Turkish people
Türkler | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
c. 80 million
 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 60,000,000–65,000,000[1][2] | |
| 315,000[d][3][4] | |
| Diaspora in the West | |
| 3,000,000 to over 7,000,000[5][6][7][8] | |
| 500,000 to over 2,000,000[c][9][10][11][12] | |
| over 1,000,000[13][14][15] | |
| over 1,000,000[16][17] | |
| 500,000[18][19][20] | |
| 360,000–500,000 (2010–11 est.)[21][22][23] | |
| 250,000–500,000[24][25] | |
| 320,000[26][27][28][29] | |
| 200,000[30] [31] | |
| 120,000 (2009 est.)[32] | |
| 70,000 (2008 est.) [f][33] | |
| over 100,000 [b][34] | |
| 50,000 [e][35] | |
| Minorities in the Arab world and Levant | |
| 3,000,000[36][37][38] | |
| 1,000,000–1,700,000[36][39][40][41] | |
| 100,000–1,500,000[42] | |
| 270,000–350,000 [b][43][44] | |
| 60,000[43] | |
| 280,000[45][46][47][48] | |
| 50,000 [b][43] | |
| Minorities in the Balkans | |
| 588,318–800,000[49][50][51][52] | |
| 77,959–200,000[53][54] | |
| 49,000–130,000 [g][55][56][57][58] | |
| 55,000–80,000[59][60] | |
| 18,700–60,000[61][62][63] | |
| Minorities in the former Soviet Union | |
| 109,883–150,000[64][65] | |
| 150,000–180,000 [h][66][31] | |
| 40,953–50,000 [h][31][67][68] | |
| 38,000–110,000 [h][31][69][70][71] | |
| 15,000–20,000[31][72][73] | |
| 8,844[74] 10,000 Meskhetian Turks (academic estimates)[72][75][76] plus 5,394 Turkish nationals (2009)[77] | |
| Languages | |
| Turkish | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Islam (Sunni · Alevi · Bektashi) Minority irreligious or converts to other religions | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Oghuz Turks | |
The Turkish people, or simply the Turks, (Turkish: Türkler) are the world's largest Turkic ethnic group; they speak various dialects of the Turkish language and form a majority in Turkey and Northern Cyprus. In addition, centuries-old ethnic Turkish communities still live across other former territories of the Ottoman Empire. The ethnic Turks can therefore be distinguished by a number of cultural and regional variants, but do not function as separate ethnic groups.[78][79] In particular, the culture of the Anatolian Turks in Asia Minor underlies the Turkish nationalist ideology.[78] Other Turkish groups include the Rumelian Turks in the Balkans;[79][80] Turkish Cypriots on the island of Cyprus (in addition to recent "mainland Turks");[81] Turkish Meskhetians originally based in Meskheti, Georgia;[82] and ethnic Turkish people across the Middle East,[79] where they are also called "Turkmen" or "Turkoman" in the Levant.[83] Consequently, the Turks form the largest minority group in Bulgaria,[50] the second largest minority group in Iraq,[37] Libya,[84] North Macedonia,[54] and Syria,[85] and the third largest minority group in Kosovo.[62] They also form substantial communities in the Western Thrace region of Greece, the Dobruja region of Romania, the Akkar region in Lebanon, as well as smaller minorities in other post-Ottoman Balkan and Middle Eastern countries. Due to mass migrations from the 19th century onward, these Turkish communities have all contributed to the formation of a Turkish diaspora outside the former Ottoman lands and constitute the largest ethnic minority group in Austria,[86] Denmark,[87] Germany,[88] and the Netherlands.[88] There are also Turkish communities in other parts of Europe as well as in North America, Australia, and the Post-Soviet states.
Turks from Central Asia settled in Anatolia in the 11th century, through the conquests of the Seljuk Turks. This began the transformation of the region, which had been a largely Greek-speaking region after previously being Hellenized, into a Turkish Muslim one.[89][90][91] The Ottoman Empire came to rule much of the Balkans, the Caucasus, the Middle East (excluding Iran, even though they controlled parts of it), and North Africa over the course of several centuries. The empire lasted until the end of the First World War, when it was defeated by the Allies and partitioned. Following the Turkish War of Independence that ended with the Turkish National Movement retaking much of the territory lost to the Allies, the Movement ended the Ottoman Empire on 1 November 1922 and proclaimed the Republic of Turkey on 29 October 1923.
Article 66 of the Turkish Constitution defines a "Turk" as "anyone who is bound to the Turkish state through the bond of citizenship". While the legal use of the term "Turkish" as it pertains to a citizen of Turkey is different from the term's ethnic definition,[92][93] the majority of the Turkish population (an estimated 70-75 percent) is of Turkish ethnicity.[94] The vast majority of Turks are Muslims.[79]
Etymology and definition[]
| hidePart of a series of articles on |
| Turkish people |
|---|
 |
The first definite references to the "Turks" mainly come from Chinese sources which date back to the sixth century. In these sources, "Turk" appears as "Tujue" (Chinese: 突厥; Wade–Giles: T’u-chüe), which referred to the Göktürks.[95][96]
There are several theories regarding the origin of the ethnonym "Turk". There is claim it may be connected to Herodotus's (c. 484–425 BC) reference to Targitaos, a king of the Scythians;[97] however, Mayrhofer (apud Lincoln) assigned Iranian etymology for Ταργιτάος Targitaos from Old Iranian *darga-tavah-, meaning "he whose strength is long-lasting".[98] During the first century AD., Pomponius Mela refers to the "Turcae" in the forests north of the Sea of Azov, and Pliny the Elder lists the "Tyrcae" among the people of the same area.;[97] yet English archaeologist Ellis Minns contended that Tyrcae Τῦρκαι is "a false correction" for Ἱύρκαι Iyrcae/Iyrkai, a people who dwelt beyond the Thyssagetae, according to Herodotus (Histories, iv. 22)[99] There are references to certain groups in antiquity whose names might have been foreign transcriptions of Tür(ü)k such as Togarma, Turukha/Turuška, Turukku and so on; but the information gap is so substantial that any connection of these ancient people to the modern Turks is not possible.[100][101]
In the 19th century, the word Türk referred to Anatolian peasants. The Ottoman ruling class identified themselves as Ottomans, not as Turks.[102][103] In the late 19th century, as the Ottoman upper classes adopted European ideas of nationalism, the term Türk took on a more positive connotation.[104]
During Ottoman times, the millet system defined communities on a religious basis, and today some Turks regard only those who profess the Sunni faith as true Turks. Turkish Jews, Christians, and Alevis are not considered Turks by some.[103] In the early 20th century, the Young Turks abandoned Ottoman nationalism in favor of Turkish nationalism, while adopting the name Turks, which was finally used in the name of the new Turkish Republic.
Article 66 of the Turkish Constitution defines a "Turk" as anyone who is "bound to the Turkish state through the bond of citizenship."[105]
History[]
Prehistory, Ancient era and Early Middle Ages[]
Anatolia was first inhabited by hunter-gatherers during the Paleolithic era, and in antiquity was inhabited by various ancient Anatolian peoples.[106][j] After Alexander the Great's conquest in 334 BC, the area was Hellenized, and by the first century BC it is generally thought that the native Anatolian languages, themselves earlier newcomers to the area, as a result of the Indo-European migrations, became extinct.[107][108]
The early Turkic peoples descended from agricultural communities in Northeast Asia who moved westwards into Mongolia in the late 3rd millennium BC, where they adopted a pastoral lifestyle.[109][110][111][112][113] By the early 1st millennium BC, these peoples had become equestrian nomads.[114] In subsequent centuries, the steppe populations of Central Asia appear to have been progressively replaced and Turkified by East Asian nomadic Turks, moving out of Mongolia.[115][116] In Central Asia, the earliest surviving Turkic-language texts, found on the eighth-century Orkhon inscription monuments, were erected by the Göktürks in the sixth century CE, and include words not common to Turkic but found in unrelated Inner Asian languages.[117] Although the ancient Turks were nomadic, they traded wool, leather, carpets, and horses for wood, silk, vegetables and grain, as well as having large ironworking stations in the south of the Altai Mountains during the 600s CE. Most of the Turkic peoples were followers of Tengrism, sharing the cult of the sky god Tengri, although there were also adherents of Manichaeism, Nestorian Christianity and Buddhism.[118][97] However, during the Muslim conquests, the Turks entered the Muslim world proper as slaves, the booty of Arab raids and conquests.[97] The Turks began converting to Islam after the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana through the efforts of missionaries, Sufis, and merchants. Although initiated by the Arabs, the conversion of the Turks to Islam was filtered through Persian and Central Asian culture. Under the Umayyads, most were domestic servants, whilst under the Abbasid Caliphate, increasing numbers were trained as soldiers.[97] By the ninth century, Turkish commanders were leading the caliphs’ Turkish troops into battle. As the Abbasid Caliphate declined, Turkish officers assumed more military and political power by taking over or establishing provincial dynasties with their own corps of Turkish troops.[97]
Seljuk era[]
During the 11th century, the Seljuk Turks, who were influenced by Persian civilization in many ways, grew in strength and succeeded in taking the eastern province of the Abbasid Empire. By 1055, the Seljuks captured Baghdad and began to make their first incursions into Anatolia.[119] When they won the Battle of Manzikert against the Byzantine Empire in 1071, it opened the gates of Anatolia to them.[120] Although ethnically Turkish, the Seljuk Turks appreciated and became carriers of Persian culture rather than Turkish culture.[121][122] Nonetheless, the Turkish language and Islam were introduced and gradually spread over the region and the slow transition from a predominantly Christian and Greek-speaking Anatolia to a predominantly Muslim and Turkish-speaking one was underway.[120]
In dire straits, the Byzantine Empire turned to the West for help, setting in motion the pleas that led to the First Crusade.[123] Once the Crusaders took Iznik, the Seljuk Turks established the Sultanate of Rum from their new capital, Konya, in 1097.[120] By the 12th century, Europeans had begun to call the Anatolian region "Turchia" or "Turkey", the land of the Turks.[124] The Turkish society in Anatolia was divided into urban, rural and nomadic populations;[125] other Turkoman (Turkmen) tribes who had arrived into Anatolia at the same time as the Seljuks kept their nomadic ways.[120] These tribes were more numerous than the Seljuks, and rejecting the sedentary lifestyle, adhered to an Islam impregnated with animism and shamanism from their central Asian steppeland origins, which then mixed with new Christian influences. From this popular and syncretist Islam, with its mystical and revolutionary aspects, sects such as the Alevis and Bektashis emerged.[120] Furthermore, intermarriage between the Turks and local inhabitants, as well as the conversion of many to Islam, also increased the Turkish-speaking Muslim population in Anatolia.[120][126]
By 1243, at the Battle of Köse Dağ, the Mongols defeated the Seljuk Turks and became the new rulers of Anatolia, and in 1256, the second Mongol invasion of Anatolia caused widespread destruction. Particularly after 1277, political stability within the Seljuk territories rapidly disintegrated, leading to the strengthening of Turkoman principalities in the western and southern parts of Anatolia called the "beyliks".[127]
Beyliks era[]

When the Mongols defeated the Seljuk Turks and conquered Anatolia, the Turks became the vassals of the Ilkhans who established their own empire in the vast area which stretched from present-day Afghanistan to present-day Turkey.[128] As the Mongols occupied more lands in Asia Minor, the Turks moved further into western Anatolia and settled in the Seljuk-Byzantine frontier.[128] By the last decades of the 13th century, the Ilkhans and their Seljuk vassals lost control over much of Anatolia to these Turkoman peoples.[128] A number of Turkish lords managed to establish themselves as rulers of various principalities, known as "Beyliks" or emirates. Amongst these beyliks, along the Aegean coast, from north to south, stretched the beyliks of Karasi, Saruhan, Aydin, Menteşe and Teke. Inland from Teke was Hamid and east of Karasi was the beylik of Germiyan.
To the north-west of Anatolia, around Söğüt, was the small and, at this stage, insignificant, Ottoman beylik. It was hemmed into the east by other more substantial powers like Karaman on Iconium, which ruled from the Kızılırmak River to the Mediterranean. Although the Ottomans was only a small principality among the numerous Turkish beyliks, and thus posed the smallest threat to the Byzantine authority, their location in north-western Anatolia, in the former Byzantine province of Bithynia, became a fortunate position for their future conquests. The Latins, who had conquered the city of Constantinople in 1204 during the Fourth Crusade, established a Latin Empire (1204–61), divided the former Byzantine territories in the Balkans and the Aegean among themselves, and forced the Byzantine Emperors into exile at Nicaea (present-day Iznik). From 1261 onwards, the Byzantines were largely preoccupied with regaining their control in the Balkans.[128] Toward the end of the 13th century, as Mongol power began to decline, the Turcoman chiefs assumed greater independence.[129]
Ottoman Empire[]
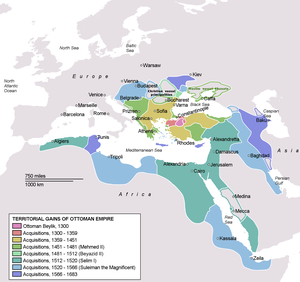
Under its founder, Osman I, the nomadic Ottoman beylik expanded along the Sakarya River and westward towards the Sea of Marmara. Thus, the population of western Asia Minor had largely become Turkish-speaking and Muslim in religion.[128] It was under his son, Orhan I, who had attacked and conquered the important urban center of Bursa in 1326, proclaiming it as the Ottoman capital, that the Ottoman Empire developed considerably. In 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and established a foothold on the Gallipoli Peninsula while at the same time pushing east and taking Ankara.[130][131] Many Turks from Anatolia began to settle in the region which had been abandoned by the inhabitants who had fled Thrace before the Ottoman invasion.[132] However, the Byzantines were not the only ones to suffer from the Ottoman advance for, in the mid-1330s, Orhan annexed the Turkish beylik of Karasi. This advancement was maintained by Murad I who more than tripled the territories under his direct rule, reaching some 100,000 square miles (260,000 km2), evenly distributed in Europe and Asia Minor.[133] Gains in Anatolia were matched by those in Europe; once the Ottoman forces took Edirne (Adrianople), which became the capital of the Ottoman Empire in 1365, they opened their way into Bulgaria and Macedonia in 1371 at the Battle of Maritsa.[134] With the conquests of Thrace, Macedonia, and Bulgaria, significant numbers of Turkish emigrants settled in these regions.[132] This form of Ottoman-Turkish colonization became a very effective method to consolidate their position and power in the Balkans. The settlers consisted of soldiers, nomads, farmers, artisans and merchants, dervishes, preachers and other religious functionaries, and administrative personnel.[135]

In 1453, Ottoman armies, under Sultan Mehmed II, conquered Constantinople.[133] Mehmed reconstructed and repopulated the city, and made it the new Ottoman capital.[136] After the Fall of Constantinople, the Ottoman Empire entered a long period of conquest and expansion with its borders eventually going deep into Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.[137] Selim I dramatically expanded the empire's eastern and southern frontiers in the Battle of Chaldiran and gained recognition as the guardian of the holy cities of Mecca and Medina.[138] His successor, Suleiman the Magnificent, further expanded the conquests after capturing Belgrade in 1521 and using its territorial base to conquer Hungary, and other Central European territories, after his victory in the Battle of Mohács as well as also pushing the frontiers of the empire to the east.[139] Following Suleiman's death, Ottoman victories continued, albeit less frequently than before. The island of Cyprus was conquered, in 1571, bolstering Ottoman dominance over the sea routes of the eastern Mediterranean.[140] However, after its defeat at the Battle of Vienna, in 1683, the Ottoman army was met by ambushes and further defeats; the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz, which granted Austria the provinces of Hungary and Transylvania, marked the first time in history that the Ottoman Empire actually relinquished territory.[141]
By the 19th century, the empire began to decline when ethno-nationalist uprisings occurred across the empire. Thus, the last quarter of the 19th and the early part of the 20th century saw some 7–9 million Muslim refugees (Turks and some Circassians, Bosnians, Georgians, etc.) from the lost territories of the Caucasus, Crimea, Balkans, and the Mediterranean islands migrate to Anatolia and Eastern Thrace.[142] By 1913, the government of the Committee of Union and Progress started a program of forcible Turkification of non-Turkish minorities.[143][144] By 1914, the World War I broke out, and the Turks scored some success in Gallipoli during the Battle of the Dardanelles in 1915. During World War I, the government of the Committee of Union and Progress continued to implement its Turkification policies, which affected non-Turkish minorities, such as the Armenians during the Armenian genocide and the Greeks during various campaigns of ethnic cleansing and expulsion.[145][146][147][148][149] In 1918, the Ottoman Government agreed to the Mudros Armistice with the Allies.
The Treaty of Sèvres —signed in 1920 by the government of Mehmet VI— dismantled the Ottoman Empire. The Turks, under Mustafa Kemal, rejected the treaty and fought the Turkish War of Independence, resulting in the abortion of that text, never ratified,[150] and the abolition of the Sultanate. Thus, the 623-year-old Ottoman Empire ended.[151]
Modern era[]

Once Mustafa Kemal Atatürk led the Turkish War of Independence against the Allied forces that occupied the former Ottoman Empire, he united the Turkish Muslim majority and successfully led them from 1919 to 1922 in overthrowing the occupying forces out of what the Turkish National Movement considered the Turkish homeland.[152] The Turkish identity became the unifying force when, in 1923, the Treaty of Lausanne was signed and the newly founded Republic of Turkey was formally established. Atatürk's presidency was marked by a series of radical political and social reforms that transformed Turkey into a secular, modern republic with civil and political equality for sectarian minorities and women.[153]
Throughout the 1920s and the 1930s, Turks, as well as other Muslims, from the Balkans, the Black Sea, the Aegean islands, the island of Cyprus, the Sanjak of Alexandretta (Hatay), the Middle East, and the Soviet Union continued to arrive in Turkey, most of whom settled in urban north-western Anatolia.[154][155] The bulk of these immigrants, known as "Muhacirs", were the Balkan Turks who faced harassment and discrimination in their homelands.[154] However, there were still remnants of a Turkish population in many of these countries because the Turkish government wanted to preserve these communities so that the Turkish character of these neighbouring territories could be maintained.[156] One of the last stages of ethnic Turks immigrating to Turkey was between 1940 and 1990 when about 700,000 Turks arrived from Bulgaria. Today, between a third and a quarter of Turkey's population are the descendants of these immigrants.[155]
Geographic distribution[]
Traditional areas of Turkish settlement[]
Turkey[]

In the latter half of the 11th century, the Seljuks began settling in the eastern regions of Anatolia. In 1071, the Seljuk Turks defeated the Byzantines at the Battle of Manzikert, beginning the enlargement of their empire and sphere of influence in Anatolia; the Turkish language and Islam were introduced to Anatolia and gradually spread over the region.[157] The slow transition from a predominantly Christian and Greek-speaking Anatolia to a predominantly Muslim and Turkish-speaking one was underway.[158]
Ethnic Turks make up between 70% to 75% of Turkey's population.[94]
Cyprus[]
The Turkish Cypriots are the ethnic Turks whose Ottoman Turkish forebears colonized the island of Cyprus in 1571. About 30,000 Turkish soldiers were given land once they settled in Cyprus, which bequeathed a significant Turkish community. In 1960, a census by the new Republic's government revealed that the Turkish Cypriots formed 18.2% of the island's population.[159] However, once inter-communal fighting and ethnic tensions between 1963 and 1974 occurred between the Turkish and Greek Cypriots, known as the "Cyprus conflict", the Greek Cypriot government conducted a census in 1973, albeit without the Turkish Cypriot populace. A year later, in 1974, the Cypriot government's Department of Statistics and Research estimated the Turkish Cypriot population was 118,000 (or 18.4%).[160] A coup d'état in Cyprus on 15 July 1974 by Greeks and Greek Cypriots favoring union with Greece (also known as "Enosis") was followed by military intervention by Turkey whose troops established Turkish Cypriot control over the northern part of the island.[161] Hence, census's conducted by the Republic of Cyprus have excluded the Turkish Cypriot population that had settled in the unrecognized Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus.[160] Between 1975 and 1981, Turkey encouraged its own citizens to settle in Northern Cyprus; a report by CIA suggests that 200,000 of the residents of Cyprus are Turkish.
Balkans[]

Ethnic Turks continue to inhabit certain regions of Greece, North Macedonia, Kosovo, Romania, and Bulgaria since they first settled there during the Ottoman period. As of 2019, the Turkish population in the Balkans is over 1 million.[162]
Modern diaspora[]
Europe[]
After World War II, West Germany began to experience its greatest economic boom ("Wirtschaftswunder") and in 1961 invited the Turks as guest workers ("Gastarbeiter") to make up for the shortage of workers. The concept of the Gastarbeiter continued with Turkey bearing agreements with Austria, Belgium, and the Netherlands in 1964, with France in 1965; and with Sweden in 1967.[165]
In 1997 Professor Servet Bayram and Professor Barbara Seels said that there was 10 million Turks living in Western Europe and the Balkans (excluding Cyprus and Turkey).[166] By 2010, Boris Kharkovsky from the Center for Ethnic and Political Science Studies said that there was up to 15 million Turks living in the European Union.[167] According to Dr Araks Pashayan 10 million "Euro-Turks" alone were living in Germany, France, the Netherlands and Belgium in 2012.[168] Yet, there are also significant Turkish communities living in Austria, the UK, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, the Scandinavian countries, and the Post-Soviet states.
Modern immigration of Turks to Western Europe began with Turkish Cypriots migrating to the United Kingdom in the early 1920s when the British Empire annexed Cyprus in 1914 and the residents of Cyprus became subjects of the Crown. However, Turkish Cypriot migration increased significantly in the 1940s and 1950s due to the Cyprus conflict. Conversely, in 1944, Turks who were forcefully deported from Meskheti in Georgia during the Second World War, known as the Meskhetian Turks, settled in Eastern Europe (especially in Russia and Ukraine). By the early 1960s, migration to Western and Northern Europe increased significantly from Turkey when Turkish "guest workers" arrived under a "Labour Export Agreement" with Germany in 1961, followed by a similar agreement with the Netherlands, Belgium and Austria in 1964; France in 1965; and Sweden in 1967.[169][170][171] More recently, Bulgarian Turks, Romanian Turks, and Western Thrace Turks have also migrated to Western Europe.
Caucasus[]
The Turkish presence in the Meskheti region of Georgia began with the Turkish military expedition of 1578.[172] The majority of Meskhetian Turks, about 70,000, went to Azerbaijan.[173] According to the 2009 Azerbaijani census, there were 38,000 Turks living in the country;[69] yet in 1999, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees stated that there were 100,000 Meskhetian Turks living in the country.[70] Furthermore, in 2001, the Baku Institute of Peace and Democracy suggested that there was between 90,000 and 110,000 Meskhetian Turks living in Azerbaijan.[71]
Central Asia[]
However, due to the ordered deportation of over 115,000 Meskhetian Turks from their homeland in 1944, during the Second World War, the majority settled in Central Asia.[174] According to the 1989 Soviet Census, which was the last Soviet Census, 106,000 Meskhetian Turks lived in Uzbekistan, 50,000 in Kazakhstan, and 21,000 in Kyrgyzstan.[174] However, in 1989, the Meshetian Turks who had settled in Uzbekistan became the target of a pogrom in the Fergana valley, which was the principal destination for Meskhetian Turkish deportees, after an uprising of nationalism by the Uzbeks.[174] The riots had left hundreds of Turks dead or injured and nearly 1,000 properties were destroyed; thus, thousands of Meskhetian Turks were forced into renewed exile.[174] Soviet authorities recorded many Meskhetian Turks as belonging to other nationalities such as "Azeri", "Kazakh", "Kyrgyz", and "Uzbek".[174][175]
North America[]
Compared to Turkish immigration to Europe, migration to North America has been relatively small. According to the US Census Bureau 196,222 Americans in 2013[176] were of Turkish descent. However, the actual number of Turks is considerably larger, as a significant number of ethnic Turks have migrated to North America not just from Turkey but also from the Balkans (such as Bulgaria and North Macedonia), Cyprus, and the former Soviet Union.[177] Hence, the Turkish American community is currently estimated to number about 500,000.[178][179] Regarding the Turkish Canadian community, Statistics Canada reports that 63,955 Canadians in the 2016 census listed "Turk" as an ethnic origin, including those who listed more than one origin.[180]
The largest concentration of Turkish Americans are in New York City, and Rochester, New York; Washington, D.C.; and Detroit, Michigan. The majority of Turkish Canadians live in Ontario, mostly in Toronto, and there is also a sizable Turkish community in Montreal, Quebec. With regards to the 2010 United States Census, the U.S government was determined to get an accurate count of the American population by reaching segments, such as the Turkish community, that are considered hard to count, a good portion of which falls under the category of foreign-born immigrants.[181] The Assembly of Turkish American Associations and the US Census Bureau formed a partnership to spearhead a national campaign to count people of Turkish origin with an organization entitled "Census 2010 SayTurk" (which has a double meaning in Turkish, "Say" means "to count" and "to respect") to identify the estimated 500,000 Turks now living in the United States.[181]
Oceania[]
A notable scale of Turkish migration to Australia began in the late 1940s when Turkish Cypriots began to leave the island of Cyprus for economic reasons, and then, during the Cyprus conflict, for political reasons, marking the beginning of a Turkish Cypriot immigration trend to Australia.[182] The Turkish Cypriot community were the only Muslims acceptable under the White Australia Policy;[183] many of these early immigrants found jobs working in factories, out in the fields, or building national infrastructure.[184] In 1967, the governments of Australia and Turkey signed an agreement to allow Turkish citizens to immigrate to Australia.[185] Prior to this recruitment agreement, there were fewer than 3,000 people of Turkish origin in Australia.[186] According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, nearly 19,000 Turkish immigrants arrived from 1968 to 1974.[185] They came largely from rural areas of Turkey, approximately 30% were skilled and 70% were unskilled workers.[187] However, this changed in the 1980s when the number of skilled Turks applying to enter Australia had increased considerably.[187] Over the next 35 years the Turkish population rose to almost 100,000.[186] More than half of the Turkish community settled in Victoria, mostly in the north-western suburbs of Melbourne.[186] According to the 2006 Australian Census, 59,402 people claimed Turkish ancestry;[188] however, this does not show a true reflection of the Turkish Australian community as it is estimated that between 40,000 and 120,000 Turkish Cypriots[189][190][191][192] and 150,000 to 200,000 mainland Turks[193][194] live in Australia. Furthermore, there has also been ethnic Turks who have migrated to Australia from Bulgaria,[195] Greece,[196] Iraq,[197] and North Macedonia.[196]
Culture[]
Language[]

Based on geographic variants, the ethnic Turks speak various dialects of the Turkish language. As of 2021, it Turkish remains "the largest and most vigorous Turkic language, spoken by over 80 million people".[198]
Historically, Ottoman Turkish was the official language and lingua franca throughout the Ottoman territories and the Ottoman Turkish alphabet used the Perso-Arabic script. However, Turkish intellectuals sought to simplify the written language during the rise of Turkish nationalism in the nineteenth century.[199]
By the twentieth century, intensive language reforms were thoroughly practiced; most importantly, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk changed the written script to a Latin-based modern Turkish alphabet in 1928.[200] Since then, the regulatory body leading the reform activities has been the Turkish Language Association which was founded in 1932.[198]
The modern standard Turkish is based on the dialect of Istanbul.[201] However, dialectal variation persists, in spite of the levelling influence of the standard used in mass media and the Turkish education system since the 1930s.[202] The terms ağız or şive often refer to the different types of Turkish dialects.
Official status[]
Today, the modern Turkish language is used as the official language of Turkey and Northern Cyprus. It is also an official language in the Republic of Cyprus (alongside Greek).[203] In Kosovo, Turkish is recognized as an official language in the municipalities of Prizren and Mamuša, whilst elsewhere in the country it is recognized as a minority language.[62] Similarly, in North Macedonia Turkish is an official language where they form at least 20% of the population (which includes the Plasnica Municipality, the Centar Župa Municipality, and the Mavrovo and Rostuša Municipality) whilst elsewhere in the country it remains a minority language only.[204] In several other countries, Turkish is officially recognized as a minority language only, including Bosnia and Herzegovina,[205] Croatia,[206] Greece,[207] Iraq,[198] North Macedonia,[198] and Romania.[198][208] Several post-Ottoman nations do not officially recognize the Turkish language but give rights to Turkish minorities to study in their own language (alongside the compulsory study of the official language of the country); this is practiced in Bulgaria[209] and Tunisia.[210]
Various variants of Turkish are also used by millions of Turkish immigrants and their descendants in Western Europe, however, there is no official recognition in these countries.[198]
Turkish dialects[]
There are three major Anatolian Turkish dialect groups spoken in Turkey: the West Anatolian dialect (roughly to the west of the Euphrates), the East Anatolian dialect (to the east of the Euphrates), and the North East Anatolian group, which comprises the dialects of the Eastern Black Sea coast, such as Trabzon, Rize, and the littoral districts of Artvin.[211][212]
The Balkan Turkish dialects are considerably closer to standard Turkish and do not differ significantly from it, despite some contact phenomena, especially in the lexicon.[213]
The Cypriot Turkish dialect was relatively isolated from standard Turkish and had strong influences by the Cypriot Greek dialect. The condition of coexistence with the Greek Cypriots led to a certain bilingualism whereby Turkish Cypriots knowledge of Greek was important in areas where the two communities lived and worked together.[214] The linguistic situation changed radically in 1974, when the island was divided into a Greek south and a Turkish north (Northern Cyprus). Today, the Cypriot Turkish dialect is being exposed to increasing standard Turkish through immigration from Turkey, new mass media, and new educational institutions.[215]

The Iraqi Turkish dialects have historically been influenced by Ottoman Turkish and neighboring Azerbaijani Turkic.[216] Nonetheless, Istanbul Turkish as a prestige language has exerted a profound influence on their dialects.[217] The syntax in Iraqi Turkish therefore differs sharply from neighboring Irano-Turkic varieties,[217] and shares characteristics which are similar with Turkish dialects in Turkey.[218] Collectively, the Iraqi Turkish dialects also show similarities with Cypriot Turkish and Balkan Turkish regarding modality.[219] The written language of the Iraqi Turkmen is based on Istanbul Turkish using the modern Turkish alphabet.[220]
The Meskhetian Turkish dialect was originally spoken in Georgia until the Turkish Meskhetian community were forcefully deported and then dispersed throughout Turkey, Russia, Central Asia, Azerbaijan, Ukraine, and the United States.[221] They speak an Eastern Anatolian dialect of Turkish, which hails from the regions of Kars, Ardahan, and Artvin.[222] The Meskhetian Turkish dialect has also borrowed from other languages (including Azerbaijani, Georgian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Russian, and Uzbek), which the Meskhetian Turks have been in contact with during the Russian and Soviet rule.[222]
Religion[]


Most ethnic Turkish people are either practicing or non-practicing Muslims who follow the teachings of the Hanafi school of Sunni Islam.[79] They form the largest Muslim community in Turkey and Northern Cyprus as well as the largest Muslim groups in Austria,[223] Bulgaria,[224] Denmark,[225] Germany,[226] Liechtenstein,[227] the Netherlands,[226] Romania[228] and Switzerland.[223] In addition to Sunni Turks, there are Alevi Turks whose local Islamic traditions have been based in Anatolia, as well as the Bektashis traditionally centered in Anatolia and the Balkans.[229]
In general, "Turkish Islam" is considered to be "more moderate and pluralistic" than in other Middle Eastern-Islamic societies.[230] Historically, Turkish Sufi movements promoted liberal forms of Islam;[231] for example, Turkish humanist groups and thinkers, such as the Mevlevis (whirling dervishes who follow Rumi), the Bektashis, and Yunus Emre emphasized faith over practicing Islam.[231] During this tolerant environment under the Seljuk Turks, more Turkish tribes arriving in Anatolia during the 13th century found the liberal Sufi version of Islam closer to their shamanists traditions and chose to preserve some of their culture (such as dance and music).[231] During the late Ottoman period, the Tanzimat policies introduced by the Ottoman intelligentsia fused Islam with modernization reforms; this was followed by Atatürk's secularist reforms in the 20th century.[230]
Consequently, there are also many non-practicing Turkish Muslims who tend to be politically secular. For example, in Cyprus, the Turkish Cypriots are generally very secular and only attend mosques on special occasions (such as for funerals).[232] Even so, the Hala Sultan Tekke in Larnaca, which is the resting place of Umm Haram, is considered to be one of the holiest sites in Islam and remains an important pilgrimage site for the secular Turkish Cypriot community too.[233] Similarly, in other urban areas of the Levant, such as in Iraq, the Turkish minority are mainly secular, having internalized the secularist interpretation of state–religion affairs practiced in the Republic of Turkey since its foundation in 1923.[234]


In North Africa, the Turkish minorities have traditionally differentiated themselves from the Arab-Berber population who follow the Maliki school; this is because the Turks have continued to follow the teaching of the Hanafi school which was brought to the region by their ancestors during the Ottoman rule.[235] Indeed, the Ottoman-Turkish mosques in the region are often distinguishable by pencil-like and octagonal minarets which were built in accordance with the traditions of the Hanafi rite.[236][237]
The tradition of building mosques in the Ottoman-style (i.e either in the imperial style based on Istanbul mosques or the provincial styles) has continued into the present day, both in traditional areas of settlement (e.g. in Turkey, the Balkans, Cyprus, and other parts of the Levant) as well as in Western Europe and North America where there are substantial immigrant communities.[238]
Since the 1960s, "Turkish" was even seen as synonymous with "Muslim" in countries like Germany because Islam was considered to have a specific "Turkish character" and visual architectural style.[239]
Arts and Architecture[]

Turkish architecture reached its peak during the Ottoman period. Ottoman architecture, influenced by Seljuk, Byzantine and Islamic architecture, came to develop a style all of its own.[240] Overall, Ottoman architecture has been described as a synthesis of the architectural traditions of the Mediterranean and the Middle East.[241]
As Turkey successfully transformed from the religion-based former Ottoman Empire into a modern nation-state with a very strong separation of state and religion, an increase in the modes of artistic expression followed. During the first years of the republic, the government invested a large amount of resources into fine arts; such as museums, theatres, opera houses and architecture. Diverse historical factors play important roles in defining the modern Turkish identity. Turkish culture is a product of efforts to be a "modern" Western state, while maintaining traditional religious and historical values.[242] The mix of cultural influences is dramatized, for example, in the form of the "new symbols of the clash and interlacing of cultures" enacted in the works of Orhan Pamuk, recipient of the 2006 Nobel Prize in Literature.[243]
Traditional Turkish music include Turkish folk music (Halk müziği), Fasıl and Ottoman classical music (Sanat müziği) that originates from the Ottoman court.[244] Contemporary Turkish music include Turkish pop music, rock, and Turkish hip hop genres.[244]
Genetics[]
Turkish genomic variation, along with several other Western Asian populations, looks most similar to genomic variation of South European populations such as southern Italians.[245] Data from ancient DNA – covering the Paleolithic, the Neolithic, and the Bronze Age periods – showed that Western Asian genomes, including Turkish ones, have been greatly influenced by early agricultural populations in the area; later population movements, such as those of Turkic speakers, also contributed.[245]
The only whole genome sequencing study of Turkish genetics (on 16 individuals) concluded that the Turkish population forms a cluster with Southern European/Mediterranean populations, and the predicted contribution from ancestral East Asian populations (presumably Central Asian) is 21.7%. Meanwhile, East Asian impact on Kazakh genome (another Turkic ethnic group) is only %55 percent.[246][247] However, that is not a direct estimate of a migration rate, due to reasons such as unknown original contributing populations.[247] Moreover, the genetic variation of various populations in Central Asia "has been poorly characterized"; Western Asian populations may also be "closely related to populations in the east".[245]
A study in 2015 found "7.9% (±0.4) East Asian ancestry in Turks", and the authors suggested that Turks are "genetically shifted towards modern Central Asians" in line with historical mixture of populations from this region.[248] A 2019 study found that Turkish people cluster with Southern and Mediterranean Europe populations along with groups in the northern part of Southwest Asia (such as the populations from Caucasus, Northern Iraq, and Iranians).[249] Another study found the Circassians are closest to the Turkish population among sampled European (French, Italian, Sardinian), Middle Eastern (Druze, Palestinian), and Central (Kyrgyz, Hazara, Uygur), South (Pakistani), and East Asian (Mongolian, Han) populations.[250] Another 2019 study found that Turkish people have the lowest Fst distances with Caucasus population group and Iranian-Syrian group, compared to East-Central European, European (including Northern and Eastern European), Sardinian, Roma, and Turkmen groups or populations. Caucasus group in the study included samples from "Abkhazians, Adygey, Armenians, Balkars, Chechens, Georgians, Kumyks, Kurds, Lezgins, Nogays, and North Ossetia."[251]
A study involving mitochondrial analysis of a Byzantine-era population, whose samples were gathered from excavations in the archaeological site of Sagalassos, found that Sagalassos samples were closest to modern samples from "Turkey, Crimea, Iran and Italy (Campania and Puglia), Cyprus and the Balkans (Bulgaria, Croatia and Greece)."[252] Modern-day samples from the nearby town of Ağlasun showed that lineages of East Eurasian descent assigned to macro-haplogroup M were found in the modern samples from Ağlasun. This haplogroup is significantly more frequent in Ağlasun (15%) than in Byzantine Sagalassos, but the study concluded that there is "no genetic discontinuity across two millennia in the region."[253] Another study concluded that the true Central Asian contributions to Anatolia was 13% for males and 22% for females (with wide ranges of confidence intervals), and the language replacement in Turkey and Azerbaijan might not have been in accordance with the elite dominance model.[254]
See also[]
Notes[]
^ a: According to the Home Affairs Committee this includes 300,000 Turkish Cypriots.[255] However, some estimates suggest that the Turkish Cypriot community in the UK has reached between 350,000[256] to 400,000.[257][258]
^ b: Includes people of mixed ethnic background.
^ c: A further 10,000–30,000 people from Bulgaria live in the Netherlands. The majority are Bulgarian Turks and are the fastest-growing group of immigrants in the Netherlands.[259]
^ d: This includes Turkish settlers. 2,000 of these Turkish Cypriots currently reside in the southern part of the island, the rest on the northern.[260]
^ e: This figure only includes Turkish citizens. Therefore, this also includes ethnic minorities from Turkey; however, it does not include ethnic Turks who have either been born and/or have become naturalised citizens. Furthermore, these figures do not include ethnic Turkish minorities from Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece, Iraq, Kosovo, Macedonia, Romania or any other traditional area of Turkish settlement because they are registered as citizens from the country they have immigrated from rather than their ethnic Turkish identity.
^ f: In addition to Turkish citizens, this figure includes people with ancestral background related to Turkey, so it includes ethnic minorities of Turkey.
^ g: This figure only includes Turks of Western Thrace. A further 5,000 live in the Rhodes and Kos.[261]
^ h: These figures only include the Meskhetian Turks. According to official census's there were 38,000 Turks in Azerbaijan (2009),[69] 97,015 in Kazakhstan (2009),[262] 39,133 in Kyrgyzstan (2009),[67] 109,883 in Russia (2010),[64] and 9,180 in Ukraine (2001).[263] A further 106,302 Turks were recorded in Uzbekistan's last census in 1989[264] although the majority left for Azerbaijan and Russia during the 1989 pogroms in the Ferghana Valley. Official data regarding the Turks in the former Soviet Union is unlikely to provide a true indication of their population as many have been registered as "Azeri", "Kazakh", "Kyrgyz", and "Uzbek".[175] In Kazakhstan only a third of them were recorded as Turks, the rest had been arbitrarily declared members of other ethnic groups.[265][266] Similarly, in Azerbaijan, much of the community is officially registered as "Azerbaijani"[267] even though the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees reported, in 1999, that 100,000 Meskhetian Turks were living there.[70]
^ i: A further 30,000 Bulgarian Turks live in Sweden.[268]
^ j: "The history of Turkey encompasses, first, the history of Anatolia before the coming of the Turks and of the civilizations—Hittite, Thracian, Hellenistic, and Byzantine—of which the Turkish nation is the heir by assimilation or example. Second, it includes the history of the Turkish peoples, including the Seljuks, who brought Islam and the Turkish language to Anatolia. Third, it is the history of the Ottoman Empire, a vast, cosmopolitan, pan-Islamic state that developed from a small Turkish amirate in Anatolia and that for centuries was a world power."[269]
^ k: The Turks are also defined by the country of origin. Turkey, once Asia Minor or Anatolia, has a very long and complex history. It was one of the major regions of agricultural development in the early Neolithic and may have been the place of origin and spread of lndo-European languages at that time. The Turkish language was imposed on a predominantly lndo-European-speaking population (Greek being the official language of the Byzantine empire), and genetically there is very little difference between Turkey and the neighboring countries. The number of Turkish invaders was probably rather small and was genetically diluted by the large number of aborigines."
"The consideration of demographic quantities suggests that the present genetic picture of the aboriginal world is determined largely by the history of Paleolithic and Neolithic people, when the greatest relative changes in population numbers took place."[270]
References[]
- ^ Garibova, Jala (2011), "A Pan-Turkic Dream: Language Unification of Turks", in Fishman, Joshua; Garcia, Ofelia (eds.), Handbook of Language and Ethnic Identity: The Success-Failure Continuum in Language and Ethnic Identity Efforts, Oxford University Press, p. 268, ISBN 9780199837991,
Approximately 200 million people,... speak nearly 40 Turkic languages and dialects. Turkey is the largest Turkic state, with about 60 million ethnic Turks living in its territories.
- ^ Hobbs, Joseph J. (2017), Fundamentals of World Regional Geography, Cengage, p. 223, ISBN 9781305854956,
The greatest are the 65 million Turks of Turkey, who speak Turkish, a Turkic language...
- ^ "Cyprus". The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ "KKTC 2011 NÜFUS VE KONUT SAYIMI" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2014.
- ^ Orvis, Stephen; Drogus, Carol Ann (2018). Introducing Comparative Politics: Concepts and Cases in Context. CQ Press. p. 305. ISBN 978-1-5443-7444-4.
Today, nearly three million ethnic Turks live in Germany, and many have raised children there.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Engstrom, Aineias, "Turkish-German "dream team" behind first COVID-19 vaccine", Portland State Vanguard, Portland State University, archived from the original on 27 March 2021, retrieved 27 March 2021,
The German census does not gather data on ethnicity, however according to estimates, somewhere between 4–7 million people with Turkish roots, or 5–9% of the population, live in Germany.
- ^ Zestos, George K.; Cooke, Rachel N. (2020), Challenges for the EU as Germany Approaches Recession (PDF), Levy Economics Institute, p. 22,
Presently (2020) more than seven million Turks live in Germany.
- ^ Szyszkowitz, Tessa (2005), "Germany", in Von Hippel, Karin (ed.), Europe Confronts Terrorism, Palgrave Macmillan, p. 53, ISBN 978-0230524590,
It is a little late to start the debate about being an immigrant country now, when already seven million Turks live in Germany.
- ^ Aalberse, Suzanne; Backus, Ad; Muysken, Pieter (2019), Heritage Languages: A language Contact Approach, John Benjamins Publishing Company, p. 90, ISBN 978-9027261762,
the Dutch Turkish community... out of a population that over the years must have numbered half a million.
- ^ Tocci, Nathalie (2004), EU Accession Dynamics and Conflict Resolution: Catalysing Peace Or Consolidating Partition in Cyprus?, Ashgate Publishing, p. 130, ISBN 9780754643104,
The Dutch government was concerned about Turkey’s reaction to the European Council’s conclusions on Cyprus, keeping in mind the presence of two million Turks in Holland and the strong business links with Turkey.
- ^ van Veen, Rita (2007), ’De koningin heeft oog voor andere culturen’, Trouw, archived from the original on 12 April 2021, retrieved 25 December 2020,
Erol kan niet voor alle twee miljoen Turken in Nederland spreken, maar hij denkt dat Beatrix wel goed ligt bij veel van zijn landgenoten.
- ^ Baker, Rauf (2021), The Netherlands: The EU’s “New Britain”?, Begin–Sadat Center for Strategic Studies, Bar-Ilan University,
The Netherlands, which has a total population of 17 million, contains around two million Turks,...
- ^ Hentz, Jean-Gustave; Hasselmann, Michel (2010). Transculturalité, religion, traditions autour de la mort en réanimation. Springer-Verlag France. doi:10.1007/978-2-287-99072-4_33. ISBN 978-2-287-99072-4.
La France d’aujourd’hui est une société multiculturelle et multiethnique riche de 4,9 millions de migrants représentant environ 8 % de la population du pays. L’immigration massive de populations du sud de l’Europe de culture catholique après la deuxième guerre mondiale a été suivie par l’arrivée de trois millions d’Africains du Nord, d’un million de Turcs et de contingents importants d’Afrique Noire et d’Asie qui ont implanté en France un islam majoritairement sunnite (Maghrébins et Africains de l’Ouest) mais aussi chiite (Pakistanais et Africains de l’Est).
- ^ Gallard, Joseph; Nguyen, Julien (2020), "Il est temps que la France appelle à de véritables sanctions contre le jeu d'Erdogan", Marianne, archived from the original on 14 February 2020, retrieved 25 November 2020,
... et ce grâce à la nombreuse diaspora turque, en particulier en France et en Allemagne. Ils seraient environ un million dans l'Hexagone, si ce n’est plus...es raisons derrière ne sont pas difficiles à deviner : l’immense population turque en Allemagne, estimée par Merkel elle-même aux alentours de sept millions et qui ne manquerait pas de se faire entendre si l’Allemagne prenait des mesures allant à l’encontre de la Turquie.
- ^ Contrat d'objectifs et de moyens (COM) 2020–2022 de France Médias Monde: Mme Joëlle Garriaud-Maylam, co-rapporteur, Sénat, 2021, retrieved 7 May 2021,
Enfin, comme vous l'avez dit au sujet de la Turquie, il est essentiel que la France investisse davantage dans les langues qui sont parlées sur le territoire national. On recense plus d'un million de Turcs en France. Ils ne partagent pas toujours nos objectifs et nos valeurs, parce qu'ils subissent l'influence d'une presse qui ne nous est pas toujours très favorable. Il est donc très utile de les prendre en compte dans le développement de nos médias.
- ^ "Remarks by Commerce Secretary Bryson, April 5, 2012", Foreign Policy Bulletin, Cambridge University Press, 22 (3): 137, 2012,
Here in the U.S., you can see our person-to-person relationships growing stronger each day. You can see it in the 13,000 Turkish students that are studying here in the U.S. You can see it in corporate leaders like Muhtar Kent, the CEO of Coca-Cola, and you can see it in more than one million Turkish-Americans who add to the rich culture and fabric of our country.
- ^ Remarks at Center for American Progress & Confederation of Businessmen and Industrialists of Turkey (TUSKON) Luncheon, U.S. Department of Commerce, 2012, retrieved 13 November 2020
- ^ Home Affairs Committee 2011, p. 38.
- ^ "UK immigration analysis needed on Turkish legal migration, say MPs". The Guardian. 1 August 2011. Retrieved 1 August 2011.
- ^ Federation of Turkish Associations UK (19 June 2008). "Short history of the Federation of Turkish Associations in UK". Archived from the original on 10 January 2012. Retrieved 13 April 2011.
- ^ Warum die Türken? (PDF), 78, Initiative Minderheiten, 2011,
Was sind die Gründe für dieses massive Unbehagen angesichts von rund 360.000 Menschen türkischer Herkunft?
- ^ Weiss, Alexia. "Erheblicher Anstieg antisemitischer Vorfälle in Wien". Jüdische Allgemeine. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
Muzicant wandte sich am Donnerstag in einem Brief an alle Gemeindemitglieder. Er sichert darin Hilfe der IKG zu und ruft alle, die Opfer solcher Übergriffe werden, auf, sich bei der Kultusgemeinde zu melden und Anzeige bei der Polizei zu erstatten. »Wir dürfen nicht zulassen, dass der Antisemitismus jetzt auf die 400.000 in Österreich lebenden Türken übergreift.«
- ^ Mölzer, Andreas. "In Österreich leben geschätzte 500.000 Türken, aber kaum mehr als 10–12.000 Slowenen". Archived from the original on 22 July 2012. Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Manço, Altay; Taş, Ertugrul (2019), "Migrations Matrimoniales: Facteurs de Risque en Sante´ Mentale", The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, SAGE Publishing, 64 (6): 444, doi:10.1177/0706743718802800, PMC 6591757, PMID 30380909
- ^ Debels, Thierry (2021), Operatie Rebel: toen de Belgische heroïnehandel in Turkse handen was, PMagazine, archived from the original on 16 August 2021, retrieved 16 August 2021,
Volgens diverse bronnen zouden eerst een half miljoen Turken die toen in Belgie verbleven – Belgen van Turkse afkomst en aanverwanten – gescreend zijn.
- ^ "Australian Government Department of Immigration and Border Protection" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ "Old foes, new friends". The Sydney Morning Herald. 23 April 2005. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ Presidency of the Republic of Turkey (2010). "Turkey-Australia: "From Çanakkale to a Great Friendship". Retrieved 14 July 2011.
- ^ OECD (2009). "International Questionnaire: Migrant Education Policies in Response to Longstanding Diversity: TURKEY" (PDF). Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. p. 3.
- ^ "Population of Sweden 31 December 2018 born in Turkey, which includes Turks, Assyrians, Kurds and others". statistikdatabasen.scb.se.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Aydıngün et al. 2006, p. 13.
- ^ Schweizer Nein könnte Europa-Skeptiker stärken, Der Tagesspiegel, 2009, retrieved 26 May 2021,
Dabei erwarten Vertreter der rund 120.000 Türken in der Schweiz nach dem Referendum keine gravierenden Änderungen in ihrem Alltag.
- ^ Larsen, Nick Aagaard (2008), Tyrkisk afstand fra Islamisk Trossamfund, Danish Broadcasting Corporation, retrieved 1 November 2020,
Ud af cirka 200.000 muslimer i Danmark har 70.000 tyrkiske rødder, og de udgør dermed langt den største muslimske indvandrergruppe.
- ^ Aytaç, Seyit Ahmet (2018), Shared issues, stronger ties: Canada's envoy to Turkey, Anadolu Agency, retrieved 7 February 2021,
Turkish diaspora of some 100,000 Turks largely in Toronto is growing, says Canadian Ambassador Chris Cooter ... We have a growing Turkish diaspora and they’re doing very well in Canada. We think it’s 100,000, largely in Toronto. We have several thousand Turkish students in Canada as well.
- ^ "I cittadini non comunitari regolarmente soggiornanti Ascolta". 5 August 2014. Archived from the original on 13 November 2014. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Taef, El-Azhari (2005). "The Turkmen Identity Crisis in the fifteenth-century Middle East: The Turkmen-Turkish Struggle for Supremacy" (PDF). Chronica. 5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 9 June 2018.
The Turkmen were always the forgotten minority in the area despite their large population. In the absence of official records, their numbers cannot be calculated, but it is widely accepted that they exceed three millions in Iraq, and one million in Syria and other countries.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Triana, María (2017), Managing Diversity in Organizations: A Global Perspective, Taylor & Francis, p. 168, ISBN 978-1-317-42368-3,
Turkmen, Iraqi citizens of Turkish origin, are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq after Arabs and Kurds and they are said to number about 3 million of Iraq's 34.7 million citizens according to the Iraqi Ministry of Planning.
- ^ Bassem, Wassim (2016). "Iraq's Turkmens call for independent province". Al-Monitor. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016.
Turkmens are a mix of Sunnis and Shiites and are the third-largest ethnicity in Iraq after Arabs and Kurds, numbering about 3 million out of the total population of about 34.7 million, according to 2013 data from the Iraqi Ministry of Planning.
- ^ Pierre, Beckouche (2017), "The Country Reports: Syria", Europe's Mediterranean Neighbourhood, Edward Elgar Publishing, pp. 178–180, ISBN 978-1786431493,
Before 2011, Syria's population was 74% Sunni Muslim, including...Turkmen (4%)...
- ^ Shoup, John A. (2018), "Syria", The History of Syria, ABC-CLIO, p. 6, ISBN 978-1-4408-5835-2,
The third largest ethnic group in Syria is the Turkish speakers...They comprise around 4-5 percent of the total population
- ^ Aikman, David (2014), The Mirage of Peace: Understand The Never-Ending Conflict in the Middle East, Baker Publishing Group, ISBN 9781441223555,
There is also about 1.7 million Turks in Syria, and about 800,000 Druze,...
- ^ Gamal, Gamal, Did the Turks sweeten Egypt's kitty?, Al-Ahram Weekly, retrieved 1 May 2018,
Today, the number of ethnic Turks in Egypt varies considerably, with estimates ranging from 100,000 to 1,500,000. Most have intermingled in Egyptian society and are almost indistinguishable from non-Turkish Egyptians, even though a considerable number of Egyptians of Turkish origin are bilingual.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Akar 1993, p. 95.
- ^ Karpat 2004, p. 12.
- ^ Al-Akhbar. "Lebanese Turks Seek Political and Social Recognition". Archived from the original on 20 June 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2012.
- ^ "Tension adds to existing wounds in Lebanon". Today's Zaman. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 6 April 2011.
- ^ Ahmed, Yusra (2015), Syrian Turkmen refugees face double suffering in Lebanon, Zaman Al Wasl, retrieved 11 October 2016
- ^ Syrian Observer (2015). "Syria's Turkmen Refugees Face Cruel Reality in Lebanon". Retrieved 10 October 2016.
- ^ National Statistical Institute of Bulgaria (2011). "2011 Population Census in the Republic of Bulgaria (Final data)" (PDF). National Statistical Institute of Bulgaria.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Aydinli-Karakulak, Arzu; Baylar, Ayben; Keleş, Seray Çağla; Dimitrova, Radosveta (2018), "Positive Affect and School Related Outcomes: Feeling Good Facilitates School Engagement Among Turkish-Bulgarian Minority Adolescents", in Dimitrova, Radosveta (ed.), Well-Being of Youth and Emerging Adults across Cultures: Novel Approaches and Findings from Europe, Asia, Africa and America, Springer, p. 149, ISBN 9783319683638,
Turks in Bulgaria represent the largest ethnic minority group in the country, constituting almost 10% of Bulgaria's seven million total population,...
- ^ Sosyal 2011, p. 369.
- ^ Bokova 2010, p. 170.
- ^ "Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Macedonia, 2002" (PDF). Republic of Macedonia – State Statistical Office. 2005. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Knowlton, MaryLee; Nevins, Debbie (2020), North Macedonia, Cavendish Square Publishing, ISBN 9781502655905,
The Turks are the second largest national minority in Macedonia. Like other ethnic groups, they claim higher numbers than the census shows, somewhere between 170,000 and 200,000.
- ^ "GREEK HELSINKI MONITOR". Minelres.lv. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ "Demographics of Greece". European Union National Languages. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
- ^ "Destroying Ethnic Identity: The Turks of Greece" (PDF). Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- ^ "Turks Of Western Thrace". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
- ^ Phinnemore, David (2006), The EU and Romania: accession and beyond, The Federal Trust for Education & Research, p. 157, ISBN 978-1-903403-78-5,
Today, there are around 55,000 Turks living in Romania and they are represented as a minority in parliament.
- ^ Constantin, Daniela L.; Goschin, Zizi; Dragusin, Mariana (2008), "Ethnic entrepreneurship as an integration factor in civil society and a gate to religious tolerance. A spotlight on Turkish entrepreneurs in Romania", Journal for the Study of Religions and Ideologies, 7 (20): 59,
The significant Turkish population living in Romania (nearly 80,000 members, including immigrants)...
- ^ 2011 census in the Republic of Kosovo.[full citation needed]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c OSCE (2010), "Community Profile: Kosovo Turks", Kosovo Communities Profile, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, p. 3,
Approximately 30,000 Kosovo Turks live in Kosovo today, while up to 250,000 people from different Kosovo communities speak or at least understand the Turkish language...The Turkish language has been granted official language status in the municipalities of Prizren and Vushtrri/ Vučitrn.
- ^ Kibaroğlu, Mustafa; Kibaroğlu, Ayșegül (2009), Global Security Watch—Turkey: A Reference Handbook, Greenwood Publishing Group, p. 107, ISBN 9780313345609,
Turks themselves are also an important ethnic minority in the region... In Kosovo, their number is estimated to be around 60,000...
- ^ Jump up to: a b Демоскоп Weekly. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 г. Национальный состав населения Российской Федерации. Archived from the original on 21 May 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- ^ Ryazantsev 2009, p. 172.
- ^ "Агентство Республики Казахстан по статистике. Этнодемографический сборник Республики Казахстан 2014". Stat.gov.kz. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b National Statistical Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic. "Population and Housing Census 2009" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 July 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ IRIN Asia (9 June 2005). "KYRGYZSTAN: Focus on Mesketian Turks". Retrieved 17 March 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Population by ethnic groups". 30 November 2012. Archived from the original on 30 November 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c UNHCR 1999a, p. 14.
- ^ Jump up to: a b NATO Parliamentary Assembly. "Minorities in the South Caucasus: Factor of Instability?". Archived from the original on 8 March 2012. Retrieved 16 January 2012.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Council of Europe 2006, p. 23.
- ^ Blacklock 2005, p. 8.
- ^ State Statistics Service of Ukraine. "Ukrainian Census (2001):The distribution of the population by nationality and mother tongue". Archived from the original on 1 May 2008. Retrieved 16 January 2012.
- ^ Pentikäinen & Trier 2004, p. 20.
- ^ Aydıngün et al. 2006, p. 14.
- ^ Çalışma ve Sosyal Güvenlik Bakanlığı. "YURTDIŞINDAKİ VATANDAŞLARIMIZLA İLGİLİ SAYISAL BİLGİLER (31.12.2009 tarihi itibarıyla)". Archived from the original on 10 March 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Nyrop, Richard F.; Benderly, Beryl Lieff; Cover, Willian W.; Cutter, Melissa J.; Evin, Ahmet Ö.; Parker, Newton B.; Teleki, Suzanne (1973), Area Handbook for the Republic of Turkey, 550, United States Government Publishing Office, ISSN 0892-8541,
Among the Turks may be distinguished a number of regional variants that do not function as ethnic groups but merely reflect differing historical and ecological circumstances. To some extent, differences of accent, customs, and outlook distinguish the regions and are popularly expressed in regional stereotypes. Three of the most important of these variants are Anatolian Turks, the peasantry of central core of Asiatic Turkey, whose culture is said to underlie Turkish nationalism; Rumelian Turks, primarily immigrants from Balkan territories of the empire of their descendants; and central Asian Turks, the assorted Turkic tibesmen from Asia who have come to Turkey. Others, such as the Black Sea Turks, whose speech largely lacks the vowel harmony valued elsewhere and whose natural predilections are thought to be toward extremely devout religion and the sea, are also distinguished.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Mayer, Ann Elizabeth (2010), "Turks", The Contemporary Middle East: A Westview Reader, Westview Press, p. 27, ISBN 9780813344652,
Generally, they speak Turkish as a primary language, are Muslims (90% are Sunni), claim a Turkish heritage... Four groups of Turks can be identified through cultural and geographic differences. First, the Anatolian Turks in Asia Minor...Second, the Rumelian Turks (from Rum, meaning "Roman", or European) are European Turks who remained in Europe after the Ottoman days... Third are descendants of Turks who stayed in various parts of the Middle East separated from the Ottoman Empire after World War I. Fourth are some 200,000 Turkish Cypriots...
- ^ Şimşir, Bilal (1989), "The Turks of Bulgaria, 1878–1985", Turkish Quarterly Review Digest, Directorate General of Press and Information, 3 (15): 6,
The Balkan Turks and the Anatolian Turks together constituted the core of the Ottoman Empire and its founding element.
- ^ Çıraklı, Mustafa (2018), "Turkish Migration into the North of Cyprus and the (Re)Construction of Turkish Cypriot Identity in the Turkish Cypriot Press (1995–2013)", in Kyritsi, Thekla; Christofis, Nikos (eds.), Cypriot Nationalisms in Context: History, Identity and Politics, Springer, p. 200, ISBN 9783319978048
- ^ Cornell, Svante E. (2005), Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus, Routledge, p. 171, ISBN 9781135796693,
Many Georgians have advocated that the Meskhetian Turks should be sent to Turkey, 'where they belong'. The Turkish authorities have, nevertheless, been reluctant to accept them, probably as they are afraid of experiencing a massive migration of ethnic Turks from different parts of the Balkans, the Middle East and the CIS. Other examples are that Turks in Western Thrace and Bulgaria, as well as Turkish Cypriots, face difficulties in obtaining Turkish citizenship. Rather, Turkey wants these minority groups, perhaps for strategic reasons, to remain in or return to their ancestral lands.
- ^ Saatçi, Suphi (2018), "The Turkman of Iraq", in Bulut, Christiane (ed.), Linguistic Minorities in Turkey and Turkic-Speaking Minorities of the Periphery, Harrassowitz Verlag, p. 331, ISBN 978-3447107235
- ^ Pan, Chia-Lin (1949), "The Population of Libya", Population Studies, 3 (1): 100–125, doi:10.1080/00324728.1949.10416359
- ^ Khalifa, Mustafa (2013), The impossible partition of Syria, Arab Reform Initiative, pp. 3–5, archived from the original on 27 March 2019, retrieved 27 March 2019,
Turkmen are the third largest ethnic group in Syria, making up around 4–5% of the population. Some estimations indicate that they are the second biggest group, outnumbering Kurds, drawing on the fact that Turkmen are divided into two groups: the rural Turkmen who make up 30% of the Turkmen in Syria and who have kept their mother tongue, and the urban Turkmen who have become Arabized and no longer speak their mother language.
- ^ "Austria", Annual Report on International Religious Freedom 2007, February 2008, 110–2 Report, United States Government Publishing Office, 2008, p. 253,
By far the largest ethnic group is Turkish, of which 123,000 have Turkish citizenship, Many more ethnic Turks are Austrian citizens.
- ^ Liversage, Anika (2013), "Transnational Families Breaking Up: Divorce among Turkish Immigrants in Denmark", in Charsley, Katharine (ed.), Transnational Marriage: New Perspectives from Europe and Beyond, Routledge, p. 146, ISBN 9781136279744,
Turkish immigrants began arriving in Denmark in the late 1960s. After subsequent family migration, people of Turkish descent now make up the largest ethnic minority group in Denmark.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Friedrichs, Jürgen; Klöckner, Jennifer; Şen, Mustafa; de Witte, Nynke (2012), "Turkish Islamic Organisations: A Comparative Study in Germany, the Netherlands and Turkey", in Beaumon, Justin; Cloke, Paul J. (eds.), Faith-based Organisations and Exclusion in European Cities, Policy Press, p. 219, ISBN 9781847428349,
Turks are the largest immigrant group in both Germany and the Netherlands.
- ^ Davison, Roderic H. (2013). Essays in Ottoman and Turkish History, 1774–1923: The Impact of the West. University of Texas Press. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-0292758940. Archived from the original on 6 August 2018. Retrieved 22 September 2016.
So the Seljuk sultanate was a successor state ruling part of the medieval Greek empire, and within it the process of Turkification of a previously Hellenized Anatolian population continued. That population must already have been of very mixed ancestry, deriving from ancient Hittite, Phrygian, Cappadocian, and other civilizations as well as Roman and Greek.
- ^ Leonard, Thomas M. (2006). "Turkey". Encyclopedia of the Developing World, Volume 3. Routledge. p. 1576. ISBN 9781579583880.
Subsequently, Hellenization of the elites transformed Anatolia into a largely Greek-speaking region
- ^ Sahadeo, Jeff; Zanca, Russell (2007). Everyday life in Central Asia : past and present. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. pp. 22–23. ISBN 978-0253013538.
- ^ Akgönül, Samim (2013). The minority concept in the Turkish context: practices and perceptions in Turkey, Greece, and France. Translated by Sila Okur. Leiden: Brill. p. 136. ISBN 978-9004222113.
- ^ Bayir, Derya (22 April 2016). Minorities and Nationalism in Turkish Law. ISBN 978-1317095798.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Turkey". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Stokes & Gorman 2010a, p. 707.
- ^ Findley 2005, p. 21.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Leiser 2005, p. 837.
- ^ Lincoln, Bruce (2014). "Once again 'the Scythian' myth of origins (Herodotus 4.5–10)". Nordlit. 33 (33): 19–34. doi:10.7557/13.3188.
- ^ Minns, Ellis Hovell (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 102.
- ^ Peter B. Golden, Introduction to the History of the Turkic People, p. 12: "... source (Herod.IV.22) and other authors of antiquity, Togarma of the Old Testament, Turukha/Turuska of Indic sources, Turukku of Assyrian..."
- ^ German Archaeological Institute. Department Teheran, Archaeologische Mitteilungen aus Iran, Vol. 19, Dietrich Reimer, 1986, p. 90
- ^ Kushner 1997, p. 219.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Meeker 1971, p. 322.
- ^ Kushner 1997, pp. 220–221.
- ^ "Turkish Citizenship Law" (PDF). 29 May 2009. Retrieved 17 June 2012.
- ^ Stokes & Gorman 2010b, p. 721.
- ^ Theo van den Hout (27 October 2011). The Elements of Hittite. Cambridge University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-139-50178-1. Retrieved 24 March 2013.
- ^ Sharon R. Steadman; Gregory McMahon (15 September 2011). The Oxford Handbook of Ancient Anatolia: (10,000–323 BCE). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-537614-2. Retrieved 23 March 2013.
- ^ Robbeets 2017, pp. 216-218.
- ^ Robbeets 2020.
- ^ Nelson et al. 2020.
- ^ Li et al. 2020.
- ^ Uchiyama et al. 2020.
- ^ Robbeets 2017, pp. 216–218.
- ^ Damgaard et al. 2018, pp. 4–5. "These results suggest that Turkic cultural customs were imposed by an East Asian minority elite onto central steppe nomad populations... The wide distribution of the Turkic languages from Northwest China, Mongolia and Siberia in the east to Turkey and Bulgaria in the west implies large-scale migrations out of the homeland in Mongolia.
- ^ Lee & Kuang 2017, p. 197. "Both Chinese histories and modern dna studies indicate that the early and medieval Turkic peoples were made up of heterogeneous populations. The Turkicisation of central and western Eurasia was not the product of migrations involving a homogeneous entity, but that of language diffusion."
- ^ Findley 2005, p. 39.
- ^ Coene, Frederik (2009). The Caucasus-An Introduction. Taylor & Francis. p. 77.
- ^ Duiker & Spielvogel 2012, p. 192.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Darke 2011, p. 16.
- ^ Chaurasia 2005, p. 181.
- ^ Bainbridge 2009, p. 33.
- ^ Duiker & Spielvogel 2012, p. 193.
- ^ Ágoston 2010, p. 574.
- ^ Delibaşı 1994, p. 7.
- ^ Turkey Foreign Policy And Government Guide. International Business Publications. 2004. p. 64. ISBN 978-0739762820.
- ^ Somel 2003, p. 266.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Ágoston 2010, p. xxv.
- ^ Kia 2011, p. 1.
- ^ Fleet 1999, p. 5.
- ^ Kia 2011, p. 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Köprülü 1992, p. 110.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Ágoston 2010, p. xxvi.
- ^ Fleet 1999, p. 6.
- ^ Eminov 1997, p. 27.
- ^ Kermeli 2010, p. 111.
- ^ Kia 2011, p. 5.
- ^ Quataert 2000, p. 21.
- ^ Kia 2011, p. 6.
- ^ Quataert 2000, p. 24.
- ^ Levine 2010, p. 28.
- ^ Karpat 2004, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Samuel Totten, William S. Parsons, ed. (2012). Century of Genocide. Routledge. pp. 118–124. ISBN 978-1135245504.
By 1913 the advocates of liberalism had lost out to radicals in the party who promoted a program of forcible Turkification.
- ^ Jwaideh, Wadie (2006). The Kurdish national movement: its origins and development (1st ed.). Syracuse, NY: Syracuse Univ. Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0815630937.
With the crushing of opposition elements, the Young Turks simultaneously launched their program of forcible Turkification and the creation of a highly centralized administrative system."
- ^ Akçam, Taner (2012). The Young Turks' crime against humanity: the Armenian genocide and ethnic cleansing in the Ottoman Empire. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. p. 29. ISBN 978-0691153339.
- ^ Bjornlund, Matthias (March 2008). "The 1914 cleansing of Aegean Greeks as a case of violent Turkification". Journal of Genocide Research. 10 (1): 41–57. doi:10.1080/14623520701850286. ISSN 1462-3528. S2CID 72975930.
In 1914, the aim of Turkification was not to exterminate but to expel as many Greeks of the Aegean region as possible as not only a "security measure," but as an extension of the policy of economic and cultural boycott, while at the same time creating living space for the muhadjirs that had been driven out of their homes under equally brutal circumstances.
- ^ Akçam, Taner (2005). From Empire to Republic: Turkish Nationalism and the Armenian Genocide. London: Zed Books. p. 115. ISBN 9781842775271.
...the initial stages of the Turkification of the Empire, which affected by attacks on its very heterogeneous structure, thereby ushering in a relentless process of ethnic cleansing that eventually, through the exigencies and opportunities of the First World War, culminated in the Armenian Genocide.
- ^ Rummel, Rudolph J. (1996). Death By Government. Transaction Publishers. p. 235. ISBN 9781412821292.
Through this genocide and the forced deportation of the Greeks, the nationalists completed the Young Turk's program-the Turkification of Turkey and the elimination of a pretext for Great Power meddling.
- ^ J.M. Winter, ed. (2003). America and the Armenian Genocide of 1915. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 60. ISBN 9780511163821.
The devising of a scheme of a correlative Turkification of the Empire, or what was left of it, included the cardinal goal of the liquidation of that Empire’s residual non-Turkish elements. Given their numbers, their concentration in geo-strategic locations, and the troublesome legacy of the Armenian Question, the Armenians were targeted as the prime object for such a liquidation.
- ^ Rozakēs, Chrēstos L (31 August 1987). The Turkish Straits. ISBN 978-9024734641. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ Levine 2010, p. 29.
- ^ Göcek 2011, p. 22.
- ^ Göcek 2011, p. 23.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Çaǧaptay 2006, p. 82.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bosma, Lucassen & Oostindie 2012, p. 17.
- ^ Çaǧaptay 2006, p. 84.
- ^ Melek Tekin: Türk Tarihi Ansiklopedisi, Milliyet yayınları, İstanbul, 1991, p. 237.
- ^ Rafis Abazov (2009). Culture and Customs of Turkey. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 1071. ISBN 978-0-313-34215-8. Retrieved 25 March 2013.
- ^ Hatay 2007, p. 22.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hatay 2007, p. 23.
- ^ "UNFICYP: United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus". United Nations.
- ^ Dursun-Özkanca, Oya (2019), Turkey–West Relations: The Politics of Intra-alliance Opposition, Cambridge University Press, p. 40, ISBN 978-1108488624,
One-fifth of the Turkish population is estimated to have Balkan origins. Additionally, more than one million Turks live in Balkan countries, constituting a bridge between these countries and Turkey.
- ^ Kötter et al. 2003, p. 55.
- ^ Haviland et al. 2010, p. 675.
- ^ Abadan-Unat 2011, p. 12.
- ^ Bayram, Servet; Seels, Barbara (1997), "The Utilization of Instructional Technology in Turkey", Educational Technology Research and Development, Springer, 45 (1): 112, doi:10.1007/BF02299617, S2CID 62176630,
There are about 10 million Turks living in the Balkan area of southeastern Europe and in western Europe at present.
- ^ 52% of Europeans say no to Turkey's EU membership, Aysor, 2010, retrieved 7 November 2020,
This is not all of a sudden, says expert at the Center for Ethnic and Political Science Studies, Boris Kharkovsky. “These days, up to 15 million Turks live in the EU countries...
- ^ Pashayan, Araks (2012), "Integration of Muslims in Europe and the Gülen", in Weller, Paul; Ihsan, Yilmaz (eds.), European Muslims, Civility and Public Life: Perspectives On and From the Gülen Movement, Continuum International Publishing Group, ISBN 978-1-4411-0207-2,
There are around 10 million Euro-Turks living in the European Union countries of Germany, France, the Netherlands and Belgium.
- ^ Akgündüz 2008, p. 61.
- ^ Kasaba 2008, p. 192.
- ^ Twigg et al. 2005, p. 33.
- ^ Aydıngün et al. 2006, p. 4.
- ^ UNHCR 1999b, p. 20–21.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e UNHCR 1999b, p. 20.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Aydıngün et al. 2006, p. 1.
- ^ U.S. Census Bureau. "TOTAL ANCESTRY REPORTED Universe: Total ancestry categories tallied for people with one or more ancestry categories reported 2013 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates". Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2012.
- ^ Karpat 2004, p. 627.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Cleveland History. "Immigration and Ethnicity: Turks". Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ^ Farkas 2003, p. 40.
- ^ "Immigration and Ethnocultural Diversity Highlight Tables". statcan.gc.ca. 25 October 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Washington Diplomat. "Census Takes Aim to Tally'Hard to Count' Populations". Retrieved 5 May 2011.
- ^ Hüssein 2007, p. 17.
- ^ Cleland 2001, p. 24.
- ^ Hüssein 2007, p. 19.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Hüssein 2007, p. 196.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Hopkins 2011, p. 116.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Saeed 2003, p. 9.
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics. "20680-Ancestry (full classification list) by Sex Australia". Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ TRNC Ministry of Foreign Affairs. "Briefing Notes on the Cyprus Issue". Retrieved 3 October 2010.
- ^ Kibris Gazetesi. "Avustralya'daki Kıbrıslı Türkler ve Temsilcilik..." Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- ^ "AVUSTURALYA'DA KIBRS TÜRKÜNÜN SESİ". BRT. Retrieved 18 July 2011.
- ^ "Sözünüzü Tutun". Star Kıbrıs. Retrieved 10 September 2012.
- ^ "Old foes, new friends". The Sydney Morning Herald. 23 April 2005. Retrieved 26 December 2008.
- ^ "Avustralyalı Türkler'den, TRT Türk'e tepki". Milliyet. Retrieved 16 May 2012.
- ^ Department of Immigration and Citizenship (2006). "Community Information Summary:Bulgaria" (PDF). Australian Government. p. 2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2007). "2006 Census Ethnic Media Package". Retrieved 13 July 2011.
- ^ Department of Immigration and Citizenship (2006). "Community Information Summary:Iraq" (PDF). Australian Government. p. 1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Johanson, Lars (2021), Turkic, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 9781009038218,
Turkish is the largest and most vigorous Turkic language, spoken by over 80 million people, a third of the total number of Turkic-speakers... Turkish is a recognized regional minority language in North Macedonia, Kosovo, Romania, and Iraq.
- ^ Kushner, David (1977), The Rise of Turkish Nationalism, 1876–1908, Cass, ISBN 9780714630755
- ^ Lewis, Geoffrey (1999), The Turkish Language Reform: A Catastrophic Success, Oxford University Press, ISBN 9780191583223
- ^ George L. Campbell (1 September 2003). Concise Compendium of the World's Languages. Taylor & Francis. pp. 547–. ISBN 978-0-415-11392-2. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- ^ Johanson 2001, p. 16. sfn error: multiple targets (2×): CITEREFJohanson2001 (help)
- ^ Presidency of the Republic of Cyprus. "The Constitution of the Republic of Cyprus" (PDF). Retrieved 26 April 2016.
Article 1...the Greek and the Turkish Communities of Cyprus respectively...Article 3 (4) Judicial proceedings shall be conducted or made and judgements shall be drawn up in the Greek language if the parties are Greek, in the Turkish language if the parties are Turkish, and in both the Greek and the Turkish languages if the parties are Greek and Turkish. The official language or languages to be used for such purposes in all other cases shall be specified by the Rules of Court made by the High Court under Article 163.
- ^ Dzankic, Jelena (2016), Citizenship in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Macedonia and Montenegro: Effects of Statehood and Identity Challenges, Routledge, p. 81, ISBN 1317165799,
With the 2001 amendments, in those municipalities where minorities constituted 20 per cent of the overall population, minority languages became official
- ^ "Bosnia and Herzegovina", The European Charter for Regional Or Minority Languages: Collected Texts, Council of Europe, 2010, pp. 107–108, ISBN 9789287166715
- ^ Rehm, Georg; Uszkoreit, Hans, eds. (2012), "The Croatian Language in the European Information Society", The Croatian Language in the Digital Age, Springer, p. 51, ISBN 9783642308826
- ^ Trudgill, Peter; Schreier, Daniel (2006), "Greece and Cyprus / Griechenland und Zypern", in Ulrich, Ammon (ed.), Sociolinguistics / Soziolinguistik, Walter de Gruyter, p. 1886, ISBN 3110199874
- ^ "Romania", The European Charter for Regional Or Minority Languages: Collected Texts, Council of Europe, 2010, pp. 135–136, ISBN 9789287166715
- ^ Schwartz, Herman (2002), The Struggle for Constitutional Justice in Post-Communist Europe, University of Chicago Press, p. 184, ISBN 0226741966
- ^ Benrabah, Mohamed (2013), Language Conflict in Algeria: From Colonialism to Post-Independence, Multilingual Matters, p. 186, ISBN 978-1847699664,
As a result of this, the Tunisian authorities decreed in June 2012 the introduction of the Turkish language in all Tunisian secondary schools, as of September 2012.
- ^ Brendemoen 2002, p. 27.
- ^ Brendemoen 2006, p. 227.
- ^ Friedman 2003, p. 51.
- ^ Johanson 2011, p. 739.
- ^ Johanson 2011, p. 738.
- ^ Bulut, Christiane (2007), "Iraqi Turkman" (PDF), in Postgate, J.N. (ed.), Languages of Iraq: Ancient and Modern, British School of Archaeology in Iraq, p. 167, ISBN 978-0903472210
- ^ Jump up to: a b Johanson, Lars (2001), Discoveries on the Turkic Linguistic Map (PDF), Stockholm: Svenska Forskningsinstitutet i Istanbul
- ^ (2010), "Optativ versus Voluntativ-Imperativ in irantürkischen Texten", in Boeschoten, Hendrik; Rentzsch, Julian (eds.), Turcology in Mainz, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, p. 244, ISBN 978-3447061131,
Damit weist das Iraktürkische hier - wie auch bei einigen anderen Merkmalen - eine großere Nähe zum Türkeitürkischen auf.
- ^ Johanson, Lars (2009), "Modals in Turkic", in Hansen, Björn; de Haan, Ferdinand (eds.), Modals in the Languages of Europe: A Reference Work, Walter de Gruyter, pp. 502–504, ISBN 978-3110219203
- ^ Bulut, Christiane (2018), "Iraq-Turkic", in Haig, Geoffrey; Khan, Geoffrey (eds.), The Languages and Linguistics of Western Asia: An Areal Perspective, Walter de Gruyter, p. 357, ISBN 978-3110421682
- ^ Dobrushina, Nina; Daniel, Michael; Koryakov, Yuri (2020), "Language and Sociolinguistics of the Caucasus", in Polinsky, Maria (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Languages of the Caucasus, Oxford University Press, p. 33, ISBN 9780190690694
- ^ Jump up to: a b Aydıngün et al. 2006, p. 23.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rabasa, Angel; Benard, Cheryl (2015), Eurojihad, Cambridge University Press, pp. 20–21, ISBN 9781107078932
- ^ Zhelyazkova, Antonina (2015), "Bulgaria", in Cesari, Jocelyne (ed.), The Oxford Handbook of European Islam, Oxford University Press, p. 574, ISBN 9780199607976,
Turks are the largest Muslim community. They are furthermore the most strongly consolidated community in the state with a very clear and unambiguous understanding of its ethnic identity. The only differences stem from affiliation to various Islamic movements. Some of in-group competition exist between Sunni Turks and Alevi/Kızılbashi/Bektashi. The Kızılbashi, a minority within a minority, have freely practiced their specific rituals with no visible confrontation with the Sunni Turks.
- ^ Jacobsen, Brian Arly (2012), "Muslims in Denmark: A Critical Evaluation of Estimations", in Nielsen, Jørgen S. (ed.), Islam in Denmark: The Challenge of Diversity, Lexington Books, p. 47, ISBN 9780739150924
- ^ Jump up to: a b Arab, Pooyan Tamimi (2021), "Strict Neutrality Reconsidered: Religion and Political Belonging in the Netherlands", in Medovoi, Leerom; Bentley, Elizabeth (eds.), Religion, Secularism, and Political Belonging, Duke University Press, p. 56, ISBN 9781478012986,
The construction of mosques by citizens with a Turkish migration background, the larges Muslim constituents in the Netherlands and in Germany, is well suited to clarify the idea of disentangling political and cultural or religious belonging
- ^ Schmidinger, Thomas (2010), "Liechtenstein", in Nielsen, Jørgen; Akgönül, Samim; Alibašić, Ahmet; Maréchal, Brigitte; Moe, Christian (eds.), Yearbook of Muslims in Europe, 2, Brill Publishers, pp. 311–17, ISBN 9789004184763
- ^ Cupcea, Adriana, "The Turkish Diyanet and it s Activities in the Muslim Community in Dobruja (Romania)", in Aslan, Ednan; Rausch, Margaret (eds.), Religious Education: Between Radicalism and Tolerance, Springer, p. 292, ISBN 9783658216771
- ^ Poulton, Hugh (1997), Muslim Identity and the Balkan State, C. Hurst & Co., ISBN 9781850652762
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rabasa, Angel; Larrabee, F. Stephen (2008), The Rise of Political Islam in Turkey, RAND Corporation, p. 96, ISBN 9780833044570
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Cagaptay, Soner (2014), The Rise of Turkey: The Twenty-First Century's First Muslim Power, , p. 85, ISBN 9781612346519
- ^ Henry Dodd, Clement (1993), The Political, Social and Economic Development of Northern Cyprus, Eothen Press, p. 266, ISBN 9780906719183
- ^ Muslim Places of Worship in Cyprus, Association of Cypriot Archaeologists, 1991, p. 7, ISBN 9789963380565
- ^ Oğuzlu, Tarik H. (2004), "Endangered community:The Turkoman identity in Iraq" (PDF), Journal of Muslim Minority Affairs, Routledge, 24 (2): 313, doi:10.1080/1360200042000296681, hdl:11693/49129, S2CID 56385519
- ^ Gordon, Louis A.; Oxnevad, Ian (2016), Middle East Politics for the New Millennium: A Constructivist Approach, Lexington Books, p. 72, ISBN 978-0739196984,
An Ottoman military class that separated itself from the general Algerian population through language, dress and religious affiliation... Unlike the Maliki Algerian masses, the Ottoman-Algerians remained affiliated with the Hanafi school of Islamic jurisprudence, and went to great lengths to replenish their ranks with Ottoman Turks from Anatolia...
- ^ Cantone, Cleo (2002), Making and Remaking Mosques in Senegal, BRILL, p. 174, ISBN 9004203370,
Octagonal minarets are generally an anomaly in the Maliki world associated with the square tower. Algeria, on other hand had Ottoman influence...
- ^ Migeon, Gaston; Saladin, Henri (2012), Art of Islam, Parkstone International, p. 28, ISBN 978-1780429939,
It was not until the 16th century, when the protectorate of the Grand Master appointed Turkish governors to the regencies of Algiers and Tunis, that some of them constructed mosques according to the Hanefit example. The resulting structures had octagonal minarets...
- ^ Rizvi, Kishwar (2015), The Transnational Mosque: Architecture and Historical Memory in the Contemporary Middle East, University of North Carolina Press, p. 33-68, ISBN 9781469621173
- ^ Byrnes, Timothy; Katzenstein, Peter (2006), Religion in an Expanding Europe, Cambridge University Press, p. 211, ISBN 978-0-521-85926-4
- ^ Necipoğlu, Gülru (1995). Muqarnas: An Annual on Islamic Art and Architecture. Volume 12. Leiden : E.J. Brill. p. 60. ISBN 9789004103146. OCLC 33228759. Retrieved 7 July 2008.
- ^ Grabar, Oleg (1985). Muqarnas: An Annual on Islamic Art and Architecture. Volume 3. Leiden : E.J. Brill. ISBN 978-9004076112. Retrieved 7 July 2008.
- ^ Ibrahim Kaya (2004). Social Theory and Later Modernities: The Turkish Experience. Liverpool University Press. pp. 57–58. ISBN 978-0-85323-898-0. Retrieved 12 June 2013.
- ^ "Pamuk wins Nobel Literature prize". BBC. 12 October 2006. Retrieved 12 December 2006.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Martin Dunford; Terry Richardson (3 June 2013). The Rough Guide to Turkey. Rough Guides. pp. 647–. ISBN 978-1-4093-4005-8. Retrieved 25 July 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Taskent RO, Gokcumen O (2017). "The Multiple Histories of Western Asia: Perspectives from Ancient and Modern Genomes". Hum Biol. 89 (2): 107–117. doi:10.13110/humanbiology.89.2.01. PMID 29299965. S2CID 6871226.
- ^ "(PDF) The analysis of the genetic structure of the Kazakh population as estimated from mitochondrial DNA polymorphism". ResearchGate. Retrieved 2 August 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Alkan, Can; Kavak, Pinar; Somel, Mehmet; Gokcumen, Omer; Ugurlu, Serkan; Saygi, Ceren; Dal, Elif; Bugra, Kuyas; Güngör, Tunga; Sahinalp, S.; Özören, Nesrin; Bekpen, Cemalettin (2014). "Whole genome sequencing of Turkish genomes reveals functional private alleles and impact of genetic interactions with Europe, Asia and Africa". BMC Genomics. 15: 963. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-963. PMC 4236450. PMID 25376095.
- ^ Tyler-Smith, Chris; Zalloua, Pierre; Gasparini, Paolo; Comas, David; Xue, Yali; Mezzavilla, Massimo; Haber, Marc (2016). "Genetic evidence for an origin of the Armenians from Bronze Age mixing of multiple populations". European Journal of Human Genetics. 24 (6): 931–936. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2015.206. ISSN 1476-5438. PMC 4820045. PMID 26486470.
- ^ Pakstis, Andrew J.; Gurkan, Cemal; Dogan, Mustafa; Balkaya, Hasan Emin; Dogan, Serkan; Neophytou, Pavlos I.; Cherni, Lotfi; Boussetta, Sami; Khodjet-El-Khil, Houssein; Ben Ammar ElGaaied, Amel; Salvo, Nina Mjølsnes; Janssen, Kirstin; Olsen, Gunn-Hege; Hadi, Sibte; Almohammed, Eida Khalaf; Pereira, Vania; Truelsen, Ditte Mikkelsen; Bulbul, Ozlem; Soundararajan, Usha; Rajeevan, Haseena; Kidd, Judith R.; Kidd, Kenneth K. (December 2019). "Genetic relationships of European, Mediterranean, and SW Asian populations using a panel of 55 AISNPs". European Journal of Human Genetics. 27 (12): 1885–1893. doi:10.1038/s41431-019-0466-6. ISSN 1476-5438. PMC 6871633. PMID 31285530.
- ^ Hodoğlugil, U. U.; Mahley, R. W. (2012). "Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations". Annals of Human Genetics. 76 (2): 128–141. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2011.00701.x. PMC 4904778. PMID 22332727.
- ^ Bánfai Z, Melegh BI, Sümegi K, Hadzsiev K, Miseta A, Kásler M, Melegh B (2019). "Revealing the Genetic Impact of the Ottoman Occupation on Ethnic Groups of East-Central Europe and on the Roma Population of the Area". Front Genet. 10: 558. doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.00558. PMC 6585392. PMID 31263480.
- ^ Ottoni, C.; Ricaut, F. O. X.; Vanderheyden, N.; Brucato, N.; Waelkens, M.; Decorte, R. (2011). "Mitochondrial analysis of a Byzantine population reveals the differential impact of multiple historical events in South Anatolia". European Journal of Human Genetics. 19 (5): 571–576. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.230. PMC 3083616. PMID 21224890.
- ^ Ottoni, Claudio; Rasteiro, Rita; Willet, Rinse; Claeys, Johan; Talloen, Peter; Van De Vijver, Katrien; Chikhi, Lounès; Poblome, Jeroen; Decorte, Ronny (2016). "Comparing maternal genetic variation across two millennia reveals the demographic history of an ancient human population in southwest Turkey". Royal Society Open Science. 3 (2). 150250. Bibcode:2016RSOS....350250O. doi:10.1098/rsos.150250. PMC 4785964. PMID 26998313.
- ^ Berkman, Ceren Caner (September 2006). Comparative Analyses For The Central Asian Contribution To Anatolian Gene Pool With Reference To Balkans (PDF) (PhD). Retrieved 30 October 2020.
- ^ Home Affairs Committee 2011, Ev 34.
- ^ Laschet, Armin (17 September 2011). "İngiltere'deki Türkler". Hürriyet Daily News. Archived from the original on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 27 September 2011.
- ^ Akben, Gözde (11 February 2010). "Olmalı mı Olmamalı mı?". Star Kıbrıs. Archived from the original on 24 July 2011. Retrieved 21 January 2011.
- ^ Cemal, Akay (2 June 2011). "Dıştaki gençlerin askerlik sorunu çözülmedikçe…". Kıbrıs Gazetesi. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ^ The Sophia Echo. "Turkish Bulgarians fastest-growing group of immigrants in The Netherlands". Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ Hatay 2007, p. 40.
- ^ Clogg 2002, p. 84.
- ^ Агентство РК по статистике. ПЕРЕПИСЬ НАСЕЛЕНИЯ РЕСПУБЛИКИ КАЗАХСТАН 2009 ГОДА (PDF). p. 10. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 December 2010. Retrieved 13 February 2011.
- ^ State statistics committee of Ukraine – National composition of population, 2001 census (Ukrainian)
- ^ Демоскоп Weekly. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР. Archived from the original on 6 January 2012. Retrieved 5 June 2011.
- ^ Khazanov 1995, p. 202.
- ^ Babak, Vaisman & Wasserman 2004, p. 253.
- ^ Helton, Arthur C. (1998). "Chapter Two: Contemporary Conditions and Dilemmas". Meskhetian Turks: Solutions and Human Security. Open Society Institute. Archived from the original on 15 April 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ^ Laczko, Stacher & von Koppenfels 2002, p. 187.
- ^ Steven A. Glazer (22 March 2011). "Turkey: Country Studies". Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ L. Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza; Paolo, Menozzi; Alberto, Piazza (1994). The history and geography of human genes. Princeton University Press. pp. 243, 299. ISBN 978-0-691-08750-4. Retrieved 14 May 2013.
Bibliography[]
- Abadan-Unat, Nermin (2011), Turks in Europe: From Guest Worker to Transnational Citizen, Berghahn Books, ISBN 978-1-84545-425-8.
- Abazov, Rafis (2009), Culture and Customs of Turkey, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0313342158.
- Abrahams, Fred (1996), A Threat to "Stability": Human Rights Violations in Macedonia, Human Rights Watch, ISBN 978-1-56432-170-1.
- Ágoston, Gábor (2010), "Introduction", in Ágoston, Gábor; Masters, Bruce Alan (eds.), Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 978-1438110257.
- Akar, Metin (1993), "Fas Arapçasında Osmanlı Türkçesinden Alınmış Kelimeler", Türklük Araştırmaları Dergisi, 7: 91–110
- Akgündüz, Ahmet (2008), Labour migration from Turkey to Western Europe, 1960–1974: A multidisciplinary analysis, Ashgate Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7546-7390-3.
- Aydıngün, Ayşegül; Harding, Çiğdem Balım; Hoover, Matthew; Kuznetsov, Igor; Swerdlow, Steve (2006), Meskhetian Turks: An Introduction to their History, Culture, and Resettelment Experiences, Center for Applied Linguistics, archived from the original on 29 October 2013
- Babak, Vladimir; Vaisman, Demian; Wasserman, Aryeh (2004), Political Organization in Central Asia and Azerbaijan: Sources and Documents, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-7146-4838-5.
- Baedeker, Karl (2000), Egypt, Elibron, ISBN 978-1402197055.
- Bainbridge, James (2009), Turkey, Lonely Planet, ISBN 978-1741049275.
- Baran, Zeyno (2010), Torn Country: Turkey Between Secularism and Islamism, Hoover Press, ISBN 978-0817911447.
- Bennigsen, Alexandre; Broxup, Marie (1983), The Islamic threat to the Soviet State, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0-7099-0619-3.
- Bokova, Irena (2010), "Recontructions of Identities: Regional vs. National or Dynamics of Cultrual Relations", in Ruegg, François; Boscoboinik, Andrea (eds.), From Palermo to Penang: A Journey Into Political Anthropology, LIT Verlag Münster, ISBN 978-3643800626
- Bogle, Emory C. (1998), Islam: Origin and Belief, University of Texas Press, ISBN 978-0292708624.
- Bosma, Ulbe; Lucassen, Jan; Oostindie, Gert (2012), "Introduction. Postcolonial Migrations and Identity Politics: Towards a Comparative Perspective", Postcolonial Migrants and Identity Politics: Europe, Russia, Japan and the United States in Comparison, Berghahn Books, ISBN 978-0857453273.
- Brendemoen, Bernt (2002), The Turkish Dialects of Trabzon: Analysis, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3447045704.
- Brendemoen, Bernt (2006), "Ottoman or Iranian? An example of Turkic-Iranian language contact in East Anatolian dialects", in Johanson, Lars; Bulut, Christiane (eds.), Turkic-Iranian Contact Areas: Historical and Linguistic Aspects, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3447052764.
- Brizic, Katharina; Yağmur, Kutlay (2008), "Mapping linguistic diversity in an emigration and immigration context: Case studies on Turkey and Austria", in Barni, Monica; Extra, Guus (eds.), Mapping Linguistic Diversity in Multicultural Contexts, Walter de Gruyter, p. 248, ISBN 978-3110207347.
- Brozba, Gabriela (2010), Between Reality and Myth: A Corpus-based Analysis of the Stereotypic Image of Some Romanian Ethnic Minorities, GRIN Verlag, ISBN 978-3-640-70386-9.
- Bruce, Anthony (2003), The Last Crusade. The Palestine Campaign in the First World War, John Murray, ISBN 978-0719565052.
- Çaǧaptay, Soner (2006), "Passage to Turkishness: immigration and religion in modern Turkey", in Gülalp, Haldun (ed.), Citizenship And Ethnic Conflict: Challenging the Nation-state, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0415368971.
- Çaǧaptay, Soner (2006a), Islam, Secularism, and Nationalism in Modern Turkey: Who is a Turk?, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0415384582.
- Campbell, George L. (1998), Concise Compendium of the World's Languages, Psychology Press, ISBN 978-0415160490.
- Cassia, Paul Sant (2007), Bodies of Evidence: Burial, Memory, and the Recovery of Missing Persons in Cyprus, Berghahn Books, ISBN 978-1845452285.
- Chaurasia, Radhey Shyam (2005), History Of Middle East, Atlantic Publishers & Dist, ISBN 978-8126904488.
- Cleland, Bilal (2001), "The History of Muslims in Australia", in Saeed, Abdullah; Akbarzadeh, Shahram (eds.), Muslim Communities in Australia, University of New South Wales, ISBN 978-0-86840-580-3.
- Clogg, Richard (2002), Minorities in Greece, Hurst & Co. Publishers, ISBN 978-1-85065-706-4.
- Constantin, Daniela L.; Goschin, Zizi; Dragusin, Mariana (2008), "Ethnic entrepreneurship as an integration factor in civil society and a gate to religious tolerance. A spotlight on Turkish entrepreneurs in Romania", Journal for the Study of Religions and Ideologies, 7 (20): 28–41
- Cornell, Svante E. (2001), Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict in the Caucasus, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-7007-1162-8.
- Darke, Diana (2011), Eastern Turkey, Bradt Travel Guides, ISBN 978-1841623399.
- Delibaşı, Melek (1994), "The Era of Yunus Emre and Turkish Humanism", Yunus Emre: Spiritual Experience and Culture, Università Gregoriana, ISBN 978-8876526749.
- Duiker, William J.; Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2012), World History, Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-1111831653.
- Elsie, Robert (2010), Historical Dictionary of Kosovo, Scarecrow Press, ISBN 978-0-8108-7231-8.
- Eminov, Ali (1997), Turkish and other Muslim minorities in Bulgaria, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, ISBN 978-1-85065-319-6.
- Ergener, Rashid; Ergener, Resit (2002), About Turkey: Geography, Economy, Politics, Religion, and Culture, Pilgrims Process, ISBN 978-0971060968.
- Evans, Thammy (2010), Macedonia, Bradt Travel Guides, ISBN 978-1-84162-297-2.
- Farkas, Evelyn N. (2003), Fractured States and U.S. Foreign Policy: Iraq, Ethiopia, and Bosnia in the 1990s, Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 978-1403963734.
- Faroqhi, Suraiya (2005), Subjects Of The Sultan: Culture And Daily Life In The Ottoman Empire, I.B.Tauris, ISBN 978-1850437604.
- Findley, Carter V. (2005), The Turks in World History, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0195177268.
- Fleet, Kate (1999), European and Islamic Trade in the Early Ottoman State: The Merchants of Genoa and Turkey, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521642217.
- Friedman, Victor A. (2003), Turkish in Macedonia and Beyond: Studies in Contact, Typology and other Phenomena in the Balkans and the Caucasus, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3447046404.
- Friedman, Victor A. (2006), "Western Rumelian Turkish in Macedonia and adjacent areas", in Boeschoten, Hendrik; Johanson, Lars (eds.), Turkic Languages in Contact, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3447052122.
- Gogolin, Ingrid (2002), Guide for the Development of Language Education Policies in Europe: From Linguistic Diversity to Plurilingual Education (PDF), Council of Europe.
- Göcek, Fatma Müge (2011), The Transformation of Turkey: Redefining State and Society from the Ottoman Empire to the Modern Era, I.B.Tauris, ISBN 978-1848856110.
- Hatay, Mete (2007), Is the Turkish Cypriot Population Shrinking? (PDF), International Peace Research Institute, ISBN 978-82-7288-244-9.
- Haviland, William A.; Prins, Harald E. L.; Walrath, Dana; McBride, Bunny (2010), Anthropology: The Human Challenge, Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-0-495-81084-1.
- Hizmetli, Sabri (1953), "Osmanlı Yönetimi Döneminde Tunus ve Cezayir'in Eğitim ve Kültür Tarihine Genel Bir Bakış" (PDF), Ankara Üniversitesi İlahiyat Fakültesi Dergisi, 32: 1–12
- Hodoğlugil, Uğur; Mahley, Robert W. (2012), "Turkish Population Structure and Genetic Ancestry Reveal Relatedness among Eurasian Populations", Annals of Human Genetics, 76 (2): 128–141, doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2011.00701.x, PMC 4904778, PMID 22332727
- Home Affairs Committee (2011), Implications for the Justice and Home Affairs area of the accession of Turkey to the European Union (PDF), The Stationery Office, ISBN 978-0-215-56114-5
- Hopkins, Liza (2011), "A Contested Identity: Resisting the Category Muslim-Australian", Immigrants & Minorities, 29 (1): 110–131, doi:10.1080/02619288.2011.553139, S2CID 145324792.
- Hüssein, Serkan (2007), Yesterday & Today: Turkish Cypriots of Australia, Serkan Hussein, ISBN 978-0-646-47783-1.
- İhsanoğlu, Ekmeleddin (2005), "Institutionalisation of Science in the Medreses of Pre-Ottoman and Ottoman Turkey", in Irzik, Gürol; Güzeldere, Güven (eds.), Turkish Studies in the History And Philosophy of Science, Springer, ISBN 978-1402033322.
- Ilican, Murat Erdal (2011), "Cypriots, Turkish", in Cole, Jeffrey (ed.), Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 978-1598843026.
- Jawhar, Raber Tal’at (2010), "The Iraqi Turkmen Front", in Catusse, Myriam; Karam, Karam (eds.), Returning to Political Parties?, Co-éditions, The Lebanese Center for Policy Studies, pp. 313–328, ISBN 978-1-886604-75-9.
- Johanson, Lars (2001), Discoveries on the Turkic Linguistic Map (PDF), Stockholm: Svenska Forskningsinstitutet i Istanbul
- Johanson, Lars (2011), "Multilingual states and empires in the history of Europe: the Ottoman Empire", in Kortmann, Bernd; Van Der Auwera, Johan (eds.), The Languages and Linguistics of Europe: A Comprehensive Guide, Volume 2, Walter de Gruyter, ISBN 978-3110220254
- Kaplan, Robert D. (2002), "Who Are the Turks?", in Villers, James (ed.), Travelers' Tales Turkey: True Stories, Travelers' Tales, ISBN 978-1885211828.
- Karpat, Kemal H. (2000), "Historical Continuity and Identity Change or How to be Modern Muslim, Ottoman, and Turk", in Karpat, Kemal H. (ed.), Studies on Turkish Politics and Society: Selected Articles and Essays, BRILL, ISBN 978-9004115620.
- Karpat, Kemal H. (2004), Studies on Turkish Politics and Society: Selected Articles and Essays, BRILL, ISBN 978-9004133228.
- Kasaba, Reşat (2008), The Cambridge History of Turkey: Turkey in the Modern World, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-62096-3.
- Kasaba, Reşat (2009), A Moveable Empire: Ottoman Nomads, Migrants, and Refugees, University of Washington Press, ISBN 978-0295989488.
- Kermeli, Eugenia (2010), "Byzantine Empire", in Ágoston, Gábor; Masters, Bruce Alan (eds.), Encyclopedia of the Ottoman Empire, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 978-1438110257.
- Khazanov, Anatoly Michailovich (1995), After the USSR: Ethnicity, Nationalism and Politics in the Commonwealth of Independent States, University of Wisconsin Press, ISBN 978-0-299-14894-2.
- Kia, Mehrdad (2011), Daily Life in the Ottoman Empire, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 978-0313064029.
- Kirişci, Kemal (2006), "Migration and Turkey: the dynamics of state, society and politics", in Kasaba, Reşat (ed.), The Cambridge History of Turkey: Turkey in the Modern World, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521620963.
- Knowlton, MaryLee (2005), Macedonia, Marshall Cavendish, ISBN 978-0-7614-1854-2.
- Köprülü, Mehmet Fuat (1992), The Origins of the Ottoman Empire, SUNY Press, ISBN 978-0791408209.
- Kötter, I; Vonthein, R; Günaydin, I; Müller, C; Kanz, L; Zierhut, M; Stübiger, N (2003), "Behçet's Disease in Patients of German and Turkish Origin- A Comparative Study", in Zouboulis, Christos (ed.), Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Volume 528, Springer, ISBN 978-0-306-47757-7.
- Kurbanov, Rafik Osman-Ogly; Kurbanov, Erjan Rafik-Ogly (1995), "Religion and Politics in the Caucasus", in Bourdeaux, Michael (ed.), The Politics of Religion in Russia and the New States of Eurasia, M.E. Sharpe, ISBN 978-1-56324-357-8.
- Kushner, David (1997). "Self-Perception and Identity in Contemporary Turkey". Journal of Contemporary History. 32 (2): 219–233. doi:10.1177/002200949703200206. S2CID 159374632.
- Laczko, Frank; Stacher, Irene; von Koppenfels, Amanda Klekowski (2002), New challenges for Migration Policy in Central and Eastern Europe, Cambridge University Press, p. 187, ISBN 978-9067041539.
- Leiser, Gary (2005), "Turks", in Meri, Josef W. (ed.), Medieval Islamic Civilization, Routledge, p. 837, ISBN 978-0415966900.
- Leveau, Remy; Hunter, Shireen T. (2002), "Islam in France", in Hunter, Shireen (ed.), Islam, Europe's Second Religion: The New Social, Cultural, and Political Landscape, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0275976095.
- Levine, Lynn A. (2010), Frommer's Turkey, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0470593660.
- Minahan, James (2002), Encyclopedia of the Stateless Nations: L-R, Greenwood Publishing Group, ISBN 978-0-313-32111-5.
- Meeker, M. E. (1971). "The Black Sea Turks: Some Aspects of Their Ethnic and Cultural Background". International Journal of Middle East Studies. 2 (4): 318–345. doi:10.1017/s002074380000129x.
- Oçak, Ahmet Yaçar (2012), "Islam in Asia Minor", in El Hareir, Idris; M'Baye, Ravane (eds.), Different Aspects of Islamic Culture: Vol.3: The Spread of Islam Throughout the World, UNESCO, ISBN 978-9231041532.
- Orhan, Oytun (2010), The Forgotten Turks: Turkmens of Lebanon (PDF), ORSAM, archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016.
- Özkaya, Abdi Noyan (2007), "Suriye Kürtleri: Siyasi Etkisizlik ve Suriye Devleti'nin Politikaları" (PDF), Review of International Law and Politics, 2 (8), archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2011.
- Öztürkmen, Ali; Duman, Bilgay; Orhan, Oytun (2011), Suriye'de değişim ortaya çıkardığı toplum: Suriye Türkmenleri, ORSAM.
- Pan, Chia-Lin (1949), "The Population of Libya", Population Studies, 3 (1): 100–125, doi:10.1080/00324728.1949.10416359
- Park, Bill (2005), Turkey's policy towards northern Iraq: problems and perspectives, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 978-0-415-38297-7
- Phillips, David L. (2006), Losing Iraq: Inside the Postwar Reconstruction Fiasco, Basic Books, ISBN 978-0-465-05681-1
- Phinnemore, David (2006), The EU and Romania: Accession and Beyond, The Federal Trust for Education & Research, ISBN 978-1-903403-78-5.
- Polian, Pavel (2004), Against Their will: The History and Geography of Forced Migrations in the USSR, Central European University Press, ISBN 978-963-9241-68-8.
- Quataert, Donald (2000), The Ottoman Empire, 1700–1922, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521633284.
- Ryazantsev, Sergey V. (2009), "Turkish Communities in the Russian Federation" (PDF), International Journal on Multicultural Societies, 11 (2): 155–173.
- Saeed, Abdullah (2003), Islam in Australia, Allen & Unwin, ISBN 978-1-86508-864-8.
- Saunders, John Joseph (1965), "The Turkish Irruption", A History of Medieval Islam, Routledge, ISBN 978-0415059145.
- Scarce, Jennifer M. (2003), Women's Costume of the Near and Middle East, Routledge, ISBN 978-0700715602.
- Seher, Cesur-Kılıçaslan; Terzioğlu, Günsel (2012), "Families Immigrating from Bulgaria to Turkey Since 1878", in Roth, Klaus; Hayden, Robert (eds.), Migration In, From, and to Southeastern Europe: Historical and Cultural Aspects, Volume 1, LIT Verlag Münster, ISBN 978-3643108951.
- Shaw, Stanford J. (1976), History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey Volume 1, Empire of the Gazis: The Rise and Decline of the Ottoman Empire 1280–1808, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521291637.
- Somel, Selçuk Akşin (2003), Historical Dictionary of the Ottoman Empire, Scarecrow Press, ISBN 978-0810843325.
- Sosyal, Levent (2011), "Turks", in Cole, Jeffrey (ed.), Ethnic Groups of Europe: An Encyclopedia, ABC-CLIO, ISBN 978-1598843026.
- Stansfield, Gareth R. V. (2007), Iraq: People, History, Politics, Polity, ISBN 978-0-7456-3227-8.
- Stavrianos, Leften Stavros (2000), The Balkans Since 1453, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, ISBN 978-1850655510.
- Stokes, Jamie; Gorman, Anthony (2010a), "Turkic Peoples", Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 978-1438126760.
- Stokes, Jamie; Gorman, Anthony (2010b), "Turks: nationality", Encyclopedia of the Peoples of Africa and the Middle East, Infobase Publishing, ISBN 978-1438126760.
- Taylor, Scott (2004), Among the Others: Encounters with the Forgotten Turkmen of Iraq, Esprit de Corps Books, ISBN 978-1-895896-26-8.
- Tomlinson, Kathryn (2005), "Living Yesterday in Today and Tomorrow: Meskhetian Turks in Southern Russia", in Crossley, James G.; Karner, Christian (eds.), Writing History, Constructing Religion, Ashgate Publishing, ISBN 978-0-7546-5183-3.
- Twigg, Stephen; Schaefer, Sarah; Austin, Greg; Parker, Kate (2005), Turks in Europe: Why are we afraid? (PDF), The Foreign Policy Centre, ISBN 978-1903558799, archived from the original (PDF) on 9 July 2011
- UNHCR (1999a), Background Paper on Refugees and Asylum Seekers from Azerbaijan (PDF), United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees.
- UNHCR (1999b), Background Paper on Refugees and Asylum Seekers from Georgia (PDF), United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees.
- Whitman, Lois (1990), Destroying ethnic identity: the Turks of Greece, Human Rights Watch, ISBN 978-0-929692-70-8.
- Wolf-Gazo, Ernest (1996), "John Dewey in Turkey: An Educational Mission", Journal of American Studies of Turkey, 3: 15–42, archived from the original on 27 April 2014, retrieved 6 March 2006
- Yardumian, Aram; Schurr, Theodore G. (2011). "Who Are the Anatolian Turks? A Reappraisal of the Anthropological Genetic Evidence". Anthropology & Archeology of Eurasia. 50 (1): 6–42. doi:10.2753/AAE1061-1959500101. S2CID 142580885.[permanent dead link]
- Yiangou, Anastasia (2010), Cyprus in World War II: Politics and Conflict in the Eastern Mediterranean, I.B.Tauris, ISBN 978-1848854369.
- Zeytinoğlu, Güneş N.; Bonnabeau, Richard F.; Eşkinat, Rana (2012), "Ethnopolitical Conflict in Turkey: Turkish Armenians: From Nationalism to Diaspora", in Landis, Dan; Albert, Rosita D. (eds.), Handbook of Ethnic Conflict: International Perspectives, Springer, ISBN 978-1461404477.
Further reading[]
- Cezayir Ülke Raporu 2008, Algeria Embassy Trade Consultancy, archived from the original on 29 September 2013.
- "Community Profile: Kosovo Turks", Kosovo Communities Profile 2010, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, 8 February 2011.
- "COMUNICAT DE PRESĂ – privind rezultatele provizorii ale Recensământului Populaţiei şi Locuinţelor – 2011" [PRESS RELEASE – on the provisional results of the Population and Housing Census – 2011] (PDF) (Press release) (in Romanian). Romania: Central Commission for the Census of Population and Housing. 2 February 2012.
- Cyprus: Bridging the Property Divide (Report). Europe Report N°210. International Crisis Group. 9 December 2010. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011.
- Turkey and the Iraqi Kurds: Conflict or Cooperation? (Report). Middle East Report N°81. International Crisis Group. 13 November 2008. Archived from the original on 12 January 2011.
- Population by ethnic groups, regions, counties and areas (PDF), Romania: National Institute of Statistics, 2002
- The Report: Algeria 2008, Oxford Business Group, 2008, ISBN 978-1-902339-09-2.
External links[]
 Media related to People of Turkey at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to People of Turkey at Wikimedia Commons
- Turkish people
- Ethnic groups in Turkey
- Ethnic groups in Cyprus
- Ethnic groups in the Middle East
- Ethnic groups in the Balkans


