Solar eclipse of August 12, 2026
| Solar eclipse of August 12, 2026 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.8977 |
| Magnitude | 1.0386 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 138 sec (2 m 18 s) |
| Coordinates | 65°12′N 25°12′W / 65.2°N 25.2°W |
| Max. width of band | 294 km (183 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 17:47:06 |
| References | |
| Saros | 126 (48 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9566 |
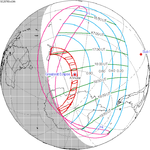
A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Wednesday, August 12, 2026, 2 days past perigee (Perigee on Monday, August 10, 2026), in North America and Europe. The total eclipse will pass over the Arctic, Greenland, Iceland, Atlantic Ocean and northern Spain. The points of greatest duration and greatest eclipse will be just 45 km off the western coast of Iceland by 65°10.3' N and 25°12.3' W, where the totality will last 2m 18.21s. It will be the first total eclipse visible in Iceland since June 30, 1954, also Solar Saros series 126 (descending node), and the only one to occur in the 21st century as the next one will be in 2196.
Occurring only 2.3 days after perigee (Perigee on August 10, 2026), the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger. Lunar Perigee will occur on Monday, August 10, 2026, two days before the total solar eclipse.
The total eclipse will pass over northern Spain from the Atlantic coast to the Mediterranean coast as well as the Balearic Islands. The total eclipse will be visible from the cities of Valencia, Zaragoza, Palma and Bilbao but both Madrid and Barcelona will be just outside the path of totality.
The last total eclipse in continental Europe occurred on March 29, 2006 and in continental part of European Union it occurred on August 11, 1999. The last total solar eclipse happened in Spain on August 30, 1905 and followed a similar path across the country. The next total eclipse visible in Spain will happen less than a year later on 2 August 2027. A partial eclipse will cover more than 90% of the area of the sun in Ireland, Great Britain, Portugal, France, Italy, the Balkans and North Africa and to a lesser extent in most of Europe, North Africa and North America.
Circumstances[]
The eclipse path proceeds from North Siberia throughout the Arctic Region, Iceland, eastern Atlantic to Spain and Mediterranean.
Solar eclipse and the aurora borealis[]
In the North Russia area where totality will begin at sunrise, the aurora borealis could also be visible up to the beginning of the nautical twilight, depending on the intensity of the auroral activity at that date. If an extremely high intensity geomagnetic storm takes place simultaneously, there might be chances of seeing the aurora simultaneously with the eclipsed sun. In the east of Taymyr Peninsula the total phase will start at August 13 at 0:00 local time during midnight sun.[1]
Solar eclipse below the horizon[]
Due to the considerable eclipse magnitude (more than 0,8), observers where the totally eclipsed sun is just below the horizon will have the chance to observe the lunar shadow in the high atmosphere, as well as shortened civil twilight and extended nautical twilight. The darkening of the twilight sky could improve the chances of observing the inner Zodiacal light.[2]
Images[]

Animated path
Related eclipses[]
Eclipses in 2026[]
- An annular solar eclipse on February 17.
- A total lunar eclipse on March 3.
- A total solar eclipse on August 12.
- A partial lunar eclipse on August 28.
Solar eclipses 2026–2029[]
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2026–2029 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| 121 | 2026 February 17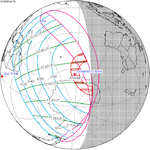 Annular |
126 | 2026 August 12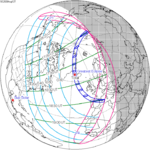 Total | |||
| 131 | 2027 February 6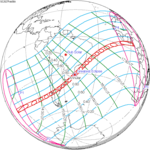 Annular |
136 | 2027 August 2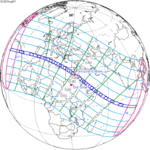 Total | |||
| 141 | 2028 January 26 Annular |
146 | 2028 July 22 Total | |||
| 151 | 2029 January 14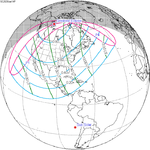 Partial |
156 | 2029 July 11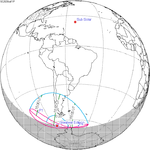 Partial | |||
| Partial solar eclipses on June 12, 2029, and December 5, 2029, occur in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Saros 126[]
It is a part of Saros cycle 126, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on March 10, 1179. It contains annular eclipses from June 4, 1323 through April 4, 1810, hybrid eclipses from April 14, 1828 through May 6, 1864 and total eclipses from May 17, 1882 through August 23, 2044. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on May 3, 2459. The longest duration of central eclipse (annular or total) was 6 minutes, 30 seconds of annularity on June 26, 1359. The longest duration of totality was 2 minutes, 36 seconds on July 10, 1972. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s descending node.
| Series members 42–52 occur between 1901 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 June 8, 1918 |
 June 19, 1936 |
 June 30, 1954 |
| 45 | 46 | 47 |
 July 10, 1972 |
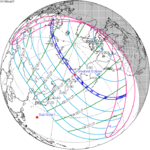 July 22, 1990 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 48 | 49 | 50 |
 August 12, 2026 |
 August 23, 2044 |
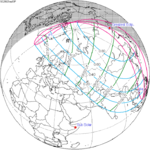 September 3, 2062 |
| 51 | 52 | |
 September 13, 2080 |
 September 25, 2098 | |
Metonic series[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 1, 2011 and June 1, 2087 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 31 – June 1 | March 19–20 | January 5–6 | October 24–25 | August 12–13 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 June 1, 2011 |
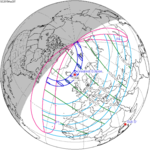 March 20, 2015 |
 January 6, 2019 |
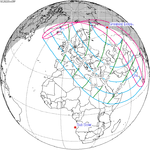 October 25, 2022 |
 August 12, 2026 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 June 1, 2030 |
 March 20, 2034 |
 January 5, 2038 |
 October 25, 2041 |
 August 12, 2045 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 31, 2049 |
 March 20, 2053 |
 January 5, 2057 |
 October 24, 2060 |
 August 12, 2064 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 31, 2068 |
 March 19, 2072 |
 January 6, 2076 |
 October 24, 2079 |
 August 13, 2083 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 June 1, 2087 |
 October 24, 2098 |
|||
References[]
- ^ 12–13 August, 2026. — Total Solar Eclipse — 75°41'N, 113°22'E. timeanddate.com
- ^ Guliaev, R. A. (1992). "On a possible use of total solar eclipse below the horizon for observations of the inner zodiacal light (as applied to the eclipse of 30 June, 1992)". Solar Physics. 138 (1): 209–211. Bibcode:1992SoPh..138..209G. doi:10.1007/BF00146206.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2026 August 12. |
- 2026 in science
- 21st-century solar eclipses
- Future solar eclipses



