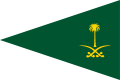
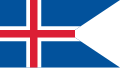
War flag

A war flag, also known as a military flag, battle flag, or standard,[1] is a variant of a national flag for use by a country's military forces when on land. The nautical equivalent is a naval ensign. Under the strictest sense of the term, few countries today currently have proper war flags, most preferring to use instead their state flag or standard national flag for this purpose. The War flags were adopted in different ages, they were not adopted at the same time.
History[]
Sound trumpets! Let our bloody colours wave! And either victory, or else a grave.
— Edward, Prince of Wales, in Henry VI, Part 3, Act II, Scene II
Field signs were used in early warfare at least since the Bronze Age. The word standard itself is from an Old Frankish term for a field sign (not necessarily a flag).

The use of flags as field signs apparently emerges in Asia, during the Iron Age, possibly in either China or India.[2] in Achaemenid Persia, each army division had its own standard, and "all officers had banners over their tents".[3] Early field signs that include, but are not limited to a flag, are also called vexilloid or "flag-like", for example the Roman Eagle standard or the dragon standard of the Sarmatians. The Roman Vexillum itself is also "flag-like" in the sense that it was suspended from a horizontal crossbar as opposed to a simple flagpole.
Use of simple flags as military ensigns becomes common during the medieval period, developing in parallel with heraldry as a complement to the heraldic device shown on shields. The maritime flag also develops in the medieval period. The medieval Japanese Sashimono carried by foot-soldiers are a parallel development.
Some medieval free cities or communes did not have coats of arms, and used war flags that were not derived from a coat of arms. Thus, the city of Lucerne used a blue-white flag as a field sign from the mid 13th century, without deriving it from a heraldic shield design.
Current war flags[]
Used by armed forces only[]
 Canadian Armed Forces ensign
Canadian Armed Forces ensign Flag of the Iranian Army
Flag of the Iranian Army
 Flag of the Armed Forces of Moldova
Flag of the Armed Forces of Moldova
Officially not the war flag of Moldova War flag (regimental color) of Portugal
War flag (regimental color) of Portugal Banner of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
Banner of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation Flag of the Armed Forces of Ukraine
Flag of the Armed Forces of Ukraine
Army (land) use only[]
 Georgia Land Forces
Georgia Land Forces War flag (regimental color) of the Hellenic Army
War flag (regimental color) of the Hellenic Army British Army non-ceremonial flag
British Army non-ceremonial flag
[]
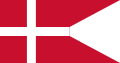 State, war flag, and state ensign of Denmark
State, war flag, and state ensign of Denmark
 Flag of the Philippines at war
Flag of the Philippines at war
Former war flags[]
 Flag of Bangladesh during Bangladesh Liberation War
Flag of Bangladesh during Bangladesh Liberation War Battle flag of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army
Battle flag of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army The original Eureka Flag specimen, rebel warflag at the 1854 Battle of Eureka Stockade
The original Eureka Flag specimen, rebel warflag at the 1854 Battle of Eureka Stockade Battle flag of the Confederate States (1861–65)
Battle flag of the Confederate States (1861–65) Cross of Burgundy Flag, Spain (1506–1843)
Cross of Burgundy Flag, Spain (1506–1843) War flag of the Japanese imperial army (1868-1945)
War flag of the Japanese imperial army (1868-1945) War flag of the People's Republic of Congo (1970–91)
War flag of the People's Republic of Congo (1970–91) The "Gadsden flag", used by some Continental forces during the American Revolutionary War (1775–83)
The "Gadsden flag", used by some Continental forces during the American Revolutionary War (1775–83) Battle flag of the United Irishmen, used at the Battle of Arklow
Battle flag of the United Irishmen, used at the Battle of Arklow War flag of East Germany (1960–90)
War flag of East Germany (1960–90) War flag of the German Wehrmacht (1938–1945)
War flag of the German Wehrmacht (1938–1945) War flag of the Chetniks (1903–1946)
War flag of the Chetniks (1903–1946) War flag of the Italian Social Republic (1943–45)
War flag of the Italian Social Republic (1943–45) War flag of Prussia (1816)
War flag of Prussia (1816) War flag of the German Empire (1903–1919)
War flag of the German Empire (1903–1919) War flag of the Roman Republic of 1849
War flag of the Roman Republic of 1849 Flag of the Red Army (Unofficial)
Flag of the Red Army (Unofficial) Royal Siamese Army in Haw wars (1885–1890)
Royal Siamese Army in Haw wars (1885–1890) War flag of Mughals (1526-1857)[4]
War flag of Mughals (1526-1857)[4] United States Cavalry guidon.
United States Cavalry guidon. War flag of the Royal Italian Army
War flag of the Royal Italian Army War ensign of the Slovak Republic (puppet state of Nazi Germany 1939–45)
War ensign of the Slovak Republic (puppet state of Nazi Germany 1939–45)
 War flag of the Royal Hungarian Army (1939–45)
War flag of the Royal Hungarian Army (1939–45)
See also[]
- Colours, standards and guidons
References[]
- ^ "standard". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ flag. (2008). Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ E. Pottier, Douris, London, 1909, p. 105 fig. 20, Plate XXV.b
- ^ "India before British Rule". www.crwflags.com.
Further reading[]
- Wise, Terence (1978) Military flags of the world, in color. New York: Arco Publishing. 184p. ISBN 0668044721. War flags of 1618–1900.
External links[]
- Military flags
- Types of flags