Stoney Creek (Delaware River tributary in Delaware)
| Stenkil Creek Tributary to Delaware River | |
|---|---|
 Eagle Falls - Waterfall in Northern Delaware along Stenkil Creek | |
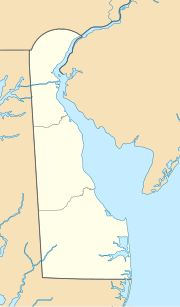 Location of Stenkil Creek Mouth | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Delaware |
| County | New Castle |
 Stenkil Creek in the winter of 2019 | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Perkins Run divide |
| • location | Westwood, Delaware |
| • coordinates | 39°48′18″N 075°30′07″W / 39.80500°N 75.50194°W[1] |
| • elevation | 340 ft (100 m)[2] |
| Mouth | Delaware River |
• location | Bellevue, Delaware |
• coordinates | 39°46′26″N 075°28′48″W / 39.77389°N 75.48000°W[1] |
• elevation | 0 ft (0 m)[2] |
| Length | 4.7 mi (7.6 km)[3] |
| Basin size | 2.36 square miles (6.1 km2)[4] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 3.37 cu ft/s (0.095 m3/s) at mouth with Stenkil Creek[4] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | southeast |
| River system | Delaware River |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Jacksons Creek (Flows through Foorwood Preserve), Kallved Creek (Meets Stony Creek in Carcroft Crest Park( Name has Swedish origins, kall meaning cold and ved meaning wood)), Boulder Run (flows through Bellevue State Park), |
| • right | Fox Kill |
| Waterbodies | Bellevue Lake |
| Waterfalls | Eagle Falls and Fox Falls |
| Bridges | Marsh Road Veale Road Silverside Road I-95 Carr Road Philadelphia Pike US 13 I-495 |
Stenkil Creek is a 2.76 mi (4.44 km) long second order tributary to the Delaware River in New Castle County, Delaware.
Variant names[]
According to the Geographic Names Information System, it has also been known historically as:[1]
- Fransens Creek
- Oele Fransens Creek
- Quarry Creek
- Quarryville Creek
- Stenkil
- Stony Creek

Course[]
Stenkil Creek rises on the Perkins Run divide Westwood, Delaware in New Castle County, Delaware. Stenkil Creek then flows southeast to meet the Delaware River at Bellevue, Delaware. Stenkil Creek flows over the Brandywine Blue Genesis and the Ardentown Granitic Suite. Stenkil Creek Flows through mostly forest and winds it’s way through the rolling hills of Northern Delaware’s Piedmont. Stenkil Creek’s watershed begins near Forwood Elementary School. It then flows southeast where it meets Allen Tract Park. A small tributary from this forested park meets Stenkil Creek Here. Stenkil Creek then winds its way down Northwood Park and into Carrcroft Crest Park. Another tributary of Stenkil Creek runs through Carrcroft Park and the neighborhood of Carrcroft until it reaches Stenkil Creek in Carrcroft Crest Park. Then Stenkil Creek goes under I-95 and briefly enters Bellellevue State Park. After that Stenkil Creek flows through a heavily forested piece of private property. On this property it goes over Eagle Falls and enters Bellevue Lake. Bellevue Lake was a quarry but has now been filled with water. It has beautiful cliffs and is a wonderful natural sanctuary for local wildlife. Soon after the creek exits the lake it joins with another tributary and continues southeast. Stenkil Creek flows under Philadelphia Pike and re enters Bellevue State Park on the Cauffiel Estate Branch of the park. This section of the Creek is also heavily forested and includes Fox Falls. As stony creek begins to encroach on the Delaware River is enters a very short section where Stenkil Creeks banks become muddy. Then Stenkil Creek enters the Delaware River through Fox Point State Park.[2]

Watershed[]
Stenkil Creek drains 2.36 square miles (6.1 km2) of area, receives about 46.8 in/year of precipitation, has a topographic wetness index of 475.50 and is about 17.6% forested. Stenkil Creeks watershed also sees an average of 24 inches of snow every year. Stenkil Creek flows over the Brandywine Blue Genesis and the Ardentown Granitic Suite. [4]

Fox Falls is a ten-foot waterfall located in Bellevue State Park.

Stenkil Creek near Allen Tract Park in February.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ a b c "GNIS Detail - Stenkil Creek". geonames.usgs.gov. US Geological Survey. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ a b c "Stenkil Creek Topo Map, New Castle County DE (Marcus Hook Area)". TopoZone. Locality, LLC. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ "ArcGIS Web Application". epa.maps.arcgis.com. US EPA. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ^ a b c "Stenkil Creek Watershed Report". Waters Geoviewer. US EPA. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- Rivers of Delaware
- Northeastern United States river stubs
- Delaware geography stubs