Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Francisco
Archdiocese of San Francisco Archidiœcesis Sancti Francisci Arquidiócesis de San Francisco | |
|---|---|
 Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption | |
 Coat of arms | |
| Location | |
| Country | |
| Territory | Counties of San Francisco, San Mateo, Marin |
| Ecclesiastical province | Province of San Francisco |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 6,023 km2 (2,325 sq mi) |
| Population - Total - Catholics (including non-members) | (as of 2017) 1,776,095 441,736[citation needed] (24.9%) |
| Information | |
| Denomination | Catholic |
| Sui iuris church | Latin Church |
| Rite | Roman Rite |
| Established | July 29, 1853 |
| Cathedral | Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption |
| Co-cathedral | Old Saint Mary's Cathedral |
| Patron saint | St. Francis of Assisi |
| Current leadership | |
| Pope | Francis |
| Archbishop | Salvatore Cordileone |
| Bishops emeritus | Ignatius C. Wang Auxiliary Bishop Emeritus of San Francisco William J. Justice Auxiliary Bishop Emeritus of San Francisco |
| Map | |
 | |
| Website | |
| sfarchdiocese.org | |
The Archdiocese of San Francisco (Latin: Archdiœcesis Sancti Francisci; Spanish: Archidiócesis de San Francisco) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in the northern California region of the United States. It covers the City and County of San Francisco and the Counties of Marin and San Mateo.[1] The Archdiocese of San Francisco was canonically erected on July 29, 1853, by Pope Pius IX and its cathedral is the Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption.
This archdiocese is the metropolitan see of a province which also has the dioceses of Honolulu (Hawaii), Las Vegas (Nevada), Reno (Nevada), Salt Lake City (Utah), Oakland (California), San Jose (California), Santa Rosa (California), Sacramento (California), and Stockton (California).
History[]
The first church in the Archdiocese of San Francisco is older than the Archdiocese itself; Mission San Francisco de Asís was founded on June 29, 1776 by Franciscan Friars. The mission church that stands today was completed in 1791 and attached next door is Mission Dolores Basilica. The Franciscans who founded the mission also are credited with naming the City and County of San Francisco, and the entire region, after their patron, Saint Francis of Assisi.[2][3]
From his installation on February 15, 2006, until the acceptance of his resignation on July 27, 2012, the archdiocese was led by Archbishop (now Emeritus) George Hugh Niederauer, formerly the bishop of the Diocese of Salt Lake City. The auxiliary bishop of the archdiocese was William J. Justice;[4] until his retirement in November 2017.[5] Robert W. McElroy[6] was auxiliary bishop from 2010 to 2015 before leaving to become Bishop of San Diego. On July 27, 2012, the Holy See announced that it had accepted the retirement of Niederauer and appointed Salvatore J. Cordileone as new archbishop of San Francisco, installed on October 4, 2012, the patronal Feast day of Saint Francis of Assisi at the Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption.[7][8] He had previously been Bishop of Oakland, California.[9]
The See of San Francisco is administered by the Archbishop of San Francisco, who as metropolitan oversees the entire ecclesiastical province of San Francisco. Its suffragans include the Dioceses of Honolulu, Las Vegas, Oakland, Reno, Sacramento, Salt Lake City, San Jose, Santa Rosa, and Stockton.
San Francisco once included among its suffragans the now-Metropolitan Archdiocese of Agaña, Guam and the former dioceses of Grass Valley, Diocese of Los Angeles-San Diego, Monterey, Monterey-Fresno, and Diocese of Monterey-Los Angeles.
The Chancellery Office of the Archdiocese of San Francisco, originally located in 1853 at California and Dupont Streets, moved in 1891 to 1100 Franklin Street, in 1955 re-located to 445 Church Street, on the Mission Dolores Basilica property. The present headquarters, as of 2001 of the Archdiocese of San Francisco are located at One Peter Yorke Way, a short street in San Francisco named after Father Peter Yorke, an Irish-American Catholic priest. Peter Yorke Way and Starr King Way are off of Geary Street as it becomes Geary Boulevard.
From May to December 2019, the Archdiocese of San Francisco provided numerous documents to California State Attorney Xavier Becerra in preparation for a series of pending lawsuits which are expected to be filed after a new California law which will temporarily remove the statute of limitations goes into effect on January 1, 2020.[10][11] The Archdiocese of San Francisco is one of six Catholic dioceses throughout the state of California which is expected to be subpoenaed in the upcoming lawsuits.[10][11]
Bishops[]
The lists of archbishops, coadjutor archbishops, and auxiliary bishops and their terms of service, followed by other priests of this diocese who became bishops:
Archbishops of San Francisco[]
- Joseph Sadoc Alemany y Conill, O.P. (1853–1884)
- Patrick William Riordan (1884–1914)
- Edward Joseph Hanna (1915–1935)
- John Joseph Mitty (1935–1961)
- Joseph Thomas McGucken (1962–1977)
- John Raphael Quinn (1977–1995)
- William Joseph Levada (1995–2005), appointed Prefect of the Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith (elevated to Cardinal in 2006)
- George Hugh Niederauer (2006–2012)
- Salvatore Joseph Cordileone (2012–present)[12]
Coadjutor Archbishops[]
- Patrick William Riordan (1883–1884)
- George Thomas Montgomery (1902–1907), did not succeed to see
- John Joseph Mitty (1932–1935)
Auxiliary bishops[]
- Denis Joseph O'Connell (1908–1912), appointed Bishop of Richmond
- Edward Joseph Hanna (1912–1914), appointed Archbishop here
- Thomas Arthur Connolly (1939–1948), appointed Coadjutor Bishop and later Bishop and Archbishop of Seattle
- Hugh Aloysius Donohoe (1947–1962), appointed Bishop of Stockton
- James Thomas O'Dowd (1948–1950)
- Merlin Joseph Guilfoyle (1950–1969), appointed Bishop of Stockton
- William Joseph McDonald (1967–1979)
- Mark Joseph Hurley (1968–1969), appointed Bishop of Santa Rosa
- Norman Francis McFarland (1970–1974), appointed Bishop of Reno-Las Vegas
- Francis Anthony Quinn (1978–1979), appointed Bishop of Sacramento
- Roland Pierre DuMaine (1978–1981), appointed Bishop of San Jose in California
- Daniel Francis Walsh (1981–1987), appointed Bishop of Reno and later Bishop of Las Vegas and Bishop of Santa Rosa in California
- Carlos Arthur Sevilla, S.J. (1988–1996), appointed Bishop of Yakima
- Patrick Joseph McGrath (1988–1998), appointed Coadjutor Bishop and later Bishop of San Jose in California
- John Charles Wester (1998–2007), appointed Coadjutor Bishop and Bishop of Salt Lake City and later Archbishop of Santa Fe
- Ignatius Chung Wang (2002–2009)
- William Joseph Justice (2008–2017)
- Robert Walter McElroy (2010–2015), appointed Bishop of San Diego
- Robert Francis Christian, O.P. (2018–2019)
Other priests of this diocese who became bishops[]
- Lawrence Scanlan, appointed Vicar Apostolic of Utah in 1887 and later Bishop of Salt Lake City
- Patrick Joseph James Keane, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of Sacramento in 1920 and later Bishop of Sacramento
- James Joseph Sweeney, appointed Bishop of Honolulu in 1941
- John Joseph Scanlan, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of Honolulu in 1954 and later Bishop of Honolulu
- William Joseph Moran, appointed auxiliary bishop of United States of America Military in 1965
- Francis Thomas Hurley, appointed Auxiliary Bishop in 1970 and Bishop of Juneau and later Archbishop of Anchorage
- John Stephen Cummins, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of Sacramento in 1974 and later Bishop of Oakland
- Richard John Garcia (priest here, 1973-1981), appointed Auxiliary Bishop of Sacramento in 1997 and later Bishop of Monterey California
- Randolph Roque Calvo, appointed Bishop of Reno in 2005
- Thomas Anthony Daly, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of San Jose in California in 2011 and later Bishop of Spokane
- Steven Joseph Lopes, appointed Bishop of the Personal Ordinariate of the Chair of Saint Peter in 2015
Cathedrals[]
- Old Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Immaculate Conception — California Street and Grant Avenue, in Chinatown (1854–1891).
- Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption — 1001 Van Ness Avenue at O'Farrell Street (1891–1962); destroyed by fire in 1962, the site of the former studios of KRON-TV.
- Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption — 1111 Gough at Geary Boulevard on Cathedral Hill; modern structure (1971–present).
Churches[]
The Archdiocese of San Francisco includes the City and County of San Francisco and the Counties of Marin and San Mateo.[13] The archdiocese includes many historic churches including Mission San Francisco de Asís, the oldest building in San Francisco, and Saints Peter and Paul Church, known as the Italian cathedral of the West. A complete list of the churches of the archdiocese is found at List of churches in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Francisco.
Education[]
All full-time faculty, librarians, and counselors at Archbishop Riordan, Junipero Serra, Marin Catholic, and Sacred Heart Cathedral high schools are represented by The San Francisco Archdiocesan Federation of Teachers, Local 2240, a labor union affiliate of the California Federation of Teachers (AFT, AFL-CIO), and have a collective bargaining agreement with the Archdiocese of San Francisco. The CBA governs the terms of their employment.
Secondary schools[]
- Marin County
- Marin Catholic High School (Kentfield in unincorporated Marin County)
- San Domenico School (San Anselmo)
- San Francisco
- Archbishop Riordan High School
- Convent of the Sacred Heart High School
- Immaculate Conception Academy
- Mercy High School (San Francisco) (Closed)
- Sacred Heart Cathedral Preparatory
- St. Ignatius College Preparatory
- Stuart Hall High School
- San Mateo County
- Junípero Serra High School (San Mateo)
- Mercy High School (Burlingame)
- Notre Dame High School (Belmont)
- Sacred Heart Preparatory (Atherton)
- Woodside Priory School, Portola Valley
Seminaries[]
- St. Joseph's Seminary (Mountain View, California) (closed)
- Saint Patrick's Seminary and University (Menlo Park, California)
Recognized lay ecclesial movements[]
- Fraternity of Communion and Liberation (CL). CL is an ecclesial association of Pontifical Right. Meetings are held weekly at St. Thomas More Church and the National Shrine of Saint Francis of Assisi.
Province of San Francisco[]
- See List of the Catholic bishops of the United States
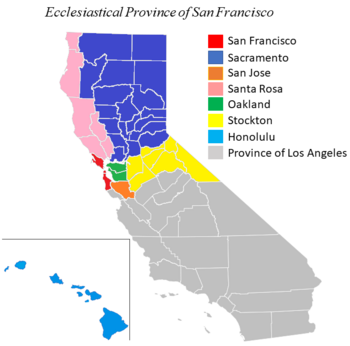
The Metropolitan Ecclesiastical Province of San Francisco covers Northern California north of the Monterey Bay, as well as all of Hawaii, Nevada, and Utah. The Archbishop of San Francisco, who is ex officio metropolitan bishop of the Province of San Francisco, has limited oversight responsibilities for the dioceses of Honolulu, Las Vegas, Oakland, Reno, Sacramento, Salt Lake City, San Jose, Santa Rosa, and Stockton.
See also[]
- Catholic Church by country
- Catholic Church in the United States
- Global organisation of the Catholic Church
- List of Roman Catholic archdioceses (by country and continent)
- List of Roman Catholic dioceses (alphabetical) (including archdioceses)
- List of Roman Catholic dioceses (structured view) (including archdioceses)
- List of the Catholic dioceses of the United States
References[]
- ^ "Catholic Hierarchy profile of the Archdiocese of San Francisco". Retrieved April 7, 2007.[self-published source]
- ^ "Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption". Retrieved April 7, 2007.
- ^ "Mission Dolores Basilica". Retrieved April 7, 2007.
- ^ "Archdiocese of San Francisco announcement of Justice becoming Auxiliary Bishop".[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Pope Francis Accepts Resignation of Auxiliary Bishop Justice of San Francisco".
- ^ "Msgr. Robert McElroy, San Mateo pastor and San Francisco native, to be auxiliary bishop". Archived from the original on 2011-07-25. Retrieved 2011-04-15.
- ^ Kuruvila, Matthai (July 27, 2012). "New S.F. archbishop appointed by pope". The San Francisco Chronicle.
- ^ catholicnews.com
- ^ "Past Bishops". Oakland, CA: Diocese of Oakland. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b https://ktla.com/2019/12/10/half-of-californias-catholic-dioceses-to-be-subpoenaed-in-priest-abuse-inquiry/
- ^ Jump up to: a b https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2019/dec/11/california-catholic-dioceses-subpoenas-sexual-abuse-investigation
- ^ "The Catholic Voice - an online publication of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Oakland". www.catholicvoiceoakland.org.
- ^ "Parish Finder". Archdiocese of San Francisco. Retrieved April 19, 2020.
External links[]
![]() Media related to Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Francisco at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Francisco at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website
- Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Assumption
- Catholic San Francisco Article on the 40th Anniversary
Coordinates: 37°47′08″N 122°25′27″W / 37.78556°N 122.42417°W
- Roman Catholic Archdiocese of San Francisco
- Religious organizations established in 1853
- Organizations based in the San Francisco Bay Area
- Roman Catholic dioceses and prelatures established in the 19th century
- Roman Catholic dioceses in the United States
- 1853 establishments in California


