Slovak Armed Forces
| Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic | |
|---|---|
| Ozbrojené sily Slovenskej Republiky | |
 The official emblem of the Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic | |
| Motto | "Česť a sláva" (Honour and Glory) |
| Founded | 1 January 1993 |
| Service branches | |
| Headquarters | Bratislava, Slovakia |
| Website | Official website |
| Leadership | |
| Commander-in-chief | |
| Minister of defense | Jaroslav Naď |
| Chief of the General Staff | General Daniel Zmeko |
| Manpower | |
| Conscription | Abolished in 2006 |
| Active personnel | 18,531[1] |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | €1.67 billion ($2.01 billion) (2021)[2] |
| Percent of GDP | 1.75% (2021)[3] |
| Industry | |
| Foreign suppliers | |
| Related articles | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of Slovakia |
The Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic were divided from the Czechoslovak army after dissolution of Czechoslovakia on January 1, 1993. Slovakia joined NATO on 29 March 2004.[5] From 2006 the army transformed into a fully professional organization and compulsory military service was abolished.[6][7][8] Slovak armed forces numbered 18,531 uniformed personnel and 4,208 civilians in 2021.[9]
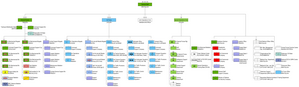
Ground forces[]
- Ground Forces Command
- 1st Mechanized Brigade
- 2nd Mechanized Brigade
- Combat Service Support Brigade
Air force[]
The Slovak Air Force, officially the Air Force of the Armed Forces of the Slovak Republic, has been defending Slovak airspace since 1939. Slovak Air Force currently comprises one wing of fighters and one wing of utility helicopters, and one SAM brigade. It operates 20 pieces aircraft, as well as 10 helicopters from 3 air bases: Malacky Air Base, Sliač Air Base, Prešov Air Base. The Air Force is currently part of the NATO Integrated Air and Missiles Defense System – NATINADS.
Special Operations Forces[]
In the future will be added Cyber Defence Unit and SOF Training base.
Missions[]
Slovakia has 169 military personnel deployed in Cyprus for UNFICYP United Nations led peace support operations.[12][13] Slovakia committed to increase the number of its troops in Afghanistan to around 45 men by the end of 2016.[14] Slovakia has 41 troops deployed in Bosnia and Herzegovina for EUFOR Althea.[15] Slovak troops were withdrawn from Kosovo because the Slovak Armed Forces set its priority to focus mainly on an Afghanistan NATO led mission.[16][17] Since the independence of Slovakia in 1993, there have been 60 uniformed personnel deaths in the line of service to the United Nations and NATO (as of April 30, 2018).[18][19][20]
Gallery[]

Armoured vehicle Tatrapan

Multiple rocket launcher RM-70 MODULAR
Slovak upgraded multirole fighter aircraft MiG-29AS

A Let L-410 Turbolet of the Slovak Air Force

Long range surface-to-air missile system S-300PMU

Slovak 5th Special Forces Regiment operating in eastern Afghanistan

In eastern Afghanistan operation

A member of the 5th Special Forces Regiment conducts security inside HMMWV

Soldiers of the 12th Mechanized Battalion
References[]
- ^ https://www1.pluska.sk/spravy/z-domova/vlada-predstavila-novy-plan-toto-udeje-bezpecnostnymi-silami
- ^ https://www.webnoviny.sk/armada-dostane-z-rozpoctu-viac-slovensko-smeruje-k-dvom-percentam-hdp-vynalozenym-na-obranu/
- ^ https://www.webnoviny.sk/armada-dostane-z-rozpoctu-viac-slovensko-smeruje-k-dvom-percentam-hdp-vynalozenym-na-obranu/
- ^ "Work, Slovakian Defense Minister Review Bilateral Relationship". Defense.gov. Archived from the original on 1 September 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "NATO Update: Seven new members join NATO - 29 March 2004". Nato.int. Archived from the original on 15 March 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "kniha o obrane SR 2013"" (PDF). Lt.justice.gov.sk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Financial and Economic Data Relating to NATO Defence" (PDF). Nato.int. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Slovenská armáda je v kritickom stave, má to fatálne následky". Komentare.sme.sk. Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ https://www1.pluska.sk/spravy/z-domova/vlada-predstavila-novy-plan-toto-udeje-bezpecnostnymi-silami
- ^ "Contracts for April 20, 2017". Defense.gov. Archived from the original on 18 September 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Colt Capitalizes on Foreign Military Sales Program - The Firearm Blog". Thefirearmblog.com. 27 April 2017. Archived from the original on 1 June 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "United Nations Mission´s Summary detailed by Country 2014" (PDF). Un.org. 30 June 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 March 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 October 2016. Retrieved 7 October 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Pôsobenie Slovenska v zahraničných misiách a operáciách" (PDF). Cenaa.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 December 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ Jasmin. "EUFOR "Exercise Quick Response 2" begins". EUFOR ALTHEA. Archived from the original on 21 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "B92 - Info - Slovakia pulling soldiers from Kosovo". B92. Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "Účasť Slovenska v mierových operáciách NATO - Slovensko v NATO - Zahraničná politika - Ministerstvo zahraničných vecí a európskych záležitostí Slovenskej republiky". Mzv.sk. Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "Two Slovakian Soldiers Killed in Kabul Suicide Car Bomb". Defense News. Archived from the original on 10 January 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "20 Years of U.S. - Slovak Diplomatic Relations". Usembassy.sk. Archived from the original on 5 August 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- ^ "Readout of Secretary of Defense Chuck Hagel". defense.gov. Archived from the original on 20 March 2017. Retrieved 19 March 2017.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Military of Slovakia. |
- Military of Slovakia
- Permanent Structured Cooperation












