Timeline of first orbital launches by country
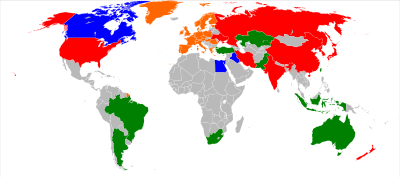
This is a timeline of first orbital launches by country. While a number of countries have built satellites, as of 2019, eleven countries have had the capability to send objects into orbit using their own launch vehicles. Russia and Ukraine inherited the space launchers and satellites capability from the Soviet Union, following its dissolution in 1991. Russia launches its rockets from its own and foreign (Kazakh) spaceports.
Ukraine launched only from foreign (Russian and Kazakh) launch facilities until 2015, after which political differences with Russia effectively halted Ukraine's ability to produce orbital rockets.[1][2] France became a space power independently, launching a payload into orbit from Algeria, before joining space launcher facilities in the multi-national Ariane project. The United Kingdom became a space power independently following a single payload insertion into orbit from Australia, before discontinuing official participation in space launch capability, including the Ariane project, in the 1970s.
Thus, as of May 2021, nine countries and one inter-governmental organisation (ESA) currently have a proven orbital launch capability,[a] and three countries (France, Italy,[3] and UK) formerly had such an independent capability. In all cases where a country has conducted independent human spaceflights (as of 2021, three - USSR/Russia, USA, and China), these launches were preceded by independent unmanned launch capability.
The race to launch the first satellite was closely contested by the Soviet Union and the United States, and was the beginning of the Space Race. The launching of satellites, while still contributing to national prestige, is a significant economic activity as well, with public and private rocket systems competing for launches, using cost and reliability as selling points.

List of first orbital launches by country[]
Countries like South Korea are not included since they have not yet developed an orbital rocket from scratch; i.e., an orbital rocket that was designed and engineered in its entirety in the country in question.
| Order | Country[a] | Sector | Satellite | Rocket | Location | Date (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Governmental | Sputnik 1 | Sputnik-PS | Baikonur, Soviet Union (today Kazakhstan) | 4 October 1957 | |
| 2 | Governmental | Explorer 1 | Juno I | Cape Canaveral, United States | 1 February 1958 | |
| 3 | Governmental | Astérix | Diamant A | CIEES/Hammaguir, Algeria | 26 November 1965 | |
| 4 | Governmental | Ohsumi | Lambda-4S | Uchinoura, Japan | 11 February 1970 | |
| 5 | Governmental | Dong Fang Hong I | Long March 1 | Jiuquan, China | 24 April 1970 | |
| 6 | Governmental | Prospero | Black Arrow | Woomera, Australia | 28 October 1971 | |
| — | European Space Agency[h] | Governmental | CAT-1 (Obélix[7]) | Ariane 1 | Kourou, French Guiana | 24 December 1979 |
| 7 | Governmental | Rohini 1 (RS-1) | SLV | Sriharikota, India | 18 July 1980 | |
| 8 | Governmental | Ofeq 1 | Shavit | Palmachim, Israel | 19 September 1988 | |
| — | Governmental | Strela-3 (x6, Russian) | Tsyklon-3 | Plesetsk, Russia | 28 September 1991 | |
| — | Governmental | Kosmos 2175 | Soyuz-U | Plesetsk, Russia | 21 January 1992 | |
| 9 | Governmental | Omid | Safir-1A | Semnan, Iran | 2 February 2009 | |
| 10 | Governmental | Kwangmyŏngsŏng-3 Unit 2 | Unha-3 | Sohae, North Korea | 12 December 2012[k] | |
| 11 | Governmental | STSat-2C | Naro-1 | Naro Space Center, South Korea | 30 January 2013;[10] |
Notes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b The ten countries and successor states/union indicated in bold retain orbital launch capability.
- ^ Sea Launch is currently 85% owned by Russia's RKK Energia.[4] Previously, it was a consortium of four companies from the United States, Russia, Ukraine and Norway: Boeing, Energia, Yuzhmash and Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and Aker Kværner, respectively. Its first demonstration satellite, DemoSat, was launched on 27 March 1999 using a Ukrainian-mainly Zenit 3SL rocket from the Ocean Odyssey (a former drilling-rig) in the equatorial Pacific Ocean. Sea Launch has launched numerous satellites since, with few failures.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c The Soviet Union's successor state, Russia, took over the Soviet space program after the 1991 Soviet Union's dissolution with Ukraine inheriting a smaller part of the Soviet space program's space launcher and satellite capability. Soviet heritage launcher designs were utilized also for the joint Sea Launch system.[b]
- ^ Jump up to: a b United States and China also have private companies capable of space launch
- ^ ESA in its current form was founded with the ESA Convention in 1975, when ESRO was merged with ELDO. France signed the ESA Convention on 30 May 1975[5] and deposited the instruments of ratification on 10 October 1980,[5] when the convention came into force.[5] During this interval the agency functioned in a de facto fashion.[6]
- ^ France launched its first satellite by its own rocket from Algeria, which had been a French territory when the spaceport was built but had achieved independence before the satellite launch. Later France provided a spaceport for ESA space launchers in French Guiana, transferring between 1975 and 1980[e] its capability to ESA as a founding member.
- ^ UK only self-launched a single satellite (in 1971) and that from a commonwealth (Australian) spaceport. Later it joined the ESA, but not the launcher consortium Arianespace, therefore becoming the only nation that developed launch capability and then officially lost it.
- ^ The European Space Agency developed the Ariane rocket family (the second European launcher program after the failed Europa rocket program under ELDO) operating from its Guiana Space Centre spaceport (first successful launch on 24 December 1979 when Ariane 1 launcher placed the technological capsule CAT-1 on orbit). ESA signatories at the time of first launch were Sweden, Switzerland, Germany, Denmark, Italy, United Kingdom, Belgium, Netherlands, Spain, France and Ireland. Private/public companies and/or governments of these countries (with the exception of Ireland and the United Kingdom) became shareholders in the commercial company Arianespace dealing with production, operation, and marketing. Later Norway became an ESA member and Arianespace shareholder. Additional subsequent ESA member states are Austria, Finland, Portugal, Greece, Luxembourg, the Czech Republic, Romania and Poland.
- ^ Ukraine provided its own space launcher to Russia and did not use its own space launcher to put satellites in orbit (first Ukrainian satellite is Sich-1 launched on August 31, 1995 by Ukrainian Tsyklon-3 from Plesetsk Cosmodrome in Russia).
- ^ Although it has signed the Outer Space Treaty, Iran is the only space launch capable nation that has not ratified the treaty.
- ^ The North Korean government first claimed a successful launch on 31 August 1998 with Kwangmyŏngsŏng-1 from Musudan-ri, which was internationally determined to be a failure. Another launch on 5 April 2009, with the Kwangmyŏngsŏng-2 satellite, was also reported by North Korea to have reached orbit;[8] however, US and South Korean officials stated that the launch failed to reach orbit.[9]
Other launches and projects[]
The above list includes confirmed satellite launches with rockets produced by the launching country. Lists with differing criteria might include the following launches:
Failed launches[]
 Brazil has yet to launch a satellite into orbit independently and its space program suffered three satellite launch failures, the latest being the explosion of a VLS-1 rocket on 22 August 2003 at the Alcântara Launch Centre, which resulted in 21 deaths.[11]
Brazil has yet to launch a satellite into orbit independently and its space program suffered three satellite launch failures, the latest being the explosion of a VLS-1 rocket on 22 August 2003 at the Alcântara Launch Centre, which resulted in 21 deaths.[11]
Launches of non-indigenous launch vehicles[]
Some countries have no self-developed rocket systems, but have provided their spaceports for launches of their own and foreign satellites on foreign launchers:
 Algeria with the first successful launch from Hammaguir of the French satellite Astérix on 26 November 1965 by French Diamant A. The last orbital launch from Hammaguir was on 15 February 1967 by French Diamant A and there are no further launches scheduled (the first Algerian satellite is AlSAT-1 launched by Russian Kosmos-3M from Plesetsk, Russia on 28 November 2002).
Algeria with the first successful launch from Hammaguir of the French satellite Astérix on 26 November 1965 by French Diamant A. The last orbital launch from Hammaguir was on 15 February 1967 by French Diamant A and there are no further launches scheduled (the first Algerian satellite is AlSAT-1 launched by Russian Kosmos-3M from Plesetsk, Russia on 28 November 2002). Italy with the first successful launch from the San Marco platform of its satellite on 26 April 1967 by US Scout B (the first Italian satellite is San Marco 1 launched by another Scout from Wallops, USA on 15 December 1964). The last orbital launch from San Marco was on 25 March 1988 by US Scout G-1 and there are no further launches scheduled.
Italy with the first successful launch from the San Marco platform of its satellite on 26 April 1967 by US Scout B (the first Italian satellite is San Marco 1 launched by another Scout from Wallops, USA on 15 December 1964). The last orbital launch from San Marco was on 25 March 1988 by US Scout G-1 and there are no further launches scheduled. Australia with the first successful launch from Woomera Test Range of its first satellite WRESAT on 29 November 1967 by US Sparta.[12] The second and final successful orbital launch from Woomera was performed on 28 October 1971 by the UK Black Arrow.
Australia with the first successful launch from Woomera Test Range of its first satellite WRESAT on 29 November 1967 by US Sparta.[12] The second and final successful orbital launch from Woomera was performed on 28 October 1971 by the UK Black Arrow. Kazakhstan with the first launch after its independence from the Baikonur Cosmodrome[14] on 21 January 1992 of the Russian Soyuz-U2 and Progress M-11 (the first Kazakh satellite is KazSat launched by Russian Proton-K from Baikonur on 17 June 2006). Currently the spaceport continues to be utilized for launches of various Russian and Ukrainian rockets.
Kazakhstan with the first launch after its independence from the Baikonur Cosmodrome[14] on 21 January 1992 of the Russian Soyuz-U2 and Progress M-11 (the first Kazakh satellite is KazSat launched by Russian Proton-K from Baikonur on 17 June 2006). Currently the spaceport continues to be utilized for launches of various Russian and Ukrainian rockets. Spain; a single Pegasus-XL was launched from Orbital Sciences' Stargazer aircraft flying from Gran Canaria Airport in April 1997.
Spain; a single Pegasus-XL was launched from Orbital Sciences' Stargazer aircraft flying from Gran Canaria Airport in April 1997. Marshall Islands with a successful launch of a Pegasus-H rocket from Orbital Sciences' Stargazer aircraft flying from Kwajalein Atoll in October 2000. Five ground-based launches were made by SpaceX using Falcon 1 rockets between 2006 and 2009, with the first success on 28 September 2008.[15] Three further Pegasus launches occurred between 2008 and 2012, using the Pegasus-XL configuration. Currently there are no plans announced for a Marshall Islands satellite.
Marshall Islands with a successful launch of a Pegasus-H rocket from Orbital Sciences' Stargazer aircraft flying from Kwajalein Atoll in October 2000. Five ground-based launches were made by SpaceX using Falcon 1 rockets between 2006 and 2009, with the first success on 28 September 2008.[15] Three further Pegasus launches occurred between 2008 and 2012, using the Pegasus-XL configuration. Currently there are no plans announced for a Marshall Islands satellite. South Korea with the first successful launch from the Goheung of its satellite STSAT-2C on 30 January 2013 by KSLV-1.[16] KSLV-1 consists of a modified Russian first-stage developed and manufactured by Russia and South Korean developed second-stage and fairing. Launch was directed by South Korean and Russian engineers. The rocket was assembled in South Korea.[17]
South Korea with the first successful launch from the Goheung of its satellite STSAT-2C on 30 January 2013 by KSLV-1.[16] KSLV-1 consists of a modified Russian first-stage developed and manufactured by Russia and South Korean developed second-stage and fairing. Launch was directed by South Korean and Russian engineers. The rocket was assembled in South Korea.[17]
Privately developed launch vehicles[]
 United States Orbital Sciences Corporation (USA) became the first company to launch a privately developed rocket into orbit, the Pegasus on April 5, 1990.[18] Orbital subsequently developed the Minotaur rocket family. Orbital joined SpaceX as one of only two private entities to supply the International Space Station with its launch of the Cygnus Orb-D1 mission on its Antares rocket on September 28, 2013.[19]
United States Orbital Sciences Corporation (USA) became the first company to launch a privately developed rocket into orbit, the Pegasus on April 5, 1990.[18] Orbital subsequently developed the Minotaur rocket family. Orbital joined SpaceX as one of only two private entities to supply the International Space Station with its launch of the Cygnus Orb-D1 mission on its Antares rocket on September 28, 2013.[19] United States SpaceX (USA) became the second company to launch a rocket into orbit using a rocket developed with private—not government—funds.[20] Its first successful launch was performed on September 28, 2008, by Falcon 1 from the Omelek Island, Marshall Islands and its first launch from US spaceport was Falcon 9 Flight 1 on June 4, 2010, from Cape Canaveral. Its Dragon spacecraft docked with the International Space Station on October 11, 2012, to deliver supplies.
United States SpaceX (USA) became the second company to launch a rocket into orbit using a rocket developed with private—not government—funds.[20] Its first successful launch was performed on September 28, 2008, by Falcon 1 from the Omelek Island, Marshall Islands and its first launch from US spaceport was Falcon 9 Flight 1 on June 4, 2010, from Cape Canaveral. Its Dragon spacecraft docked with the International Space Station on October 11, 2012, to deliver supplies. United States American private company Rocket Lab successfully launched its Electron rocket from Mahia Launch Center in New Zealand on January 21, 2018, carrying three cubesats into low earth orbit. This was the first time that a rocket entered orbit after launching from a privately owned and operated spaceport.
United States American private company Rocket Lab successfully launched its Electron rocket from Mahia Launch Center in New Zealand on January 21, 2018, carrying three cubesats into low earth orbit. This was the first time that a rocket entered orbit after launching from a privately owned and operated spaceport. China Chinese private company i-Space successfully launched its Hyperbola 1 rocket from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center and sent several small payloads, including the CAS-7B amateur radio satellite into earth orbit on July 25, 2019.[21]
China Chinese private company i-Space successfully launched its Hyperbola 1 rocket from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center and sent several small payloads, including the CAS-7B amateur radio satellite into earth orbit on July 25, 2019.[21] China Galactic Energy successfully launched its Ceres-1 solid rocket from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center into sun-synchronous orbit on November 7, 2020, becoming the second Chinese private company capable of launching satellites into orbit.[22]
China Galactic Energy successfully launched its Ceres-1 solid rocket from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center into sun-synchronous orbit on November 7, 2020, becoming the second Chinese private company capable of launching satellites into orbit.[22] United States Virgin Orbit successfully achieved orbit on January 17, 2021, using their LauncherOne vehicle to deploy 10 CubeSats into Low Earth Orbit for NASA.[23]
United States Virgin Orbit successfully achieved orbit on January 17, 2021, using their LauncherOne vehicle to deploy 10 CubeSats into Low Earth Orbit for NASA.[23]
Abandoned projects[]
 /
/ Germany was developing larger designs in the Aggregat series as early as 1940. A combination of A9 to A12 components could have produced orbital capability as early as 1947 if work had continued. Further preliminary development of numerous rocket space launchers and re-usable launch systems (Sänger II, etc.) took place after WWII, although these were never realized as national or European projects. Also, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the private German company OTRAG tried to develop low-cost commercial space launchers. Only sub-orbital tests of the first prototypes of these rockets were carried out.
Germany was developing larger designs in the Aggregat series as early as 1940. A combination of A9 to A12 components could have produced orbital capability as early as 1947 if work had continued. Further preliminary development of numerous rocket space launchers and re-usable launch systems (Sänger II, etc.) took place after WWII, although these were never realized as national or European projects. Also, in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the private German company OTRAG tried to develop low-cost commercial space launchers. Only sub-orbital tests of the first prototypes of these rockets were carried out. United Kingdom did not proceed with a 1946 proposal to develop German V-2 technology into the "Megaroc" system to be launched in 1949.
United Kingdom did not proceed with a 1946 proposal to develop German V-2 technology into the "Megaroc" system to be launched in 1949. Canada had developed the gun-based space launchers Martlet and GLO as the joint Canadian-American Project HARP in the 1960s. These rockets were never tested.
Canada had developed the gun-based space launchers Martlet and GLO as the joint Canadian-American Project HARP in the 1960s. These rockets were never tested. South Africa developed the space launcher RSA-3 in the 1980s. This rocket was tested 3 times without a satellite payload in 1989 and 1990. The program was postponed and canceled in 1994.
South Africa developed the space launcher RSA-3 in the 1980s. This rocket was tested 3 times without a satellite payload in 1989 and 1990. The program was postponed and canceled in 1994. Iraq claimed to have developed and tested "Al-Abid", a three-stage space launch vehicle without a payload or its upper two stages on 5 December 1989. The rocket's design had a clustered first stage composed of five modified scud rockets strapped together and a single scud rocket as the second stage in addition to a SA-2 liquid-fueled rocket engine as the third stage. The video tape of a partial launch attempt which was retrieved by UN weapons inspectors, later surfaced showing that the rocket prematurely exploded 45 seconds after its launch.[24][25][26]
Iraq claimed to have developed and tested "Al-Abid", a three-stage space launch vehicle without a payload or its upper two stages on 5 December 1989. The rocket's design had a clustered first stage composed of five modified scud rockets strapped together and a single scud rocket as the second stage in addition to a SA-2 liquid-fueled rocket engine as the third stage. The video tape of a partial launch attempt which was retrieved by UN weapons inspectors, later surfaced showing that the rocket prematurely exploded 45 seconds after its launch.[24][25][26] Argentina previous attempts at developing space launcher based on their Condor missile were scrapped in 1993.[27][28]
Argentina previous attempts at developing space launcher based on their Condor missile were scrapped in 1993.[27][28] Brazil The VLS-1 was cancelled after decades of development and high expenditures with poor results and a failed association with Ukraine that slowed the program for years.[29][30]
Brazil The VLS-1 was cancelled after decades of development and high expenditures with poor results and a failed association with Ukraine that slowed the program for years.[29][30] Egypt tried to develop space launcher as part of its various ballistic missile programs in the second half of the 20th century. In different periods they worked independently or in cooperation with Argentina, Iraq and North Korea.[31]
Egypt tried to develop space launcher as part of its various ballistic missile programs in the second half of the 20th century. In different periods they worked independently or in cooperation with Argentina, Iraq and North Korea.[31] Spain developed the space launcher Capricornio (Capricorn) in the 1990s. This rocket was related to Argentina's Condor missile and its test scheduled for 1999/2000 was not conducted.[32]
Spain developed the space launcher Capricornio (Capricorn) in the 1990s. This rocket was related to Argentina's Condor missile and its test scheduled for 1999/2000 was not conducted.[32] Switzerland Swiss Space Systems company planned to develop the micro satellite launcher-spaceplane SOAR to 2018 but went bankrupt.
Switzerland Swiss Space Systems company planned to develop the micro satellite launcher-spaceplane SOAR to 2018 but went bankrupt.
Future projects[]
 Argentina is developing an orbital rocket called Tronador II, whose maiden flight is expected to take place in the next four years as of late 2020.[33]
Argentina is developing an orbital rocket called Tronador II, whose maiden flight is expected to take place in the next four years as of late 2020.[33]
 Australia's Gilmour Space Technologies is developing an orbital launch vehicle called Eris, scheduled to launch in 2022.
Australia's Gilmour Space Technologies is developing an orbital launch vehicle called Eris, scheduled to launch in 2022. Brazil announced that it will launch its VLM rocket from the Alcântara Launch Center in 2022[34]
Brazil announced that it will launch its VLM rocket from the Alcântara Launch Center in 2022[34] South Korea will continue its space program with the completely homegrown KSLV-2 for launch in 2021.[35]
South Korea will continue its space program with the completely homegrown KSLV-2 for launch in 2021.[35] Japan is planning to start launching small satellite launcher in FY2021.[36]
Japan is planning to start launching small satellite launcher in FY2021.[36] Japan The private company CAMUI is scheduled to launch its Winged Reusable Sounding rocket in 2020.[citation needed]
Japan The private company CAMUI is scheduled to launch its Winged Reusable Sounding rocket in 2020.[citation needed] Japan The private company Interstellar Technologies is scheduled to launch its first orbital ZERO rocket in 2023.[37]
Japan The private company Interstellar Technologies is scheduled to launch its first orbital ZERO rocket in 2023.[37] Romania is planning to launch military and security satellites. The first phase will begin in 2022.[38]
Romania is planning to launch military and security satellites. The first phase will begin in 2022.[38] Algeria is planning to launch military and security satellites. The first phase will begin in 2024.
Algeria is planning to launch military and security satellites. The first phase will begin in 2024. United Kingdom Orbex is developing its Prime launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned in 2022 from Sutherland spaceport.
United Kingdom Orbex is developing its Prime launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned in 2022 from Sutherland spaceport. United States Blue Origin is developing its New Glenn launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned for sometime in 2022.
United States Blue Origin is developing its New Glenn launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned for sometime in 2022. Spain The private company PLD Space is developing Miura 5 orbital launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned for 2024.
Spain The private company PLD Space is developing Miura 5 orbital launch vehicle, whose first launch is planned for 2024. Philippines OrbitX, a private company, plans to develop Haribon, a biofuel-powered launch vehicle.[39][40]
Philippines OrbitX, a private company, plans to develop Haribon, a biofuel-powered launch vehicle.[39][40]
Satellite operators[]
Many other countries have launched their own satellites on one of the foreign launchers listed above, the first being British owned and operated; American-built satellite Ariel 1, was launched by a US rocket in April 1962. In September 1962 the Canadian satellite, Alouette-1, was launched by a US rocket, but unlike Ariel 1 it was constructed by Canada.
See also[]
- List of orbital launch systems
- List of missiles by country
- Orbital spaceflight
- Satellite
- Spaceport (including timeline of first orbital launches by spaceport)
- Discovery and exploration of the Solar System (including exploration by country)
- Timeline of first satellites by country
- Timeline of Solar System exploration
References[]
- ^ "Zenit successfully launches on likely swansong with Elektro-L - NASASpaceFlight.com". Nasaspaceflight.com. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Dnipro will not let Ukraine's space glory be forgotten". Euromaidan Press. 10 January 2017. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ https%3A%2F%2Fwww.esa.int%2Fesapub%2Fhsr%2FHSR_30.pdf&usg=AOvVaw0yniaMjSHGab8cpNTHXR3G
- ^ "Russian money to drive Sea Launch relaunch". Flightglobal.com. August 6, 2010. Retrieved August 9, 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Esa.int (PDF). 28 January 2012 https://web.archive.org/web/20120128184621/http://www.esa.int/esapub/sp/sp1300/sp1300EN1.pdf. Archived from the original on 28 January 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2017. Missing or empty
|title=(help)CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Convention for the establishment of a European Space Agency" (PDF). ESA. 2003. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-07-06. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- ^ "N° 2994 - Rapport de M. Robert Lecou sur le projet de loi autorisant l'approbation de l'accord-cadre entre le Gouvernement de la République française et le Gouvernement de la République de l'Inde relatif à la coopération dans le domaine de l'utilisation de l'espace extra-atmosphérique à des fins pacifiques (n°2709)". www.assemblee-nationale.fr. Retrieved 1 May 2020..
- ^ "North Korea fires long-range rocket: reports". The Sydney Morning Herald. 5 April 2009. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ "North Korea space launch 'fails'". BBC News. 5 April 2009. Retrieved 22 November 2011.
- ^ Krebs, Gunter. "STSAT-2C". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- ^ "At Least 21 Killed, 20 Hurt in Brazil Rocket Explosion". News-Press. Fort Myers, Florida. Associated Press. August 23, 2003. p. 2A.
- ^ "Woomera, Encyclopedia Astronautica". Astronautix.com. Archived from the original on 30 October 2013. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Bayterek system launch shifted to 2017". Tengrinews.kz. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ Currently its Bayterek expansion to accommodate the Russian Angara rockets is delayed into 2017.[13]
- ^ "SpaceX Launch manifest". Archived from the original on April 14, 2009.
- ^ "Naro-1 space rocket carries future of S. Korean satellites". Yonhap. 30 January 2013. Retrieved 1 February 2013.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (30 January 2013). "South Korea launch STSAT-2C via KSLV-1". NASASpaceflight.com. Retrieved 1 February 2013.
- ^ "Pegasus Mission History". Orbital.com. Retrieved 2013-08-12.
- ^ "Cygnus Cargo Ship Captured by International Space Station". CBS News. 2013-09-23.
- ^ "Sweet success at last for Falcon 1 rocket by STEPHEN CLARK, SPACEFLIGHT NOW". Spaceflightnow.com. Retrieved 2012-10-09.
- ^ "iSpace completes China's first private commercial satellite launch". ZDNet. Retrieved 2019-07-27.
- ^ Jones, Andrew (1 October 2019). "New Chinese commercial rocket firms move toward maiden launches". SpaceNews. Retrieved 10 May 2021.
- ^ Christian Davenport (2021-01-17). "Virgin Orbit rocket reaches Earth orbit, adding an entrant to the commercial space race". The Washington Post.
- ^ UNMOVIC report, United Nations Monitoring, Verification and Inspection Commission, p. 434 ff.
- ^ "Deception Activities". Fas.org. Retrieved 2017-08-09.
- ^ "Al-Abid LV". B14643.de. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "ORBIT LSA". B14643.de. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Argentina Missile Chronology" (PDF). Nti.org. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Problemas de "Governança" e Gestão Explicam em Parte Extinção do VLS-1".
- ^ [1] Archived 2016-08-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Egypt Missile Chronology" (PDF). Nti.org. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Capricornio". B14643.de. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ "Argentina Aspires to Have its Own Pitcher in Four Years". infoespecial.com. Retrieved 2021-04-28.
- ^ "Brazil Plans Launch of Brazilian Orbital Rocket from Brazilian Soil in 2022". Parabolic Arc. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ^ "이제는 한국형 발사체...2018년 첫 발사". News.naver.com. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ^ 本州最南端に民間ロケット発射場 人工衛星打ち上げ可能 21年完成へ整備進む (in Japanese). The Mainichi Newspaper. 24 December 2020. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ 宇宙輸送事業の実現を後押しする法人サポーターズクラブ「みんなのロケットパートナーズ」始動 (PDF) (in Japanese). Interstellar Technologies. 19 March 2019. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- ^ "România vrea să lanseze sateliți de telecomunicații geostaționari în spațiu pentru Armată și alte structuri de securitate. Când ar putea fi lansat primul satelit". www.hotnews.ro. Retrieved 22 November 2018.
- ^ Felongco, Gilbert (30 August 2019). "Filipino dreams of developing space vehicle for countrymen". Gulf News. Retrieved 6 November 2020.
- ^ Samson, Oliver (14 July 2019). "Algae as spacecraft fuel? Possible, youth group says". BusinessMirror. Retrieved 6 November 2020.
External links[]
- First Satellites Launched By Spacefaring Nations, Anthony R. Curtis, Ph.D., Space Today Online, accessed 17 February 2006.
- National Briefings: Iraq, Ranger Associates, accessed 17 February 2006.
- The 31 August 1998 North Korean Satellite Launch: Factsheet, Kevin Orfall and Gaurav Kampani, with Michael Dutra, Center for Nonproliferation Studies, Monterey Institute of International Studies, accessed 17 February 2006.
- News Release 25-98, United States Space Command, 8 September 1998, accessed 17 February 2006.
- Daily Press Briefing, James P. Rubin, United States Department of State, 14 September 1998, accessed 17 February 2006.
- BBC World: Brazil Launches rocket into space
- Space.com: Brazil completes successful rocket launch
- Herald Tribune: Brazil launches rocket for gravity research
- AFP: Iran rocket test 'unfortunate': White House
- Space-Travel.com: Iran opens its first space centre, riling the US
- New York Times: Iran Launches Rocket to Commemorate New Space Center
- MSNBC: Iran unveils space center, launches rocket
- Lists of firsts in space
- Spaceflight timelines
- First artificial satellite of a country
