Silesian Interurbans
| Silesian Interurbans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Pesa Twist in Katowice | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Upper Silesia metropolitan area, Poland | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Silesian Interurbans (Polish: Tramwaje Konurbacji Śląskiej) is one of the largest tram systems in the world and has been in existence since 1894. The system is spread over more than 50 kilometres (east-west axis) and covers thirteen towns in the Upper Silesia metropolitan area (Southern Poland) and their suburbs (Katowice, the capital town of the region, Będzin, Bytom, Chorzów, Czeladź, Dąbrowa Górnicza, Gliwice, Mysłowice, Ruda Śląska, Siemianowice Śląskie, Sosnowiec, Świętochłowice, and Zabrze, until 2006 also in Piekary Śląskie and Wojkowice), which is densely industrialised (coal, coke, steel and other industries; though decreasing since the 1990s) and inhabited by more than two million people.
Basic information[]
- Total track length: 299.7 route km (340.3 track km)[1]
- Number of routes: 29[2]
- Number of revenue vehicles: 336[3]
- Number of vehicles on-duty daily (Mon-Fri): ca. 200
- Number of depots: 5 (R-1 Będzin, R-2 Katowice-Zawodzie, R-3 Bytom-Stroszek, R-4 Gliwice, ZUR (Tram Repair Facility, ex. Chorzów-Batory Depot)
- Longest route length: 22.45 km (Route 21)
- Shortest route length: 1.34 km (Route 38)
History[]
The system was established by German Empire in 1894 as a unique 785 mm (2 ft 6+29⁄32 in) narrow gauge steam interurban railway. The first line was 36.5 km long and connected Gliwice with Piekary Śląskie through Zabrze, Chebzie, Chorzów and Bytom, another connected Katowice and Siemianowice. After four years (in 1898) electrification started. In 1912 the first short 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge line was built in Katowice. In 1913 a separate standard gauge system connecting Bytom with suburbs and villages west of the town was opened. After World War I and the Silesian Uprisings the region (and the tram network) was divided between newly independent Poland and Germany, and international services appeared (the last one ran until 1937). In 1928 another standard gauge system was established in Sosnowiec, Będzin and Dąbrowa Górnicza (the so-called Dabrowa Coal Basin - a region adjoining the Upper Silesian Coal Basin). Between 1928 and 1936 most of the original narrow gauge network was converted to standard (although the last narrow gauge line, Siemianowice Śląskie-Chorzów, remained till 1952), which allowed a connection with the new system in Sosnowiec (a service between Chorzow and Sosnowiec through Katowice was established in 1931).

During World War II the German authorities decided to merge all the systems and administrations, and they have remained as one united network to the present day (though the old boundaries are still easily traceable). The new route numbering system introduced in 1940 to integrate the systems is still used. In 1951 the system was taken over by a state-owned company () and until the 1970s it was widely extended and partly modernised, reaching its maximum length at the end of the 1970s (ca. 235 km). Since the late 1960s, the classic rolling stock has been replaced by modern cars based on PCC streetcar technology. In the 1980s some of the non-modernised, rural lines were abandoned (the longest one from Bytom to Wieszowa with a branch to Stolarzowice).

The end of the 1980s brought changes in Poland (the Round Table talks and the fall of communism), but unfortunately that did not improve the tramway service in the region – on the contrary, the condition of the tram company () had been steadily deteriorating since the middle of the 1990s. The last new line was built in 1980–1982 (between Sosnowiec and Zagórze). At the end of the 1990s the Bytom – Chorzów – Katowice line was to be upgraded to light-rail (LRT) standards. Due to a lack of funds, the investment was only partially carried out, but included the purchase of 17 new Alstom Citadis low-floor cars). The journey time on this highly overcrowded line did not change.
Present day[]

Today, Tramwaje Śląskie and ZTM are slowly reversing the effects of the lack of long-term investment. There are many renovations, and new rolling stock has been bought. In 2012 the network operator bought 30 low-floor Pesa 2012N "Twist-Step" cars, and 12 partially low-floor trams from . They were paid for in part by the European Development Fund.
Routes[]
| Line[4] | Terminus | Length | Stops | Cities | Depot | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
Gliwice Zajezdnia | Chebzie Pętla | 12.60 km | 22 | Gliwice, Zabrze, Ruda Śląska | Gliwice |
| 2 | 
|
Gliwice Zajezdnia | Bytom Plac Sikorskiego | 16.50 km | 25 | Gliwice, Zabrze | Gliwice, Stroszek |
| 3 | 
|
Mikulczyce Pętla | Makoszowy Pętla | 10.45 km | 20 | Zabrze | Gliwice |
| 4 | 
|
Gliwice Zajezdnia | Zaborze Pętla | 7.85 km | 16 | Gliwice, Zabrze | Gliwice |
| 5 | 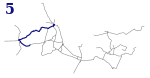
|
Bytom Plac Sikorskiego | Zaborze Pętla | 16.30 km | 24 | Zabrze, Bytom | Gliwice, Stroszek |
| 6 | 
|
Bytom Szkoła Medyczna | Brynów Centrum Przesiadkowe | 20.45 km | 45 | Bytom, Chorzów, Katowice | Stroszek, Zawodzie |
| 7 | 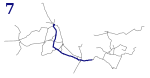
|
Bytom Plac Sikorskiego | Zawodzie Centrum Przesiadkowe | 18.55 km | 37 | Bytom, Świętochłowice, Chorzów, Katowice | Stroszek, Zawodzie |
| 9 | 
|
Chebzie Pętla | Chorzów Batory Zajezdnia | 10.70 km | 20 | Ruda Śląska, Świętochłowice, Chorzów | Gliwice |
| 11 | 
|
Chorzów Metalowców | Katowice Plac Miarki | 18.50 km | 16 | Chorzów, Katowice | Stroszek |
| 13 | 
|
Siemianowice Plac Skargi | Katowice Plac Wolności | 6.45 km | 12 | Siemianowice Śląskie, Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 14 | 
|
Brynów Centrum Przesiadkowe | Mysłowice Dworzec PKP | 15.15 km | 33 | Katowice, Mysłowice | Zawodzie |
| 15 | 
|
Katowice Plac Wolności | Zagórze Pętla | 14.75 km | 28 | Katowice, Sosnowiec | Zawodzie |
| 16 | 
|
Wełnowiec Plac Alfreda | Brynów Centrum Przesiadkowe | 8.15 km | 18 | Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 17 | 
|
Lipiny Mijanka | Chorzów Batory Zajezdnia | 9.40 km | 17 | Świętochłowice, Bytom, Chorzów | Gliwice, Stroszek |
| 19 | 
|
Stroszek Zajezdnia | Katowice Plac Wolności | 21.75 km | 43 | Bytom, Chorzów, Katowice | Stroszek, Zawodzie |
| 20 | 
|
Chorzów Batory Zajezdnia | Szopienice Pętla | 12.35 km | 25 | Chorzów, Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 21 | 
|
Milowice Pętla | Tworzeń Huta Katowice | 22.55 km | 42 | Sosnowiec, Będzin, Dąbrowa Górnicza | Będzin |
| 22 | 
|
Czeladź Kombatantów | Tworzeń Huta Katowice | 15.80 km | 26 | Czeladź, Będzin, Dąbrowa Górnicza | Będzin |
| 23 | 
|
Chorzów Stadion Śląski Pętla Zachodnia | Zawodzie Centrum Przesiadkowe | 10.40 km | 24 | Chorzów, Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 24 | 
|
Sosnowiec Ostrogórska | Konstantynów Okrzei | 3.35 km | 8 | Sosnowiec | Będzin |
| 26 | 
|
Mysłowice Dworzec PKP | Pogoń Akademiki | 12.60 km | 23 | Mysłowice, Sosnowiec | Będzin |
| 27 | 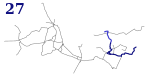
|
Kazimierz Górniczy Pętla | Osiedle Zamkowe Pętla | 18.20 km | 36 | Sosnowiec, Będzin | Będzin |
| 28 | 
|
Osiedle Zamkowe Pętla | Tworzeń Huta Katowice | 13.10 km | 23 | Będzin, Dąbrowa Górnicza | Będzin |
| 35 | 
|
Milowice Pętla | Zagórze Pętla | 8.90 km | 16 | Sosnowiec | Będzin |
| 36 | 
|
Szopienice Pętla | Brynów Centrum Przesiadkowe | 11.35 km | 26 | Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 38 | 
|
Bytom Powstańców Śląskich | Bytom Kościół św. Trójcy | 1.35 km | 5 | Bytom | Stroszek |
| 43 | 
|
Chorzów Batory Zajezdnia | Koszutka Słoneczna Pętla | 6.75 km | 15 | Chorzów, Katowice | Gliwice |
| 46 | 
|
Brynów Centrum Przesiadkowe | Koszutka Słoneczna Pętla | 5.65 km | 16 | Katowice | Zawodzie |
| 49 | 
|
Stroszek Zajezdnia | Bytom Plac Sikorskiego | 7.55 km | 16 | Bytom | Stroszek |
Rolling stock[]

| Series | Units | Seats | Low floor | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 2 | 16 | 0% | |
| 105N | 1 | 20 | 0% | |
| 105Na | 89 | 20 | 0% | |
| 105N-2k | 31 | 20 | 0% | |
| 105N-2k | 20 | 0% | ||
| 105N HF 11 AC | 45 | 20 | 0% | |
| 105NF S | 31 | |||
| 111N | 6 | 20 | 0% | |
| 116Nd Citadis | 17 | 46 | 73% | |
| 2012N Twist | 30 | 77 | 73% | Pesa |
| 2012N-10 Twist | 2 z 8 | 77 | 75% | Pesa |
| 2017N Twist | 15 z 32 | 59 | 65,6% | Pesa |
| E1 | 18 | 40 | 0% | SGP / Lohner |
| Pt8 | 8 | 62 | 0% | Düwag |
| Ptm | 7 | 57 | 23% | Düwag |
| MF 16 AC BD Beta | 12 | 46 | 26% | |
| MF 10 AC Beta | 13 | ≥ 18 | ≥ 20% | |
| MF 11 AC BD Beta | 2 | ≥ 18 | ≥ 20% |
Museum cars[]
| Series | Nr | Year | Manufactuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1100 | 1953 | Konstal |
| 1167 | 1957 | Konstal | |
| 1263 | 1959 | Konstal | |
| 13N | 308 | 1967 | Konstal |
| 102N | 8 | 1970 | Konstal |
| 183 | 1970 | Konstal | |
| 105N | 338 | 1975 | Konstal |
| 105N | 546 | 1978 | Konstal |
References[]
- ^ "Infrastruktura techniczna" (in Polish). Tramwajów Śląskich. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "KZK GOP" (in Polish). Komunikacyjny Związek Komunalny GOP. 27 September 2015. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "Tramwajach Śląskich" (in Polish). Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "ZTM Schematy sieci i mapy". rj.metropoliaztm.pl. Retrieved 2021-02-15.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trams in Upper Silesian urban area. |
- "Zarząd Transportu Metropolitalnego website". Local authority website
- "Official website" (in Polish).
- Tram transport in Poland
- Interurban railways
- Transport in Katowice
- Silesian Voivodeship
- 785 mm gauge railways in Poland
















