Timoric languages
| Timoric | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Indonesia, East Timor |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian |
| Subdivisions | (disputed) |
| Glottolog | None timo1260 (Ramelaic) timo1259 (Fabronic/Extra-Ramelaic) |
The Timoric languages are a group of Austronesian languages (belonging to the Central–Eastern subgroup) spoken on the islands of Timor, neighboring Wetar, and (depending on the classification) Southwest Maluku to the east.
Within the group, the languages with the most speakers are Uab Meto of West Timor and Tetum of East Timor, each with about half a million speakers, though in addition Tetum is an official language and a lingua franca among non-Tetum East Timorese.
Languages[]
Hull (1998) & van Engelenhoven (2009)[]
Geoffrey Hull (1998) proposes a Timoric group as follows:
- Timoric A ("Extra-Ramelaic", Fabronic; whatever is not Ramelaic)
- Timoric B ("Ramelaic", near the Ramelau range)
Van Engelenhoven (2009) accepts Hull's classification, but further includes Makuva and the Luangic–Kisaric languages (Kisar, Romang, Luang, Wetan, Leti) in the Eastern branch of Timoric A.[1]
Taber (1993)[]

In a lexicostatistical classification of the languages of Southwest Maluku, Taber (1993:396) posits a "Southwest Maluku" branch of the Timoric languages, that comprises all languages of the area, except for West Damar and the Babar languages.
- Timoric
- (other branches on Timor)
- Southwest Maluku
- East Damar
- Wetar: Talur, Wetar cluster (Aputai, Perai, Tugun, Iliun)
- Kisar-Roma: Kisar, Roma
- Luang: Leti, Luang, Wetan
- TNS (Teun-Nila-Serua): Teun, Nila-Serua (Nila, Serua)
- (other branches of CMP, including Babar languages and West Damar)
Edwards (2018, 2019)[]
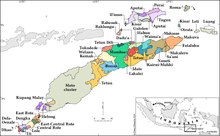

Edwards (2018, 2019) divides the languages of Timor and Southwest Maluku into three branches:[3][4]
- Helong
- Central Timor: Kemak, Tokodede, Mambae, Welaun
- "Timor-Wetar-Babar"
The latter subgroup includes all other languages grouped by Hull as Timoric, as well all languages of Southwest Maluku (including the Babar languages). Within "Timor-Wetar-Babar", Edwards proposes a Rote-Meto branch, with languages spoken on Rote Island and in West Timor.
- Rote-Meto
References[]
- ^ van Engelenhoven, Aone (2009). "The position of Makuva among the Austronesian languages in East Timor and Southwest Maluku". In Adelaar, K. Alexander; Pawley, Andrew (eds.). Austronesian historical linguistics and culture history: a festschrift for Robert Blust. Canberra: Australian National University. pp. 425–442.
- ^ a b Edwards O (2020). Metathesis and unmetathesis in Amarasi (pdf). Berlin: Language Science Press. doi:10.5281/zenodo.3700413. ISBN 978-3-96110-223-5.
- ^ Edwards, Owen (2018). Top-down Historical Phonology of Rote-Meto. JSEALS 11.1 (2018).
- ^ Edwards, Owen (2019). Reintroducing Welaun. Oceanic Linguistics, Volume 58, Number 1, June 2019, pp. 31-58. https://doi.org/10.1353/ol.2019.0002
- Hull, Geoffrey. 1998. "The basic lexical affinities of Timor's Austronesian languages: a preliminary investigation." Studies in Languages and Cultures of East Timor 1:97–202.
- Taber, Mark (1993). "Toward a Better Understanding of the Indigenous Languages of Southwestern Maluku." Oceanic Linguistics, Vol. 32, No. 2 (Winter, 1993), pp. 389–441. University of Hawai'i.
External links[]
- LexiRumah (part of the Lesser Sunda linguistic databases)
- Reconstructing the past through languages of the present: the Lesser Sunda Islands
- The Languages of East Timor: Some Basic Facts (Revised 24.8.2004) Geoffrey Hull
- Languages of Indonesia
- Languages of East Timor
- Timor–Babar languages