Yami language
| Yami | |
|---|---|
| ciciring no Tao | |
| Native to | Taiwan |
| Ethnicity | Tao |
Native speakers | 3,800 (2006)[1] |
Language family | Austronesian
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | tao |
| Glottolog | yami1254 |
| ELP | Tao |
| Linguasphere | 31-CAA-a |
 Yami Orchid Island in Taiwan | |
| Coordinates: 22°03′N 121°32′E / 22.050°N 121.533°ECoordinates: 22°03′N 121°32′E / 22.050°N 121.533°E | |
Yami language (Chinese: 雅美語), also known as Tao language (Chinese: 達悟語), is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Tao people of Orchid Island, 46 kilometers southeast of Taiwan. It is a member of the Ivatan dialect continuum.
Yami is known as ciriciring no Tao 'human speech' by its native speakers. Native speakers prefer the 'Tao' name.[1]
Classification[]
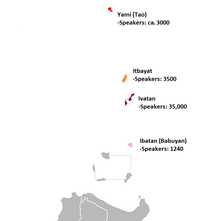
Yami is the only native language of Taiwanese aborigines that is not a member of the Formosan grouping of Austronesian; it is one of the Batanic languages also found in the northern Philippines.
Phonology[]
Yami has 20 consonants and 4 vowels:[2]
Vowels[]
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | ||
| Mid | ə | o | |
| Open | a |
- /o/ can be heard as [ʊ] after labial stop consonants.
Iraralay Yami, spoken on the north coast, distinguishes between geminative consonants (e.g., opa 'thigh' vs. oppa 'hen' form one such minimal pair).[3]
Consonants[]
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Retroflex | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||
| Plosive/ Affricate |
voiceless | p | t | t͡ʃ | k | (q) | ʔ | |
| voiced | b | d͡ʒ | ɖ | ɡ | ||||
| Fricative | v | ʂ | ʁ | (ɦ) | ||||
| Approximant | l | j | ɻ | w | ||||
| Trill | r | |||||||
- /k ʁ/ can also be heard as sounds [q ɦ] when between vowel /a/ intervocalically.
- Sounds /n l ʂ/ can be heard as sounds [ɲ ɮ ʃ] before /i/.
Grammar[]
Pronouns[]
The following set of pronouns are found in the Yami language.[4]
| Nominative | Genitive | Locative | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| free | bound | free | bound | ||
| 1st person singular | yaken | ko | niaken | ko | jiaken |
| 2nd person singular | imo | ka | nimo | mo | jimo |
| 3rd person singular | iya | ya | nia | na | jia |
| 1st person plural inclusive | yaten | ta, tamo, takamo | niaten | ta | jiaten |
| 1st person plural exclusive | yamen | namen | niamen | namen | jiamen |
| 2nd person plural | inio | kamo, kanio | ninio | nio | jinio |
| 3rd person plural | sira | sia | nira | da | jira |
Verbs[]
The following list are verbal inflections found in Yami.[5]
- Dynamic intransitive
- -om-/om- (subjunctive: N-)
- mi-
- ma-
- maN-
- maka-
- maci-/masi-/macika-/macipa-
- Stative
- ma- (subjunctive: a-)
- ka- ... -an (subjunctive: ka- ... -i)
- Dynamic
- pi-
- pa-
- paN- (subjunctive: maN-)
- paka- (subjunctive: maka-)
- paci- (subjunctive: maci-)
- Transitive
- -en (subjunctive: -a)
- -an (subjunctive: -i)
- i- (subjunctive: -an)
- Stative functioning as transitive
- ma- (subjunctive: a- ... -a)
- ka- ... -an (subjunctive: a- ... -a)
Affixes[]
The following list are the affixes found in Yami.[6]
- icia- 'fellows such and such who share the same features or fate'
- ikeyka- 'even more so'
- ika- 'feel such and such because...'
- ika- 'ordinal number'
- ipi- 'multiple number'
- ji a- 'negation or emphatic'
- ka- 'company, as ... as, abstract noun'
- ka- 'and then, just now, only'
- ka- 'stative verb prefix reappearing in forming transitive verbs'
- ka- (reduplicated root) 'very'
- ka- (reduplicated root) 'animals named after certain features'
- ka- ... -an 'common noun'
- ma- ... -en 'love to do such and such'
- mapaka- 'pretend to be such and such'
- mapi- 'do such and such as an occupation'
- mi-/mala- 'kinship relationships in a group of two or three'
- mika-/mapika-/ipika- 'all, gradually, one by one'
- mala- 'taste or look like...'
- mipa- 'getting more and more...'
- mipipa- 'even more...'
- mapi-/mapa-/pa- ... -en/ipa- 'causative verb affixes'
- ni- 'perfective'
- ni- ... na 'superlative'
- noka- 'past'
- noma- 'future (remote)'
- sicia- 'present'
- sima- 'future (proximal)'
- tey- 'direction'
- tey- 'very, too'
- tey- (reduplicated root) 'amount allocated to each unit
Vocabulary[]
This section does not cite any sources. (December 2021) |
Cognates with Philippine languages[]
| English | Yami | Tagalog/Ilokano/Visayan, etc. |
|---|---|---|
| Person | tao | tao (Tagalog), tawo (Cebuano Vis.) |
| Mother | ina | ina |
| Father | ama | ama |
| Head | oo | ulo |
| Yes | nohon | oho (opo) |
| Friend | kagagan | kaibigan |
| who | sino | sino, sin-o (Hiligaynon Vis.), hin-o (Waray Vis.) |
| they | sira | sila (Tagalog), sira/hira (Waray Vis.) |
| their | nira | nila |
| offspring | anak | anak |
| I (pronoun) | ko | ko, -ko (Ilokano) |
| you | ka | ka, -ka (Ilokano) |
| day | araw | araw, aldaw (Ilokano), adlaw (Cebuano Vis.) |
| eat | kanen | kain, kanen (Ilokano), kaon (all Visayan) |
| drink | inomen | inumin, inomen (Ilokano) |
| speech | ciriciring | chirichirin (Itbayaten Ivatan), siling (Hiligaynon Vis., say), siring (Waray Vis., say) |
| and | aka | saka |
| ouch | Ananay | Aray, Agay (Cebuano Vis.), Annay (Ilokano) |
| home | vahay | bahay, balay (Ilokano, Cebuano Vis.) |
| piglet | viik | biik (Tagalog, piglet) |
| goat | kadling | kambing, kanding (Cebuano Vis.), kalding (Ilokano) |
| stone | vato | bato (Tagalog, all Visayan, etc.) |
| town | ili | ili (Ilokano) |
| one | ása | isa (Tagalog, Hiligaynon Vis.), maysa (Ilokano), usa (Cebuano Vis.) |
| two | dóa (raroa) | dalawa (Tagalog), duha (Cebuano), dua (Ilokano) |
| three | tílo | tatlo, tulo/tuto (Cebuano Vis.), tallo (Ilokano) |
| four | ápat | apat (Tagalog, Hiligaynon Vis.), upat (Cebuano Vis.), uppat (Ilokano) |
| five | líma | lima |
| six | ánem | anim (Tagalog), innem (Ilokano), unom (Cebuano Vis.), anum (Hiligaynon Vis.) |
| seven | píto | pito |
| eight | wáo | walo |
| nine | síam | siyam, siam (Ilokano) |
| ten | póo | sampu (Tagalog), sangapulo (Ilokano), napulo (all Visayan) |
Japanese loanwords[]
| English | Yami | Japanese |
|---|---|---|
| Airplane | sikoki | hikouki (飛行機) |
| Alcohol | saki | sake (酒) |
| Battleship | gengkang | gunkan (軍艦) |
| Bible | seysio | seisho (聖書) |
| Christ | Kizisto | kirisuto (キリスト) |
| Doctor | koysang | o-isha-san? (お医者さん) |
| Flashlight | dingki | denki (電気) |
| Holy Spirit | seyzi | seirei (聖霊) |
| Key | kagi | kagi (鍵) |
| Medicine | kosozi | kusuri (薬) |
| Monkey | sazo | saru (猿) |
| Motorcycle | otobay | ōtobai (オートバイ; auto bike) |
| Police | kisat | keisatsu (警察) |
| School | gako | gakkō (学校) |
| School bag | kabang | kaban (鞄) |
| Teacher | sinsi | sensei (先生) |
| Ticket | kipo | kippu (切符) |
| Truck | tozako | torakku (トラック; truck) |
Chinese loanwords[]
| English | Yami | Mandarin Chinese |
|---|---|---|
| Wine | potaw cio | pútáojiǔ (葡萄酒) |
See also[]
- Languages of Taiwan
- Taiwanese aborigines
- Tao people
- Batanic languages
- Ivatan language
References[]
- ^ a b Rau & Dong 2006, p. 79
- ^ Rau & Dong 2006, pp. 79–80
- ^ Rau & Dong 2006, p. 81
- ^ Rau & Dong 2006, p. 123
- ^ Rau & Dong 2006, p. 135
- ^ Rau & Dong 2006, p. 135–136
Sources[]
- Rau, D. Victoria; Dong, Maa-Neu (2006). 達悟語:語料、參考語法、及詞彙/ Yami Texts with Reference Grammar and Dictionary (PDF) (in Chinese and English). Taipei: Academia Sinica.
- Rau, D. Victoria 何德華; Dong, Maa-Neu 董瑪女; Chang, Ann Hui-Huan 張惠環 (2012). Dáwù yǔ cídiǎn / Yami (Tao) Dictionary 達悟語詞典 / Yami (Tao) Dictionary (in Chinese and English). Taibei shi: Guoli taiwan daxue chuban zhongxin. ISBN 978-986-03-2519-5.
- Rau, Der-Hwa 何德華; Dong, Maa-Neu 董瑪女 (2018). Dáwù yǔ yǔfǎ gàilùn 達悟語語法概論 [Introduction to Tao Grammar] (in Chinese). Xinbei shi: Yuanzhu minzu weiyuanhui. ISBN 978-986-05-5695-7 – via alilin.apc.gov.tw.
Further reading[]
- Lai, Li-Fang; Gooden, Shelome (2016). Acoustic Cues to Prosodic Boundaries in Yami: A First Look. Proceedings of Speech Prosody 8, May 31 – June 3, Boston, USA. doi:10.21437/SpeechProsody.2016-128.
- Lai, Li-Fang; Gooden, Shelome (2015). What Does the Question Sound Like: Exploring Wh- and Yes/No Interrogative Prosody in Yami. ICPhS.
- Lai, Li-Fang; Gooden, Shelome (2018). Tonal Hybridization in Yami-Mandarin Contact. Proceedings of the 6th Tonal Aspects of Languages. ISCA. doi:10.21437/TAL.2018-7.
External links[]
| Yami language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
- Yami wordlists at the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database: language.psy.auckland.ac.nz/austronesian/language.php?id=254, language.psy.auckland.ac.nz/austronesian/language.php?id=335
- Yami Language Documentation Project website – hosted by Providence University, Taiwan
- Online Yami language course – hosted by Providence University, Taiwan
- Yami Dictionary Project website – hosted by Providence University, Taiwan
- Yuán zhù mínzú yǔyán xiànshàng cídiǎn 原住民族語言線上詞典 (in Chinese) – Yami search page at the "Aboriginal language online dictionary" website of the Indigenous Languages Research and Development Foundation
- Yami teaching and leaning materials published by the Council of Indigenous Peoples of Taiwan
- Yami translation of President Tsai Ing-wen's 2016 apology to indigenous people – published on the website of the presidential office
- Languages of Taiwan
- Batanic languages

