Naval ensign
This article does not cite any sources. (June 2019) |
A naval ensign is an ensign (maritime flag) used by naval ships of various countries to denote their nationality. It can be the same or different from a country's civil ensign or state ensign.
It can also be known as a war ensign. A large version of a naval ensign that is flown on a warship's mast just before going into battle is called a battle ensign. An ensign differs from a jack, which is flown from a jackstaff at the bow of a vessel.
Most countries have only one national flag and ensign for all purposes. In other countries, a distinction is made between the land flag and the civil, state and naval ensigns. The British ensigns, for example, differ from the flag used on land (the Union Flag) and have different versions of plain and defaced Red and Blue ensigns for civilian and state use, as well as the naval ensign (White Ensign). Some naval ensigns differ in shape from the national flag, such as the Nordic naval ensigns, which have 'tongues'.
[]
Naval ensigns that are different from the civil ensign and the national flag:

Abkhazia

Albania

Algeria

Australia (details)

Azerbaijan

The Bahamas

Bangladesh
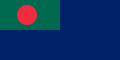
Bangladesh (Coast Guard)

Barbados
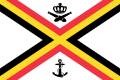
Belgium

Bolivia

Brunei

Bulgaria

Canada (details)

China

Colombia

Croatia

Croatia (Croatian Coast Guard)

Denmark

Dominican Republic

Egypt

Estonia

Finland

France

Georgia

Ghana

Germany

Grenada

Guyana

Honduras

Hungary
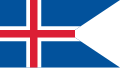
Iceland

India (details)

India (auxiliary ships)

India (Coast Guard)

Israel

Italy

Jamaica

Japan

Jordan

Kazakhstan

Kenya

Latvia

Libya

Lithuania

Malaysia

Mauritius

Montenegro

Morocco

Myanmar

Namibia
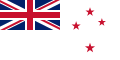
New Zealand (details)

Nigeria

DPR Korea

Norway

Oman

Pakistan

Papua New Guinea

Poland

Russia

Russia (naval auxiliary ships)

Russia (Coast Guard)

Saint Kitts and Nevis

Saudi Arabia


Serbia

Sierra Leone

Singapore

Solomon Islands

South Africa

Sri Lanka

Sri Lanka (Coast Guard)

Sudan

Sweden

Thailand
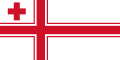
Tonga

Trinidad and Tobago

Turkmenistan

Ukraine

Ukraine (Sea Guard)

United Kingdom (details)

United Kingdom (Auxiliary ships)

United Kingdom (Coast Guard)

United States (Coast Guard)

Uzbekistan

Vanuatu

Vietnam

Yemen
[]

Albania (1946–1954)

Albania (1954–1958)

Albania (1958–1992)

Albania (Coast Guard) (1958–1992)

Argentina (1818-1820)

Austria-Hungary (1869-1914)

Austria-Hungary (1915-1918) - never formally flown by the navy
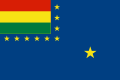
Bolivia (1966–2013)

British East Africa (1953-1962)

Brunei (1984-1990)

Bulgaria (1878–1944)

Bulgaria (1949–1955)

Bulgaria (1955–1990)

Bulgaria (1991–2005)

Burma (1948–1974)
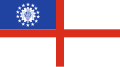
Burma (1974-2010)

Qing Dynasty (1862-1890)

Republic of China (1911)

Collaborationist China (1942-1945)

Ceylon (1950–1972)

Confederate States (1863–1865)

Croatia (1941–1944)

Croatia (1944-1945)

Czechoslovakia (1935-1939) (1945-1955)

Czechoslovakia (1955-1960)

Ethiopia (1955-1974)

Ethiopia (1974-1975)

Ethiopia (1975-1996)

France (?-1789, 1814–1815, 1830)

France (1790-1794)

French Algeria (1848–1910)

French Cochinchina (1868-1945)

Georgia (1997–2004)

Georgia (2004-2008)

Prussia (1816-1819)

Prussia (1819-1850)

North German Confederation and later Germany (1867–1892)

Germany (1892–1903)

Germany (1903–1918)

Germany (1919–1921)

Germany (1921-1933)

Germany (1933–1935)

Germany (1935–1938)

Germany (1938–1945)

East Germany (1960–1990)

Ghana (1964–1966)

Greece (1833-1858)

Greece (1858-1862)

Greece (1863-1924 and 1935–1970)

Greece (1935)

Hungary (1919)

Hungary (1939-1945)

Hungary (1946-1948)

Hungary (1948-1950)

Hungary (1950-1955)

Hungary (1955-1957)

Hungary (1957-1991)

India (1950–2001)

India (2001–2004)

India (2004–2014)

Afsharid Empire (1736–1796)

Iran (1907-1933)

Iran (1933-1964)

Iran (1964–1979)

Iran (1979-1980)

Italy (1861-1946)

Italy (1947-2013)

Japan (1889-1945)
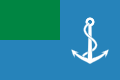
Libya (1977–2011)

Lithuania (1927–1940)

Malaya (1895–1946)

Malaya (1957–1963)
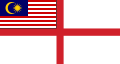
Malaya (1963–1968)

Manchukuo (1932-1945)

Netherlands (1795-1806)
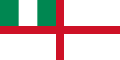
Nigeria (1960–1998)

Norway (1844-1905)

Poland (1815–1867)

Poland (1919-1928)

Poland (1980-1993)

Portugal (1830-1911)

Romania (1922-1947)

Romania (1948–1952)

Romania (1952–1965)
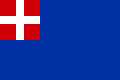
Sardinia (1785-1802)

Sardinia (1802-1814)
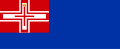
Sardinia (1816-1848)

South Africa (1946–1951)

South Africa (1951–1952)
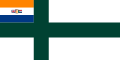
South Africa (1952–1959)
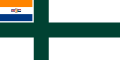
South Africa (1959–1981)

South Africa (1981–1994)

South Vietnam (1954–1975)

Russian Soviet Socialist Republic (1920-1923)

Soviet Union (1924–1935)

Soviet Union (1935-1950)

Soviet Union (1950-1991)

Russia (1992-2000)

Soviet Union (naval auxiliary ships) (1924-1935)

Soviet Union (naval auxiliary ships) (1935-1950)

Soviet Union (naval auxiliary ships) (1950-1992)

Russia (naval auxiliary ships) (1992-2000)

Soviet Union (Coast Guard) (1924-1935)

Soviet Union (coast Guard) (1935-1950)

Soviet Union (Coast Guard) (1950-1993)

Serbia (1882–1918)

Sudan (1956–1970)

Sweden (1815-1844)

Sweden (1844-1905)

Siam (1910-1917)

Ukrainian People's Republic (1917–1921)

Ukrainian State (1918)

Ukrainian State (1918-1920)

Black Sea Fleet of Russia and Ukraine (1992-1995)

Ukraine (1994-1997)

United Arab Republic (1958–1971)

Federation of Arab Republics (1972–1977)

Tudor Ensign (1485-1603)

England (1620–1707)

Great Britain (1707–1800)

State of Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs and later Yugoslavia (1918-1922)

Yugoslavia (1922–1945)

Yugoslavia (1942)

Yugoslavia (1942-1944)

Yugoslavia (1943–1949)

Yugoslavia (1949–1992)
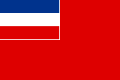
Yugoslavia and later Serbia and Montenegro (1993–2003)
- Naval ensigns
- Types of flags


















































































































































































































