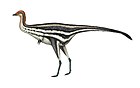
Therizinosauria
| Therizinosaurs Temporal range: Early–Late Cretaceous, 139–66 Ma
PreꞒ
Ꞓ
O
S
D
C
P
T
J
K
Pg
N
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Collection of five therizinosaurs, clockwise from top left: Suzhousaurus, Erliansaurus, Nothronychus, Falcarius and Jianchangosaurus. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | Maniraptora |
| Clade: | †Therizinosauria Russell, 1997 |
| Subgroups | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Therizinosaurs (once called segnosaurs) were small to giant-sized, mainly herbivorous, theropod dinosaurs that have been found across the Early to Late Cretaceous deposits in Asia and North America. Various features of the forelimbs, skull and pelvis unite these finds as both theropods and maniraptorans, close relatives to birds. The representative genus, Therizinosaurus, is derived from the Greek θερίζω (therízō, meaning 'to reap') and σαῦρος (saûros, meaning 'lizard'). The older representative, Segnosaurus, is derived from the Latin word sēgnis (meaning 'slow') and the Greek σαῦρος.
History of research[]

Therizinosaurs were long considered an enigmatic group, whose mosaic of features resembling those of various different dinosaur groups, and scarcity of their fossils, led to controversy over their evolutionary relationships for decades after their initial discovery. The first genus, Therizinosaurus, was originally identified as a turtle when described from forelimb elements in 1954.[2] Perle noted in 1979 that the Segnosaurus fossils were possibly representative of a new family of dinosaurs, which he tentatively classified as theropods (traditionally thought of as the "meat-eating" dinosaurs). He named the family Segnosauridae, with Segnosaurus as type genus and sole member. He distinguished Segnosauridae from the theropod families Deinocheiridae and Therizinosauridae (then only known from the genera Deinocheirus and Therizinosaurus, both mainly represented by large forelimbs found in Mongolia) by features of their humeri and hand claws.[3] Later in 1979, Barsbold and Perle found the pelvic features of segnosaurids and dromaeosaurids so different from those of "true" theropods that they should be separated into three taxa of the same rank, possibly at the level of infraorder within Saurischia (one of the two main divisions of dinosaurs, the other being Ornithischia).[4]
In 1980, Barsbold and Perle named the new theropod infraorder Segnosauria, containing only Segnosauridae. In the same article, they named the new genus Erlikosaurus (known from a well-preserved skull and partial skeleton) which they tentatively considered a segnosaurid, and reported a partial pelvis of an undetermined segnosaurian, both from the same formation as Segnosaurus. Combined, the specimens provided relatively complete data on this group; they were united by their opisthopubic pelvis, slender mandible, and the toothless front of their jaws. Barsbold and Perle stated that though some of their features resembled those of ornithischians and sauropods, these similarities were superficial, and were distinct when examined in detail. While they were essentially different from other theropods (perhaps due to diverging from them relatively early), and therefore warranted a new infraorder, they did show similarities with them. Since the Erlikosaurus specimen lacked a pelvis, the authors were unsure if that of the undetermined segnosaurian could belong to it, in which case they would consider it part of a separate family.[5] Though Erlikosaurus was difficult to compare directly to Segnosaurus due to the incompleteness of their remains, Perle stated in 1981 that there was no justification for separating it into another family.[6]

In 1982, Perle reported hindlimb fragments similar to those of Segnosaurus, and assigned them to Therizinosaurus, whose forelimbs had been found in almost the same location. He concluded that Therizinosauridae, Deinocheiridae, and Segnosauridae, which all had enlarged forelimbs, represented the same taxonomic group. Segnosaurus and Therizinosaurus were particularly similar, leading Perle to suggest they belonged in a family to the exclusion of Deinocheiridae (today, Deinocheirus is recognized as an ornithomimosaur).[7][8] Barsbold retained Segnosaurus and Erlikosaurus in the family Segnosauridae in 1983, and named the new genus Enigmosaurus based on the previously undetermined segnosaurian pelvis, which he placed in its own family, Enigmosauridae, within Segnosauria. Though the structure of the pelvis of Erlikosaurus was unknown, Barsbold considered it unlikely the Enigmosaurus pelvis belonged to it, since Erlikosaurus and Segnosaurus were so similar in other respects, while the pelvis of Enigmosaurus was very different from that of Segnosaurus. Barsbold found that segnosaurids were so peculiar compared to more typical theropods that they were either a very significant deviation in theropod evolution, or that they went "beyond the borders" of this group, but opted to retain them within Theropoda.[9] In the same year, Barsbold stated that the segnosaurian pelvis deviated strongly from the theropod norm, and found the configuration of their ilia generally similar to those of sauropods.[10]

Paleontologist Gregory S. Paul concluded in 1984 that segnosaurs did not possess any theropodan features, but were instead derived, late-surviving Cretaceous prosauropods with adaptations similar to those of ornithischians. He found segnosaurs similar to prosauropods in the morphology of their snout, mandible, and hindfoot, and to ornithischians in their cheek, palate, pubis, and ankle, and similar to early dinosaurs in other respects. He proposed that ornithischians were descended from prosauropods, and that the segnosaurs were an intermediate relict of this transition, which supposedly took place during the Triassic period. In this way, he considered segnosaurians to be to herbivorous dinosaurs what monotremes are to mammals. He did not rule out that segnosaurs could be derived from theropods, or that segnosaurs, prosauropods and ornithischians were each independently derived from early dinosaurs, but found these options unlikely. He considered the common descent of these groups as support for the idea that dinosaurs were a monophyletic (natural) group, which was contested by some paleontologists at the time (who instead thought different dinosaurs groups evolved independently from thecodonts).[11] Paleontologist David B. Norman considered Paul's idea a contentious claim "bound to provoke much argument" in 1985.[12] In 1988, Paul maintained that segnosaurs were late surviving ornithischian-like prosauropods, and proposed a segnosaurian identity for Therizinosaurus. He also placed segnosauria within Phytodinosauria, a superorder that palaontologist Robert Bakker had created in 1985 to retain all plant-eating dinosaurs.[13] In a 1986 study of the interrelationships of saurischian dinosaurs, paleontologist Jacques Gauthier concluded that segnosaurs were prosauropods. While he conceded they had similarities with ornithischians and theropods, he proposed these featured had evolved independently.[14] In a 1989 conference abstract about sauropodomorph interrelatonships, paleontologist Paul Sereno also considered segnosaurs as prosauropods, based on skull features.[15]

In a 1990 review article, Barsbold and paleontologist Teresa Maryańska found Segnosauria to be a rare and aberrant group of saurischians, in an unresolved position among sauropodomorphs and theropods, probably closer to the former. They therefore listed them as Saurischia sedis mutabilis ("position subject to change"). Though they agreed the hindlimbs assigned to Therizinosaurus in 1982 were segnosaurian, they did not consider this justification for Therizinosaurus itself being a segnosaur, since it was only known from forelimbs.[16] In 1993, paleontologists Dale A. Russell and Dong Zhi-Ming described the new genus Alxasaurus from China, at the time the most complete large theropod from its time and place. While it was similar to prosauropods in some respects, the detailed morphology of its limbs linked it to Therizinosaurus and segnosaurs. Since it preserved both fore and hindlimbs, Alxasaurus showed that Perle's assignment of segnosaurian hindlimbs to Therizinosaurus was probably correct. Russell and Dong therefore proposed that Segnosauridae was a junior synonym of Therizinosauridae (since the latter name was older), with Alxasaurus being the most completely known representative so far, providing a better understanding of the group. They also named the new higher taxonomic rank Therizinosauroidea to contain Alxasaurus and Therizinosauridae (since the new genus was somewhat different from its relatives), which they placed in the group Tetanurae within Theropoda. They considered therizinosaurs most closely related to ornithomimids, troodontids, and oviraptorids, which they placed together in the group Oviraptorosauria (since they found Maniraptora, the conventional grouping of these, invalid, and the higher level taxonomy of theropods was in flux at the time).[17][18]

The synonymy of Segnosauridae with Therizinosauridae was accepted by Perle himself and co-authors of a redescription of the holotype skull of Erlikosaurus in 1994, and they considered therizinosaurs maniraptoran theropods, the group that also includes modern birds (since they did find Maniraptora to be valid through their analysis). They also discussed the previous ornithischian and sauropod hypotheses for therizinosaur affinities in detail and demonstrated various faults with them.[19] Palaeontologist Lev Alexandrovich Nessov rejected that therizinosaurs were theropods in 1995, and instead considered them a distinct group within saurischia.[20] In 1996, paleontologist Thomas R. Holtz Jr. found therizinosaurs to group with oviraptorosaurs in a phylogenetic analysis of coelurosauria.[21] In 1999, paleontologist Xing Xu and colleagues described a small, basal therizinosauroid from China, Beipiaosaurus, which confirmed that the group belonged among the coelurosaurian theropods, and that similarities with prosauropods had evolved independently. They published the first ever cladogram showing the evolutionary relationships of Therizinosauria, and demonstrated that Beipiaosaurus had features of more basal theropods, coelurosaurs, and therizinosaurs.[22]
By the early 21st century, many more therizinosaur taxa had been discovered, including outside Asia (the first being Nothronychus from North America), as well as various basal taxa that helped understanding of the early evolution of the group (such as Falcarius, also form North America). Therizinosaurs were not considered as rare or aberrant anymore, but more diverse than previously thought (including in size), and their classification as maniraptoran theropods was generally accepted.[23][24][25] The placement of Therizinosauria within Maniraptora continued to be unclear; in 2017, paleontologist Alan H. Turner and colleagues found them to group with oviraptorosaurs, while Zanno and colleagues found them to be the most basal clade within Maniraptora in 2009, bracketed by Ornithomimosauria and Alvarezsauridae.[26][27] Despite the additional fossil material, the interrelations within the group were also still uncertain by 2010, when Zanno conducted the most detailed phylogenetic analysis of the Therizinosauria until that point. She cited the inaccessibility, damage, potential loss of holotype specimens, scarcity of cranial remains, and fragmentary specimens with few overlapping elements as the most significant obstacles to resolving the evolutionary relationships within the group.[28]
Description[]

Therizinosaurs spanned a large range of sizes, from the smaller Beipiaosaurus (2.2 m (7.2 ft) long)[22] and Jianchangosaurus (2 m (6.6 ft) long)[29] to the large-sized 6–7 m (20–23 ft) long Segnosaurus and Suzhousaurus.[30][31] Therizinosaurus itself, obtained the top dimensions of the group, growing up to 10 m (33 ft) long and weighing over 5 t (11,000 lb), dimensions that make the genus among the largest-known theropods.[31]
Therizinosaurs had a very distinctive, often confusing set of characteristics. Their long necks, wide torsos, and hind feet with four toes used in walking resembled those of basal sauropodomorph dinosaurs. Their unique hip bones, which pointed backwards and were partially fused together, initially reminded paleontologists of the "bird-hipped" ornithischians. Among the most striking characteristics of therizinosaurs are the enormous claws on their hands, which reached lengths of around one meter in Therizinosaurus. The unusual range of motion in therizinosaur forelimbs, which allowed them to reach forward to a degree other theropods could not achieve, also supports the idea that they were mainly herbivorous. Therizinosaurs may have used their long reach and strongly curved claws to grasp and shear leafy branches, in a manner similar to large mammals that lived later on, such as chalicotheres, ground sloths, great apes, and giant pandas.[32] Skin impressions from Beipiaosaurus indicate that therizinosaurs were covered with a coat of primitive, down-like feathers similar to those seen in the compsognathid Sinosauropteryx, as well as longer, simpler, quill-like feathers that may have been used in display.[22][33]
Classification and systematics[]
Taxonomy[]

Barsbold and Perle named the group Segnosauria as an infraorder of Theropoda in 1980.[5] Dong Zhiming went further, placing the segnosaurs in their own order, Segnosaurischia.[34] This name has been abandoned since the discovery that segnosaurs are a specialized group within the suborder Theropoda. Clark et al. 2004 considered Segnosaurischia a synonym of Therizinosauroidea.[19]
The infraorder Therizinosauria was first coined by Dale Russell in 1997—effectively replacing the older name Segnosauria, which has not yet been defined as a clade—to contain all therizinosaurian dinosaurs.[35] The superfamily Therizinosauroidea was first coined in 1993 as a superfamily with no phylogenetic definition.[17] The family Therizinosauridae had been established by Maleev in 1954 to include only the bizarre, giant-clawed theropod Therizinosaurus.[2] Subsequent analyses have proven this family to be more diverse and synonymous with Segnosauridae.[28][36]
The following taxonomy follows Zanno 2010, unless otherwise noted.[28]
- Branch Therizinosauria
- Genus Falcarius
- Genus Martharaptor[37]
- Genus Jianchangosaurus[29]
- Superfamily Therizinosauroidea
- Genus Beipiaosaurus
- Genus Enigmosaurus
- Genus Erliansaurus (more related to Therizinosauridae)
- Genus Neimongosaurus (more related to Therizinosauridae)
- Genus Suzhousaurus
- Family Alxasauridae (dubious utility)
- Family Therizinosauridae
Phylogeny[]

Therizinosauria is defined as Alxasaurus, Enigmosaurus, Erlikosaurus, Nanshiungosaurus, Segnosaurus, Therizinosaurus, and all taxa closer to them than to oviraptorosaurs, ornithomimids, and troodontids.[35] Paul Sereno, in 2005, modified this definition to the most inclusive clade containing Therizinosaurus but not Ornithomimus, Oviraptor, Shuvuuia, Tyrannosaurus, or Troodon.[38]
When it was later realized that Therizinosaurus was an advanced therizinosaur more related to Alxasaurus than other dinosaur lineages, Therizinosauroidea was coined to include Alxasaurus and Therizinosauridae, and has largely replaced the use of the older name Segnosauria in phylogenetic studies, mainly because of the association of the name Segnosauria with the discredited idea that these animals were relatives of prosauropods.[17] Therizinosauroidea was first defined by Zhang et al. in 2001, as the clade containing all theropods more closely related to Therizinosaurus than to birds. This definition, however, defines the same group as the pre-existing Therizinosauria. An alternate definition was given by Clark in 2004 (as the last common ancestor of Therizinosaurus and Beipiaosaurus and all its descendants), comprising a narrower group that excludes more primitive therizinosaurs, such as Falcarius, and allows the name Therizinosauria to remain in use for the larger group comprising all therizinosaurs.[39] This definition was followed by Sereno (2005), Zanno et al. (2009) and Zanno (2010),[28][38][40] though other subsequent studies, such as Senter (2007, 2012) have continued to use Therizinosauroidea for the therizinosaur "total group".[41]
The cladogram below follows the extensive phylogenetic analysis of the Therizinosauria by Lindsay E. Zanno in 2010.[28]
| Therizinosauria |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Below is the recently performed phylogenetic analysis performed by Hartman et al. 2019 using the data provided by Zanno in 2010:[36]
| Therizinosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleobiology[]
Senses[]
CT scans published by Stephan Lautenschlager et al. 2012 focused on the skull and brain cavity of Erlikosaurus, revealing it to have a large forebrain, and suggesting it had well developed senses of balance, hearing and smell, all of which would have been useful in evading predators, finding food, or in performing complex social behavior. These senses were also well-developed in earlier coelurosaurs and other theropods, indicating that therizinosaurs may have inherited many of these features from their carnivorous ancestors and used them for their specialized dietary purposes.[42]
Reproduction[]

Dinosaur eggs with embryos of the Dendroolithidae type from the Nanchao Formation were identified as belonging to therizinosaurs based on anatomical features, and described by paleontologist Martin Kundrát and colleagues in 2007. The development of the embryos (their bones were extensiely ossified) and the fact that no adults were found in association with the nests indicate that theirzinosaur hatchlings were precocial, capabale of locomotion from birth, and able to leave their nests to feed alone, independently of their parents. The development of the teeth of the hatchlings was consistent with an omnivorous diet. Subterraneously constructed nests are also indicative of a lack of parental care during the incubation period.[43][44]
In a 2013 conference abstract, paleontologist Yoshitsugu Kobayashi and colleagues reported a nesting ground of theropod dinosaurs at the Javkhlant Formation, which contained at least 17 egg clutches from the same layer within an area of 22 m by 52 m. Each clutch contained 8 spherical eggs with rough surfaces which were in contact with each other and arranged in a circular structure without a central opening. Based on microscopical features in the eggshells, the researchers identified the eggs as the type Dendroolithidae, which had previously been attributed to therizinosaurs. Though therizinosaurs are not known from the Javkhlant Formation, it overlies the Bayan Shireh Formation, where Segnosaurus, Erlikosaurus, and Enigmosaurus were found. The multiple clutches indicate that some therizinosaurs were colonial nesters, like hadrosaurs, prosauropods, titanosaurs, and birds, and the fact that they were found in a single stratigraphic layer suggests the dinosaurs nested at the site on a single occasion, and therefore did not exhibit site fidelity. The discovery was the first record of colonially nesting non-avian theropods from Asia, as well as the largest known non-avian theropod colony.[45]
Timeline of genera descriptions[]

References[]
- ^ Xu, X.; Zhao, X.; Clark, J. (2001). "A New Therizinosaur from the Lower Jurassic Lower Lufeng Formation of Yunnan, China". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 21 (3): 477–483. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2001)021[0477:antftl]2.0.co;2. JSTOR 20061976.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Maleev, E. A. (1954). "Noviy cherepachoobrazhniy yashcher v Mongolii" [New turtle−like reptile in Mongolia]. Priroda (3): 106–108. Translated paper
- ^ Perle, A. (1979). Translated by Siskron, C.; Welles, S. P. "Segnosauridae – novoe semeistvo teropod is posdnego mela Mongolii" [Segnosauridae – a new family of Theropoda from the Lower Cretaceous of Mongolia] (PDF). Trudy – Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya (in Russian). 8: 45–55. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-11-28. Retrieved 2016-10-18.
- ^ Barsbold, R.; Perle, A. (1979). "Modiphikatsiy tasa sayrisziy i parallelinoe rasvitie zishchnich dinosavrov. MODIFICATION IN THE SAURISCHIAN PELVIS AND THE PARALLEL DEVELOPMENT OF PREDATORY DINOSAURS". Transactions of the Joint Soviet Mongolian Paleontological Expedition. 8: 39–44.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Barsbold, R.; Perle, A. (1980). "Segnosauria, a new infraorder of carnivorous dinosaurs" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 25 (2): 190–192.
- ^ Altangerel Perle (1981). "Noviy segnozavrid iz verchnego mela Mongolii". Trudy – Sovmestnaya Sovetsko-Mongol'skaya Paleontologicheskaya Ekspeditsiya. 15: 50–59.
- ^ Perle, A. (1982). "A hind limb of Therizinosaurus from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia". Problems in Mongolian Geology (in Russian). 5: 94–98. Translated paper
- ^ Lee, Y.N.; Barsbold, R.; Currie, P.J.; Kobayashi, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Godefroit, P.; Escuillié, F.O.; Chinzorig, T. (2014). "Resolving the long-standing enigmas of a giant ornithomimosaur Deinocheirus mirificus". Nature. 515 (7526): 257–260. Bibcode:2014Natur.515..257L. doi:10.1038/nature13874. PMID 25337880.
- ^ Barsbold, R. (1983). "Хищные динозавры мела Монголии" [Carnivorous dinosaurs from the Cretaceous of Mongolia] (PDF). Transactions of the Joint Soviet-Mongolian Paleontological Expedition (in Russian). 19: 89. Translated paper
- ^ Barsbold, R. (1983). "O ptich'ikh chertakh v stroyenii khishchnykh dinozavrov" [Avian features in the morphology of predatory dinosaurs]. Transactions of the Joint Soviet Mongolian Paleontological Expedition (in Russian). 24: 96–103. Translated paper
- ^ Paul, G. S. (1984). "The Segnosaurian Dinosaurs: Relics of the Prosauropod-Ornithischian Transition?". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 4 (4): 507–515. doi:10.1080/02724634.1984.10012026. ISSN 0272-4634. JSTOR 4523011.
- ^ Norman, D. B. (1985). "Dromaeosaurids". The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs: An Original and Compelling Insight into Life in the Dinosaur Kingdom. New York: Crescent Books. pp. 52–53. ISBN 978-0-517-46890-6.
- ^ Paul, G. S. (1988). Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 185, 283. ISBN 978-0-671-61946-6.
- ^ Gauthier, J. (1986). "Saurischian monophyly and the origin of birds". Memoirs of the California Academy of Sciences. 8: 45. Archived from the original on 2019-08-16. Retrieved 2019-12-03.
- ^ Sereno, P. (1989). "Prosauropod monophyly and basal sauropodomorph phylogeny". Abstract of Papers. Forty-Ninth Annual Meeting Society of Vertebrate Paleontology. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 9 (3 Supplement). p. 39A. ISSN 0272-4634. JSTOR 4523276.
- ^ Barsbold, R. (1990). "Saurischia Sedis Mutabilis: Segnosauria". In Weishampel, D. B.; Osmolska, H.; Dodson, P. (eds.). The Dinosauria (1st ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 408–415. ISBN 978-0-520-06727-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Russell, D. A.; Dong, Z.-M. (1993). "The affinities of a new theropod from the Alxa Desert, Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 30 (10): 2107–2127. Bibcode:1993CaJES..30.2107R. doi:10.1139/e93-183.
- ^ Russell, D. A. (1997). "Therizinosauria". In Currie, Philip J.; Padian, Kevin (eds.). Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 729–730. ISBN 978-0-12-226810-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Clark, J. M.; Perle, A.; Norell, M. (1994). "The skull of Erlicosaurus andrewsi, a Late Cretaceous "Segnosaur" (Theropoda, Therizinosauridae) from Mongolia". American Museum Novitates. 3115: 1–39. hdl:2246/3712.
- ^ Nessov, L. A., 1995, Dinosaurs of northern Eurasia: New data about assemblages, ecology and paleobiogeography. Saint Petersburg
- ^ Holtz, T. R. (1996). "Phylogenetic Taxonomy of the Coelurosauria (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Paleontology. 70 (3): 536–538. doi:10.1017/S0022336000038506. ISSN 0022-3360. JSTOR 1306452.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, X. (1999). "A therizinosauroid dinosaur with integumentary structures from China". Nature. 399 (6734): 350–354. Bibcode:1999Natur.399..350X. doi:10.1038/20670.
- ^ Kirkland, James I.; Wolfe, Douglas G. (2001). "First Definitive Therizinosaurid (Dinosauria; Theropoda) from North America". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 21 (3): 410–414. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2001)021[0410:FDTDTF]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. JSTOR 20061971.
- ^ Zhang, X.-H.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Sereno, P. C.; Kuang, X.-W.; Tan, L. (2001). "A long-necked therizinosauroid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Iren Dabasu Formation of Nei Mongol, People's Republic of China" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 39 (4): 282–290.
- ^ Kirkland, J. I.; Zanno, L. E.; Sampson, S. D.; Clark, J. M.; DeBlieux, D. D. (2005). "A primitive therizinosauroid dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Utah". Nature. 435 (7038): 84–87. Bibcode:2005Natur.435...84K. doi:10.1038/nature03468. PMID 15875020.
- ^ Turner, A. H.; Pol, D.; Clarke, J. A.; Erickson, G. M.; Norell, M. A. (2007). "A Basal Dromaeosaurid and Size Evolution Preceding Avian Flight". Science. 317 (5843): 1378–1381. Bibcode:2007Sci...317.1378T. doi:10.1126/science.1144066. PMID 17823350.
- ^ Zanno, L. E.; Gillette, D. D.; Albright, L. B.; Titus, A. L. (2009). "A New North American Therizinosaurid and the Role of Herbivory in 'Predatory' Dinosaur Evolution". Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 276 (1672): 3505–3511. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1029. ISSN 0962-8452. JSTOR 30244145. PMC 2817200. PMID 19605396.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Zanno, L. E. (2010). "A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-evaluation of Therizinosauria (Dinosauria: Maniraptora)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (4): 503–543. doi:10.1080/14772019.2010.488045.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Pu, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Lü, J.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jia, S. (2013). "An Unusual Basal Therizinosaur Dinosaur with an Ornithischian Dental Arrangement from Northeastern China". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e63423. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...863423P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063423. PMC 3667168. PMID 23734177.
- ^ Holtz, T. R.; Rey, L. V. (2007). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages. Random House. ISBN 9780375824197. Genus List for Holtz 2012 Weight Information
- ^ Jump up to: a b Paul, G. S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs (2nd ed.). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 162–168. ISBN 9780691167664.
- ^ * Burch, S. (2006). "The range of motion of the glenohumeral joint of the therizinosaur Neimongosaurus yangi (Dinosauria: Theropoda)." Chicago Biological Investigator, 3(2): 20. (Abstract).
- ^ Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; You, H.L. (2009). "A new feather type in a nonavian theropod and the early evolution of feathers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (3): 832–4. Bibcode:2009PNAS..106..832X. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810055106. PMC 2630069. PMID 19139401.
- ^ Dong, Z. (1992). Dinosaurian Faunas of China. Beijing: China Ocean Press. p. 187. ISBN 3-540-52084-8.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Russell, D. A. (1997). "Therizinosauria". In Currie, P. J.; Padian, K. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. San Diego: Academic Press. pp. 729−730. ISBN 978-0-12-226810-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hartman, S.; Mortimer, M.; Wahl, W. R.; Lomax, D. R.; Lippincott, J.; Lovelace, D. M. (2019). "A new paravian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of North America supports a late acquisition of avian flight". PeerJ. 7: e7247. doi:10.7717/peerj.7247. PMC 6626525. PMID 31333906.
- ^ Senter, P.; Kirkland, J. I.; Deblieux, D. D. (2012). "Martharaptor greenriverensis, a New Theropod Dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah". PLOS ONE. 7 (8): e43911. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...743911S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0043911. PMC 3430620. PMID 22952806.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Sereno, P. C. 2005. Stem Archosauria—TaxonSearch Archived 2009-01-15 at the Wayback Machine [version 1.0, 2005 November 7]
- ^ Clark, J.M., Maryanska, T., and Barsbold, R. (2004). "Therizinosauroidea." Pp. 151– 164 in Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., and Osmólska, H. (eds.). The Dinosauria, Second Edition. University of California Press., 861 pp.
- ^ Zanno, L. E.; Gillette, D. D.; Albright, L. B.; Titus, A. L. (2009). "A new North American therizinosaurid and the role of herbivory in predatory dinosaur evolution". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 276 (1672): 3505−3511. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1029. JSTOR 30244145. PMC 2817200. PMID 19605396.
- ^ Senter, P (2007). "A new look at the phylogeny of Coelurosauria (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 5: 429–463. doi:10.1017/S1477201907002143.
- ^ Lautenschlager, S.; Emily, J. R.; Perle, A.; Lindsay, E. Z.; Lawrence, M. W. (2012). "The Endocranial Anatomy of Therizinosauria and Its Implications for Sensory and Cognitive Function". PLoS ONE. 7 (12): e52289. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...752289L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052289. PMC 3526574. PMID 23284972.
- ^ Kundrát, M.; Cruickshank, A. R. I.; Manning, T. W.; Nudds, J. (2007). "Embryos of therizinosauroid theropods from the Upper Cretaceous of China: diagnosis and analysis of ossification patterns". Acta Zoologica. 89 (3): 231–251. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6395.2007.00311.x.
- ^ Clark, J. M.; Maryańska, T.; Barsbold, R. (2004). "Therizinosauroidea". In Weishampel, D. B.; Dodson, P.; Osmolska, H. (eds.). The Dinosauria (2 ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 151–164. ISBN 978-0-520-24209-8.
- ^ "First record of a dinosaur nesting colony from Mongolia reveals nesting behavior of therizinosauroids". Hokkaido University. 2013.
External links[]
- Therizinosaurs
- Early Cretaceous first appearances
- Maastrichtian extinctions
- Clawed herbivores