The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) Regulations 2020
| Statutory Instrument | |
 | |
| Citation | 2020 No. 1374 |
|---|---|
| Introduced by | Matt Hancock, Secretary of State for Health and Social Care |
| Territorial extent | England |
| Dates | |
| Made | 30 November 2020 |
| Laid before Parliament | 30 November 2020 |
| Commencement | 2 December 2020 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repeals | The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (England) (No. 4) Regulations 2020 |
| Made under | Public Health (Control of Disease) Act 1984 |
| Repealed by | The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (Steps) (England) Regulations 2021 |
Status: Repealed | |
| Text of the The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) Regulations 2020 as in force today (including any amendments) within the United Kingdom, from legislation.gov.uk. | |

Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Tier 4
The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) Regulations 2020 (SI 2020/1374) is an English emergency statutory instrument that replaced the second lockdown regulations from 2 December 2020. As initially made, it brought back the three-tier legal framework first introduced by the first COVID-19 tier regulations in England (in effect 14 October – 5 November 2020), but with changes to the restrictions within each tier.
More relaxed rules on gatherings were to be permitted during the Christmas period, 23–27 December 2020. Following a continued rise in infections in London and the South East, parts of those areas were moved up to the highest level, tier 3, on 17 December (ahead of the formal review date)[1] and 19 December (the formal review date). On the 20th, following continued significant concerns, a new tier 4 was added with restrictions similar to those of the second lockdown regulations that applied to London and those parts of the South East and the East of England that were in tier 3 on the 19th.[2] At the same time the Christmas period was reduced to Christmas Day only for tiers 1 to 3, and was abolished entirely for tier 4.
The regulations were sometimes referred as the "second tier regulations" or the "all tiers regulations".
From 6 January 2021, further amendments moved all areas of England to tier 4 in what was described by politicians and the press as a third national lockdown.
The regulations were originally stated to expire on 2 February 2021,[3] later changed to 31 March,[4] but in the event were replaced on 29 March by The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (Steps) (England) Regulations 2021.
Context and earlier regulations[]
In response to the developing COVID-19 pandemic, the UK government issued advice to English schools on 12 March 2020 that they should cancel trips abroad,[5] and on 16 March that the public should avoid non-essential travel, crowded places, and visits to care homes.[6] This was followed by the closure of schools, colleges and nurseries from 21 March.[7]
On 21 March the government used emergency powers to make business closure regulations, enforcing the closure in England of businesses selling food and drink for consumption on the premises, as well as a range of other businesses such as nightclubs and indoor leisure centres where a high risk of infection could be expected. Five days later the restrictions were made more extensive.[8] On 26 March 2020 the even more stringent Lockdown Regulations came into force. These became the principal delegated English legislation restricting freedom of movement, gatherings, and business closures, and were progressively relaxed on 22 April, 13 May, 1 June, and 13/15 June. The No. 2 regulations of 4 July 2020 further relaxed the rules throughout most of England,[9] apart from City of Leicester and the surrounding area[10] which became the subject of the first of a series of local regulations. Between July and September 2020, more extensive and increasingly rigorous ad hoc local regulations were introduced, which in many areas proved unsuccessful in controlling spread of the virus.[11]
These were followed by the first COVID-19 tier regulations (in effect 14 October – 4 November 2020), which placed each local authority area under one of three levels of restrictions. As infections increased in many areas, these were replaced by the more rigorous nationwide second lockdown regulations (in effect 5 November – 1 December 2020).
On 2 December 2020 SI 2020/1374 revoked the second lockdown regulations one day before they were due to expire,[12] and reintroduced a countrywide three-tier legal framework.[13] Later amendments introduced a fourth tier.[14]
Legal basis[]
The regulations were made on 30 November 2020 by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care, Matt Hancock, using emergency powers under the Public Health (Control of Disease) Act 1984, the stated legal basis being "the serious and imminent threat to public health which is posed by the incidence and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in England". Hancock used section 45R of the Public Health (Control of Disease) Act 1984 to enact the regulations without prior parliamentary consideration, subject to retrospective approval by resolution of each House of Parliament within twenty-eight days.[15] The regulations entered into force on 2 December 2020[15] and expire at the end of 31 March 2021[4] (originally 2 February 2021).[16]
Return of the tiers[]
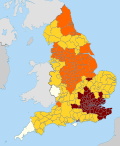
The regulations revived the three-tier legal framework from the first COVID-19 tier regulations in England, though with changes to the restrictions defined by each tier. The areas within each tier were also different: almost all of England was placed into tier 2 or 3, with only Cornwall, the Isles of Scilly, and the Isle of Wight being placed in tier 1.[17] A fourth tier was added by SI 1611 on 20 December 2020.[14] By 6 January 2021, all areas of England were in tier 4,[18] where they remained until the regulations were repealed on 29 March.
- Government posters, October 2020

Tier 1 (Medium)

Tier 2 (High)

Tier 3 (Very High)

Tier 4 (Stay at Home) (prior to modifications in 2021)
Restrictions on gatherings, all tiers[]
In all tiers, gatherings are restricted by size. In the spaces listed, the only permitted gatherings are as follows unless one of the exceptions applies:
| Space | Tier 1[19] | Tier 2[20] | Tier 3[21] | Tier 4[22] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private dwelling
(indoors) |
Up to 6 | None permitted | None permitted | None permitted |
| Other private
indoor space |
Up to 6 | None permitted | None permitted | None permitted |
| Private dwelling
(outdoors, e.g. garden) |
Up to 6 | Up to 6 | None permitted | None permitted |
| Private outdoor
space |
Up to 6 | Up to 6 | None permitted | None permitted |
| Public outdoor
space |
Up to 6 | Up to 6 | Up to 6 * | Up to 2 ** |
* For tier 3, gatherings of no more than 6 people are allowed only in free-to-access public outdoor areas, and pay-to-access public outdoor sports grounds and facilities, botanical gardens and the gardens of castles, stately homes, historic houses or other heritage sites.[23] All gatherings in outdoor areas that do not fall within that definition are prohibited, as are all gatherings at fairgrounds and funfairs.[23]
** For tier 4, an individual is allowed to meet one other person only in free-to-access public outdoor areas, and pay-to-access botanical gardens and the gardens of castles, stately homes, historic houses or other heritage sites,[24] as well as sculpure parks and allotments.[25] All gatherings in outdoor areas that do not fall within that definition are prohibited, as are all gatherings at fairgrounds and funfairs.[24]
Large gathering offence[]
On 29 January 2021 SI 97/2021 introduced a new 'large gathering offence' subject to penalty charges on a sliding scale between £400 and £6400. The offence is committed when the above restrictions are breached by more than 15 people who are gathered in a private dwelling, in educational accommodation, or at an indoor rave.[26]
Exceptions to the restrictions on gatherings[]
General and tier 1 exceptions[]
A substantial list of exceptions is provided for. All apply to tier 1, with more restricted and fewer exceptions applying to tiers 2, 3 and 4.
| Type | Indoor and outdoor exceptions | Applies | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | Tier 2 | Tier 3 | Tier 4 | |||
| Same or linked households | All are members of a common household, or of two linked households ("support bubble") | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [27][28] |
| Permitted organised gatherings | Organised with precautions by a business, charity or public body after a risk assessment. Participants must attend either alone or as part of a sub-group of no more than 6 (apart from larger single or linked household groups). | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Not Allowed | [29] |
| Education and training | A variety of specified situations including early years provision, school activities, apprenticeships, work experience, applying for a job, professional training and exams | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [30][28] |
| Gatherings necessary for certain purposes | Work, voluntary services, emergency assistance, avoiding harm, providing care to a vulnerable or disabled person, for the purposes of a house move | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [31][28] |
| Legal obligations and proceedings | Fulfilling a legal obligation or participating in legal proceedings | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [32][28] |
| Criminal justice accommodation | Any gathering in criminal justice accommodation | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [33][28] |
| Support groups | Formally organised support groups of no more than 15 people (not counting children below the age of five). Not allowed at a private dwelling | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [34][28] |
| Respite care | Respite care for a vulnerable or disabled person; a short break for a looked-after child | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [35][28] |
| Births | Attending a person giving birth | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [36][28] |
| Marriages and civil partnerships etc | Ceremonies of no more than 15 people (6 in tier 4)[28] that are organised with precautions after a risk assessment; includes non-faith ceremonies, but not at a private dwelling. Some restrictions are relaxed for ceremonies of no more than six where one of the parties is seriously ill and is not expected to recover | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 6 people | [37] |
| Wedding and civil partnership receptions | Receptions of no more than 15 people that are organised with precautions after a risk assessment. Not allowed at a private dwelling | Allowed | Allowed | Not Allowed | Not Allowed | [38] |
| Funerals | No more than 30 people. Organised with precautions after a risk assessment. Must be in a public outdoor space or a business or charity premises. Not allowed at a private dwelling | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [39][28] |
| Commemorative event following a person's death | No more than 15 people (six in tier 4). Organised with precautions after a risk assessment. Not allowed at a private dwelling | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 6 people | [40][28] |
| Protests | Organised with precautions by a business, charity, public body or political body after a risk assessment | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Not Allowed | [41] |
| Elite sports | Training and competition for elite sportspersons and coaches | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [42][28] |
| Other sports | Organised outdoor sports or fitness activities with precautions after a risk assessment; indoor activities for disabled people. This exception does not extend to spectators or to parents of a child taking part | Allowed | Not Allowed | Not Allowed | Not Allowed | [43] |
| Outdoor activities | An outdoor physical activity for which a licence or permit issued by a public body is required | Allowed | Not Allowed | Not Allowed | Not Allowed | [44] |
| Children | Formal childcare; informal childcare provided by a linked childcare household; access arrangements; contact between siblings who do not live together; prospective adopters | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Some allowed, with more restrictions[45] | [46][28] |
| Parent and child groups | Formally-organised groups of no more than 15 people (not counting children below the age of five). Not allowed at a private dwelling | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | Max 15 people | [47][28] |
| Student and vacation households | Allows a student in higher education to move to another household on a single occasion for the purpose of a vacation and to return afterwards. This was originally allowed before 8 February, and then between 8 March and 28 April 2021.[48] The student becomes a part of the vacation household during the vacation period | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [49][28][48] |
| Christmas period | Certain gatherings on 25 December 2020 only[50] of no more than three linked Christmas households. See #Linked Christmas households | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Not Allowed | [51] |
| Picketing | Picketing with precautions after a risk assessment (in tier 4 from 26 December 2020)[52] | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [53] |
| Nomination of candidates and petitioning | From 8 March 2021: Participating in the nomination of an election candidate, or petitioning for a referendum | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | [54] |
| Campaigning | From 8 March 2021: Campigning in an election or referendum. This can be to support or to prejudice the prospects of any particular party or candidate.[55] Not allowed inside a private dwelling | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | Max 2 people | [56] |
| Observing an election or referendum | From 8 March 2021: Observing at an election or referendum | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed | [57] |
Tier 2 exceptions[]
These are the same as for tier 1 except as follows:
- "Other sports": organised outdoor sports are still exempt, but organised fitness activities are not[58]
- "Outdoor activities": outdoor physical activities involving a licence or permit now require a risk assessment[59]
- Additional indoor exceptions are provided to the general tier 2 rule prohibiting gatherings in private indoor spaces:
| Type | Applies | Indoor exceptions | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visiting a dying person | Tiers 2, 3 and 4 | Visitor is a member of that person's household, a close family member, or a friend | [60] |
| Visiting persons receiving treatment etc | Tiers 2, 3 and 4 | Visitor is a member of that person's household, a close family member, or a friend. Applies to hospitals, hospices and care homes | [61] |
| Indoor sports | Tiers 2, 3 and 4 | Organised indoor sports for disabled people. This exception does not extend to spectators or to parents of a child taking part | [62] |
Tier 3 exceptions[]
These are largely the same as tier 2 but there is no exception for wedding and civil partnership receptions.[63]
Tier 4 exceptions[]
These are the same as tier 3 with the following exceptions:[28]
- No 'permitted organised gatherings'
- Wedding or civil partnership ceremonies are limited to six people
- Commemorative events following a death are limited to six people
- No special Christmas arrangements, thus normal tier 4 rules apply on 25 December.
Restrictions on leaving home in tier 4[]
As originally made, SI 1374 controlled social interactions by imposing rules on gatherings; there was no general prohibition against leaving home. The amendments introduced on 20 December 2020 by SI 1611, however, brought in a new tier 4 with much stricter rules, very similar to those of the second lockdown that was in place between 5 November and 2 December. There remains no general prohibition against leaving home in tiers 1 to 3.
In tier 4 the general rule is that no-one is allowed to leave or be outside their own home (which includes any associated garden or yard) without "reasonable excuse".[64] No exhaustive definition of "reasonable excuse" is provided, though it includes any of the following exceptions:
Reasonable excuses for leaving home in tier 4[]
| Exception | Name | Details | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Necessary for certain purposes | See below | [65] |
| 2 | Work, voluntary services, education, training etc | To work or provide voluntary or charitable services, where it is not reasonably possible to do this from home; to access charitable services; for education or training; to provide care or assistance to a vulnerable person (anyone over 70, pregnant, or with a serious health condition); to provide emergency assistance; to fulfil a legal obligation; to access critical public services | [66] |
| 3 | Elite athletes | For the purposes of training or competition | [67] |
| 4 | Medical need etc | To seek medical assistance, to get a test, to be vaccinated, or to access health, medical, or mental health services | [68] |
| 5 | Support and respite | To attend a permitted support group meeting; respite-related reasons | [69] |
| 6 | Death bed visit | To visit a household member, close family member, or friend you believe to be dying | [70] |
| 7 | Funerals etc | To attend a funeral or an event commemorating a person's life; or certain visits to a burial ground or garden of remembrance | [71] |
| 8 | Marriages and civil partnerships | To attend a licensed wedding where one of the participants is seriously ill and is not expected to recover | [72] |
| 9 | Children | To take a child to school; childcare access arrangements; children in care; prospective adopters; informal childcare by linked childcare household. To take a child to registered childcare or supervised activities for children but only where necessary to enable a critical worker to work, search for work or undertake training or education (until 6 January 2021 anyone with parental responsibility could make use of this exemption)[73] | [74] |
| 10 | Animal welfare | To care for or exercise a pet; to attend a vet | [75] |
| 11 | Returning home | Returning home from a holiday that was started before the regulations came into force | [76] |
| 12 | Prison visits | Visits by a close family member or friend | [77] |
| 13 | Voting | For the purpose of voting | [78] |
| 14 | Permitted outdoor sports gatherings | Attending an organised outdoor sports gathering for disabled people. Does not include spectators. (Until 6 January 2021 gatherings for children were also permitted).[79] | [80] |
| 15 | Parent and child groups | Attending a permitted parent and child group meeting | [81] |
| 16 | Student and vacation households | A higher education student can leave to switch households for a vacation on one occasion before 8 February 2021, and can return afterwards. Also permitted on one occasion between 8 March and 28 April 2021.[48] | [82] |
| 17 | Picketing | From 26 December 2020: Attending a lawful picket line | [52] |
| 18 | Nomination of candidates and petitioning | From 8 March 2021: Participating in the nomination of an election candidate, or petitioning for a referendum | [83] |
| 19 | Campaigning | From 8 March 2021: Campigning in an election or referendum. This can be to support or to prejudice the prospects of any particular party or candidate[55] | [84] |
| 20 | Observing an election or referendum | From 8 March 2021: Observing at an election or referendum | [85] |
Exception 1: leaving tier 4 home necessary for certain purposes[]
This exception covers a variety of situations:[65]
| Exception | Details |
|---|---|
| 1a | Where reasonably necessary to leave home to buy goods or services for oneself, a household member, a vulnerable person (anyone over 70, pregnant, or with a serious health condition) or someone in their household |
| 1b | To obtain or deposit money |
| 1c | To take exercise outside. This may be either alone, or with household or linked household members. Also permitted is to exercise outside in a public place with any one other person (for this purpose, children under five and up to two carers for a disabled person are not counted) |
| 1d
[Not between 6 Jan and 7 Mar 2021] |
This exception originally applied until 5 January 2021, when it was removed;[86] it was restored on 8 March 2021:[87] To visit a public outdoor place for open air recreation with any one other person (for this purpose, children under five and up to two carers for a disabled person are not counted). Visiting a public outdoor place for open air recreation with any number of household or linked household members is also permitted |
| 1da
[abolished] |
From 26 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 only: To visit outdoor attractions at an aquarium, zoo, safari park, or other outdoor animal attractions.[88] This exception was removed from 6 January 2021.[86] |
| 1e | To attend a place of worship |
| 1f | In connection with the purchase, sale, letting or rental of residential property |
| 1g | To visit a linked household |
| 1h | To collect pre-ordered food, drink, or other goods, or visit a food or drink service business to obtain a takeaway |
| 1i | To visit a waste disposal or recycling centre |
Movement between tiers[]
There is no general prohibition against leaving a home tier area, or against movement between tiers. An individual who travels between tiers to join a gathering is generally subject to the rules of their home tier, or the tier of the place to which they have travelled, whichever is higher. Anyone living in tier 1, 2 or 3 is permitted to travel to a higher tier area, but must not participate in any gathering that is prohibited in the higher tier area. Anyone living in tier 2, 3 or 4 who travels to a lower tier area must not participate in any gathering that would be prohibited in their home area.[89] As noted above, people who are resident in tier 4 are permitted to leave home and travel only if they have a 'reasonable excuse' to do so.[64]
Business closures[]
Certain businesses are required to close or limit their operations.
General and tier 1 business restrictions[]
| Applies | Details | Ref | Exceptions | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Businesses that must close | All tiers | Must close: nightclubs, dance halls, discotheques and facilities for public dancing to music at night, sexual entertainment venues, hostess bars, shisha bars/hookah lounges | [90] | Where the owner runs a separate shop, cafe or restaurant, or an online delivery service | [91] |
| Opening hours restrictions | Tiers 1 and 2 | Must stop accepting orders at 22:00, and must close between 23:00 and 05:00: restaurants*, food and drink takeaways*, cafes and workplace canteens*, bars*, pubs*, social clubs*, casinos*, bowling alleys, cinemas, theatres, amusement arcades or other indoor leisure centres, funfairs (indoors or outdoors), theme and adventure parks and activities, bingo halls, concert halls, sportsgrounds | [92] | Supermarkets, convenience stores, corner shops, newsagents, pharmacists, petrol stations;[93] motorway service stations;[94] air and sea ports;[95] on public transport;[96] online food and drink deliveries and collections, drive-through takeaways.[97] Cinemas, theatres and concert halls may remain open after 22:00 for the purpose of completing performances which began before that time[98] | [99] |
| Table service and customer eating | Tier 1 only | Restrictions on service: venues marked * above which sell alcohol must serve all food and drink to customers seated at tables. Customers must order at the table, and must remain seated while eating and drinking. Venues so marked which do not sell alcohol need not serve customers at a table, but they must ensure that customers eating and drinking on the premises remain seated | [100] |
Tier 2 business restrictions[]
The tier 1 list of businesses that must close and the opening hour restrictions also apply in tier 2. In addition, there are the following restrictions:
| Applies | Details | Ref | Exceptions | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pubs and bars to serve alcohol as part of a table meal | Tier 2 | Restrictions on service: pubs, bars, and other venues selling alcohol for consumption on the premises may remain open only if they serve alcohol only as part of a table meal (at least equivalent to breakfast or the main course of a midday or evening meal). The meal must be eaten while seated at a table (not at a serving counter). This rule applies equally to areas adjacent to the premises used by customers | [101] | Alcohol served as part of a hotel's room service | [102] |
| Bars and non-food pubs to close | Tiers 2 and 3 | Must close: pubs, bars, and other venues that sell alcohol for consumption on the premises other than as part of a table meal | [90] |
Tier 3 business restrictions[]
The tier 1 and tier 2 lists of businesses that must close also apply in tier 3. In addition, there are the following restrictions:
| Applies | Details | Ref | Exceptions | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Further businesses to close | Tier 3 | Must close: indoor play areas, trampoline/inflatable parks; casinos; bingo halls; bowling alleys; snooker and pool halls; amusement arcades; laser quest and escape rooms; theatres and cinemas; concert halls; many conference centres and exhibition halls; indoor skating rinks; circuses; the indoor parts of many visitor and heritage attractions | [103] | Where the owner runs a separate shop, cafe or restaurant, or an online delivery service; drive-in theatres and cinemas;[104] visitor toilets[105] | [106] |
| Holiday accommodation to close | Tier 3 | Must close: holiday accommodation | [107] | Various special cases including venue used as a main residence, and where needed for work or education; also, any accommodation provided during the period 24 to 26 December 2020.[108] | [109] |
| No consumption of food or drink on the premises | Tier 3 | Must close: restaurants, cafes and workplace canteens, bars, pubs, social clubs providing food and drink | [110] | Where the owner runs a separate cafe or restaurant, or an online delivery service; food or drink served as part of a hotel's room service;[111] motorway service stations, air and sea ports[96] | [112] |
| Opening hours restrictions | Tier 3 | Must close between 23:00 and 05:00: drive-in theatres and cinemas; outdoor concert venues; outdoor attractions at theme parks, fairgrounds and funfairs | [113] | Venues may stay open after 23:00 to conclude a performance starting before 22:00 | [114] |
| Food and drink takeaways | Tier 3 | Limited service between 23:00 and 05:00: between those hours food and drink takeaways may operate click-and-collect and drive-through services only | [115] |
Tier 4 business restrictions[]
These are similar but not identical to those of the second lockdown that was in place between 5 November and 2 December.
| Restrictions | Exceptions | |
|---|---|---|
| Businesses | Must close: Nightclubs, dance halls, discos, sexual entertainment venues, hostess bars, venues with waterpipes or that provide for the consumption of nicotine or other substances on the premises[116]
Must close: Restaurants, cafes, bars, pubs, social clubs, food and drink takeaways[117] Must close: Dance and fitness studios, gyms, sports courts, swimming pools, playgrounds, soft play areas, indoor leisure centres and entertainment venues, casinos, bingo halls, bowling alleys, indoor riding centres, amusement arcades, cinemas, theatres, concert halls, skating rinks, circuses, water parks, theme parks, fairgrounds and funfairs, adventure parks, model villages, kitchen, bathroom, tile and glazing showrooms, museums and galleries, indoor venues at visitor attractions, film studio attractions, conference centres, exhibition halls, betting shops, spas, tanning salons, nail salons, beauty salons, hair salons and barbers, massage parlours, tattoo and piercing parlours, carpet stores, motor showrooms, manual car washes, most auction houses, most outdoor markets[118] Must close: From 6 January 2021: outdoor sportsgrounds and facilities, including outdoor gyms, sports courts, swimming pools, water sports, shooting and archery venues, golf courses, and driving ranges; retail travel agents[119] |
Food and drink takeaways operated by supermarkets, convenience stores, pharmacists and petrol stations[120] Food and drink provided at motorway service stations, ports, airports and international rail terminals,[121] or on public transport[122] Restaurants etc may offer a takeaway service between 05:00 and 23:00 (with click and collect only outside those hours)[123] From 6 January 2021, hospitality venues can no longer sell alcohol to take away.[124] Outdoor markets selling food or livestock, and outdoor markets consisting of permitted retailers (see below)[125] |
| Retail shops | Must close: All retail shops, apart from permitted retailers (see below)[126] | Delivery and collection in response to pre-booked orders (click and collect). The customer collecting must not enter the premises[126] |
| Libraries | Must close: Libraries[126] | Libraries may open for voting purposes, support groups, childcare, education and training, voluntary or public services[127] |
| Holiday accommodation | Must close: All types of holiday accommodation[128] | Various exceptions including work, self-isolation, use while moving house, people unable to return home etc[128] |
| Community centres and halls | Must close: Community centres and halls[129] | Essential voluntary services, education and training, support groups, childcare and supervised activities[129] |
| Permitted retailers | May remain open: Food retailers, including food markets, supermarkets, convenience stores and corner shops, off licences, pharmacies and chemists, newsagents, animal rescue centres, building merchants, petrol stations, car repair and MOT services, bicycle shops, taxi or vehicle hire businesses, banks, building societies, cash points, currency exchange offices, post offices, funeral directors, laundrettes and dry cleaners, medical, health and mental health services, vets, pet shops, agricultural supplies, storage and distribution facilities, delivery drop off or collection points, car parks, public toilets, garden centres, automatic car washes, mobility and support shops[130] | |
Linked households[]
The concept of "linked households" (referred to in government statements as "support bubbles")[131] is brought forward from previous regulations, but in extended form. Two households that are linked under these regulations can generally meet as if they were one household. First and second households may link if all the adults in both households agree.[132] The first household must comprise:
- A single adult
- Any number of children and no adults
- One adult and any number of children who are under the age of 18 on 12 June 2020
- Any number of adults and a child who was under the age of one on 2 December 2020
- Any number of adults and a child who has a disability that requires continuous care, and who was under the age of five on 2 December 2020
- One or more persons who have a disability that requires continuous care, on their own or together with any number of individuals who do not have such a disability (but only one of the non-disabled individuals may be aged 18 or over on 12 June 2020).[133]
Where the first household includes a higher education student on vacation, the presence of the student is ignored for this purpose.[134]
There are no limits on the second household, which may include any number of adults and children.[135]
A household may only be linked with one other household at any one time.[136] But for the first time, linked households may be changed if all members of a linked household agree;[137] this is subject to a minimum 10 day period (14 days prior to 14 December 2020),[138] counted from when the old household first met or did something they could only do by virtue of being a linked household.[139]
Linked childcare households[]
The concept of "linked childcare households" is brought forward from previous regulations. It is separate from "linked households".
A household with at least one child aged 13 or under can link with another household who will be providing informal childcare[140] (formal childcare, for example by a childminder, is excluded).[141] Only one linked childcare household is permitted at any one time, and all adults in both households have to agree.[140] Changes to the linking now are allowed subject to a minimum 14 day period (reduced to 10 days from 14 December 2020)[138] between the final meeting of the former linked childcare households and the first meeting of the new.[142]
Linked Christmas households[]
As originally made, the regulations provided for more relaxed Christmas rules on gatherings during the 'Christmas period', defined as 23–27 December 2020,[143][144][145] but three days before they were due to enter into effect SI 1611 altered the definition and restricted the Christmas period to 25 December only.[50] The amended Christmas rules given below applied to tiers 1 to 3 only; there were no special Christmas arrangements in tier 4.
The Christmas rules introduced a new concept of "linked Christmas households", separate from "linked households" and 'linked childcare households".
One or more members of one household could form a linked Christmas household with one or more members of no more than two other households from a tier 1, 2 or 3 area, regardless of size, to form a linked Christmas household for the purpose of gathering during the Christmas 2020 period, if all people to be so linked agreed.[146] Two households that were already linked households counted as one household for this purpose.[147] A person could be a member of only one linked Christmas household, except that a child who did not live in the same household as both parents could be a member of a linked Christmas household formed by each parent.[148] There was a special exception for higher education students on vacation.[134]
Linked Christmas households were exempted from some of the restrictions on gatherings on 25 December. During that period, gatherings of no more than three linked Christmas households were permitted provided that they took place in a private dwelling, a place of worship or a public outdoor place (defined as anywhere the public are admitted free of charge, as well as outdoor sports grounds, botanical gardens, gardens or grounds of a castle, stately home, historic house or other heritage site, but excluding fairgrounds and funfairs). Attendees could also travel together, as gatherings in conveyances were permitted.[143][144][145]
A Christmas gathering could extend beyond the Christmas period (25 December)[50] in the event that an attendee could not return home due to unforeseen travel disruption.[149]
These Christmas-specific rules were ultimately revoked on 19 January 2021.[150]
Declaration on leaving the United Kingdom[]
On 8 March 2021, SI 2021/247 introduced a new requirement for travellers leaving the United Kingdom to have with them a completed travel declaration form when they arrive at an embarkation point. On the form, the traveller must give a variety of personal details, must state the reason for being away from home, and must certify that the information provided is true.[151] Anyone who has failed to complete the form and who does not do so when directed by an authorised person may be required to return home or to leave the embarkation point without departing from the UK.[152] Failure to comply is an offence.[153] The regulations provide a long list of travellers who are exempt from the declaration requirement, including diplomats, essential government workers, transit passengers, hauliers, seamen, aircraft crews and channel tunnel workers.[154]
Reviews and expiry[]
The Secretary of State must review the need for the restrictions every 28 days, and also the applicability of the tier areas every 14 days, with the first review (for tiers 2 and 3 only) due by 16 December 2020 and subsequent reviews required for tiers 2, 3 and 4.[155][156]
The regulations were originally stated to expire at the end of 2 February 2021.[3] This was later moved to 31 March 2021.[4]
Enforcement[]
Breaches of the regulations are offences and can be prosecuted or dealt with by fixed penalty notices with penalties ranging up to £10,000 for repeated violations.[157]
Inconsistency in government guidelines on exercise[]
The regulations do not define what constitutes exercise, nor how far an individual may travel to in order to undertake exercise. Government guidelines state that individuals should exercise in their "local area", but there is no such requirement in the regulations. Similarly, the guidelines state that exercise "should be limited to once per day", but the regulations do not require or even mention such a thing.[158]
On 6 January 2021 fixed penalty notices were handed to two women by Derbyshire Police, reportedly for travelling five miles (eight kilometres) to go for a walk.[159] The police force subsequently stated that it was reviewing the action based on new national guidelines,[160] but issuance of the notices was nevertheless supported by the health secretary, Matt Hancock.[161] This led to calls for greater clarity as to what travel was legally permitted for the purpose of exercise.[162][163] Four days later it was announced that the notices had been revoked and that Derbyshire Police had apologised to the women.[164]
It was subsequently reported that, on 10 January 2021, Boris Johnson has been cycling in the Queen Elizabeth Olympic Park which is eleven miles (eighteen kilometres) from Downing Street.[165] Metropolitan Police Commissioner Dame Cressida Dick stated that the trip had not been "against the law - that's for sure"[166] but called for greater clarity in the regulations.[167]
Summary of main changes, by date[]
This chronological table lists the main changes to the second tier regulations.
| SI | In effect | Main changes | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1533 | 16 Dec 2020 | All London boroughs, Essex (except Colchester, Tendring and Uttlesford) and the Hertfordshire districts of Broxbourne, Hertsmere, Three Rivers and Watford were moved up from tier 2 to tier 3 | [168] |
| 1572 | 19 Dec 2020 | The counties of Bedfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Berkshire, the Cambridgeshire district of Peterborough, the rest of Hertfordshire, Surrey (except Waverley), the East Sussex districts of Hastings and Rother and the Hampshire districts of Gosport, Havant and Portsmouth moved up to tier 3. Bristol and North Somerset moved down to tier 2. Herefordshsire moved down to tier 1 | [169] |
| 1611 | 20 Dec 2020 | The counties of Bedfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Berkshire, the Cambridgeshire district of Peterborough, Essex (except Colchester, Tendring and Uttlesford), Hertfordshire, Surrey (except Waverley), the East Sussex districts of Hastings and Rother, the Hampshire districts of Gosport, Havant and Portsmouth and all London boroughs moved up to a newly created tier 4. | [14] |
| 1646 | 26 Dec 2020 | The rest of Cambridgeshire, the rest of Essex, the rest of Hampshire (except New Forest), Norfolk, Oxfordshire, Suffolk, the Surrey district of Waverley and the rest of Sussex moved up to tier 4.
The counties of Bristol, Cheshire (apart from Halton), the rest of Gloucestershire, the rest of Somerset (except Bath and North East Somerset), Northamptonshire, the Wiltshire district of Swindon, the Isle of Wight, the Hampshire district of New Forest moved up to tier 3. Cornwall (except the Isles of Scilly) and Herefordshire moved up to tier 2. |
[170][171] |
| 1654 | 31 Dec 2020 | Leicester, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire, Northamptonshire, Derby, Derbyshire, Nottingham, Nottinghamshire, Birmingham, Black Country, Coventry, Solihull, Warwickshire, Staffordshire, Stoke-on-Trent, Lancashire, Cheshire (apart from Halton), Cumbria, Manchester, Tees Valley, County Durham, Gateshead, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, North Tyneside, Northumberland, South Tyneside, Sunderland, Gloucestershire, Somerset, the Wiltshire district of Swindon, Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole, Isle of Wight and the New Forest moved up to tier 4.
Rutland, Shropshire, Telford & Wrekin, Worcestershire, Herefordshire, Liverpool, York, North Yorkshire, Bath and North East Somerset, Devon, Plymouth, Torbay, Cornwall (except the Isles of Scilly), Dorset (except Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole) and Wiltshire (except Swindon) moved up to tier 3. |
[172] |
| 8 | 6 Jan 2021 | All areas of England moved into a stricter tier 4; expiry date moved from 2 Feb to 31 March; no longer allowed to meet with one other person for 'recreation' in an outdoor public place; children's outdoor sports gatherings no longer allowed; outdoor zoos & wildlife attractions closed again; hospitality venues can no longer sell takeaway alcohol; various new business closures | [173] |
| 53 | 20 Jan 2021 | Spent Christmas rules revoked; minor amendments and corrections | |
| 97 | 29 Jan 2021 | Fines for attending gatherings of more than 15 attendees in private dwellings or educational accommodation, or indoor raves of more than 15 attendees, increased to range from £400 to £6,400. Other minor amendments and corrections. | [174] |
| 247 | 8 Mar 2021 | Added requirement for people leaving the UK to fill in a travel declaration form; added new exception to allow people to leave home to meet one other person for recreation in a public outdoor space, and also for election purposes. Allowed students to leave their student household for one vacation visit to be taken before 29 April | [175] |
Local authority areas in each tier, by date[]
This table lists the dates during which specific areas were within each tier.
| Tier | Area | Periods in Tier 1 | Periods in Tier 2 | Periods in Tier 3 | hidePeriods in Tier 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 4 | South East: Kent County Council, Medway Council, Slough Borough Council | N/A | N/A | 2 December 2020 – 19 December 2020[180] | 20 December 2020[181]– 28 March 2021 |
| East of England: Basildon Borough Council,[a] Braintree District Council,[a] Brentwood Borough Council,[a] Broxbourne Borough Council,[b] Castle Point Borough Council,[a] Chelmsford City Council,[a] Epping Forest District Council,[a] Harlow District Council,[a] Hertsmere Borough Council,[b] Maldon District Council,[a] Rochford District Council,[a] Southend-on-Sea Borough Council, Three Rivers District Council,[b] Thurrock Council, Watford Borough Council[b]
London: London boroughs of: Westminster, Barking and Dagenham, Barnet, Bexley, Brent, Bromley, Camden, Croydon, Ealing, Enfield, Hackney, Hammersmith and Fulham, Haringey, Harrow, Havering, Hillingdon, Hounslow, Islington, Lambeth, Lewisham, Merton, Newham, Redbridge, Richmond upon Thames, Southwark, Sutton, Tower Hamlets, Waltham Forest, and Wandsworth. Royal boroughs of: Greenwich, Kensington and Chelsea and Kingston upon Thames. City of London, Inner Temple and Middle Temple |
N/A | 2 December 2020[180]–15 December 2020[168] | 16 December 2020[168]–19 December 2020 | 20 December 2020[181]– 28 March 2021 | |
| East of England: Bedford Borough Council, Central Bedfordshire Council, Dacorum Borough Council,[b] East Hertfordshire District Council,[b] Luton Borough Council, Milton Keynes Council, North Hertfordshire District Council,[b] Peterborough City Council, Stevenage Borough Council,[b] St Albans City and District Council,[b] Welwyn Hatfield Borough Council[b]
South East: Bracknell Forest Council, Buckinghamshire Council, Elmbridge Borough Council,[c] Epsom and Ewell Borough Council,[c] Gosport Borough Council,[d] Guildford Borough Council,[c] Hastings Borough Council,[e] Havant Borough Council,[d] Mole Valley District Council,[c] Portsmouth City Council, Reading Borough Council, Reigate and Banstead Borough Council,[c] Rother District Council,[e] Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead, Runnymede Borough Council,[c] Spelthorne Borough Council,[c] Surrey Heath Borough Council,[c] Tandridge District Council,[c] West Berkshire Council, Woking Borough Council,[c] Wokingham Borough Council |
N/A | 2 December 2020[180]–18 December 2020[182] | 19 December 2020[182] | 20 December 2020[181]– 28 March 2021 | |
| East of England: Cambridgeshire County Council, Colchester Borough Council,[a] Norfolk County Council, Suffolk County Council, Tendring District Council,[a] Uttlesford District Council[a]
South East: Basingstoke and Deane Borough Council,[d] Brighton and Hove City Council, East Hampshire District Council,[d] Eastbourne Borough Council,[e] Eastleigh Borough Council,[d] Fareham Borough Council,[d] Hart District Council,[d] Lewes District Council,[e] Oxfordshire County Council, Rushmoor Borough Council,[d] Southampton City Council, Test Valley Borough Council,[d] Waverley Borough Council,[c] Wealden District Council,[e] West Sussex County Council, Winchester City Council |
N/A | 2 December 2020 – 25 December 2020[183] | N/A | 26 December 2020[184]– 28 March 2021 | |
| North West: Blackburn with Darwen Borough Council, Blackpool Council, Bolton Metropolitan Borough Council, Bury Metropolitan Borough Council, Lancashire County Council, Manchester City Council, Oldham Metropolitan Borough Council, Rochdale Borough Council, Salford City Council, Stockport Metropolitan Borough Council, Tameside Metropolitan Borough Council, Trafford Metropolitan Borough Council, Wigan Metropolitan Borough Council
'North East: Darlington Borough Council, Durham County Council, Gateshead Borough Council, Hartlepool Borough Council, Middlesbrough Council, Newcastle upon Tyne City Council, North Tyneside Borough Council, Northumberland County Council, Redcar and Cleveland Borough Council, South Tyneside Borough Council, Stockton-on-Tees Borough Council, Sunderland City Council East Midlands: Derby City Council, Derbyshire County Council, Leicester City Council, Leicestershire County Council, Lincolnshire County Council, Nottingham City Council, Nottinghamshire County Council West Midlands: Birmingham City Council, City of Wolverhampton Council, Coventry City Council, Dudley Metropolitan Borough Council, Sandwell Metropolitan Borough Council, Solihull Metropolitan Borough Council, Staffordshire County Council, Stoke-on-Trent Borough Council, Walsall Metropolitan Borough Council, Warwickshire County Council |
N/A | N/A | 2 December 30 December 2020[185] | 31 December 2020[186] – 28 March 2021 | |
| North West: Cheshire East Council, Cheshire West and Chester Council, Warrington Borough Council
East Midlands: Northamptonshire County Council South East: New Forest District Council[d] South West: Gloucestershire County Council, Somerset County Council, Swindon Borough Council |
N/A | 2 December 2020–25 December 2020 | 26 December 2020–30 December 2020[185] | 31 December 2020[186]–28 March 2021 | |
| Isle of Wight Council | 2 December 2020–25 December 2020[187] | N/A | 26 December 2020[187]–30 December 2020[185] | 31 December 2020[188]–28 March 2021 | |
| North West: Cumbria County Council
South West Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole Council, |
N/A | 2 December 2020–30 December 2020[189] | N/A | 31 December 2020[186]–28 March 2021 | |
| Council of the Isles of Scilly | 2 December 2020[190]–5 January 2021[191] | N/A | N/A | 6 January 2021[191]–28 March 2021 | |
| Yorkshire and The Humber: Barnsley Metropolitan Borough Council, Calderdale Metropolitan Borough Council, City of Bradford Metropolitan District Council, Doncaster Metropolitan Borough Council, East Riding of Yorkshire Council, Hull City Council, Kirklees Metropolitan Borough Council, Leeds City Council, North Lincolnshire Council, Rotherham Metropolitan Borough Council, Sheffield City Council, Wakefield Metropolitan District Council, North East Lincolnshire Council
South West: South Gloucestershire Council |
N/A | N/A | 2 December 2020[192]–5 January 2021[193] | 6 January 2021[191]–28 March 2021 | |
| South West: Bristol City Council, North Somerset Council, | N/A | 19 December 2020[182]–25 December 2020[194] | 2 December 2020[180]–18 December 2020,[182] | 6 January 2021[191]– 28 March 2021 | |
| North West: Halton Borough Council, Knowsley Metropolitan Borough Council, Liverpool City Council, Sefton Borough Council, St Helens Borough Council, Wirral Metropolitan Borough Council
Yorkshire and The Humber: City of York Council, North Yorkshire County Council East Midlands: Rutland County Council West Midlands: Shropshire Council, Telford and Wrekin Borough Council, Worcestershire County Council South West: Bath and North East Somerset Council, Devon County Council, Dorset Council, Plymouth City Council, Torbay Council, Wiltshire Council |
N/A | 2 December 2020[180]–30 December 2020[189] | 31 December 2020[185]–5 January 2021[193] | 6 January 2021[191]– 28 March 2021 | |
| Herefordshire Council | 19 December 2020[182]–25 December 2020 | 2 December 2020[180]–18 December 2020,[182] | 31 December 2020[185]–5 January 2021[193] | 6 January 2021[191]– 28 March 2021 | |
| Cornwall Council | 2 December 2020[180]–25 December 2020 | 26 December 2020[197]–30 December 2020[189] | 31 December 2020[198]–5 January 2021[193] | 6 January 2021[191]– 28 March 2021 |
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l The local boroughs within the area covered by Essex County Council were subject to separate restrictions by borough from 20 December 2020 to 26 December 2020. From 26 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 the restrictions were applied in the regulations to the area of Essex County Council. From 6 January 2021 to 28 March 2021 regulations were applied to England as a whole rather than to individual local authority areas.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j The local boroughs within the area covered by Hertfordshire County Council were subject to separate restrictions by borough from 16 December 2020 to 19 December 2020. From 20 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 the restrictions were applied in the regulations to the area of Hertfordshire County Council. From 6 January 2021 to 28 March 2021 regulations were applied to England as a whole rather than to individual local authority areas.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k The local boroughs within the area covered by Surrey County Council were subject to separate restrictions by borough from 20 December 2020 to 26 December 2020. From 26 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 the restrictions were applied in the regulations to the area of Surrey County Council. From 6 January 2021 to 28 March 2021 regulations were applied to England as a whole rather than to individual local authority areas.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j The local boroughs within the area covered by Hampshire County Council were subject to separate restrictions by borough from 19 December 2020 to 31 December 2020. From 31 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 the restrictions were applied in the regulations to the area of Hampshire County Council. From 6 January 2021 to 28 March 2021 regulations were applied to England as a whole rather than to individual local authority areas.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e The local boroughs within the area covered by East Sussex County Council were subject to separate restrictions by borough from 20 December 2020 to 26 December 2020. From 26 December 2020 to 5 January 2021 the restrictions were applied in the regulations to the area of East Sussex County Council. From 6 January 2021 to 28 March 2021 regulations were applied to England as a whole rather than to individual local authority areas.
- ^ "Covid: London to move into tier 3 as infections rise". BBC. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ "Covid: Christmas rules tightened, new tier 4 announced - Boris Johnson". BBC News live. Retrieved 3 August 2021. (2:40
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Reg 15(1).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(2).
- ^ "People with fever or cough told to self-isolate". BBC News. 12 March 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ "Avoid office, pubs and travel to stop virus – PM". BBC News. 16 March 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ "UK schools to close from Friday". BBC News. 18 March 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ SI 350 (2020), Reg 2(1).
- ^ SI 684 (2020), Reg 2.
- ^ SI 685 (2020).
- ^ Halliday, Josh; Pidd, Helen (22 September 2020). "Local lockdowns failing to stop Covid spread in England, experts warn". The Guardian. Retrieved 14 October 2020.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 16.
- ^ "Local restriction tiers: what you need to know". Gov.uk. 23 November 2020. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1611 (2020).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Introductory text.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 15 (1).
- ^ "Full list of local restriction tiers by area". GOV.UK. Department of Health and Social Care. 26 November 2020. Retrieved 2 December 2020.
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(13)(b).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1 paragraph 1.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2 paragraph 1.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3 paragraph 1.
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A paras 3 and 4.
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3 paragraph 2 (4).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 4.
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(6), inserting into Sch 3A para 2(4).
- ^ SI 97 (2021), Para 2(2)(d).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(1).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 6.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(5).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(6).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(7).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(8).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(9).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(11).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(12).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(13)–(15).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(17).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(18).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(19).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(20).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(21).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(22)–(23).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(24).
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(6).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(25).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(26).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(6), replacing Sch 3A para 2(22).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(28)–(29).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(3)(a).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(30)–(35).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1646 (2020), Reg 2(6)(m).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(36).
- ^ SI 274 (2021), Reg 3(7)(b), inserting Sch 3A para 6(26).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(2)(b).
- ^ SI 274 (2021), Reg 3(7)(b), inserting Sch 3A para 6(27).
- ^ SI 274 (2021), Reg 3(7)(b), inserting Sch 3A para 6(28).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2, para 6(2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2, para 6(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2, para 5(2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2, para 5(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2, para 5(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, part 1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(2).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(5).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(6).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(7).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(8).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(9).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(10).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(11).
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(4)(e)).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(13).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(15).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(16).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(17).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(18).
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(5).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(19).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(21).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 2(22).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(6), adding Sch 3A para 2(25).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(6), adding Sch 3A para 2(26).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(6), adding Sch 3A para 2(27).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(4)(a).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(7).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg 2(6)(d).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Sc 1, para 1(3); Sch 2, paras 1(2) & 2(4); Sch 3, paras 1(2) & 2(2).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 6(1).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 7(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 11.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 11(2)(b).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9(4).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9(5).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9(1).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9(2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 9.
- ^ SI 1103 (2020), Schedule 1, para 10.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 14(1)–(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 14(3)(a).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 8.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 13(7).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 13(8).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 10(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 12(1).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(12)(d), amending the previously-stated period of 22–28 Dec.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 12(2)–(5).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 9(1).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 9(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 9(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 14(1).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 14(3).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3, para 11(1).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 15(2) to (5).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 15(6).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 15(7).
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(10)(d).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 15(6)(e).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 11(5).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 13(3).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 13(1).
- ^ SI 8 (2021), Reg 3(9).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 15(7)(gg).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 16(1).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 16(2).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 14(1).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 16(5).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(13), inserting Sch 3A para 17.
- ^ "Rule of six comes into effect to tackle coronavirus". Gov.uk. Retrieved 14 September 2020.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(3)(a).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(2).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(29)(b).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(3)(b).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(6)(b).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1518 (2020), Reg 4.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 3(8).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Reg 5(2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 5(8).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 5(6) and (7).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1 section 3 (30).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 2 section 4 (27).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 3 section 4 (25).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 4 (2).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 4 (8).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 4 (7).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 1, para 3(31).
- ^ SI 53 (2021), Regs 2(2)–(4).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(7)(b).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(3).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(3)(b).
- ^ SI 247 (2021), Reg 3(8), inserting new Schedule 4A.
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 14(1).
- ^ SI 1611 (2020), Reg 2(9).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Regs 9–13.
- ^ Holland, Charles (9 January 2020). "Boris's latest lockdown rules are more baffling than ever". The Spectator.
- ^ "Covid: Women on exercise trip 'surrounded by police'". BBC News.
- ^ "Covid: Fines reviewed after women 'surrounded by police'". BBC News.
- ^ Sparrow, Andrew (10 January 2021). "Matt Hancock says every 'flex' of lockdown rules could be fatal". The Guardian.
- ^ Holland, Charles (9 January 2020). "Boris's latest lockdown rules are more baffling than ever". The Spectator.
- ^ Smith, Oliver (10 January 2021). "How far can I travel under Lockdown 3?". The Telegraph.
- ^ "COVID-19: Police cancel fines for women who met for walk with coffees five miles from home". Sky News. 12 January 2021. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Boris Johnson criticised over bike ride seven miles from home". BBC News.
- ^ "Covid: Johnson's bike ride 'didn't break rules'". BBC News.
- ^ Campbell, Lucy (12 January 2021). "Stay local England exercise rule open to interpretation, minister admits". The Guardian.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1533 (2020), Reg 2.
- ^ SI 1572 (2020).
- ^ BBC News https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-55428017
- ^ "Covid: Cornwall in tier 2 but Scilly stays in tier 1". BBC. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19: Twenty million in England added to toughest level of restrictions". BBC News. 30 December 2020. Retrieved 30 December 2020.
- ^ SI 8 (2021).
- ^ SI 97 (2021).
- ^ SI 247 (2021).
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ [3]
- ^ [4]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 4, part 1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1611 (2020), Part 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f SI 1572 (2020), Reg 2.
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(7).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(9).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e SI 1654 (2020), Reg(2)(5).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c SI 1654 (2020), Reg(2)(6).
- ^ Jump up to: a b SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(8)(c).
- ^ SI 1654 (2020), Reg(2)(6)(a)(iii).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d SI 1654 (2020), Reg(2)(4).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Reg 8(4)(b).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g SI 8 (2021), Reg(3)(13)(b).
- ^ SI 1374 (2020), Schedule 4, part 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e SI 8 (2021), Reg(3)(13)(a).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(7)(f).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(8)(d).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(7)(c).
- ^ SI 1646 (2020), Reg(2)(7)(g).
- ^ SI 1654 (2020), Reg(2)(5)(g)(ii).
Bibliography[]
- "SI 350". Legislation.gov.uk. 26 March 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (England) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- "SI 684". Legislation.gov.uk. 4 July 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (England) (No. 2) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- "SI 685". Legislation.gov.uk. 4 July 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (Leicester) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- "SI 1103". Legislation.gov.uk. 14 October 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Local COVID-19 Alert Level) (Medium) (England) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- "SI 1374". Legislation.gov.uk. 2 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2020.
- "SI 1518". Legislation.gov.uk. 14 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (Self- Isolation and Linked Households) (England) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- "SI 1533". Legislation.gov.uk. 16 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- "SI 1572". Legislation.gov.uk. 19 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) (No. 2) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- "SI 1611". Legislation.gov.uk. 20 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers and Obligations of Undertakings) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 20 December 2020.
- "SI 1646". Legislation.gov.uk. 26 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) (No. 3) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 24 December 2020.
- "SI 1654". Legislation.gov.uk. 31 December 2020. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) (No. 4) Regulations 2020. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- "SI 8". Legislation.gov.uk. 6 January 2021. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (No. 3) and (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2021. Retrieved 5 January 2021.
- "SI 53". Legislation.gov.uk. 20 January 2021. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2021. Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- "SI 97". Legislation.gov.uk. 29 January 2021. The Health Protection (Coronavirus, Restrictions) (All Tiers and Self-Isolation) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2021. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- "SI 247". Legislation.gov.uk. 8 March 2021. The Health Protection (Coronavirus) (Wearing of Face Coverings in a Relevant Place and Restrictions: All Tiers) (England) (Amendment) Regulations 2021. Retrieved 7 March 2021.
External links[]
- Guidance: Local restriction tiers: what you need to know – Department of Health and Social Care, 30 November 2020, updated 19 December
- Guidance: Closing certain businesses and venues in England – Cabinet Office, updated 24 December 2020
- Guidance: National lockdown – Cabinet office, 4 January 2021, updated 8 March
- Guidance: Children of critical workers and vulnerable children who can access schools or educational settings – referred to as "the relevant guidance" in SI 8 (2021) – Department for Education, updated 5 January 2021
- Statutory Instruments of the United Kingdom
- 2020 in England
- 2021 in England
- COVID-19 pandemic in England
- Public health in the United Kingdom
- 2020 in British law
- Law associated with the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom