Solar eclipse of May 31, 2003
| Solar eclipse of May 31, 2003 | |
|---|---|
 Annular from Culloden, Scotland | |
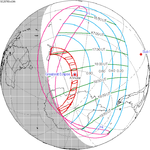
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.996 |
| Magnitude | 0.9384 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 217 sec (3 m 37 s) |
| Coordinates | 66°36′N 24°30′W / 66.6°N 24.5°W |
| Max. width of band | - km |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:09:22 |
| References | |
| Saros | 147 (22 of 80) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9515 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on May 31, 2003. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible across central Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Jan Mayen and northern Scotland. Partiality was visible throughout Europe, Asia, and far northwestern Canada.

Images[]

Chassepierre, Belgium

From Belfort, France

Wonneberg, Germany

From Oria, Italy

From Venice, Italy

Willeskop, Netherlands

From Oslo, Norway

From Ringerike, Norway

Grantown-on-Spey, Scotland
Related eclipses[]
Eclipses of 2003[]
- A total lunar eclipse on May 16.
- An annular solar eclipse (one limit) on May 31.
- A total lunar eclipse on November 9.
- A total solar eclipse on November 23.
Tzolkinex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of April 17, 1996
- Followed: Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010
Half-Saros[]
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of May 25, 1994
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of June 4, 2012
Tritos[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of June 30, 1992
- Followed: Solar eclipse of April 29, 2014
Solar Saros 147[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of May 19, 1985
- Followed: Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
Inex[]
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of June 20, 1974
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 9, 2032
Solar eclipses 2000–2003[]
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[1]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 5, 2000 and July 31, 2000 occur in the previous lunar year set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2000–2003 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 117 | 2000 July 01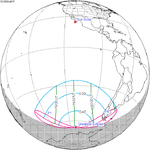 Partial (south) |
-1.28214 | 122 | 2000 December 25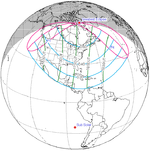 Partial (north) |
1.13669 | |
127 Totality from Lusaka, Zambia |
2001 June 21 Total |
-0.57013 | 132 Partial from Minneapolis, MN |
2001 December 14 Annular |
0.40885 | |
137 Partial from Los Angeles, CA |
2002 June 10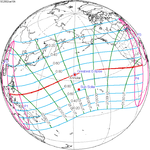 Annular |
0.19933 | 142 Totality from Woomera |
2002 December 04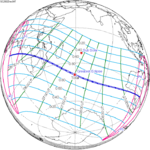 Total |
-0.30204 | |
147 Culloden, Scotland |
2003 May 31 Annular |
0.99598 | 152 | 2003 November 23 Total |
-0.96381 | |
Saros 147[]
Solar saros 147, repeating every about 18 years and 11 days, contains 80 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on October 12, 1624. It has annular eclipses from May 31, 2003, to July 31, 2706. There are no total eclipses in this series. The series ends at member 80 as a partial eclipse on February 24, 3049. The longest annular eclipse will be on November 21, 2291, at 9 minutes and 41 seconds.[2]
| Series members 17–27 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 17 | 18 | 19 |
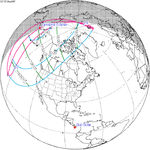 April 6, 1913 |
 April 18, 1931 |
 April 28, 1949 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 |
 May 9, 1967 |
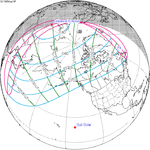 May 19, 1985 |
 May 31, 2003 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 |
 June 10, 2021 |
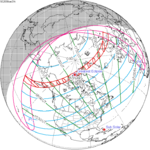 June 21, 2039 |
 July 1, 2057 |
| 26 | 27 | |
 July 13, 2075 |
 July 23, 2093 | |
Tritos series[]
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1901 and 2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
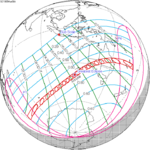 March 6, 1905 (Saros 138) |
 February 3, 1916 (Saros 139) |
 January 3, 1927 (Saros 140) | |
 December 2, 1937 (Saros 141) |
 November 1, 1948 (Saros 142) |
 October 2, 1959 (Saros 143) | |
 August 31, 1970 (Saros 144) |
 July 31, 1981 (Saros 145) |
 June 30, 1992 (Saros 146) | |
 May 31, 2003 (Saros 147) |
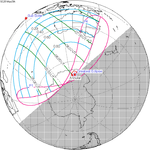 April 29, 2014 (Saros 148) |
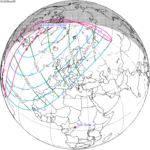 March 29, 2025 (Saros 149) | |
 February 27, 2036 (Saros 150) |
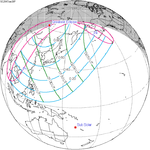 January 26, 2047 (Saros 151) |
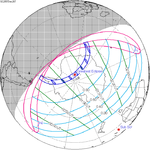 December 26, 2057 (Saros 152) | |
 November 24, 2068 (Saros 153) |
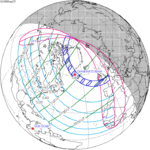
 October 24, 2079 (Saros 154) |
 September 23, 2090 (Saros 155) |
|
Metonic series[]
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 22 eclipse events between January 5, 1935 and August 11, 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January 4-5 | October 23-24 | August 10-12 | May 30-31 | March 18-19 |
| 111 | 113 | 115 | 117 | 119 |
 January 5, 1935 |
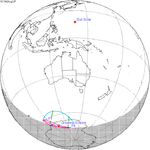 August 12, 1942 |
 May 30, 1946 |
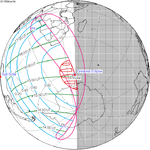 March 18, 1950 | |
| 121 | 123 | 125 | 127 | 129 |
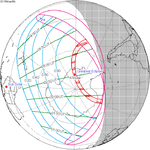 January 5, 1954 |
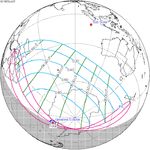 October 23, 1957 |
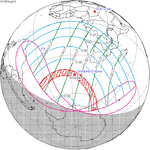 August 11, 1961 |
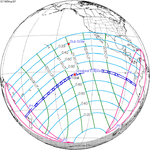 May 30, 1965 |
 March 18, 1969 |
| 131 | 133 | 135 | 137 | 139 |
 January 4, 1973 |
 October 23, 1976 |
 August 10, 1980 |
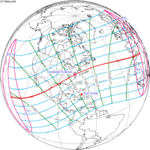 May 30, 1984 |
 March 18, 1988 |
| 141 | 143 | 145 | 147 | 149 |
 January 4, 1992 |
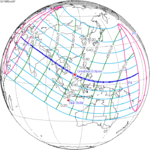 October 24, 1995 |
 August 11, 1999 |
 May 31, 2003 |
 March 19, 2007 |
| 151 | 153 | 155 | ||
 January 4, 2011 |
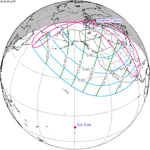 October 23, 2014 |
 August 11, 2018 |
||
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ Saros Series Catalog of Solar Eclipses NASA Eclipse Web Site.
References[]
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
Photos:
- Spaceweather.com solar eclipse gallery
- Czech Republic. Prof. Druckmüller's eclipse photography site
- Eclipse in the Mist, APOD 6/4/2003, Dawn partial from Charneux, Belgium
- Ring of Fire from Cape Wrath, APOD 6/5/2003, Annular eclipse from Cape Wrath, northwestern coast of Scotland
- Sun, Moon, Hot Air Balloon, APOD 6/6/2003, partial eclipse from Bonn, Germany
- Clouds and the Moon Move to Block the Sun, APOD 6/18/2003, partial eclipse from Vienna, Austria
- Photos of solar eclipse around the world
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2003 May 31. |
- Annular solar eclipses
- 2003 in science
- 21st-century solar eclipses
- May 2003 events












