Solar eclipse of March 9, 2016
| Solar eclipse of March 9, 2016 | |
|---|---|
 Totality with Baily's beads from Balikpapan, Indonesia | |
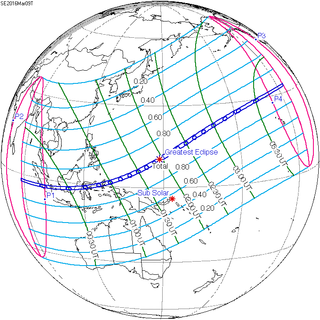 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | 0.2609 |
| Magnitude | 1.045 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 249 sec (4 m 9 s) |
| Coordinates | 10°06′N 148°48′E / 10.1°N 148.8°E |
| Max. width of band | 155 km (96 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 1:58:19 |
| References | |
| Saros | 130 (52 of 73) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9543 |
A total solar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on March 8–9, 2016. If viewed from east of the International Date Line (for instance from Hawaii), the eclipse took place on March 8th (Tuesday) (local time) and elsewhere on March 9th (Wednesday). A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's and the apparent path of the Sun and Moon intersect, blocking all direct sunlight and turning daylight into darkness; the sun appears to be black with a halo around it. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse of March 8–9, 2016 had a magnitude of 1.0450 visible across an area of Pacific Ocean, which started in the Indian Ocean, and ended in the northern Pacific Ocean.[1]
It was the 52nd eclipse of the 130th Saros cycle, which began with a partial eclipse on August 20, 1059 and will conclude with a partial eclipse on October 25, 2394.
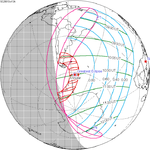
The eclipse was clearly visible in many parts of Indonesia, including Central Sulawesi and Ternate, but obscured by clouds and smokes in Palembang, the largest city on the path of totality.[2][3] The eclipse coincided with Nyepi, a public holiday in Indonesia and the end of the Balinese saka calendar. Because Nyepi is normally a day of silence, Muslims in Bali had to be given special dispensation to attend special prayer services during the eclipse.[4]
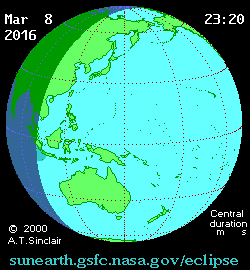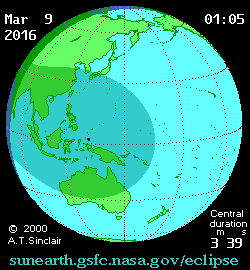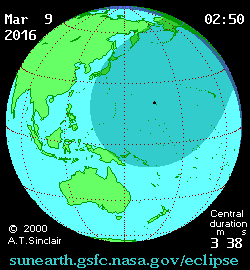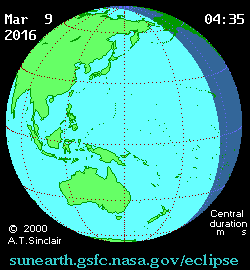
Path of the eclipse[]
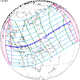
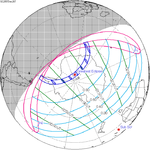
On March 9, 2016, a large area of the Pacific, covering Indonesia, Borneo, but also large parts of Southeast Asia and Australia, witnessed a partial solar eclipse. It was total in multiple islands of Indonesia, three atolls of the Federated States of Micronesia (Eauripik, Woleai and Ifalik) and the central Pacific, starting at sunrise over Sumatra and ending at sunset north of Hawaii. In the Eastern Pacific Ocean, the totality exceeded a duration of more than 4 minutes.[5]
In most parts of India and Nepal, the sunrise was partially eclipsed, and much of East Asia witnessed more than 50% partial eclipse.[5][6]
The largest city along the path of totality was Palembang in southern Sumatra (423 km (263 mi) from Jakarta and 478 km (297 mi) from Singapore).[3]
In order to watch the total solar eclipse, Alaska Airlines adjusted the flight plan for Flight 870. The flight passed through the umbral shadow about 695 miles (1,118 km) north of Hawaii.[7]
Maps[]
|
 Animation assembled from 13 images acquired by NASA's Earth Polychromatic Imaging Camera. |
 Path of the eclipse in Southeast Asia | |
 Path of the eclipse in Indonesia | |
Gallery[]
Partial in Jakarta, Indonesia, 0:23 UTC

Partial in Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 0:23 UTC

Partial in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 0:26 UTC

Partial in Marina Bay, Singapore, 0:26 UTC

Partial in Dompu, Indonesia, 0:38 UTC

Diamond ring effect in Tanjung Pandan, Indonesia. 0:42 UTC

Partial in Khon Kaen University, Thailand, 0:46 UTC
Partial in Nonthaburi, Thailand, 0:52 UTC

Partial in Jerudong, Brunei, 1:01 UTC

Partial in Langkawi, Malaysia, 1:16 UTC
Partial in Hefei, China, 1:40 UTC
Related eclipses[]
Tzolkinex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of January 26, 2009
- Followed: Solar eclipse of April 20, 2023
Half-Saros cycle[]
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of March 3, 2007
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of March 14, 2025
Tritos[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 8, 2005
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 6, 2027
Solar Saros 130[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 26, 1998
- Followed: Solar eclipse of March 20, 2034
Inex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of March 29, 1987
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 16, 2045
Triad[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of May 9, 1929
- Followed: Solar eclipse of January 8, 2103
This solar eclipse is related to other eclipses including in the current set predictions between 2015 and 2018. It is also a part of long period Saros cycle 130, and a 19-year Metonic cycle.
Eclipses of 2016[]
- A total solar eclipse on March 9.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on March 23.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on August 18.
- An annular solar eclipse on September 1.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on September 16.
Solar eclipses descending node 2015-2018[]
- Saros 120: Total Solar Eclipse March 20, 2015
- Saros 130: Total Solar Eclipse March 8–9, 2016
- Saros 140: Annular Solar Eclipse February 26, 2017
- Saros 150: Partial Solar Eclipse February 15, 2018
Solar eclipses 2015–18[]
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[8]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2015–2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
120 Longyearbyen, Svalbard |
2015 March 20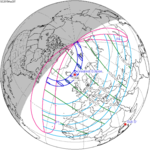 Total |
0.9453 | 125 Solar Dynamics Observatory |
2015 September 13  Partial |
-1.1004 | |
130 Balikpapan, Indonesia |
2016 March 9 Total |
0.2609 | 135 L'Étang-Salé, Réunion |
2016 September 1 Annular |
-0.3330 | |
140 Partial from Buenos Aires |
2017 February 26 Annular |
-0.4578 | 145 Casper, Wyoming |
2017 August 21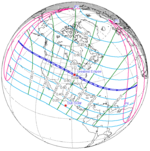 Total |
0.4367 | |
150 Partial from Olivos, Buenos Aires |
2018 February 15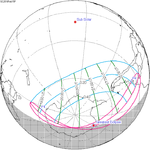 Partial |
-1.2117 | 155 Partial from Huittinen, Finland |
2018 August 11 Partial |
1.1476 | |
| Partial solar eclipses on July 13, 2018, and January 6, 2019, occur during the next semester series. | ||||||
Saros 130[]
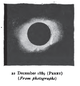
This eclipse is a part of Saros cycle 130, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 73 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on August 20, 1096. It contains total eclipses from April 5, 1475 through July 18, 2232. The series ends at member 73 as a partial eclipse on October 25, 2394. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 41 seconds on July 11, 1619.
| 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| 1853/11/30 | 1871/12/12 | 1889/12/22 | 1908/1/3 | 1926/1/14 | 1944/1/25 | 1962/2/5 |

|

|
|

|
|||
| 4m 28s | 4m 23s | 4m 18s | 4m 14s | 4m 11s | 4m 9s | 4m 8s |
| 50 | 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 |

|

|
|

|

|

|

|
| 1980/2/16 | 1998/2/26 | 2016/3/9 | 2034/3/20 | 2052/3/30 | 2070/4/11 | 2088/4/21 |

|

|
|||||
| 4m 8s | 4m 9s | 4m 9s | 4m 9s | 4m 8s | 4m 4s | 3m 58s |
Metonic series[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.[9]
| Octon series with 21 events between May 21, 1993 and August 2, 2065 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 20–21 | March 8–9 | December 25–26 | October 13–14 | August 1–2 |
| 98 | 100 | 102 | 104 | 106 |
| May 21, 1955 | March 9, 1959 | December 26, 1962 | October 14, 1966 | August 2, 1970 |
| 108 | 110 | 112 | 114 | 116 |
| May 21, 1974 | March 9, 1978 | December 26, 1981 | October 14, 1985 | August 1, 1989 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 May 21, 1993 |
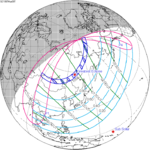 March 9, 1997 |
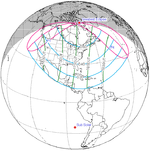 December 25, 2000 |
 October 14, 2004 |
 August 1, 2008 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 May 20, 2012 |
 March 9, 2016 |
 December 26, 2019 |
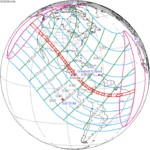 October 14, 2023 |
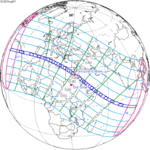 August 2, 2027 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 21, 2031 |
 March 9, 2035 |
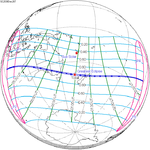 December 26, 2038 |
 October 14, 2042 |
 August 2, 2046 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
 May 20, 2050 |
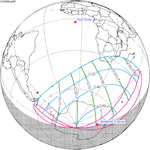 March 9, 2054 |
 December 26, 2057 |
 October 13, 2061 |
 August 2, 2065 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 May 20, 2069 |
March 8, 2073 | December 26, 2076 | October 13, 2080 | August 1, 2084 |
Notes[]
- ^ Espenak, Fred. "Google Maps and Solar Eclipse Paths: 2001 �� 2020". Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA's GSFC. NASA. Retrieved April 11, 2009.
- ^ Graham, Chris (March 10, 2016). "Solar eclipse sweeps across Asia". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 2016-03-10.
- ^ a b Graham Jones (November 15, 2015). "'Completely Off the Charts': Indonesia Prepares for March 9 Eclipse". Jakata Globe. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ "Do's and Don'ts on Nyepi: Religious Leaders in Bali Issue Guidelines for Nyepi Observance on March 9, 2016". Bali Discovery Tours. February 20, 2016. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ a b Ade Ashford (March 8, 2016). "Get ready for the 9 March total solar eclipse". Astronomy Now. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ PTI (March 9, 2016). "Part of total solar eclipse seen in India". Economic Times. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
- ^ Cosgrove, Cole. "Chasing the shadow of the moon: To intercept eclipse, Alaska Airlines adjusts flight plan to delight astronomers". Alaska Airlines.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Note S1: Eclipses & Predictions in Freeth, Tony (2014). "Eclipse Prediction on the Ancient Greek Astronomical Calculating Machine Known as the Antikythera Mechanism". PLOS ONE. 9 (7): e103275. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9j3275F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103275. PMC 4116162. PMID 25075747.
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2016 March 9. |
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- F. Espenak, J. Meeus: Five Millennium Catalog of Solar eclipses, NASA/TP-2009-213174
- "Total solar eclipse of 2016 Mar 09, Google Maps and Solar Eclipse Paths". NASA. Retrieved March 10, 2016.
- hermit.org: Total Solar Eclipse: March 9 2016
- Interactive map of the eclipse with local circumstances and diagram
- EU project Stars4All: Eclipse online broadcast from Palu (Indonesia)
- Video with Total Solar Eclipse March 09 2016 (From the Beginning to the Total Phase) on YouTube
External links[]
- High-resolution animation of eclipse shadow by Seán Doran from JAXA's Himawari imagery
- 2016 in Asia
- 2016 in science
- 21st-century solar eclipses
- Total solar eclipses
- March 2016 events
- 2016 in Indonesia














