Narthex
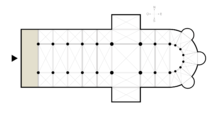

The narthex is an architectural element typical of early Christian and Byzantine basilicas and churches consisting of the entrance or lobby area, located at the west end[1] of the nave, opposite the church's main altar. Traditionally the narthex was a part of the church building, but was not considered part of the church proper.
In early Christian churches the narthex was often divided into two distinct parts: an esonarthex (inner narthex) between the west wall and the body of the church proper, separated from the nave and aisles by a wall, arcade, colonnade, screen, or rail, and an external closed space, the exonarthex (outer narthex),[2] a court in front of the church facade delimited on all sides by a colonnade as in the first St. Peter's Basilica in Rome or in the Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio in Milan. The exonarthex may have been either open or enclosed with a door leading to the outside, as in the Byzantine Chora Church.[3]
By extension, the narthex can also denote a covered porch or entrance to a building.
Etymology[]
The word comes from narthex (Medieval Latin from Classical Greek narthex νάρθηξ[4] "giant fennel, scourge") and was the place for penitents.[5] In Modern Greek narthekas (νάρθηκας) no longer has this meaning and is either the porch of a church, as English, or the brace of a sprained wrist or sling of a broken arm. In English the narthex is now the porch outside the church at the west end, formerly it was a part of the church itself.[6]
Purpose[]
The purpose of the narthex was to allow those not eligible for admittance into the general congregation (particularly catechumens and penitents) to hear and partake of the service. The narthex would often include a baptismal font so that infants or adults could be baptized there before entering the nave, and to remind other believers of their baptisms as they gathered to worship. The narthex is thus traditionally a place of penitence, and in Eastern Christianity some penitential services, such as the Little Hours during Holy Week are celebrated there, rather than in the main body of the church. In the Russian Orthodox Church funerals are traditionally held in the narthex.
Later reforms removed the requirement to exclude people from services who were not full members of the congregation, which in some traditions obviated the narthex. Church architects continued, however, to build a room before the entrance of the nave. This room could be called an inside vestibule (if it is architecturally part of the nave structure) or a porch (if it is a distinct, external structure). Some traditions still call this area the narthex as it represents the point of entry into the church, even if everyone is admitted to the nave itself.
In the Eastern Orthodox Church, the esonarthex and exonarthex had, and still have, distinct liturgical functions. For instance, the procession at the Paschal Vigil will end up at the exonarthex for the reading of the Resurrection Gospel, while certain penitential services are traditionally chanted in the esonarthex.
In some Eastern Orthodox temples, the narthex will be referred to as the trapeza (refectory), because in ancient times, tables would be set up there after the Divine Liturgy for the faithful to eat a common meal, similar to the agape feast of the early church. To this day, this is where the faithful will bring their baskets at Pascha (Easter) for the priest to bless the Paschal foods which they will then take back to their homes for the festive break-fast. Traditionally, the narthex is where candles and prosphora will be sold for offering during Divine Services.
The doorway leading from the narthex to the nave is sometimes referred to as the "Royal Doors",[7] because in major cathedrals (catholica) there were several sets of doors leading into the nave, the central one being reserved only for the use of the Byzantine emperor.[8]
On feast days there will be a procession to the narthex, followed by intercessory prayers, called the Litiy.
In Armenia the local style of narthex is known as a gavit.

In the narthex of a small Orthodox church in Romania, looking through the doorway into the nave and Holy Doors.
Side view of a narthex in an Eastern Orthodox temple. In the center is an analogion at which the priest hears confessions, to the right of that is a silver baptismal font and vessels for dispensing holy water. The main hall is to the left (Pechersky Ascension Monastery, Nizhny Novgorod).
See also[]
- Antechamber
- Cathedral diagram
- Liturgical east and west
- Lobby
- Scarsella
- Westwork
References[]
- ^ By convention, ecclesiastical floor plans are shown map-fashion, with north to the top and the liturgical east to the right. Therefore, some may refer to the narthex as being at the western end of the floor plan. This is done for symbolic reasons, as scriptures say to look for Christ appearing in the east, thus the location of the altar is known as the liturgical east, regardless of the actual cardinal directions.
- ^ In other languages a different terminology can arise confusion. For example, in Italian the inner narthex is called endonartece and the outer narthex esonartece, as the inner narthex in English. Krautheimer (1986), passim
- ^ "narthex". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 23 April 2012.
- ^ LSJ narthex
- ^ The national encyclopædia. ed. John H F. Brabner – 1884 "This space was the narthex or " scourge," and was for the use of penitents. The name was also extended to the outer court "
- ^ William George Clark Peloponnesus: notes of study and travel 1858 Page 110 "One of the most perplexing words in etymology and application is the word narthex. In modern times it can be applied to the porch outside the church at the west end; in old days it was given to a part of the church itself, ..."
- ^ Sometimes the term "Royal Doors" is imprecisely applied to the Holy Doors.
- ^ See Ezekiel 44:1–3)
Further reading[]
- Krautheimer, Richard (1986). Architettura paleocristiana e bizantina (in Italian). Turin: Einaudi. ISBN 88-06-59261-0.
External links[]
 Media related to Narthexes at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Narthexes at Wikimedia Commons
- Church architecture
- Eastern Christian liturgy
- Architectural elements

