Posen-West Prussia
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
| Frontier March of Posen-West Prussia Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Prussia | |||||||||||||||
| 1922–1938 | |||||||||||||||
 Flag
 Coat of arms
| |||||||||||||||
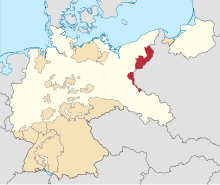 Posen-West Prussia (red) within the Free State of Prussia (light beige). | |||||||||||||||
| Capital | Schneidemühl | ||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||
• 1925 | 7,695 km2 (2,971 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||
• 1925 | 332400 | ||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||
• Created from Posen and West Prussia | 1 July 1922 | ||||||||||||||
• Ruled by Brandenburg | 1934 | ||||||||||||||
| 1 October 1938 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Today part of | show
| ||||||||||||||
The Frontier March of Posen-West Prussia (German: Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen, Polish: Marchia Graniczna Poznańsko-Zachodniopruska) was a province of Prussia from 1922 to 1938. Posen-West Prussia was established in 1922 as a province of the Free State of Prussia within Weimar Germany, formed from merging three remaining non-contiguous territories of Posen and West Prussia, which had lost the majority of their territory to the Second Polish Republic and Free City of Danzig in the Treaty of Versailles. From 1934, Posen-West Prussia was de facto ruled by Brandenburg until it was dissolved by Nazi Germany, effective 1 October 1938 and its territory divided between the Prussian provinces of Pomerania, Brandenburg and Silesia.[1] Schneidemühl (present-day Piła) was the provincial capital. Today, the province is entirely contained within the modern state of Poland.
Background[]
The lands had been part of the Greater Poland and East Pomeranian (Pomerelian) regions, which until the late 18th century partitions of Poland had been incorporated into the Poznań and Pomeranian Voivodeships of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Kingdom of Prussia had established the West Prussian province on Pomerelian and Greater Polish territories annexed during the 1772 First Partition, followed by the annexation of remaining Greater Poland in the Second Partition of 1793, which ended the existence of the Polish state.
After the Napoleonic Wars and the Congress of Vienna in 1815, Prussia maintained the acquired lands, that however still lay beyond the borders of the German Confederation. Their population was predominantly Catholic and Polish-speaking, while a sizable Protestant German minority settled mainly in the western parts. The annexed lands were internally re-arranged within the West Prussia Province and the Greater Polish Grand Duchy of Posen, which finally lost its semi-autonomous status after the failed Greater Poland Uprising of 1848. With Prussia, these provinces became part of the unified German Empire in 1871. Ethnic tensions were exacerbated by the Germanisation policies of the Berlin government and the anti-Catholic Kulturkampf measures enacted by Chancellor Otto von Bismarck.
The territory of the march did not include the Posen city or any ancient Prussian territory.
History[]

Upon the German defeat in World War I, another Greater Poland Uprising broke out in 1918, which aimed to incorporate the lands once annexed by Prussia into a re-established Polish state. The forces of the Polish Military Organisation were able to oust the German administration from the bulk of the Greater Polish lands, whereafter the Posen governor (Landeshauptmann) Ernst von Heyking was forced to retire to Meseritz (Międzyrzecz) and de facto only ruled over the far western, predominantly German settled districts at the border with the adjacent Prussian provinces of Pomerania, Brandenburg and Silesia.
The Polish advance was halted, after the German forces had re-organised in several Freikorps units and the demarcation line became the basis of the ruling by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, adjudicating the parts occupied by Polish forces uti possidetis to the Second Polish Republic. The governmental power of the German administration was confined to the smaller western parts of Posen and West Prussia, the Prussian state government was represented by the former Bromberg supervisor (Regierungspräsident) Friedrich von Bülow, who relocated his administrative seat to Schneidemühl. With the entry into force of the German Ostmark law on 1 July 1922, the province was created out of those smaller western parts of former Posen and West Prussia that remained with the Weimar Republic.
In view of the previous clashes of arms and the "lost" territories, the remaining German population from the beginning had a strong nationalistic attitude, with the national conservative German National People's Party (DNVP) emerging as the strongest political power in the provincial elections. Friedrich von Bülow, himself a member of the national liberal German People's Party, remained Oberpräsident until his retirement in 1933, whereafter he was succeeded by the Meseritz DNVP politician Hans von Meibom. After the DNVP dissolved in the course of the Nazi Gleichschaltung process, von Meibom was disempowered and replaced by the Nazi Oberpräsident of neighbouring Brandenburg, Wilhelm Kube. Kube, notorious for his corruption, ruled over both provinces until he was deposed after entering into a conflict with the Nazi jurist Walter Buch, father-in-law of mighty Martin Bormann. Posen-West Prussia was further on ruled with Brandenburg under Nazi Oberpräsident Emil Stürtz until it was dissolved in 1938, when its territory was divided between the adjacent provinces of Silesia, Pomerania and Brandenburg.[citation needed]
Subdivision[]

Despite the name, the city of Posen, Polish: Poznań, was no longer part of the province, as it had become the capital of the re-established Greater Polish Poznań Voivodeship of the Second Polish Republic. The capital of the Prussian Posen-Westpreußen province and seat of the Oberpräsident supervisor was Schneidemühl. The seat of the province's Landeshauptmann elected by the Landtag assembly remained at Meseritz.
Regierungsbezirk Schneidemühl[]
- former Province of Posen:
- Urban district (Stadtkreis)
- Schneidemühl (formerly Bromberg Region)
- Rural districts (Kreise)
- Bomst (formerly Posen Region), seat at Bomst (now Babimost)
- Fraustadt (formerly Posen Region), seat at Fraustadt (now Wschowa)
- Meseritz (formerly Posen Region), seat at Meseritz (now Międzyrzecz)
- Netzekreis (formerly parts of the Czarnikau, Filehne and Kolmar districts in Bromberg Region), seat at Schönlanke (now Trzcianka)
- Schwerin an der Warthe (formerly Posen Region), seat at Schwerin an der Warthe (now Skwierzyna)
- former West Prussia:
Rural districts (Kreise)
- Deutsch Krone (formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Deutsch Krone (now Wałcz)
- Flatow (formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Flatow (now Złotów)
- Schlochau (formerly Marienwerder Region), seat at Schlochau (now Człuchów)
Administration[]

The office of an Oberpräsident (i.e. upper president) appointed by the Prussian state government had to carry out central prerogatives on the provincial level and to supervise the implementation of central policy on the lower levels of administration.
As to common interests and tasks to be fulfilled on the provincial level, such as schools, traffic installations, hospitals, cultural institutions, sanitary premises, jails etc., the urban and rural districts (Kreise) within each province (sometimes within each government region) formed a corporation with common assets to these ends, called Provinzialverband (provincial association, or – within government regions or smaller entities – Bezirksverband or Kommunalverband, i.e. municipal or regional association). Since 1875 all provinces had this double identity, being based on central Prussian prerogatives from above, on the one hand, and being bottom-up corporations of province-wide or region-wide self-rule, on the other hand. Initially, the assemblies of the urban and rural districts elected representatives for the provincial diets (Provinziallandtage; or as to regional diets, the so-called Kommunallandtage), which were thus indirectly elected.
After the end of the Prussian monarchy, the provincial or regional diets were all directly elected by the citizens of the provinces (or regions, respectively), with direct elections first held in 1921 and 1922. These parliaments legislated within the competences transferred to the provincial or regional associations. Before the formal establishment of the new Province, the rural and urban district assemblies elected representatives for the Kommunallandtag Posen-West Prussia, legislating within the competences of the former Posen and West Prussia provincial associations and its premises within the territory of the future Posen-West Prussia. After the formal formation of the province, its parliament was called the provincial diet of Posen-West Prussia which elected a provincial executive body (government), the provincial committee (Provinzialausschuss), and a head of province, the Landeshauptmann ("Land Captain").[2]
Oberpräsident[]
- 1922–1933: , DVP
- 1933–1934: , DNVP
- 1934–1936: Wilhelm Kube, NSDAP (acting), Oberpräsident of Brandenburg
- 1936–1938: Emil Stürtz, NSDAP, Oberpräsident of Brandenburg
Landeshauptmann[]
- 1922–1933: , SPD
- 1933–1938: , NSDAP
Population[]
- 1910: 309,200 (in areas which later became parts of this province)
- 1919: 326,900
- 1925: 332,400
- 1933: 470,600
Polish minority[]
After the Treaty of Versailles came into force, some members of the local Polish minority emigrated to Poland. In 1925, 13,284 people declared themselves to be either Polish-speaking or bilingual German/Polish. This corresponded to a population share of 4.3%. The share of the vote of the Polish-Catholic People's Party was stable at around 3% in all state and Reichstag elections in the Weimar Republic. The settlement centers of the Polish minority were unevenly distributed. According to the census of 1925, the districts of Bomst (20.6%), Flatow (16.8%) and Meseritz (5.8%) had the highest proportions of Polish speakers (including bilinguals). A special achievement of the Polish minority was the establishment of a network of Polish private schools.[3]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Werner Buchholz: Pommern, Siedler, 1999, p.511, ISBN 3-88680-272-8
- ^ In some Prussian provinces the same office continued to be called Landesdirektor according to the naming usual until the 1880s. Cf. article: "Landesdirektor", in: Der Große Brockhaus: Handbuch des Wissens in zwanzig Bänden: 21 vols.; Leipzig: Brockhaus, 151928–1935; vol. 11 (1932), p. 71.
- ^ "De Gruyter". De Gruyter. Retrieved 2021-03-14.
- States and territories established in 1922
- States and territories disestablished in 1938
- Posen-West Prussia
- Provinces of Prussia
- Former administrative regions of Greater Poland
- 1922 establishments in Germany
- 1938 disestablishments in Germany