Tellurium tetraiodide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
tellurium(IV) iodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.282 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| TeI4 | |
| Molar mass | 635.218 g/mol |
| Appearance | black crystals |
| Density | 5.05 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
 
| |
Signal word
|
Danger |
| H302, H312, H314, H332 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P322, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
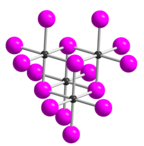
Tellurium tetraiodide (TeI4) is an inorganic chemical compound. It has a tetrameric structure which is different from the tetrameric solid forms of TeCl4 and TeBr4.[2] In TeI4 the Te atoms are octahedrally coordinated and edges of the octahedra are shared.[2]
TeI4 can be prepared from the elements or by reacting Te and iodomethane, CH3I.[2] In the vapour TeI4 dissociates:[3]
- TeI4 → TeI2 + I2
It is a conductor when molten, dissociating into the ions TeI3+ and I−. In solvents with donor properties such as acetonitrile, CH3CN ionic complexes are formed which make the solution conducting:[3]
- TeI4 + 2 CH3CN → (CH3CN)2TeI3+ + I−
References[]
- ^ "Tellurium tetraiodide". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- ^ a b c Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b Inorganic Chemistry,Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman Elsevier 2001 ISBN 0-12-352651-5
Categories:
- Iodides
- Tellurium halides
- Tellurium compounds
- Chalcohalides
- Inorganic compound stubs