1788 establishments in Pennsylvania