Trams in Warsaw
 Tramwaje Warszawskie sp. z o.o. logo | |||
 Pesa Swing tram on Poniatowski Bridge | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Native name | Tramwaje Warszawskie | ||
| Locale | Warsaw, Poland | ||
| Transit type | tram | ||
| Number of lines | 25 | ||
| Website | Official website | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 11 December 1866 | ||
| Operator(s) | Tramwaje Warszawskie | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 150 km (93 mi)[1][note 1] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| |||
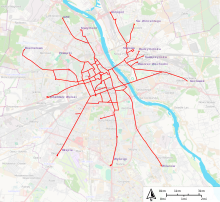






The Warsaw tram network is a 150-kilometre (93 mi)[1][note 1] tram system serving a third of Warsaw, Poland, and serving half the city's population.[3] It operates 726 cars,[4] and is the second-largest system in the country (after the Silesian system) and one of the biggest in Europe.[5] There are about 25 regular lines,[6] forming a part of the city's integrated public transport system organized by the Warsaw Transport Authority. Since 1994 the system is operated by the municipally-owned company Tramwaje Warszawskie sp. z.o.o.
History[]
Horse tram[]
The history of tram transport in Warsaw dates back to 1866 when a 6-kilometre (3.7 mi) long horse tram line was built to transport goods and passengers between the Vienna Railway Station and the Petersburg and Terespol railway stations across the Vistula River. This was in order to circumvent limitations imposed by Russian authorities, which prevented the construction of a railway bridge for strategic reasons. In 1880, a second line was constructed with the help of Belgian capital, this time intended as public transit within the city. The Belgian company quickly expanded its own lines, and in 1882 took over the line between the railway stations, which has lost most of its original purpose after a railway bridge was finally built in 1875. In 1899 the entire tram system, by then 30 kilometres (19 mi) of tracks with 234 tram cars and 654 horses operating 17 lines, was purchased by the city. By 1903, plans were drafted to convert the system to electric trams, which was done by 1908.
Interbellum[]
The development mostly stagnated for the next 10 years with only a few short stretches built. After World War I, the network developed rapidly handling increased traffic and extending to the outskirts of the city with the network reaching the length of 60 kilometres (37 mi) and 757 tram cars in 1939. In 1927, a privately owned light rail line called EKD (today Warszawska Kolej Dojazdowa) was built, connecting several neighboring towns with the center of Warsaw using electric motor coaches similar to trams, only faster, larger and more massive, with frequent stops and tracks running along the streets in city; however the system was incompatible with the Warsaw trams as it used standard gauge tracks while the city network still used Russian gauge left from Russian times. In 1925, the company operating the Warsaw trams decided to construct a underground system. Preliminary boring started, but the work was suspended because of the Great Depression; the idea resurfaced in 1938, but was again buried with the outbreak of World War II.
Second half of the 20th century[]
The tram system remained operational, although gradually deteriorating, during most of the Nazi occupation until the Warsaw Uprising in 1944, after which all the infrastructure was systematically destroyed. After the war it was rebuilt relatively fast. As the system was practically built from scratch the occasion was used to convert it to standard gauge. During the 1950s and 1960s, the network was extended to newly built districts of soviet style panel houses and industrial plants and newer trams based on the design of Presidents' Conference Committee were introduced. Due to the city's lack of a metro system and restriction on car ownership, the tram system remained the backbone of Warsaw's transport system. In the 1960s, however, a political decision was made to increase the dependency on oil imported from Russia, while Polish coal was to be exported to Western Europe in exchange for hard currency; as a result, newly developed districts were connected with the city center by buses rather than trams, and some of the existing tracks were closed.
Present situation[]
After 1989, the tram system in Warsaw initially received little investment with a large part of the city's budget spent on the construction of the first Warsaw Metro line. However, since 2005, the situation has been changing with the purchase of new rolling stock, modernization of key tram lines, and deployment of a passenger information system. Plans also include extension of the network and an "intelligent" traffic management system which is to prioritize trams at traffic lights. In August 2008, a tender for delivery of 186 low-floor, air-conditioned trams was launched, allowing for a dramatic overhaul of the look of the tramway system.
In 2014 a first entirely new line since a quarter century was opened, connecting a quickly growing remote residential district Tarchomin on the north-eastern outskirts of the city with the existing tram network and the M1 metro line. The route is undergoing further expansion with the latest 1km long segment finished in September of 2021 after multiple delays.[7] Two more new lines are being planned: one with 4km of new tracks to Gocław, and another almost 20km to a southern suburb of Wilanów, but it is unclear when work will start on either of them.[8][9]
Rolling stock[]
| Image | Tram car type | Low-floor | Number of cars | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 
|
Konstal 105Na
and derived |
385 cars
(189 two-car sets + 7 single cars) |
The most commonly used model in Warsaw. Produced from 1973 to 2001.
An evolution of the earlier Konstal 13N, the city's first modern tram, a copy of the PCC streetcar derived Czechoslovak Tatra T1 widely used throughout the Soviet Bloc. First cars were based on the electrical systems from the 13N placed in a lighter body, later ones had them replaced with more efficient ones. Most commonly used in sets of two, however single units also appear. Sets of three had been used in the past, but they were replaced by new low-floor trams. | |

|
30 cars (15 two-car sets) | Based on 105Na. Produced in 2007. | ||

|
partly | 1 + 29 | A single prototype Konstal 112N, partially low-floor, two-section articulated tram based on 105Na, built in 1995. Other vehicles feature three sections and larger percentage of low-floor area (approx. 60%), designated 116N/116Na, produced between 1998 and 2000. | |

|
Pesa 120N | 15 | Pesa 120N was first tram in Warsaw with 100% of low floor. It was bought in 2007 to operate modernized route in the city center. | |

|
Pesa Swing (120Na) | 180 + 6 | In 2009 186 vehicles (120Na) were purchased to operate a planned new line and to replace some of the oldest trams.
At the request of the city, 6 units were manufactured as bi-directional, designated 120NaDuo, to allow using them on a partially-built line with no balloon loop. | |

|
Pesa Jazz Duo (128N) | 50 | In 2013 50 bi-directional trams of a new design were purchased from PESA to be delivered in 2014, planned to allow operating on possible new lines during their construction and sections of existing tracks during maintenance works that made balloon loop inaccessible. | |

|
PESA 134N | 30 | Ordered in January 2014 from PESA in Bydgoszcz[10] They are used on less loaded lines. They were bought to replace old single cars from Konstal. | |
| [1] | Hyundai 140N | 6 of 85 | Bi-directional, articulated, five-section vehicles, ordered in June 2019, to be delivered by April 2023. | |
| Hyundai 141N | 1 of 18 | Unidirectional version of 140N, ordered in June 2019, to be delivered by April 2023. | ||
| Hyundai 142N | 0 of 20 | Short (three-section) version of 141N, ordered in June 2019, to be delivered by April 2023. | ||
| Total number of sets: | 492 | |||
| Percentage of low-floor sets: | 63% | |||
Tram depots[]
| Depot | Address | Year est. | Lines |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZET R-1 Wola | Młynarska 2 | 1903 | 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 20, 23, 24, 26, 27, 28 |
| ZET R-2 Praga | Kawęczyńska 16 | 1925 | 3, 6, 7, 9, 13, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 28 |
| ZET R-3 Mokotów | Woronicza 27 | 1955 | 1, 4, 7, 9, 10, 14, 15, 17, 18, 25, 31, 33, 35 |
| ZET R-4 Żoliborz | Zgrupowania Kampinos 10 | 1963 | 1, 2, 4, 6, 11, 15, 17, 18, 22, 24, 26, 28, 33, 35 |
Historic fleet[]
| Image | Model | Tram car type | Year of manufacture | Fleet number |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
A | Falkenried/MAN | 1907 | 43 |

|
Lw | Linke-Hoffman Werke | 1925 | 541 |
| [2] | C | Lilpop, Rau i Loewenstein | 1925 | 257 |

|
K | 1940 | 403-1 | |

|
1940 | 445 | ||
| [3] | ? | 1940 | 446 | |
| [4] | N | Konstal | 1949 | 607 |

|
1951 | 734 | ||
| [5] | ND | Sanocka Fabryka Wagonów | 1951 | 1620 |

|
Konstal | 1961 | 873 | |
| [6] | 4ND | 1960 | 1811 | |

|
4Nj | 1957 | 838 | |

|
13N | 1959 | 503 | |
| [7] | 1967 | 407 | ||
| [8] | 1968 | 462 | ||

|
1969 | 795 | ||

|
1969 | 821+818 | ||

|
102N | 1969 | 5 | |

|
102Na | 1971 | 42 | |

|
105N | 1975 | 1000, 1001 |
Tickets[]

There is a single fare system for every mode of transportation. Tickets can be purchased at ticket machines and newsagents all over the city, as well as using a mobile app.

Route list[]
This section needs to be updated. (September 2021) |
This is a list of Warsaw Tramway lines. As of 2015, there were several track closures all over the tramway system, due to the construction of the second metro line. This list shows tram lines which are operating as of 4 September 2019 and the routes they operate on as of the same date.[6]
| Route number | Description | Map |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Annopol ↔ (Pl. Narutowicza) ↔ Banacha Annopol – Rembielińska – Matki Teresy z Kalkuty – Odrowąża – rondo Żaba – Starzyńskiego – most Gdański – Słomińskiego – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – Okopowa – Towarowa – rondo Daszyńskiego – Towarowa – plac Zawiszy – Grójecka – plac Narutowicza – Grójecka – Banacha |
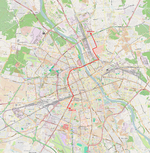
|
| 2 | Tarchomin Kościelny ↔ Metro Młociny Światowida – Kuklińskiego – most Skłodowskiej-Curie – Zgrupowania AK „Kampinos” |
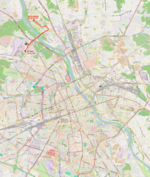
|
| 3 | Annopol ↔ Gocławek Annopol – Rembielińska – Matki Teresy z Kalkuty – Odrowąża – rondo Żaba – 11 Listopada – Targowa – plac Wileński – Targowa – Zamoyskiego – Grochowska |

|
| 4 | Wyścigi ↔ Żerań Wschodni Puławska – plac Unii Lubelskiej – Marszałkowska – plac Zbawiciela – Marszałkowska – rondo Dmowskiego – Marszałkowska – plac Bankowy – aleja Solidarności – most Śląsko-Dąbrowski – aleja Solidarności – Jagiellońska – Ratuszowa – Targowa – 11 Listopada – rondo Żaba – Odrowąża – Matki Teresy z Kalkuty – Rembielińska – Annopol |
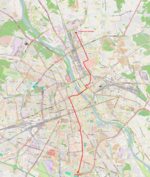
|
| 6 | Gocławek ↔ Metro Młociny Grochowska – Zamoyskiego – Targowa – plac Wileński – Targowa – Ratuszowa – Jagiellońska – Starzyńskiego – most Gdański – Słomińskiego – Międzyparkowa – Andersa – Mickiewicza – plac Inwalidów – Mickiewicza – plac Wilsona – Słowackiego – Marymoncka – Zgrupowania AK „Kampinos” |
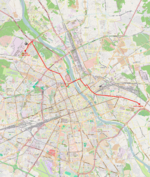
|
| 7 | Kawęczyńska-Bazylika ↔ P+R Aleja Krakowska Kawęczyńska – Kijowska – Targowa – aleja Zieleniecka – aleja Poniatowskiego – most Poniatowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – rondo Dmowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – plac Zawiszy – Grójecka – plac Narutowicza – Grójecka – aleja Krakowska |
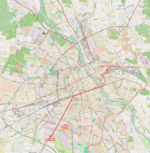
|
| 9 | Gocławek ↔ (Wiatraczna) ↔ P+R Aleja Krakowska (Pl. Narutowicza) Grochowska – aleja Waszyngtona – aleja Poniatowskiego – most Poniatowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – rondo Dmowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – plac Zawiszy – Grójecka – plac Narutowicza – Grójecka – aleja Krakowska |
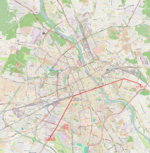
|
| 10 | Metro Młociny ↔ Wyścigi Młociny – Powstańców Śląskich – Połczyńska – Wolska – Skierniewicka– Kasprzaka – Prosta – aleja Jana Pawła II – Chałubińskiego – aleja Niepodległości – Nowowiejska – plac Politechniki – Nowowiejska – plac Zbawiciela – Marszałkowska – plac Unii Lubelskiej – Puławska |
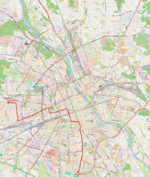
|
| 11 | Rondo Daszyńskiego ↔ Piaski Rondo Daszyńskiego – Prosta – Kasprzaka – Skierniewicka – Wolska – Połczyńska – Powstańców Śląskich – al. Reymonta – Broniewskiego |

|
| 13 | Kawęczyńska-Bazylika ↔ Cmentarz Wolski Kawęczyńska – Kijowska – Targowa – plac Wileński – aleja Solidarności – most Śląsko-Dąbrowski – aleja Solidarności – Wolska |
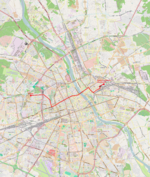
|
| 14 | Banacha ↔ Metro Wilanowska Banacha – Grójecka – plac Narutowicza – Filtrowa – Krzywickiego – Nowowiejska – plac Politechniki – Nowowiejska – plac Zbawiciela – Marszałkowska – plac Unii Lubelskiej – Puławska |
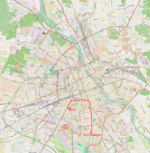
|
| 15 | Marymont-Potok ↔ P+R Aleja Krakowska Mickiewicza – plac Wilsona – Mickiewicza – plac Inwalidów – Mickiewicza – Andersa – Pl.Bankowy – Marszałkowska – rondo Dmowskiego – Marszałkowska – plac Konstytucji – Marszałkowska – plac Zbawiciela – Nowowiejska – plac Politechniki – Nowowiejska – Krzywickiego – Filtrowa – plac Narutowicza – Grójecka – aleja Krakowska |
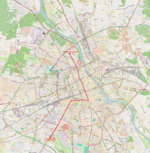
|
| 17 | Winnica ↔ PKP Służewiec Nowodwory - Światowida – Kuklińskiego – Most Skłodowskiej-Curie – Marymoncka – Słowackiego – Popiełuszki – aleja Jana Pawła II – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – rondo ONZ – aleja Jana Pawła II – Chałubińskiego – aleja Niepodległości – Rakowiecka – Boboli – Wołoska – Marynarska |
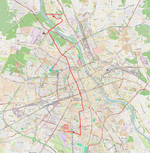
|
| 18 | Żerań FSO ↔ PKP Służewiec Jagiellońska – Starzyńskiego – most Gdański – Słomińskiego – Międzyparkowa – Andersa – Pl.Bankowy – Marszałkowska – rondo Dmowskiego – Marszałkowska – plac Konstytucji – Marszałkowska – plac Zbawiciela – Marszałkowska – plac Unii Lubelskiej – Puławska – Woronicza – Wołoska – Marynarska |
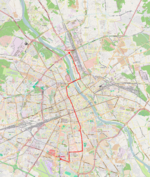
|
| 20 | Boernerowo ↔ Żerań FSO Kaliskiego – Dywizjonu 303 – Obozowa – Młynarska – aleja Solidarności – most Śląsko-Dąbrowski – aleja Solidarności – plac Wileński – Targowa – Ratuszowa – Jagiellońska |
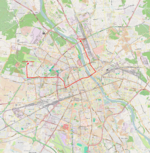
|
| 22 | Wiatraczna ↔ Piaski Grochowska – Zamoyskiego – aleja Zieleniecka – aleja Poniatowskiego – most Poniatowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – rondo Dmowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – plac Zawiszy – Towarowa – rondo Daszyńskiego – Towarowa – Okopowa – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – Broniewskiego |

|
| 23 | Czynszowa ↔ Nowe Bemowo Czynszowa – Stalowa (Stalowa – Środkowa – plac Wileński – Czynszowa) – 11 Listopada – Targowa – Ratuszowa – Jagiellońska – aleja Solidarności – most Śląsko-Dąbrowski – aleja Solidarności – Młynarska – Obozowa – Dywizjonu 303 – Radiowa – Powstańców Śląskich |
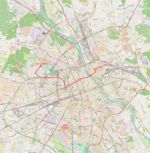
|
| 24 | Gocławek ↔ Nowe Bemowo Grochowska – aleja Waszyngtona – aleja Poniatowskiego – most Poniatowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – rondo Dmowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – plac Zawiszy – Towarowa – rondo Daszyńskiego – Towarowa – Okopowa – aleja Solidarności – Młynarska – Obozowa – Dywizjonu 303 – Radiowa – Powstańców Śląskich |
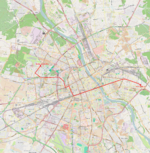
|
| 25 | Annopol ↔ Banacha Annopol – Rembielińska – Matki Teresy z Kalkuty – Odrowąża – rondo Żaba – 11 Listopada – Targowa – plac Wileński – Targowa – aleja Zieleniecka – aleja Poniatowskiego – most Poniatowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – rondo Dmowskiego – Aleje Jerozolimskie – plac Zawiszy – Grójecka – plac Narutowicza – Grójecka – Banacha |
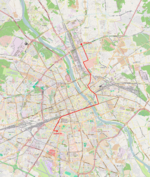
|
| 26 | Koło ↔ Wiatraczna Powstańców Śląskich – Połczyńska – Wolska – aleja Solidarności – most Śląsko-Dąbrowski – aleja Solidarności – plac Wileński – Targowa – Zamoyskiego – Grochowska |
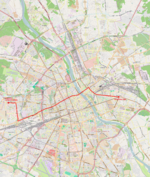
|
| 27 | Cmentarz Wolski ↔ Metro Marymont Wolska – aleja Solidarności – Okopowa – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – Popiełuszki |
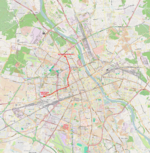
|
| 28 | Dw. Wschodni (Kijowska) ↔ Piaski Kijowska – Targowa – plac Wileński – Targowa – Ratuszowa – Jagiellońska – Starzyńskiego – most Gdański – Słomińskiego – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – Broniewskiego |

|
| 31 | Metro Wierzbno ↔ PKP Służewiec Woronicza – Wołoska – Marynarska |

|
| 33 | Kielecka ↔ Metro Młociny Rakowiecka – aleja Niepodległości – Chałubińskiego – aleja Jana Pawła II – rondo ONZ – aleja Jana Pawła II – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – Broniewskiego – Wólczyńska – Nocznickiego |
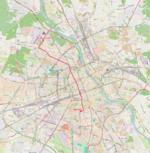
|
| 35 | Nowe Bemowo ↔ Wyścigi Powstańców Śląskich – Reymonta – Broniewskiego – aleja Jana Pawła II – rondo Zgrupowania AK „Radosław” – aleja Jana Pawła II – Stawki – Andersa – Pl.Bankowy – Marszałkowska – rondo Dmowskiego – Marszałkowska – plac Konstytucji – Marszałkowska – plac Zbawiciela – Marszałkowska – plac Unii Lubelskiej – Puławska |
|
| 36 | Metro Marymont ↔ Pl.Narutowicza Filtrowa - Nowowiejska - Pl.Konstytucji - Marszałkowska - Pl.Bankowy - Andersa - Mickiewicza - Słowackiego |
|
| 41 | Żerań Wschodni ↔ PKP Służewiec – Annopol – Rembielińska – Odrowąża – Starzyńskiego – Most Gdański – Słomińskiego – al. Jana Pawła II – Chałubińskiego – al. Niepodległości – Rakowiecka – Boboli – Wołoska – Marynarska |
|
The standard headway is every 8 minutes during peak hours and every 12 minutes off-peak, but the trams on lines 1, 9, 17, 31 and 33 run every 4–6 minutes. Line 2 has the most frequent service with trams running every 2 minutes during peak hours.
See also[]
Notes[]
References[]
- ^ a b "Infrastruktura torowa". Tramwaje Warszawskie. September 2018. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ "Warszawa w negliżu" (PDF). Świat. 2 (29). Warsaw: Tow. Akc. S. Orgelbranda Synów. 20 July 1907. p. 17 – via Mazovian Digital Library.
- ^ "Ultimate Warsaw Guide". Poland Travel Planner. 4 April 2019. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ^ "Stan inwentarzowy taboru - Tramwaje Warszawskie" [Rolling stock - Tramwaje Warszawskie]. Tramwaje Warszawskie. 23 September 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ "Tramwaje Warszawskie Sp. z o. o. — O nas: Tabor tramwajowy". Tramwaje Warszawskie. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2013.
- ^ a b "Timetables". Warsaw Public Transport. Retrieved 17 September 2021.
- ^ "Trasa do Winnicy gotowa". Warszawski Transport Publiczny.
- ^ "Warszawa: Niebawem przetarg na tramwaj do Wilanowa. Będzie fazowanie". transport-publiczny.pl.
- ^ "Warszawa rezygnuje z dofinansowania dla tramwaju na Gocław. Powstanie później?". transport-publiczny.pl.
- ^ Barrow, Keith (2014-01-21). "Warsaw Tramways orders Pesa Jazz LRVs". International Railway Journal. International Railway Journal. Retrieved 2014-01-22.
WARSAW Tramways signed a Zlotys 167.9m ($US 54.8m) contract with Pesa, Poland on January 15 for 30 type 134N Jazz low-floor LRVs, which will be used on lower-density routes in the city.
- ^ "Tramwaje". Klub Miłośników Komunikacji Miejskiej w Warszawie (in Polish). 31 December 1999. Retrieved 23 January 2018.
- ^ "Tram hire pricelist" (PDF). Tramwaje Warszawskie (in Polish).
External links[]
 Media related to Trams in Warsaw at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trams in Warsaw at Wikimedia Commons- Warsaw Transport Authority – network maps
- Tramwar – a private website about trams in Warsaw (in Polish)
- Transport in Warsaw
- Tram transport in Poland
- Town tramway systems by city

