Port Jersey
 Port Jersey, with the Statue of Liberty in the foreground | |
| Type | Intermodal freight transport facility |
|---|---|
| Locale | Bayonne & Jersey City New Jersey |
| Official name | Port Jersey Port Authority Marine Terminal |
| Operator | Port Authority of New York and New Jersey New York New Jersey Rail, LLC Conrail Shared Assets Operations GCT Bayonne, LP |
| Characteristics | |
| Clearance below | 50 feet (15 m) |
| History | |
| Coordinates | 40°40′16″N 74°04′26″W / 40.671°N 74.074°WCoordinates: 40°40′16″N 74°04′26″W / 40.671°N 74.074°W |

Port Jersey, officially the Port Jersey Port Authority Marine Terminal and referred to as the Port Jersey Marine Terminal, is an intermodal freight transport facility that includes a container terminal located on the Upper New York Bay in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The municipal border of the Hudson County cities of Jersey City and Bayonne runs along the long pier extending into the bay.[1]
The facility was created between 1972 and 1976 and acquired by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey in July 2010.[2][3] Its major tenant is GCT Bayonne, a post-panamax shipping facility operated by Global Container Terminals.[4]
GCT Bayonne has been modernized. In May 2013 a 900 foot (270m) berth extension was completed, increasing the total dock face to 2,700 feet (820m) of contiguous berth, allowing the facility to handle the latest Suez Max vessels.[5]
Much of Port Jersey is part of United States Foreign-Trade Zone 49.[6] Most of the area in and around the facility is restricted, though a walkway along its northern side is accessible to the general public and may eventually connect with the Hudson River Waterfront Walkway. A very small bird sanctuary (specifically for the least tern)[7] is also located on the promenade.
History[]

The area, east of the Greenville section of Jersey City where was originally tidal marshes and white cedar swamps, which was first used for industrial purposes beginning in the 1800s.
The pier that become Port Jersey was created in the between 1972 and 1976 using landfill.[8]
The facility was once known as the NorthEast Auto Terminal (NEAT) and was operated as a private auto import and export facility for several decades before its purchase in 2008 by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. The location of the PA Auto Marine Terminal and its relatively airdraft-free deepwater access for larger vessels led to the PANYNJ to convert the facility into a container terminal. Anticipating the needs of the planned and existing super-panamax containerships which will call in the port upon the completion of the new Panama Canal Megalocks, NEAT was incrementally shut down and its share of the auto import/export market completely transferred to the Bayonne Auto Terminal and the Port Newark FAPS facility by 2011.
After the PANYNJ purchase the container terminal facilities were expanded in conjunction with the main tenant, Global Terminals.[9][10][11]
The largest ship ever to call at the Port of New York-New Jersey, the MOL Benefactor, docked at Port Jersey in July 2016 after sailing from China through the newly widened Panama Canal.[12]
Modernization brought to GCT Bayonne has been multifaceted. In May 2013 a 900 foot berth extension was completed, increasing the total dock face to 2,700 feet of contiguous berth, allowing the facility to handle the latest Suez Max vessels. https://www.ajot.com/premium/ajot-gct-bayonne-mixing-things-up-in-ny-nj
Channels[]
Ambrose Channel is the main shipping channel in and out of the Port of New York and New Jersey. Branching canal to the south the Port Jersey Channel separates the pier from the peninsula pier of a former military base, Military Ocean Terminal at Bayonne (MOTBY). The a multi-use area is home to the Cape Liberty Cruise Port (one of the New York metropolitan area's three cruise ship terminals), residential and commercial buildings, and land owned by the PANYNJ to be further developed as port facilities. Deepening of the Port Jersey Channel to 50 feet was authorized by the Army Corps of Engineers in 2010.[13][14][15] and completed in 2016.[16] To the north lies Claremeont Terminal.[17]
Rail[]
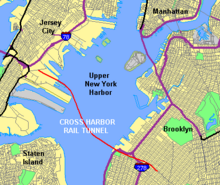
Port Jersey is one of the few areas on the Bergen Neck peninsula where freight rail lines are still in use.[18][19][20] In October 2010 the PANYNJ announced plans to develop ExpressRail Port Jersey, allowing for more transfers to trains, and thus reducing transfers to trucks.[21] Trains will use a renovated National Docks Secondary freight line to access the national network, part of the Liberty Freight Corridor.[22] In December 2016, construction began on the $600 million Express Rail facility. The facility will feature 9,600 feet of track serviced by rail mounted gantry cranes that will have an annual capacity of 250,000 container lifts. Construction was scheduled to be completed by mid-2018.[23] The first phase of the project, with four tracks and two gantry cranes, opened on January 7, 2019. The second and final phase of the project, with four additional tracks bringing the total number of tracks to eight, was opened on June 17, 2019.[24]
Road[]
Port Jersey is served by New Jersey Route 440 which connects with Bayonne Bridge. Nearby is Exit 14A of the Newark Bay Extension of the New Jersey Turnpike.[25] New Jersey Route 185 connects the facility to Greenville Yard.
Wind turbines[]

In 2010 the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey announced its intentions to build a five tower wind farm at Port Jersey within three years.[26][27] The windfarm is part of a larger plan to expand the container port on the manmade peninsula to accommodate post-panamax ships.[28] In May 2012, Global Container Terminals announced detailed plan of the port extension. It included the installation of 9 wind turbines in order to meet a zero emissions footprint of their crane operation during periods of wind power generation.[29] As of mid-2017, this proposal has not seen any meaningful progress.
Solid waste[]
Port Jersey is the key transload terminal for solid waste from New York City barges to railcars. In 2004, the city announced its plans to minimize haulage of waste by truck.[30] Jersey City benefits from a $10 million initial payment and annual payments of $250,000 for the arrangement.[31] The plan faced opposition initially.[32] In 2010, the plan was approved, with $118 million budgeted by the Port Authority.[33] In 2010, the PANYNJ purchased the yard to begin the project. Waste handling improvement projects have continued in context of other improvements to the Greenville Rail Yard.[34]
See also[]
- Geography of New York Harbor
- Rail freight transportation in New York City and Long Island
- Wind power in New Jersey
References[]
- ^ Hudson County New Jersey Street Map. Hagstrom Map Company, Inc. 2008. ISBN 978-0-88097-763-0.
- ^ "Press Release Article - Port Authority of NY & NJ". Panynj.gov. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
- ^ Willner, Andrew (September 12, 2010). "Saving the Bayonne Bridge, and the N.J./N.Y. port". The Record. Bergen County. Retrieved 2011-08-25.
- ^ "Global Terminals Bayonne". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ "GCT Bayonne mixing things up in NY/NJ". www.ajot.com. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ^ "Foreign-Trade Zone 49 - Services - Port of New York and New Jersey - Port Authority of New York & New Jersey". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Hudson County Master Plan
- ^ New York Harbor and Adjacent Channels Feasibility Report, Port Jersey Channel, Bayonne: Environmental Impact Statement (Report). United States Army Corps of Engineers. 1988. Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ Conte, Michaelangelo (June 19, 2014). "Global Container Terminals in Jersey City unveils $325M expansion project". The Jersey Journal. Retrieved June 25, 2014.
- ^ Sullivan, Al (June 22, 2014). "JC hosts high tech container port Global unveils most modern facility in the nation". Hudson Reporter. Archived from the original on July 10, 2014. Retrieved June 28, 2014.
- ^ "Jersey City's Global Container Terminals unveils $325 million expansion project". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ BERGER, PAUL. "Mega-ship's arrival in Bayonne a sign of the future". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ "Port Jersey Channel, New Jersey" (PDF). Report of Channel Conditions 400 feet or wider. USACE. 22 September 2011. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ^ "Port Jersey Channe Jersey City & Bayonne, New Jersey" (PDF). USACE. February 2013. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ^ "Port Jersey Channel Deepening". Maritime Development. New Jersey Department of Transportation. Retrieved 2013-03-16.
- ^ "NY-NJ port completes 50-foot channel project". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ "Claremont Terminal Channel, Jersey City, Navigation Study on Improvements to Existing Channel: Environmental Impact Statement". 1 January 1987. Retrieved 28 March 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ "New York New Jersey Rail, LLC". Retrieved 28 March 2017.
- ^ NY Harbor Intermodal Facilities
- ^ "The Port Authority ExpressRail System". Retrieved 2016-12-11.
- ^ Strunsky, Steve (October 21, 2010). "Port Authority begins development of ship-to-rail container facility in Jersey City". The Star-Ledger. Newark.
- ^ Tirella, Tricia (October 17, 2010). "$24 million in railway improvements celebrated". Hudson Reporter. Retrieved 2011-08-25.
- ^ "Ground Breaking for New ExpressRail Port Jersey Facility". Global Trade Magazine. December 21, 2016. Retrieved December 27, 2017.
- ^ "PORT OF NY/NJ AT STRONGEST COMPETITIVE POSITION IN DECADES WITH COMPLETION OF EXPRESSRAIL NETWORK, CAPSTONE OF MULTI-BILLION PORT MODERNIZATION PROGRAM". The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. June 17, 2019. Retrieved June 19, 2019.
- ^ Frassinelli, Mike (July 11, 2011). "N.J. Turnpike Authority wants to expand Bayonne interchange". The Star-Ledger. Newark. Retrieved 2011-07-15.
- ^ McGeehan, Patrick (August 16, 2010). "Wind Turbine Projects Sprouting Around New York". The New York Times.
- ^ "Port Authority plans windfarm for New Jersey". environmentalleader.com. May 10, 2010. Retrieved 2011-06-06.
- ^ Hack, Charles (May 18, 2010), "Port Authority plans to build 5 big windmills to power new container port on Bayonne and Jersey City border", The Jersey Journal, retrieved 2011-06-06
- ^ Terminal Overview - Global Terminal: 2014, Global Container Terminals - accessed June 1, 2012
- ^ Urbina, Ian (October 7, 2004). "City Trash Plan Forgoes Trucks, Favoring Barges". The New York Times. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
- ^ "Jersey City to get $10 million up front, $250,000 annually under settlement for waste transfer station". NJBIZ. 7 October 2014.
- ^ "Not so fast on that Jersey City garbage transfer station, Port Authority says". NJ.com.
- ^ "Port Authority Board Approves Purchase and Redevelopment of Greenville Yards, Including a Barge-to-Rail Facility to Take Trucks off the Road" (Press release). PANYNJ. May 18, 2010. Retrieved 2014-12-09.
- ^ Dupin, Chris (Dec 20, 2016). "GCT, Port Authority of NY/NJ break ground on new intermodal terminal". American Shipper. Retrieved July 28, 2017.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Port Jersey. |
- The Port of New York and New Jersey
- GCT Bayonne
- New York New Jersey Rail
- Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) No. NJ-49, "Greenville Yard"
- Container terminals
- Economy of Jersey City, New Jersey
- Geography of Hudson County, New Jersey
- Historic American Engineering Record in New Jersey
- Neighborhoods in Hudson County, New Jersey
- Piers in New Jersey
- Port Authority of New York and New Jersey
- Port of New York and New Jersey
- Ports and harbors of New Jersey
- Transportation buildings and structures in Hudson County, New Jersey
- 1976 establishments in New Jersey

